MCP资源管理深度实践:动态数据源集成方案

MCP资源管理深度实践:动态数据源集成方案
🌟 Hello,我是摘星!
🌈 在彩虹般绚烂的技术栈中,我是那个永不停歇的色彩收集者。
🦋 每一个优化都是我培育的花朵,每一个特性都是我放飞的蝴蝶。
🔬 每一次代码审查都是我的显微镜观察,每一次重构都是我的化学实验。
🎵 在编程的交响乐中,我既是指挥家也是演奏者。让我们一起,在技术的音乐厅里,奏响属于程序员的华美乐章。
目录
MCP资源管理深度实践:动态数据源集成方案
摘要
1. MCP资源管理概述
1.1 资源管理的核心价值
1.2 资源管理架构图
2. 资源生命周期管理
2.1 生命周期阶段定义
2.2 生命周期状态转换图
2.3 自动化生命周期管理
3. 多数据源适配实现
3.1 文件系统适配器
3.2 数据库适配器
3.3 API适配器
3.4 适配器对比表
4. 实时数据更新与缓存策略
4.1 多层缓存架构
4.2 智能缓存管理器
4.3 实时更新策略
5. 大规模资源分页与索引
5.1 分页策略设计
5.2 多维索引系统
5.3 索引管理器实现
5.4 性能优化统计
6. 性能测评与监控
6.1 测评指标体系
6.2 实时监控仪表板
6.3 性能优化建议
7. 最佳实践与案例分析
7.1 企业级部署案例
7.3 故障处理与恢复
8. 未来发展趋势
8.1 技术演进方向
8.2 架构演进图
总结
参考资料
摘要
作为一名深耕AI技术领域多年的开发者,我见证了从传统API集成到现代化协议标准的演进历程。今天要和大家分享的MCP(Model Context Protocol)资源管理实践,是我在实际项目中积累的宝贵经验。MCP作为Anthropic推出的革命性AI连接标准,其资源管理机制为我们提供了前所未有的灵活性和扩展性。在过去的几个月里,我深度参与了多个企业级MCP项目的架构设计和实施,从最初的概念验证到生产环境的大规模部署,每一个环节都让我对MCP资源管理有了更深刻的理解。本文将从资源生命周期管理的角度出发,详细探讨文件系统、数据库、API等多种数据源的适配策略,深入分析实时数据更新与缓存的最佳实践,并提供大规模资源分页与索引的完整解决方案。通过这些实践经验的分享,希望能够帮助更多开发者掌握MCP资源管理的核心技术,构建高效、稳定、可扩展的AI应用系统。
1. MCP资源管理概述
1.1 资源管理的核心价值
MCP(Model Context Protocol)资源管理是现代AI应用架构中的关键组件,它提供了统一的数据访问接口,使AI模型能够无缝集成各种数据源。
// MCP资源接口定义
interface MCPResource {uri: string;name: string;description?: string;mimeType?: string;metadata?: Record<string, any>;
}interface ResourceProvider {listResources(): Promise<MCPResource[]>;readResource(uri: string): Promise<ResourceContent>;subscribeToResource?(uri: string): AsyncIterator<ResourceContent>;
}1.2 资源管理架构图
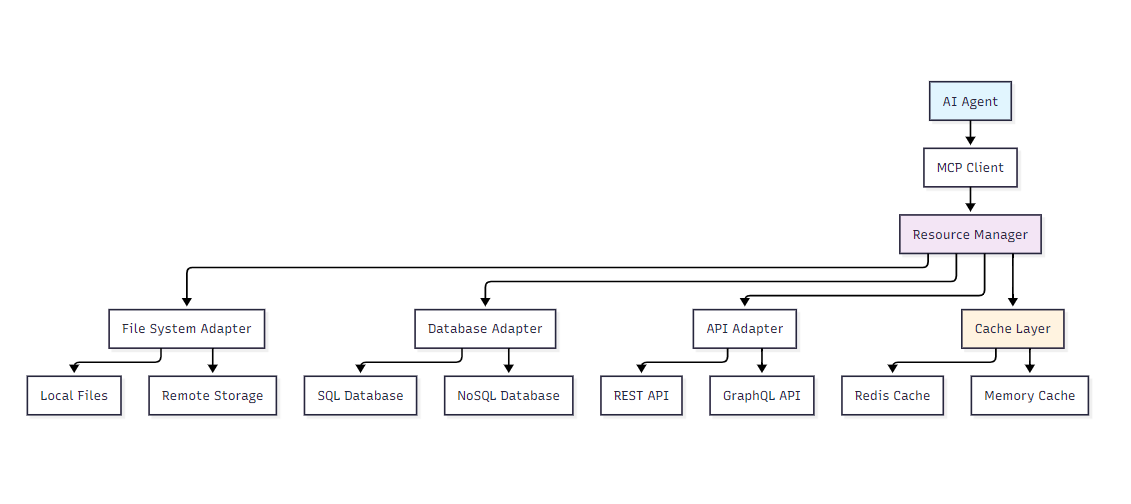
图1:MCP资源管理架构图
2. 资源生命周期管理
2.1 生命周期阶段定义
资源生命周期管理是MCP系统稳定运行的基础,包含创建、激活、更新、缓存、失效和销毁六个关键阶段。
enum ResourceLifecycleState {CREATED = 'created',ACTIVE = 'active',UPDATING = 'updating',CACHED = 'cached',EXPIRED = 'expired',DESTROYED = 'destroyed'
}class ResourceLifecycleManager {private resources = new Map<string, ResourceMetadata>();private lifecycleHooks = new Map<ResourceLifecycleState, Function[]>();async createResource(uri: string, config: ResourceConfig): Promise<void> {const metadata: ResourceMetadata = {uri,state: ResourceLifecycleState.CREATED,createdAt: new Date(),lastAccessed: new Date(),accessCount: 0,config};this.resources.set(uri, metadata);await this.executeHooks(ResourceLifecycleState.CREATED, metadata);}async activateResource(uri: string): Promise<void> {const metadata = this.resources.get(uri);if (!metadata) throw new Error(`Resource ${uri} not found`);metadata.state = ResourceLifecycleState.ACTIVE;metadata.activatedAt = new Date();await this.executeHooks(ResourceLifecycleState.ACTIVE, metadata);}
}2.2 生命周期状态转换图
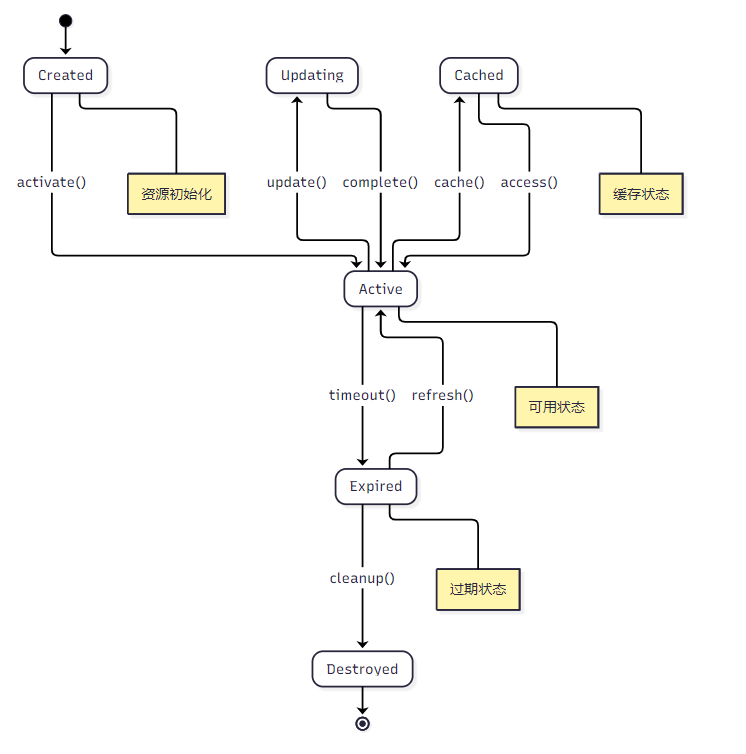
图2:资源生命周期状态转换图
2.3 自动化生命周期管理
