数据结构学习之二叉树
之前我们已经学习了二叉树的一种特殊的结构:堆。接下来我们将从特殊到普通,接着来学习普通二叉树的性质及其模拟实现。
本篇内容建议和前面数据结构——堆的内容一起看:数据结构学习之堆-CSDN博客
这是作者的个人gitee:楼田莉子 (riko-lou-tian) - Gitee.com喜欢请支持一下
目录
实现链式二叉树
遍历规则
思路理解:
前序遍历
中序遍历
后序遍历
代码实现
创建一棵二叉树
前序遍历
中序遍历
后序遍历
求二叉树结点个数
求二叉树的高度
二叉树的查找
销毁二叉树
二叉树的层序遍历
判断是否为完全二叉树
源代码
二叉树
队列
测试
实现链式二叉树
⽤链表来表⽰⼀棵⼆叉树,即⽤链来指⽰元素的逻辑关系。
通常的⽅法是链表中每个结点由三个域组成,数据域和左右指针域,左右指针分别⽤来给出该结点左孩⼦和右孩⼦所在的链结点的存储地址 ,其结构如下:
//数据类型
typedef char Binary_Data_Type;
typedef Binary_Data_Type BDT;
//链式树节点结构
typedef struct Binary_Tree_Node
{BDT Data;//节点数据struct Binary_Tree_Node* leftchild;//左子树指针struct Binary_Tree_Node* rightchild;//右子树指针
}BTNode;在本篇内容中我们不会讲解如何插入删除结点。因为在现在的内容插入数据和删除数据是比较随意的,等到C++中学习到二叉树的其他版本(红黑树等)才会对插入和删除有一定限制
遍历规则
接下来我们将讲解二叉树的遍历:前序/中序/后序遍历
1)前序遍历(Preorder Traversal 亦称先序遍历):访问根结点的操作发⽣在遍历其左右⼦树之前访问顺序为:根结点、左⼦树、右⼦树(根左右)
2)中序遍历(Inorder Traversal):访问根结点的操作发⽣在遍历其左右⼦树之中(间)访问顺序为:左⼦树、根结点、右⼦树(左根右)
3)后序遍历(Postorder Traversal):访问根结点的操作发⽣在遍历其左右⼦树之后访问顺序为:左⼦树、右⼦树、根结点(左右根)
如对于下图所示的简单满二叉树 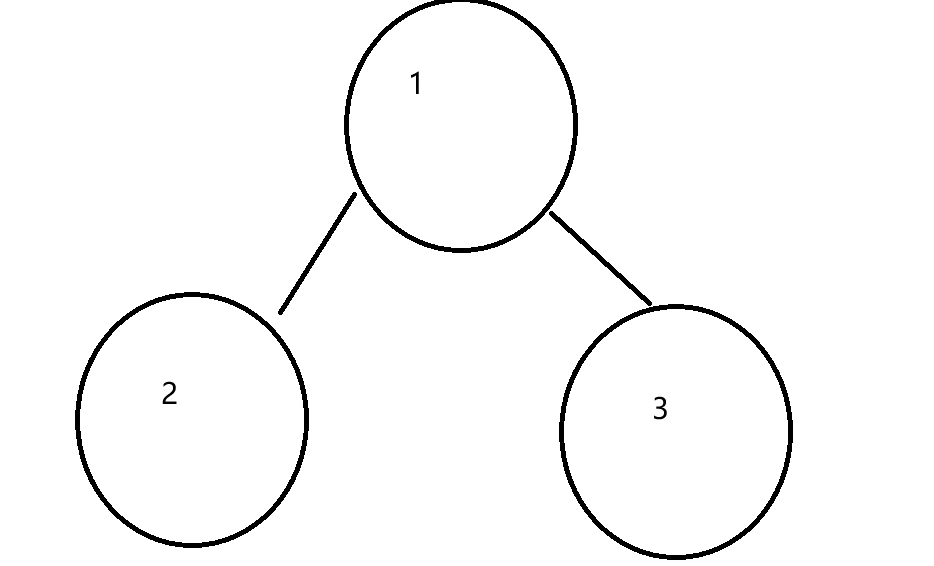
前序遍历:1 2 3
中序遍历:2 1 3
后序遍历:2 3 1
思路理解:
前序遍历
根左右
先从红色最高处开始从左子树遍历到最下一层,直到碰到NULL后开始从右子树递归回到跟结点。
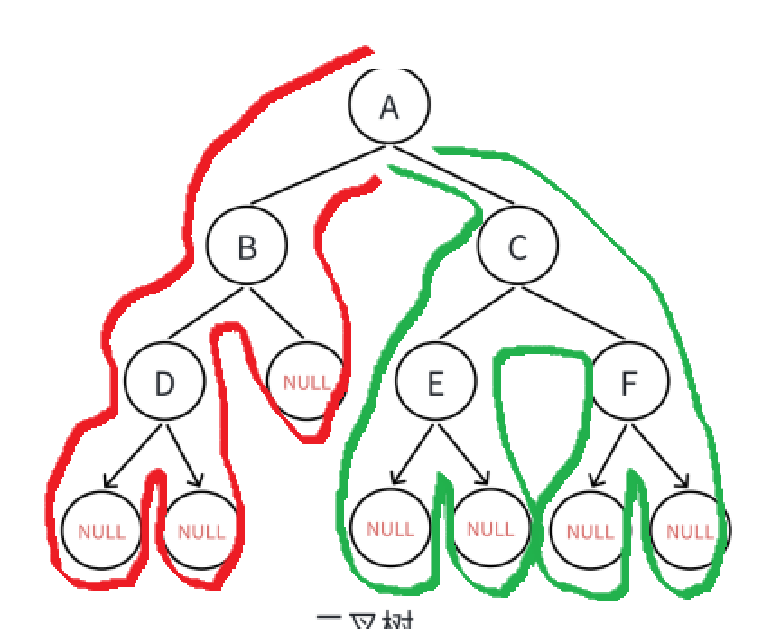
结果为:A 、B、D、NULL、NULL、NULL、C、E、NULL、NULL、F、NULL、NULL
中序遍历
左根右
从最下层的左子树返回根节点,然后遍历右子树,遍历此子树后返回上一层循环这个过程,直到遇到祖结点。
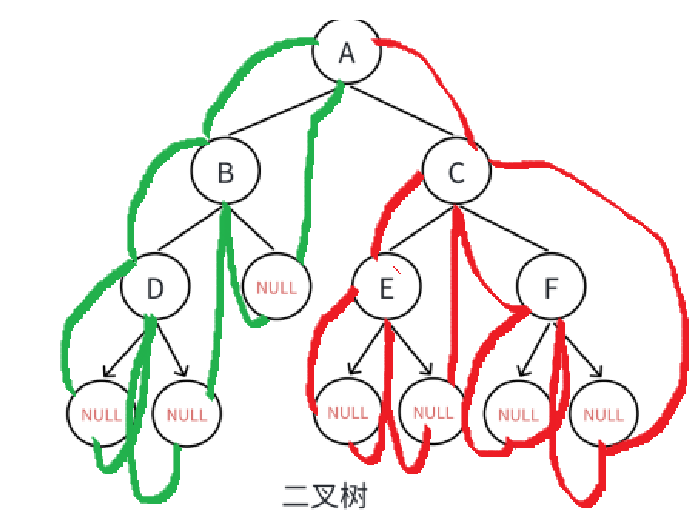
结果为:NULL、D、NULL、B、NULL、A、NULL、E、NULL、C、NULL、F、NULL
后序遍历
左右根
从最下层的左子树遍历右子树然后返回根结点循环遍历,直到到祖结点
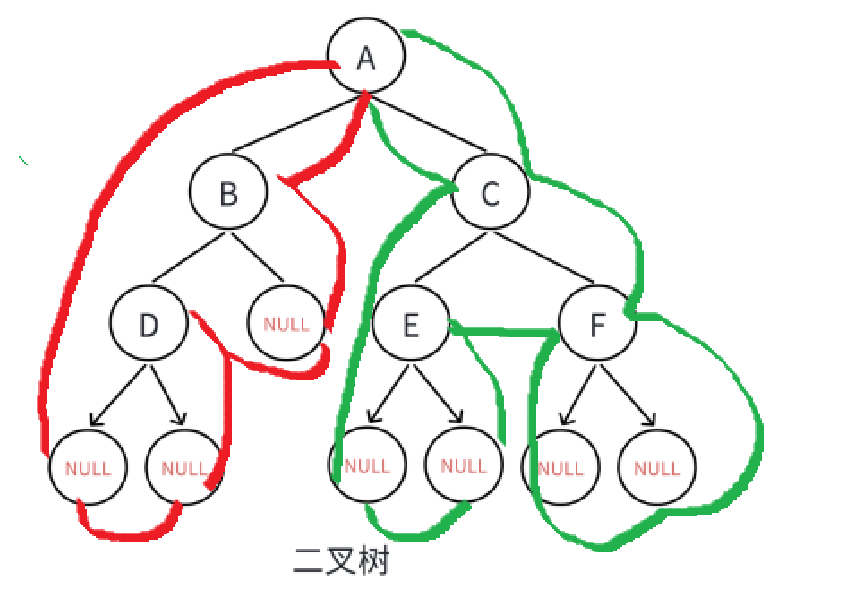
遍历结果为:NULL、NULL、D、NULL、B、NULL、NULL、E、NULL、NULL、F、C、A
代码实现
创建一棵二叉树
创建一个树的结点
//创建一个二叉树的结点
BTNode* BuyBTNode(BDT val)
{BTNode* newnode = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BDT));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc error");exit(1);}newnode->Data=val;newnode->leftchild=newnode->rightchild=NULL;return newnode;
}创建一棵树
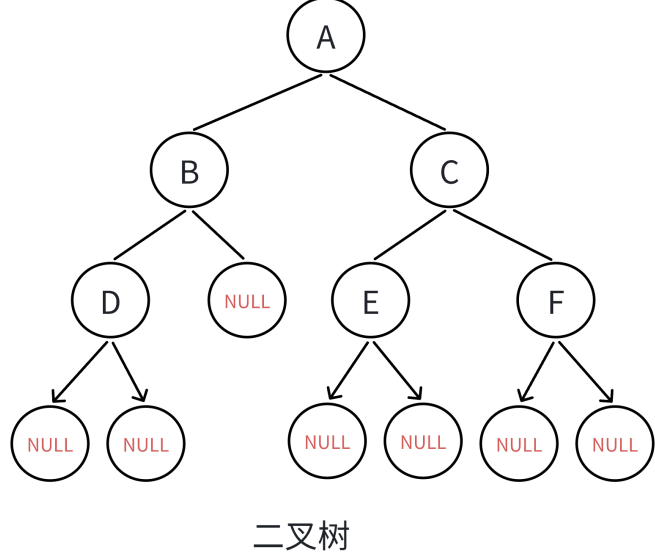
图为下图:
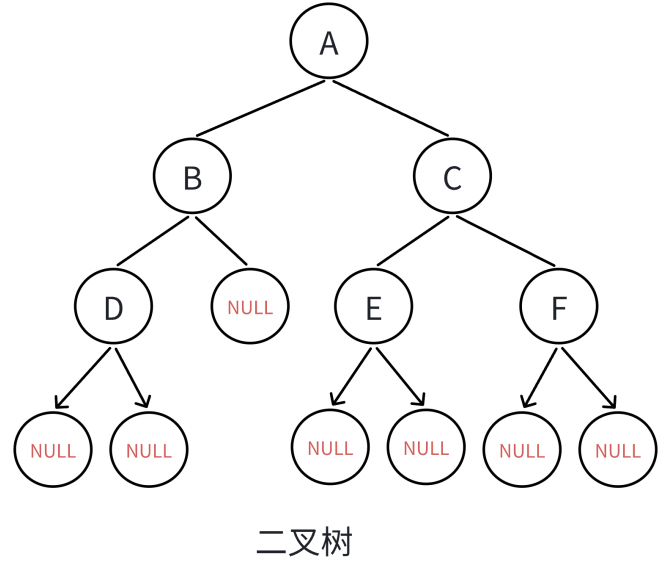
代码:
//创建一个树
BTNode* BTNodeCreate()