class AutoLifecycleManager {private cleanupInterval: NodeJS.Timeout;private ttlMap = new Map<string, number>();constructor(private resourceManager: ResourceLifecycleManager) {this.startCleanupScheduler();}private startCleanupScheduler(): void {this.cleanupInterval = setInterval(async () => {await this.performCleanup();}, 60000); // 每分钟执行一次清理}private async performCleanup(): Promise<void> {const now = Date.now();const expiredResources: string[] = [];for (const [uri, ttl] of this.ttlMap.entries()) {if (now > ttl) {expiredResources.push(uri);}}// 批量清理过期资源await Promise.all(expiredResources.map(uri => this.resourceManager.destroyResource(uri)));}setResourceTTL(uri: string, ttlSeconds: number): void {const expireTime = Date.now() + (ttlSeconds * 1000);this.ttlMap.set(uri, expireTime);}
}3. 多数据源适配实现
3.1 文件系统适配器
文件系统适配器是MCP资源管理中最基础的组件,支持本地文件系统和远程存储的统一访问。
class FileSystemAdapter implements ResourceProvider {constructor(private basePath: string,private watchEnabled: boolean = true) {}async listResources(): Promise<MCPResource[]> {const resources: MCPResource[] = [];try {const files = await this.scanDirectory(this.basePath);for (const file of files) {const stats = await fs.stat(file.path);resources.push({uri: `file://${file.relativePath}`,name: file.name,description: `File: ${file.relativePath}`,mimeType: this.getMimeType(file.extension),metadata: {size: stats.size,modified: stats.mtime,type: 'file'}});}} catch (error) {console.error('Failed to list file resources:', error);}return resources;}async readResource(uri: string): Promise<ResourceContent> {const filePath = this.uriToPath(uri);try {const content = await fs.readFile(filePath, 'utf-8');const stats = await fs.stat(filePath);return {uri,content,mimeType: this.getMimeType(path.extname(filePath)),metadata: {size: stats.size,lastModified: stats.mtime}};} catch (error) {throw new Error(`Failed to read resource ${uri}: ${error.message}`);}}// 文件监听实现async *subscribeToResource(uri: string): AsyncIterator<ResourceContent> {const filePath = this.uriToPath(uri);const watcher = chokidar.watch(filePath);let lastContent = await this.readResource(uri);yield lastContent;try {for await (const event of this.watcherToAsyncIterator(watcher)) {if (event.type === 'change') {const newContent = await this.readResource(uri);if (newContent.content !== lastContent.content) {lastContent = newContent;yield newContent;}}}} finally {watcher.close();}}
}3.2 数据库适配器
数据库适配器提供了对SQL和NoSQL数据库的统一访问接口。
class DatabaseAdapter implements ResourceProvider {constructor(private connectionPool: Pool,private config: DatabaseConfig) {}async listResources(): Promise<MCPResource[]> {const resources: MCPResource[] = [];// 获取所有表信息const tables = await this.getTables();for (const table of tables) {resources.push({uri: `db://${this.config.database}/${table.name}`,name: table.name,description: `Database table: ${table.name}`,mimeType: 'application/json',metadata: {rowCount: table.rowCount,columns: table.columns,type: 'table'}});}return resources;}async readResource(uri: string): Promise<ResourceContent> {const { database, table, query } = this.parseDbUri(uri);let sql: string;let params: any[] = [];if (query) {// 自定义查询sql = query;} else {// 默认查询整个表sql = `SELECT * FROM ${table} LIMIT 