{BTNode* nodeA = BuyBTNode('A');BTNode* nodeB = BuyBTNode('B');BTNode* nodeC = BuyBTNode('C');BTNode* nodeD = BuyBTNode('D');BTNode* nodeE = BuyBTNode('E');BTNode* nodeF = BuyBTNode('F');nodeA->leftchild = nodeB;nodeA->rightchild = nodeC;nodeB->leftchild = nodeD;nodeB->rightchild = NULL;nodeC->leftchild = nodeE;nodeC->rightchild = nodeF;nodeD->leftchild = NULL;nodeD->rightchild = NULL;nodeE->leftchild = NULL;nodeE->rightchild = NULL;nodeF->leftchild = NULL;nodeF->rightchild = NULL;//也可以这么写/*nodeA->leftchild = nodeB;nodeA->rightchild = nodeC;nodeB->leftchild = nodeD;nodeC->leftchild = nodeE;nodeC->rightchild = nodeF;*/return nodeA;
}前序遍历
//前序遍历——跟左右
void PreOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL) {printf("NULL ");return;}printf("%c ", root->Data);PreOrder(root->leftchild);PreOrder(root->rightchild);}测试:
void test1()
{BTNode* root = BTNodeCreate();PreOrder(root);
}结果为:
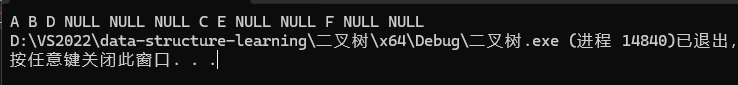
递归流程:
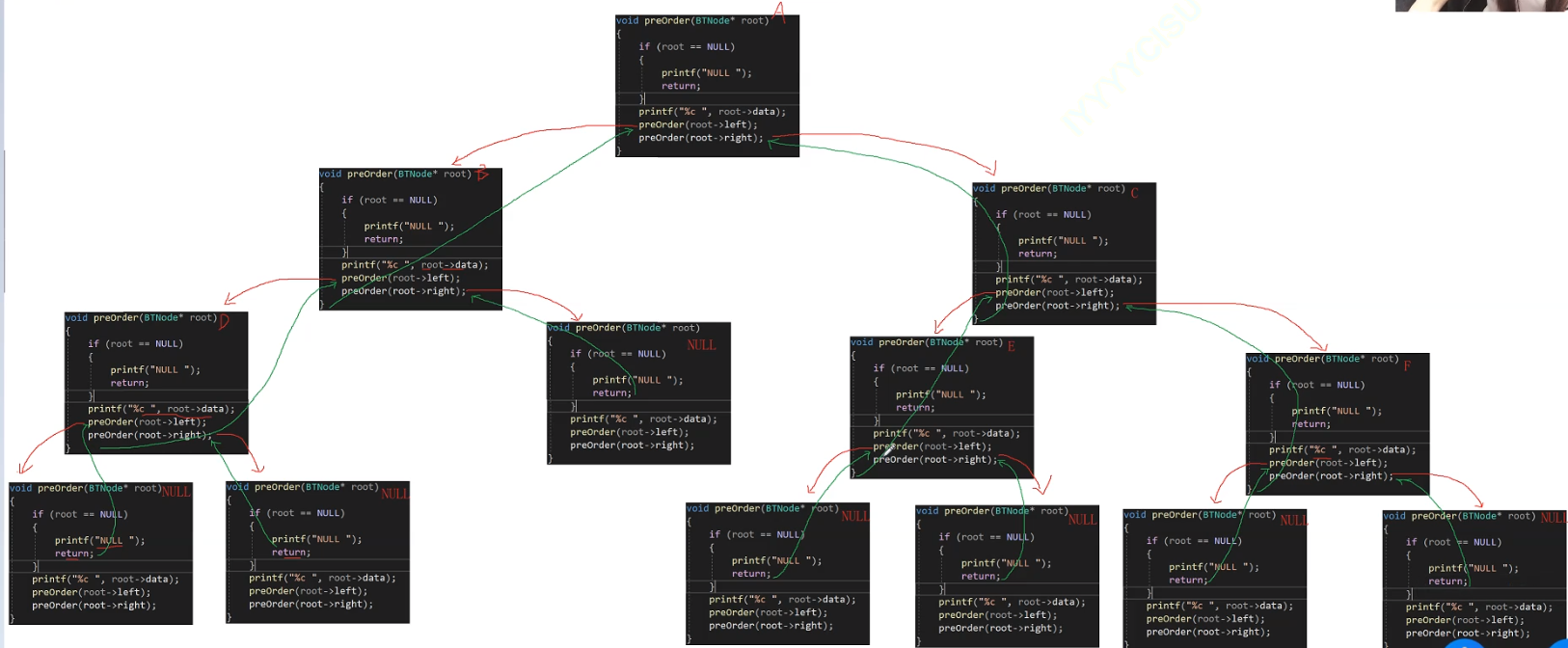
中序遍历
//中序遍历——左根右
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){printf("NULL ");return;}InOrder(root->leftchild);printf("%c ", root->Data);InOrder(root->rightchild);
}后序遍历
//后序遍历——左右根
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){printf("NULL ");return;}PostOrder(root->leftchild);PostOrder(root->rightchild);printf("%c ", root->Data);}求二叉树结点个数
结点个数=根节点个数+左子树节点个数+右子树节点个数
老办法:
//求二叉树结点个数
// 老方法:不合适,因为size为全局变量,多次调用size无法置空
int size = 0;
int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}//结点非空size++;BinaryTreeSize(root->leftchild);BinaryTreeSize(root->rightchild);return size;
}不合适,因为size为全局变量,所以多次调用会主次增加,导致失败。
新办法1:
//新方法:多参数
int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root, int *size)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}//结点非空 (*size)++;BinaryTreeSize(root->leftchild, size);BinaryTreeSize(root->rightchild,size);return *size;
}缺点是测试的时候需要额外添加一个变量且需要多个参数,相比之下比较麻烦。
新方法2:
//新方法:
int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}return 1 + BinaryTreeSize(root->leftchild) + BinaryTreeSize(root->rightchild);
}求二叉树的高度
二叉树的高度=根节点+max(左子树,右子树)
//求二叉树高度
int BinaryTreeHeight(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}int leftdep = BinaryTreeHeight(root->leftchild);int rightdep = BinaryTreeHeight(root->rightchild);return (leftdep > rightdep ? leftdep : rightdep) + 1;
}二叉树的查找
//查找为x的结点
BTNode* SearchBTNode(BTNode* root,BDT x)
{if (root == NULL){return NULL;}if (root->Data == x){return root;}BTNode*leftfind = SearchBTNode(root->leftchild, x);if (leftfind != NULL){return leftfind;}BTNode*rightfind = SearchBTNode(root->rightchild, x);if (rightfind != NULL){return rightfind;}return NULL;
}销毁二叉树
//销毁二叉树
void BinaryTreeDestory(BTNode** root)
{//后序遍历法销毁if (*root == NULL){return;}BinaryTreeDestory(&((*root)->leftchild));BinaryTreeDestory(&((*root)->rightchild));free(*root);*root = NULL;
}二叉树的层序遍历
二叉树的层序遍历需要数据结构——队列的辅助。有先进先出的特性。
前置准备:
//typedef int QTypeData;
//前置声明:
typedef struct Binary_Tree_Node* QTypeData;
//队列结点结构
typedef struct queuenode
{QTypeData data;struct queuenode* next;
}QN;代码实现:
//二叉树的层序遍历
//借助数据结构——队列
void levelOrder(BTNode* root)
{queue q;initqueue(&q);enqueue(&q, root);while (!isempty(&q)){//取队头,出队头BTNode* top = gethead(&q);dequeue(&q);printf("%c ", top->Data);//将队头非空左右孩子入队列if (top->leftchild)enqueue(&q, top->leftchild);if (top->rightchild)enqueue(&q, top->rightchild);}destroyqueue(&q);
}判断是否为完全二叉树
完全二叉树特点:
1)最后一层结点不一定到最大
2)结点从左到右依次排列

借助数据结构队列来实现。
思路:第一层循环,取到空结点循环结束;第二层循环从非空队列取到非空结点循环结束。若从非空队列中取到非空结点则该二叉树一定不是完全二叉树,反之是完全二叉树。
//判断是否为完全二叉树
//借助数据结构——队列来实现
bool isCompleteBinaryTree(BTNode* root)
{queue q;initqueue(&q);enqueue(&q, root);while(!isempty(&q)){//取队头结点,出队头BTNode* top = gethead(&q);dequeue(&q);if (top == NULL){break;}enqueue(&q, top->leftchild);enqueue(&q, top->rightchild);}//队列不一定为空while (!isempty(&q)){BTNode* top = gethead(&q);gethead(&q);if (top != NULL){destroyqueue(&q);return false;}}destroyqueue(&q);return true;
}源代码
二叉树
binary_tree.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include"queue.h"
//数据类型
typedef char Binary_Data_Type;
typedef Binary_Data_Type BDT;
//链式树节点结构
typedef struct Binary_Tree_Node
{BDT Data;//节点数据struct Binary_Tree_Node* leftchild;//左子树指针struct Binary_Tree_Node* rightchild;//右子树指针
}BTNode;
//创建一个二叉树的结点
BTNode* BuyBTNode(BDT val);
//创建一个树
BTNode* BTNodeCreate();
//前序遍历
void PreOrder(BTNode* root);
//中序遍历
void InOrder(BTNode* root);
//后序遍历
void PostOrder(BTNode* root);
//求二叉树结点个数
int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root);
//二叉树的层序遍历
void levelOrder(BTNode* root);
// 多参数
//int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root, int *size);
//求二叉树叶子结点个数
int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root);
//求二叉树高度
int BinaryTreeHeight(BTNode* root);
//查找二叉树第K层所在的结点
int BinaryTreeK_Size(BTNode* root,int k);
//查找为x的结点
BTNode* SearchBTNode(BTNode* root,BDT x);
//判断是否为空树
bool empty(BTNode* root);
//判断是否为满二叉树
bool isFull(BTNode* root);
//判断是否为完全二叉树
bool isCompleteBinaryTree(BTNode* root);
//销毁二叉树
void BinaryTreeDestory(BTNode** root);binary_tree.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"binary_tree.h"
//创建一个二叉树的结点
BTNode* BuyBTNode(BDT val)
{BTNode* newnode = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc error");exit(1);}newnode->Data=val;newnode->leftchild=newnode->rightchild=NULL;return newnode;
}
//创建一个树
BTNode* BTNodeCreate()
{BTNode* nodeA = BuyBTNode('A');BTNode* nodeB = BuyBTNode('B');BTNode* nodeC = BuyBTNode('C');BTNode* nodeD = BuyBTNode('D');BTNode* nodeE = BuyBTNode('E');BTNode* nodeF = BuyBTNode('F');nodeA->leftchild = nodeB;nodeA->rightchild = nodeC;nodeB->leftchild = nodeD;nodeB->rightchild = NULL;nodeC->leftchild = nodeE;nodeC->rightchild = nodeF;nodeD->leftchild = NULL;nodeD->rightchild = NULL;nodeE->leftchild = NULL;nodeE->rightchild = NULL;nodeF->leftchild = NULL;nodeF->rightchild = NULL;//也可以这么写/*nodeA->leftchild = nodeB;nodeA->rightchild = nodeC;nodeB->leftchild = nodeD;nodeC->leftchild = nodeE;nodeC->rightchild = nodeF;*/return nodeA;