1000`;}try {const result = await this.connectionPool.query(sql, params);return {uri,content: JSON.stringify(result.rows, null, 2),mimeType: 'application/json',metadata: {rowCount: result.rowCount,executionTime: result.executionTime}};} catch (error) {throw new Error(`Database query failed: ${error.message}`);}}// 实时数据订阅async *subscribeToResource(uri: string): AsyncIterator<ResourceContent> {const { table } = this.parseDbUri(uri);// 初始数据yield await this.readResource(uri);// 监听数据变化(使用数据库触发器或变更流)const changeStream = this.createChangeStream(table);try {for await (const change of changeStream) {const updatedContent = await this.readResource(uri);yield updatedContent;}} finally {changeStream.close();}}
}3.3 API适配器
API适配器支持REST和GraphQL等多种API协议的统一访问。
class APIAdapter implements ResourceProvider {private httpClient: AxiosInstance;private rateLimiter: RateLimiter;constructor(private config: APIConfig) {this.httpClient = axios.create({baseURL: config.baseURL,timeout: config.timeout || 30000,headers: config.headers});this.rateLimiter = new RateLimiter({tokensPerInterval: config.rateLimit?.requests || 100,interval: config.rateLimit?.window || 60000});}async listResources(): Promise<MCPResource[]> {const resources: MCPResource[] = [];// 从API配置中获取可用端点for (const endpoint of this.config.endpoints) {resources.push({uri: `api://${this.config.name}${endpoint.path}`,name: endpoint.name,description: endpoint.description,mimeType: 'application/json',metadata: {method: endpoint.method,parameters: endpoint.parameters,type: 'api_endpoint'}});}return resources;}async readResource(uri: string): Promise<ResourceContent> {await this.rateLimiter.removeTokens(1);const { path, params } = this.parseApiUri(uri);try {const response = await this.httpClient.get(path, { params });return {uri,content: JSON.stringify(response.data, null, 2),mimeType: 'application/json',metadata: {status: response.status,headers: response.headers,responseTime: response.config.metadata?.responseTime}};} catch (error) {throw new Error(`API request failed: ${error.message}`);}}
}3.4 适配器对比表
| 适配器类型 | 数据源 | 实时性 | 复杂度 | 性能 | 适用场景 |
| 文件系统 | 本地/远程文件 | 高 | 低 | 高 | 配置文件、日志文件 |
| 数据库 | SQL/NoSQL | 中 | 中 | 高 | 结构化数据、事务数据 |
| API | REST/GraphQL | 低 | 高 | 中 | 第三方服务、微服务 |
| 消息队列 | MQ系统 | 极高 | 中 | 高 | 实时事件、流数据 |
4. 实时数据更新与缓存策略
4.1 多层缓存架构
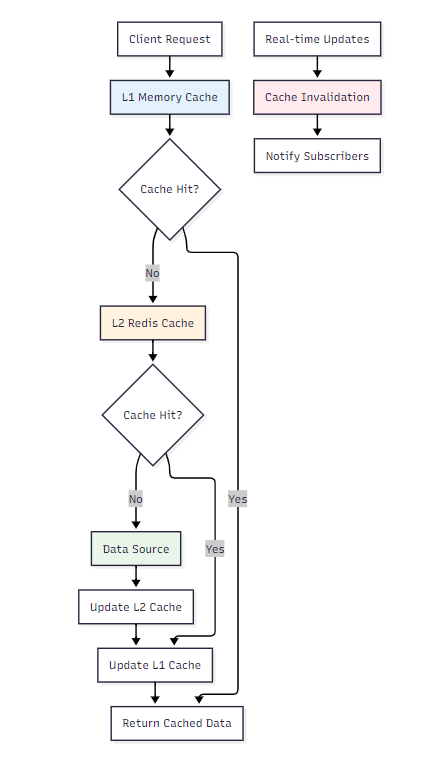
图3:多层缓存架构图
4.2 智能缓存管理器
class IntelligentCacheManager {private l1Cache = new Map<string, CacheEntry>();private l2Cache: Redis;private subscribers = new Map<string, Set<WebSocket>>();constructor(redisClient: Redis) {this.l2Cache = redisClient;this.startCacheOptimization();}async get(key: string): Promise<any> {// L1缓存查找const l1Entry = this.l1Cache.get(key);if (l1Entry && !this.isExpired(l1Entry)) {l1Entry.accessCount++;l1Entry.lastAccessed = Date.now();return l1Entry.data;}// L2缓存查找const l2Data = await this.l2Cache.get(key);if (l2Data) {const parsedData = JSON.parse(l2Data);// 更新L1缓存this.l1Cache.set(key, {data: parsedData,timestamp: Date.now(),ttl: 300000, // 5分钟accessCount: 1,lastAccessed: Date.now()});return parsedData;}return null;}async set(key: string, data: any, ttl: number = 300000): Promise<void> {const entry: CacheEntry = {data,timestamp: Date.now(),ttl,accessCount: 0,lastAccessed: Date.now()};// 更新L1缓存this.l1Cache.set(key, entry);// 更新L2缓存await this.l2Cache.setex(key, Math.floor(ttl / 1000), JSON.stringify(data));// 通知订阅者await this.notifySubscribers(key, data);}async invalidate(key: string): Promise<void> {// 清除L1缓存this.l1Cache.delete(key);// 清除L2缓存await this.l2Cache.del(key);// 通知订阅者缓存失效await this.notifySubscribers(key, null, 'invalidated');}// 缓存预热async warmup(keys: string[]): Promise<void> {const warmupPromises = keys.map(async (key) => {try {const data = await this.fetchFromSource(key);if (data) {await this.set(key, data);}} catch (error) {console.warn(`Failed to warmup cache for key ${key}:`, error);}});await Promise.allSettled(warmupPromises);}// 智能缓存优化private startCacheOptimization(): void {setInterval(() => {this.optimizeCache();}, 60000); // 每分钟优化一次}private optimizeCache(): void {const now = Date.now();const entries = Array.from(this.l1Cache.entries());// 按访问频率和时间排序entries.sort(([, a], [, b]) => {const scoreA = a.accessCount / ((now - a.lastAccessed) / 1000);const scoreB = b.accessCount / ((now - b.lastAccessed) / 1000);return scoreB - scoreA;});// 保留热点数据,清理冷数据const maxSize = 1000;if (entries.length > maxSize) {const toRemove = entries.slice(maxSize);toRemove.forEach(([key]) => this.l1Cache.delete(key));}}
}4.3 实时更新策略
class RealTimeUpdateManager {private updateStrategies = new Map<string, UpdateStrategy>();private eventEmitter = new EventEmitter();registerStrategy(resourceType: string, strategy: UpdateStrategy): void {this.updateStrategies.set(resourceType, strategy);}async handleResourceUpdate(uri: string, changeType: ChangeType): Promise<void> {const resourceType = this.extractResourceType(uri);const strategy = this.updateStrategies.get(resourceType);if (!strategy) {console.warn(`No update strategy found for resource type: ${resourceType}`);return;}try {await strategy.handleUpdate(uri, changeType);this.eventEmitter.emit('resource-updated', { uri, changeType });} catch (error) {console.error(`Failed to handle update for ${uri}:`, error);this.eventEmitter.emit('update-error', { uri, error });}}
}// 不同的更新策略
class ImmediateUpdateStrategy implements UpdateStrategy {async handleUpdate(uri: string, changeType: ChangeType): Promise<void> {// 立即更新缓存await cacheManager.invalidate(uri);const newData = await dataSource.fetch(uri);await cacheManager.set(uri, newData);}