}
//前序遍历——跟左右
void PreOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL) {printf("NULL ");return;}printf("%c ", root->Data);PreOrder(root->leftchild);PreOrder(root->rightchild);}
//中序遍历——左根右
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){printf("NULL ");return;}InOrder(root->leftchild);printf("%c ", root->Data);InOrder(root->rightchild);
}
//后序遍历——左右根
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){printf("NULL ");return;}PostOrder(root->leftchild);PostOrder(root->rightchild);printf("%c ", root->Data);}
//求二叉树结点个数
// 老方法:不合适,因为size为全局变量,多次调用size无法置空
//int size = 0;
//int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root)
//{
// if (root == NULL)
// {
// return 0;
// }
// //结点非空
//
// size++;
// BinaryTreeSize(root->leftchild);
// BinaryTreeSize(root->rightchild);
// return size;
//}
//新方法:多参数
//int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root, int *size)
//{
// if (root == NULL)
// {
// return 0;
// }
// //结点非空
// (*size)++;
// BinaryTreeSize(root->leftchild, size);
// BinaryTreeSize(root->rightchild,size);
// return *size;
//}
//新方法:
int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}return 1 + BinaryTreeSize(root->leftchild) + BinaryTreeSize(root->rightchild);
}
//求二叉树高度
int BinaryTreeHeight(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}int leftdep = BinaryTreeHeight(root->leftchild);int rightdep = BinaryTreeHeight(root->rightchild);return (leftdep > rightdep ? leftdep : rightdep) + 1;
}
//查找二叉树第K层所在的结点
int BinaryTreeK_Size(BTNode* root,int k)
{// 如果根节点为空或者k小于1,返回0if (root == NULL || k < 1) {return 0;}// 当k为1时,当前节点就是第1层的节点if (k == 1) {return 1;}// 递归计算左子树和右子树中第k-1层的节点数return BinaryTreeK_Size(root->leftchild, k - 1) +BinaryTreeK_Size(root->rightchild, k - 1);
}
//求二叉树叶子结点个数
int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{// 空节点没有叶子节点if (root == NULL) {return 0;}// 叶子节点:没有左子树和右子树的节点if (root->leftchild == NULL && root->rightchild == NULL) {return 1;}// 递归计算左右子树的叶子节点数return BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->leftchild) +BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->rightchild);
}
//判断是否为完全二叉树
//借助数据结构——队列来实现
bool isCompleteBinaryTree(BTNode* root)
{queue q;initqueue(&q);enqueue(&q, root);while(!isempty(&q)){//取队头结点,出队头BTNode* top = gethead(&q);dequeue(&q);if (top == NULL){break;}enqueue(&q, top->leftchild);enqueue(&q, top->rightchild);}//队列不一定为空while (!isempty(&q)){BTNode* top = gethead(&q);gethead(&q);if (top != NULL){destroyqueue(&q);return false;}}destroyqueue(&q);return true;
}
//二叉树的层序遍历
//借助数据结构——队列
void levelOrder(BTNode* root)
{queue q;initqueue(&q);enqueue(&q, root);while (!isempty(&q)){//取队头,出队头BTNode* top = gethead(&q);dequeue(&q);printf("%c ", top->Data);//将队头非空左右孩子入队列if (top->leftchild)enqueue(&q, top->leftchild);if (top->rightchild)enqueue(&q, top->rightchild);}destroyqueue(&q);
}
//查找为x的结点
BTNode* SearchBTNode(BTNode* root,BDT x)
{if (root == NULL){return NULL;}if (root->Data == x){return root;}BTNode*leftfind = SearchBTNode(root->leftchild, x);if (leftfind != NULL){return leftfind;}BTNode*rightfind = SearchBTNode(root->rightchild, x);if (rightfind != NULL){return rightfind;}return NULL;
}
//判断是否为空树
bool empty(BTNode* root)
{return root == NULL;
}
//判断是否为满二叉树
bool isFull(BTNode* root)
{// 空树被认为是满二叉树if (root == NULL) {return true;}// 检查当前节点的子节点情况bool hasLeft = (root->leftchild != NULL);bool hasRight = (root->rightchild != NULL);// 情况1:有左子节点但没有右子节点(无效)if (hasLeft && !hasRight) {return false;}// 情况2:有右子节点但没有左子节点(无效)if (!hasLeft && hasRight) {return false;}// 递归检查左右子树return isFull(root->leftchild) && isFull(root->rightchild);