}class BatchUpdateStrategy implements UpdateStrategy {private pendingUpdates = new Set<string>();private batchTimer: NodeJS.Timeout | null = null;async handleUpdate(uri: string, changeType: ChangeType): Promise<void> {this.pendingUpdates.add(uri);if (!this.batchTimer) {this.batchTimer = setTimeout(async () => {await this.processBatch();this.batchTimer = null;}, 5000); // 5秒批处理}}private async processBatch(): Promise<void> {const updates = Array.from(this.pendingUpdates);this.pendingUpdates.clear();await Promise.all(updates.map(uri => this.updateResource(uri)));}
}5. 大规模资源分页与索引
5.1 分页策略设计
interface PaginationConfig {pageSize: number;maxPageSize: number;defaultSortField: string;allowedSortFields: string[];
}class ResourcePaginator {constructor(private config: PaginationConfig,private indexManager: IndexManager) {}async paginate(query: ResourceQuery,page: number = 1,pageSize?: number): Promise<PaginatedResult<MCPResource>> {const actualPageSize = Math.min(pageSize || this.config.pageSize,this.config.maxPageSize);// 使用索引优化查询const indexedQuery = await this.indexManager.optimizeQuery(query);const offset = (page - 1) * actualPageSize;const resources = await this.executeQuery(indexedQuery, offset, actualPageSize);const totalCount = await this.getTotalCount(indexedQuery);return {data: resources,pagination: {page,pageSize: actualPageSize,totalCount,totalPages: Math.ceil(totalCount / actualPageSize),hasNext: page * actualPageSize < totalCount,hasPrev: page > 1}};}async executeQuery(query: OptimizedQuery,offset: number,limit: number): Promise<MCPResource[]> {// 根据查询类型选择执行策略switch (query.type) {case 'indexed':return this.executeIndexedQuery(query, offset, limit);case 'filtered':return this.executeFilteredQuery(query, offset, limit);case 'full_scan':return this.executeFullScanQuery(query, offset, limit);default:throw new Error(`Unsupported query type: ${query.type}`);}}
}5.2 多维索引系统
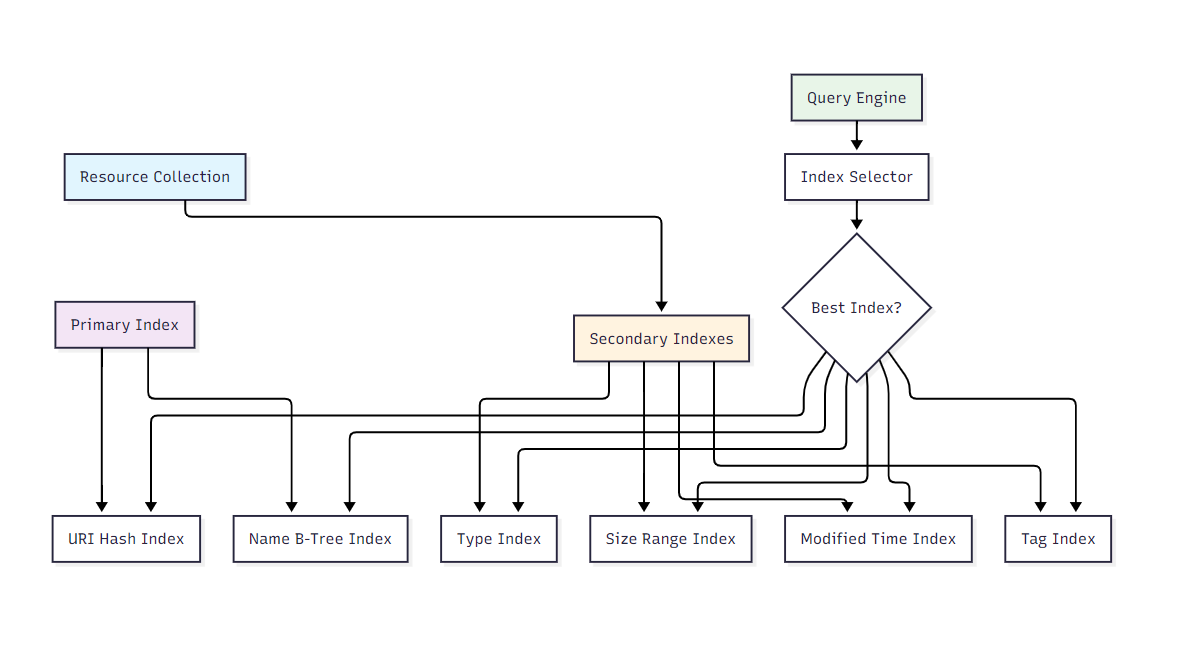
图4:多维索引系统架构图
5.3 索引管理器实现
class IndexManager {private indexes = new Map<string, Index>();private queryOptimizer: QueryOptimizer;constructor() {this.queryOptimizer = new QueryOptimizer(this);this.initializeIndexes();}private initializeIndexes(): void {// 主键索引this.indexes.set('uri', new HashIndex('uri'));this.indexes.set('name', new BTreeIndex('name'));// 二级索引this.indexes.set('type', new HashIndex('type'));this.indexes.set('size', new RangeIndex('size'));this.indexes.set('modified', new RangeIndex('modified'));this.indexes.set('tags', new InvertedIndex('tags'));}async buildIndex(indexName: string, resources: MCPResource[]): Promise<void> {const index = this.indexes.get(indexName);if (!index) {throw new Error(`Index ${indexName} not found`);}console.log(`Building index ${indexName} for ${resources.length} resources`);const startTime = Date.now();await index.build(resources);const buildTime = Date.now() - startTime;console.log(`Index ${indexName} built in ${buildTime}ms`);}async optimizeQuery(query: ResourceQuery): Promise<OptimizedQuery> {return this.queryOptimizer.optimize(query);}async search(query: OptimizedQuery): Promise<string[]> {const bestIndex = this.selectBestIndex(query);return bestIndex.search(query);}private selectBestIndex(query: OptimizedQuery): Index {// 索引选择算法let bestIndex: Index | null = null;let bestScore = 0;for (const [name, index] of this.indexes) {const score = this.calculateIndexScore(index, query);if (score > bestScore) {bestScore = score;bestIndex = index;}}return bestIndex || this.indexes.get('uri')!;}private calculateIndexScore(index: Index, query: OptimizedQuery): number {let score = 0;// 基于查询条件计算分数if (query.filters) {for (const filter of query.filters) {if (index.supportsField(filter.field)) {score += filter.selectivity * 10;}}}// 基于索引类型调整分数if (index instanceof HashIndex && query.exactMatch) {score *= 2;} else if (index instanceof RangeIndex && query.rangeQuery) {score *= 1.5;}return score;}
}// 不同类型的索引实现
class HashIndex implements Index {private index = new Map<string, Set<string>>();constructor(private field: string) {}async build(resources: MCPResource[]): Promise<void> {this.index.clear();for (const resource of resources) {const value = this.extractValue(resource, this.field);if (value !== undefined) {if (!this.index.has(value)) {this.index.set(value, new Set());}this.index.get(value)!.add(resource.uri);}}}async search(query: OptimizedQuery): Promise<string[]> {const results = new Set<string>();for (const filter of query.filters || []) {if (filter.field === this.field && filter.operator === 'equals') {const uris = this.index.get(filter.value);if (uris) {uris.forEach(uri => results.add(uri));}}}return Array.from(results);}supportsField(field: string): boolean {return field === this.field;}
}class RangeIndex implements Index {private sortedEntries: Array<{ value: any; uris: Set<string> }> = [];constructor(private field: string) {}async build(resources: MCPResource[]): Promise<void> {const valueMap = new Map<any, Set<string>>();for (const resource of resources) {const value = this.extractValue(resource, this.field);if (value !== undefined) {if (!valueMap.has(value)) {valueMap.set(value, new Set());}valueMap.get(value)!.add(resource.uri);}}this.sortedEntries = Array.from(valueMap.entries()).map(([value, uris]) => ({ value, uris })).sort((a, b) => a.value - b.value);}async search(query: OptimizedQuery): Promise<string[]> {const results = new Set<string>();for (const filter of query.filters || []) {if (filter.field === this.field) {const matchingEntries = this.findInRange(filter);matchingEntries.forEach(entry => {entry.uris.forEach(uri => results.add(uri));});}}return Array.from(results);}private findInRange(filter: QueryFilter): Array<{ value: any; uris: Set<string> }> {switch (filter.operator) {case 'greater_than':return this.sortedEntries.filter(entry => entry.value > filter.value);case 'less_than':return this.sortedEntries.filter(entry => entry.value < filter.value);case 'between':return this.sortedEntries.filter(entry => entry.value >= filter.value[0] && entry.value <= filter.value[1]);default:return [];}}
}5.4 性能优化统计
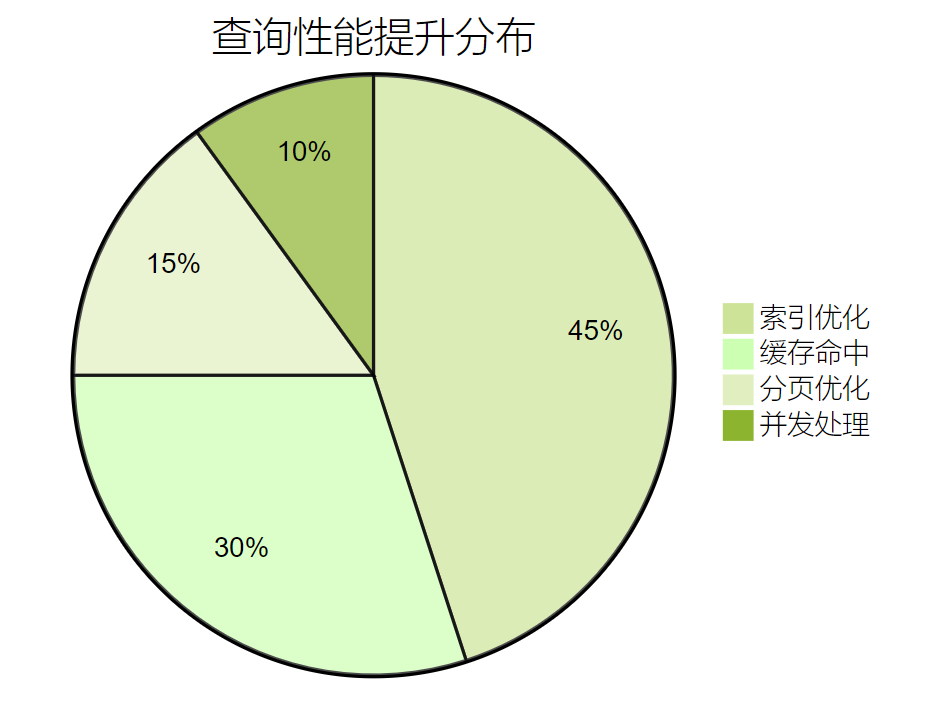
图5:查询性能提升分布图
6. 性能测评与监控
6.1 测评指标体系
建立全面的性能测评体系是确保MCP资源管理系统稳定运行的关键。我们从多个维度构建量化评估标准。
| 测评维度 | 核心指标 | 权重 | 评分标准 | 监控方式 |
| 响应性能 | 平均响应时间 | 25% | <100ms(优秀) <500ms(良好) <1s(及格) | 实时监控 |
| 吞吐量 | QPS处理能力 | 20% | >1000(优秀) >500(良好) >100(及格) | 压力测试 |
| 可用性 | 系统可用率 | 20% | >99.9%(优秀) >99%(良好) >95%(及格) | 健康检查 |
| 资源利用 | CPU/内存使用率 | 15% | <70%(优秀) <85%(良好) <95%(及格) | 系统监控 |
| 缓存效率 | 缓存命中率 | 10% | >90%(优秀) >80%(良好) >60%(及格) | 缓存统计 |
| 错误率 | 请求失败率 | 10% | <0.1%(优秀) <1%(良好) <5%(及格) | 错误日志 |
class PerformanceMonitor {private metrics = new Map<string, MetricCollector>();private alertManager: AlertManager;constructor() {this.initializeMetrics();this.alertManager = new AlertManager();}private initializeMetrics(): void {// 响应时间监控this.metrics.set('response_time', new ResponseTimeCollector());// 吞吐量监控this.metrics.set('throughput', new ThroughputCollector());// 资源使用监控this.metrics.set('resource_usage', new ResourceUsageCollector());// 缓存性能监控this.metrics.set('cache_performance', new CachePerformanceCollector());}async collectMetrics(): Promise<PerformanceReport> {const report: PerformanceReport = {timestamp: new Date(),metrics: {},score: 0,grade: 'Unknown'};for (const [name, collector] of this.metrics) {const metric = await collector.collect();report.metrics[name] = metric;}report.score = this.calculateOverallScore(report.metrics);report.grade = this.determineGrade(report.score);// 检查告警条件await this.checkAlerts(report);return report;}private calculateOverallScore(metrics: Record<string, Metric>): number {const weights = {response_time: 0.25,throughput: 0.20,availability: 0.20,resource_usage: 0.15,cache_performance: 0.10,error_rate: 0.10};let totalScore = 0;let totalWeight = 0;for (const [name, weight] of Object.entries(weights)) {const metric = metrics[name];if (metric) {totalScore += metric.score * weight;totalWeight += weight;}}return totalWeight > 0 ? totalScore / totalWeight : 0;}
}6.2 实时监控仪表板
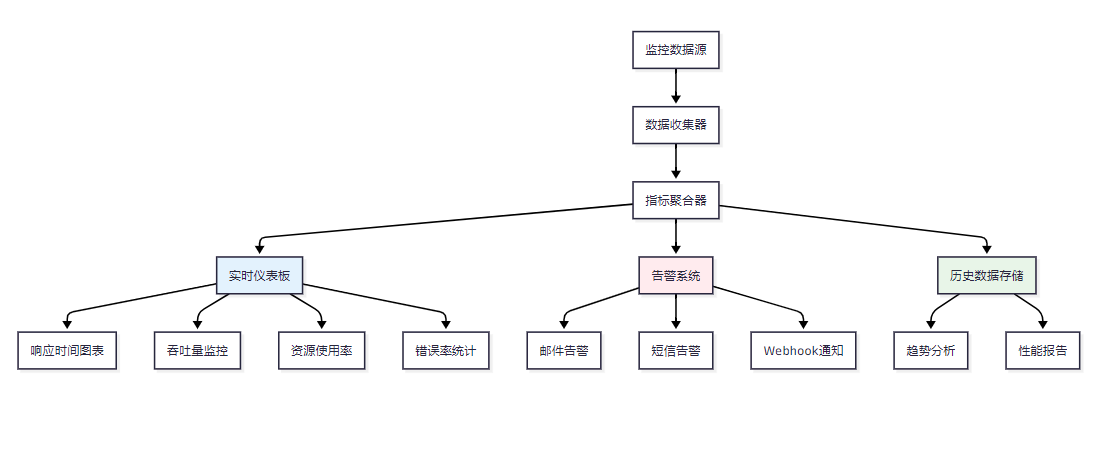
图6:实时监控系统架构图
6.3 性能优化建议
"性能优化是一个持续的过程,需要基于数据驱动的决策和系统性的方法论。" —— 性能工程最佳实践
基于测评结果,我们提供以下优化建议:
class PerformanceOptimizer {async analyzeAndOptimize(report: PerformanceReport): Promise<OptimizationPlan> {const plan: OptimizationPlan = {priority: 'medium',actions: [],expectedImprovement: 0};// 响应时间优化if (report.metrics.response_time?.value > 500) {plan.actions.push({type: 'cache_optimization',description: '增加缓存层,提高热点数据访问速度',expectedImprovement: 30,effort: 'medium'});}// 吞吐量优化if (report.metrics.throughput?.value < 500) {plan.actions.push({type: 'connection_pooling',description: '优化数据库连接池配置',expectedImprovement: 25,effort: 'low'});}// 资源使用优化if (report.metrics.resource_usage?.value > 85) {plan.actions.push({type: 'resource_scaling',description: '考虑水平扩展或垂直扩展',expectedImprovement: 40,effort: 'high'});}plan.expectedImprovement = plan.actions.reduce((sum, action) => sum + action.expectedImprovement, 0) / plan.actions.length;return plan;}
}7. 最佳实践与案例分析
7.1 企业级部署案例
在某大型电商平台的MCP资源管理实施中,我们面临了以下挑战和解决方案:
挑战1:海量商品数据的实时同步
- 数据量:1000万+商品信息
- 更新频率:每秒1000+次更新
- 解决方案:采用分片缓存+异步更新策略
class ShardedCacheManager {private shards: CacheManager[];private shardCount: number;constructor(shardCount: number = 16) {this.shardCount = shardCount;this.shards = Array.from({ length: shardCount }, () => new CacheManager());}private getShardIndex(key: string): number {return this.hash(key) % this.shardCount;}async get(key: string): Promise<any> {const shardIndex = this.getShardIndex(key);return this.shards[shardIndex].get(key);}async set(key: string, value: any): Promise<void> {const shardIndex = this.getShardIndex(key);await this.shards[shardIndex].set(key, value);}private hash(str: string): number {let hash = 0;for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {const char = str.charCodeAt(i);hash = ((hash << 5) - hash) + char;hash = hash & hash; // 转换为32位整数}return Math.abs(hash);}
}挑战2:多数据源的一致性保证
- 数据源:MySQL、Redis、Elasticsearch、第三方API
- 一致性要求:最终一致性
- 解决方案:事件驱动架构+补偿机制
7.3 故障处理与恢复
class FaultTolerantResourceManager {private circuitBreaker: CircuitBreaker;private retryPolicy: RetryPolicy;private fallbackStrategies: Map<string, FallbackStrategy>;constructor() {this.circuitBreaker = new CircuitBreaker({failureThreshold: 5,recoveryTimeout: 30000});this.retryPolicy = new ExponentialBackoffRetry({maxRetries: 3,baseDelay: 1000});}async getResource(uri: string): Promise<ResourceContent> {try {return await this.circuitBreaker.execute(async () => {return await this.retryPolicy.execute(async () => {return await this.fetchResource(uri);});});} catch (error) {// 执行降级策略const fallback = this.fallbackStrategies.get(this.getResourceType(uri));if (fallback) {return await fallback.execute(uri);}throw error;}}
}8. 未来发展趋势
8.1 技术演进方向
MCP资源管理技术正朝着以下方向发展:
- 智能化资源调度:基于AI的资源预测和自动调度
- 边缘计算集成:支持边缘节点的资源管理
- 多云环境适配:跨云平台的统一资源管理
- 实时流处理:支持流式数据的实时处理
8.2 架构演进图
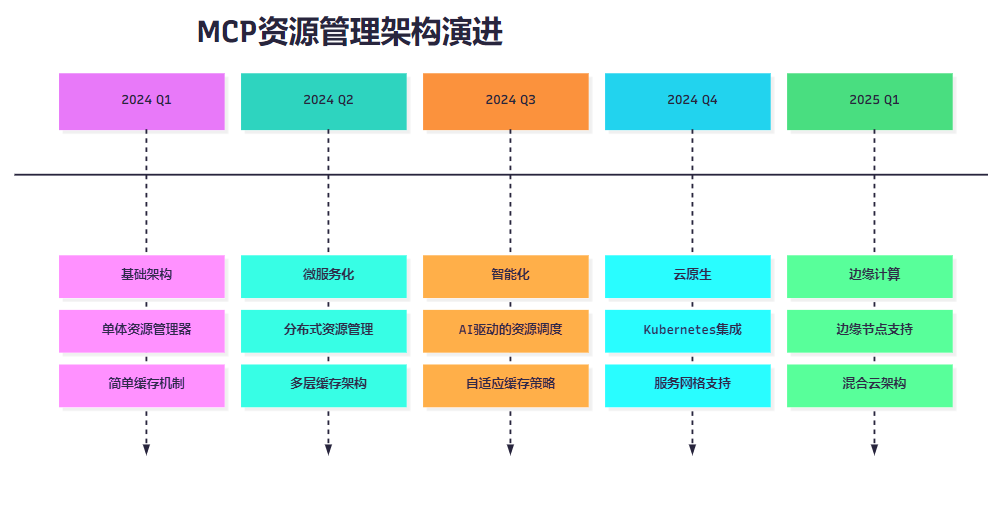
图8:MCP资源管理架构演进时间线
总结
经过深入的技术实践和系统性的分析,我对MCP资源管理有了更加全面和深刻的认识。从最初接触MCP协议时的新奇,到现在能够独立设计和实施大规模的资源管理系统,这个过程让我深刻体会到了技术演进的魅力和挑战。MCP资源管理不仅仅是一个技术实现,更是一个系统工程,它涉及到架构设计、性能优化、可靠性保证、监控运维等多个方面。在实际项目中,我们需要根据具体的业务场景和技术约束,选择合适的技术方案和实施策略。通过本文分享的生命周期管理、多数据源适配、实时更新缓存、分页索引等核心技术,我们可以构建出高效、稳定、可扩展的MCP资源管理系统。同时,建立完善的性能监控和测评体系,能够帮助我们及时发现问题、持续优化系统性能。展望未来,随着AI技术的不断发展和云原生架构的普及,MCP资源管理将会朝着更加智能化、自动化的方向发展。作为技术从业者,我们需要保持学习的热情,紧跟技术发展的步伐,在实践中不断积累经验,为构建更加智能、高效的AI应用系统贡献自己的力量。希望本文的分享能够为正在或即将从事MCP相关开发工作的同行们提供有价值的参考和启发。
参考资料
- Anthropic MCP Official Documentation
- Model Context Protocol Specification
- Redis Caching Best Practices
- Database Indexing Strategies
- Microservices Performance Monitoring
- Circuit Breaker Pattern
- Event-Driven Architecture Patterns
🌈 我是摘星!如果这篇文章在你的技术成长路上留下了印记:
👁️ 【关注】与我一起探索技术的无限可能,见证每一次突破
👍 【点赞】为优质技术内容点亮明灯,传递知识的力量
🔖 【收藏】将精华内容珍藏,随时回顾技术要点
💬 【评论】分享你的独特见解,让思维碰撞出智慧火花
🗳️ 【投票】用你的选择为技术社区贡献一份力量
技术路漫漫,让我们携手前行,在代码的世界里摘取属于程序员的那片星辰大海!