}
//销毁二叉树
void BinaryTreeDestory(BTNode** root)
{//后序遍历法销毁if (*root == NULL){return;}BinaryTreeDestory(&((*root)->leftchild));BinaryTreeDestory(&((*root)->rightchild));free(*root);*root = NULL;
}队列
queue.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
//相较于之前的队列,这里将类型改为了二叉树相关
//typedef int QTypeData;
//前置声明:
typedef struct BTNode* QTypeData;
//队列结点结构
typedef struct queuenode
{QTypeData data;struct queuenode* next;
}QN;
//队列结构
typedef struct queue
{QN* phead;//队头指针QN* ptail;//队尾指针//频繁调用的时候需要用到size//int size;//队列长度
}queue;
//初始化队列
void initqueue(queue* pq);
//入队
void enqueue(queue* pq, QTypeData data);
//出队
void dequeue(queue* pq);
//判断队列是否为空
bool isempty(queue* pq);
//取队头数据
QTypeData gethead(queue* pq);
//取队尾数据
QTypeData gettail(queue* pq);
//销毁队列
void destroyqueue(queue* pq);
//取队列长度
int size(queue* pq);
queue.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"queue.h"
//初始化队列
void initqueue(queue* pq)
{assert(pq!= NULL);pq->phead = pq->ptail = 0;}
//入队-队尾入队
void enqueue(queue* pq, QTypeData data)
{assert(pq!= NULL);QN*new_node=(QN*)malloc(sizeof(QN));//队列空间申请失败if (new_node == NULL){perror("malloc 失败");exit(1);}new_node->data = data;new_node->next = NULL;//判断队列是否为空if (pq->phead==NULL){//队列为空,则new_node既是头结点也是尾结点pq->phead = pq->ptail = new_node;}else{//队列不为空,则new_node是尾结点pq->ptail->next = new_node;pq->ptail = pq->ptail->next;}//方式二://++pq->size;
}
//判断队列是否为空
bool isempty(queue* pq)
{assert(pq!= NULL);return pq->phead == NULL;
}
//出队—队头出队
void dequeue(queue* pq)
{assert(!isempty(pq));if (pq->phead == pq->ptail){free(pq->phead);pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;}else{QN*next=pq->phead->next;free(pq->phead);pq->phead=next;}//方式二://--pq->size;
}
//取队头数据
QTypeData gethead(queue* pq)
{assert(!isempty(pq));return pq->phead->data;
}
//取队尾数据
QTypeData gettail(queue* pq)
{assert(!isempty(pq));return pq->ptail->data;
}
//销毁队列
void destroyqueue(queue* pq)
{assert(pq != NULL);QN* new_node = pq->phead;while (new_node != NULL){QN*next=new_node->next;free(new_node);new_node=next;}pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
}
//取队列长度
int size(queue* pq)
{assert(!isempty(pq));//适用于不频繁调用的情况QN* new_node = pq->phead;int count = 0;while (new_node != NULL){count++;new_node = new_node->next;}return count;//适用于频繁调用的情况//return pq->size;//但是出队列size--
}测试
test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "binary_tree.h"
//前序遍历
void test1()
{BTNode* root = BTNodeCreate();PreOrder(root);
}
//中序遍历
void test2()
{BTNode* root = BTNodeCreate();InOrder(root);
}
//后序遍历
void test3()
{BTNode* root = BTNodeCreate();PostOrder(root);
}
//计算结点数目
void test4()
{BTNode* root = BTNodeCreate();/*int size = 0;printf("个数为:%d",BinaryTreeSize(root,&size)); */printf("个数为:%d\n", BinaryTreeSize(root));printf("个数为:%d\n", BinaryTreeSize(root));printf("个数为:%d\n", BinaryTreeSize(root));
}
//查找结点
void test5()
{BTNode* root = BTNodeCreate();if (SearchBTNode(root, 'E')){printf("找到了!\n");}else{printf("没找到!\n");}
}
// 层序遍历
void test6()
{BTNode* root = BTNodeCreate();printf("层序遍历:\n");levelOrder(root);
}
//计算第K层节点数
void test7()
{// 创建二叉树BTNode* root = BTNodeCreate();// 测试第K层节点数printf("Level 1 node count: %d\n", BinaryTreeK_Size(root, 1)); // 应输出1 (A)printf("Level 2 node count: %d\n", BinaryTreeK_Size(root, 2)); // 应输出2 (B, C)printf("Level 3 node count: %d\n", BinaryTreeK_Size(root, 3)); // 应输出3 (D, E, F)printf("Level 4 node count: %d\n", BinaryTreeK_Size(root, 4)); // 应输出0// 测试叶子节点数printf("Leaf node count: %d\n", BinaryTreeLeafSize(root)); // 应输出3 (D, E, F)
}
//判断是否是完全二叉树
void test8()
{// 创建二叉树BTNode* root = BTNodeCreate();bool ret = isCompleteBinaryTree(root);if (ret!=0){printf("是完全二叉树!\n");}else{printf("不是完全二叉树! \n");}
}
int main()
{//test1();//test2();//test3();//test4();//test5();//test6();//test7();//test8();return 0;
}本期内容就到这里了,喜欢庆典个赞,谢谢
封面图自取:

