规则引擎架构-基于easy-rules
目录
- 概念理解
- 实例和编码
- 抽象出2条规则
- 简单的规则引擎
- 事实1的处理
- 事实2的处理
- easy-rules 规则的抽象和执行
- 事实描述
- 规则的抽象
- 默认的规则
- 动态代理执行规则和动作
- 规则的执行:org.jeasy.rules.core.DefaultRulesEngine#doFire
- public class RuleProxy implements InvocationHandler
- 规则执行监听器
- 回顾规则执行和监听器的执行过程
- 扩展
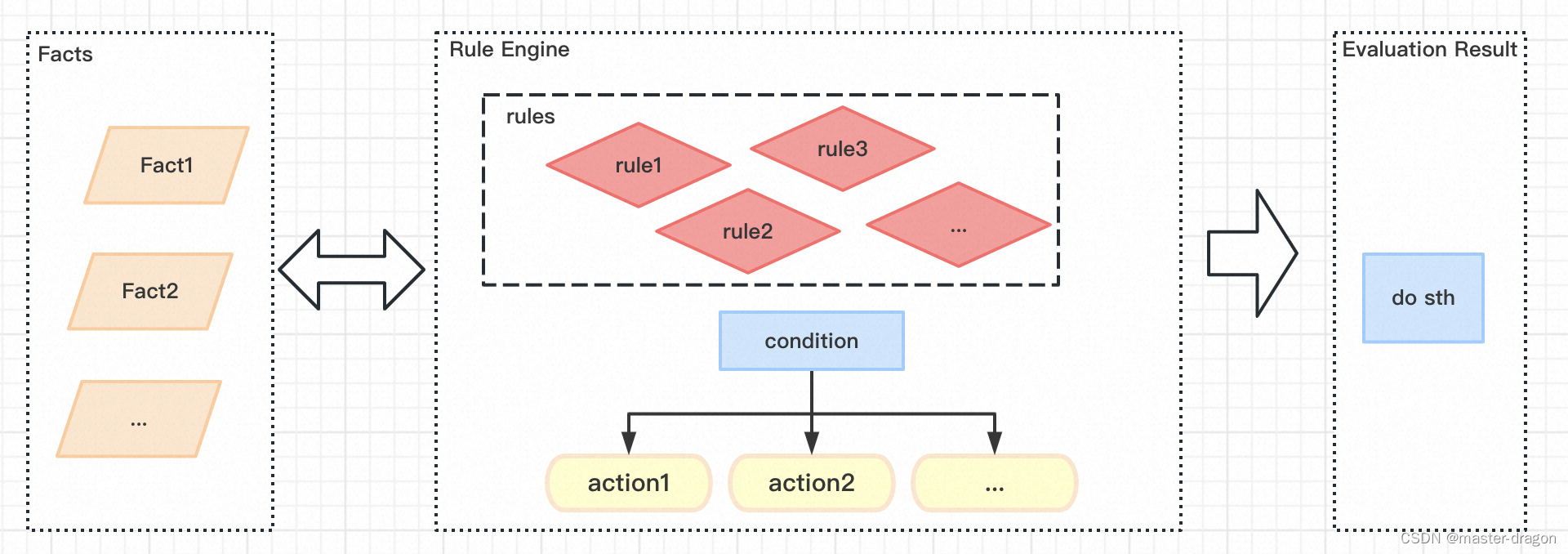
概念理解
描述一个简单的处理:基于一堆现实情况,运用规则引擎、经过处理得到对应的结果,然后再据此做后续的事情。
- fact: 事实,已有的现实情况,即输入信息
- rules: 规则集合,由一系列规则组成,可能有不同的规则排列
- rule: 规则,包含基本的判断条件和条件符合要做的动作。
- condition: 规则的判定条件(特定的判断逻辑 if else)
- action: 规则判定符合后执行的动作
实例和编码
一句话描述: 人提着包去酒店买酒,需要判断是否成年人,成年人才能购买酒,商店据此卖你酒,你买到了酒就装包里走人,回家喝酒去。
接下来看easy-rules的定义和处理。
抽象出2条规则
@Rule(name = "age-rule", description = "age-rule", priority = 1)
public class AgeRule {@Conditionpublic boolean isAdult(@Fact("person") Person person) {return person.getAge() > 18;}@Actionpublic void setAdult(@Fact("person") Person person) {person.setAdult(true);}
}
package org.jeasy.rules.tutorials.shop;import org.jeasy.rules.annotation.Action;
import org.jeasy.rules.annotation.Condition;
import org.jeasy.rules.annotation.Fact;
import org.jeasy.rules.annotation.Rule;/*** @author dingqi on 2023/5/26* @since 1.0.0*/
@Rule(name = "alcohol-rule", description = "alcohol-rule", priority = 2)
public class AlcoholRule {@Conditionpublic boolean shopRule(@Fact("person") Person person) {return person.isAdult() == true;}@Actionpublic void shopReply(@Fact("bag") Bag bag) {bag.setSuccess(true);bag.add("Vodka");}
}
简单的规则引擎
// create a rule set
Rules rules = new Rules();
rules.register(new AgeRule());
rules.register(new AlcoholRule());//create a default rules engine and fire rules on known facts
DefaultRulesEngine rulesEngine = new DefaultRulesEngine();事实1的处理
Facts facts = new Facts();
Person tom = new Person("Tom", 19);
facts.put("person", tom);
Bag bag = new Bag();
facts.put("bag", bag);System.out.println("Tom: Hi! can I have some Vodka please?");
rulesEngine.fire(rules, facts);
System.out.println("Tom: bag is " + bag);
输出:Tom成年了,买到了伏特加
Tom: Hi! can I have some Vodka please?
Tom: bag is Bag{success=true, goods=[Vodka]}
事实2的处理
Person jack = new Person("Jack", 10);
facts.put("person", jack);
Bag bag2 = new Bag();
facts.put("bag", bag2);System.out.println("Jack: Hi! can I have some Vodka please?");
rulesEngine.fire(rules, facts);
System.out.println("Jack: bag is " + bag2);
输出:Jack未成年,无功而返
Jack: Hi! can I have some Vodka please?
Jack: bag is Bag{success=false, goods=[]}
easy-rules 规则的抽象和执行
事实描述
public class Facts implements Iterable<Fact<?>> {private final Set<Fact<?>> facts = new HashSet<>();/*** A class representing a named fact. Facts have unique names within a {@link Facts}* instance.* * @param <T> type of the fact* @author Mahmoud Ben Hassine*/
public class Fact<T> {private final String name;private final T value;事实简单就是key、value对, 某个事实的名称,和事实的属性特征(以一切皆对象来看,就是一个一个的对象组成了事实)。(只要在规则条件真正执行前,能明确这些事实就行)
规则的抽象
- 名称
- 描述
- 优先级
- 执行Facts的的方法
见org.jeasy.rules.api.Rule接口 和基础实现类org.jeasy.rules.core.BasicRule
条件和动作注解:
@Inherited
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface Condition {}
@Inherited
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface Condition {}
默认的规则
class DefaultRule extends BasicRule {private final Condition condition;private final List<Action> actions;DefaultRule(String name, String description, int priority, Condition condition, List<Action> actions) {super(name, description, priority);this.condition = condition;this.actions = actions;}@Overridepublic boolean evaluate(Facts facts) {return condition.evaluate(facts);}@Overridepublic void execute(Facts facts) throws Exception {for (Action action : actions) {action.execute(facts);}}}
动态代理执行规则和动作
使用org.jeasy.rules.api.Rules添加规则时如下:
- org.jeasy.rules.api.Rules#register
public void register(Object... rules) {Objects.requireNonNull(rules);for (Object rule : rules) {Objects.requireNonNull(rule);this.rules.add(RuleProxy.asRule(rule));}}
使用org.jeasy.rules.annotation.Rule注解构造的规则是使用RuleProxy构造的
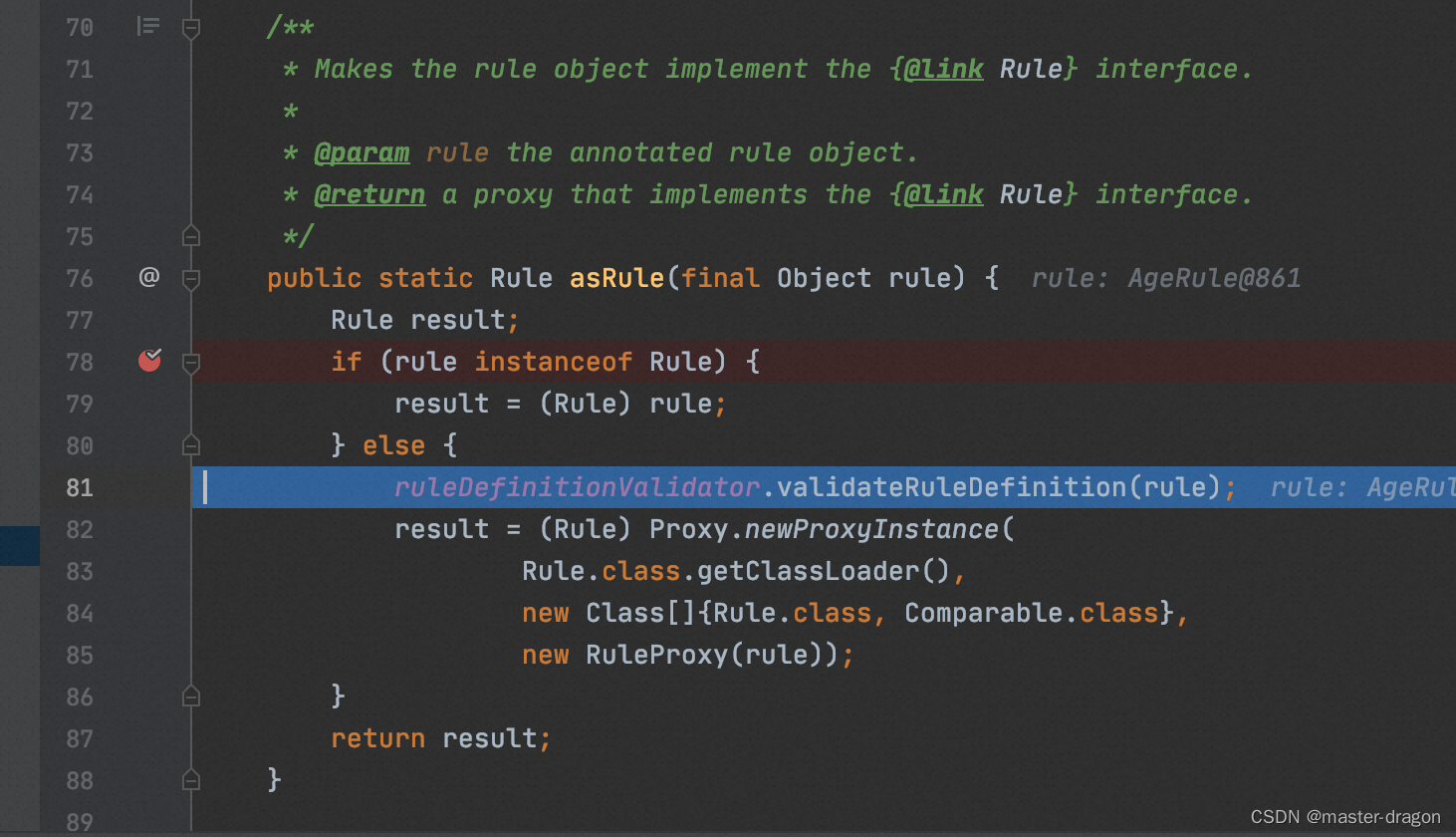
规则的执行:org.jeasy.rules.core.DefaultRulesEngine#doFire
void doFire(Rules rules, Facts facts) {if (rules.isEmpty()) {LOGGER.warn("No rules registered! Nothing to apply");return;}logEngineParameters();log(rules);log(facts);LOGGER.debug("Rules evaluation started");for (Rule rule : rules) {final String name = rule.getName();final int priority = rule.getPriority();if (priority > parameters.getPriorityThreshold()) {LOGGER.debug("Rule priority threshold ({}) exceeded at rule '{}' with priority={}, next rules will be skipped",parameters.getPriorityThreshold(), name, priority);break;}if (!shouldBeEvaluated(rule, facts)) {LOGGER.debug("Rule '{}' has been skipped before being evaluated", name);continue;}boolean evaluationResult = false;try {evaluationResult = rule.evaluate(facts);} catch (RuntimeException exception) {LOGGER.error("Rule '" + name + "' evaluated with error", exception);triggerListenersOnEvaluationError(rule, facts, exception);// give the option to either skip next rules on evaluation error or continue by considering the evaluation error as falseif (parameters.isSkipOnFirstNonTriggeredRule()) {LOGGER.debug("Next rules will be skipped since parameter skipOnFirstNonTriggeredRule is set");break;}}if (evaluationResult) {LOGGER.debug("Rule '{}' triggered", name);triggerListenersAfterEvaluate(rule, facts, true);try {triggerListenersBeforeExecute(rule, facts);rule.execute(facts);LOGGER.debug("Rule '{}' performed successfully", name);triggerListenersOnSuccess(rule, facts);if (parameters.isSkipOnFirstAppliedRule()) {LOGGER.debug("Next rules will be skipped since parameter skipOnFirstAppliedRule is set");break;}} catch (Exception exception) {LOGGER.error("Rule '" + name + "' performed with error", exception);triggerListenersOnFailure(rule, exception, facts);if (parameters.isSkipOnFirstFailedRule()) {LOGGER.debug("Next rules will be skipped since parameter skipOnFirstFailedRule is set");break;}}} else {LOGGER.debug("Rule '{}' has been evaluated to false, it has not been executed", name);triggerListenersAfterEvaluate(rule, facts, false);if (parameters.isSkipOnFirstNonTriggeredRule()) {LOGGER.debug("Next rules will be skipped since parameter skipOnFirstNonTriggeredRule is set");break;}}}
}
默认的规则引擎直接遍历规则去执行,如果condition执行命中后,则去执行action
public class RuleProxy implements InvocationHandler
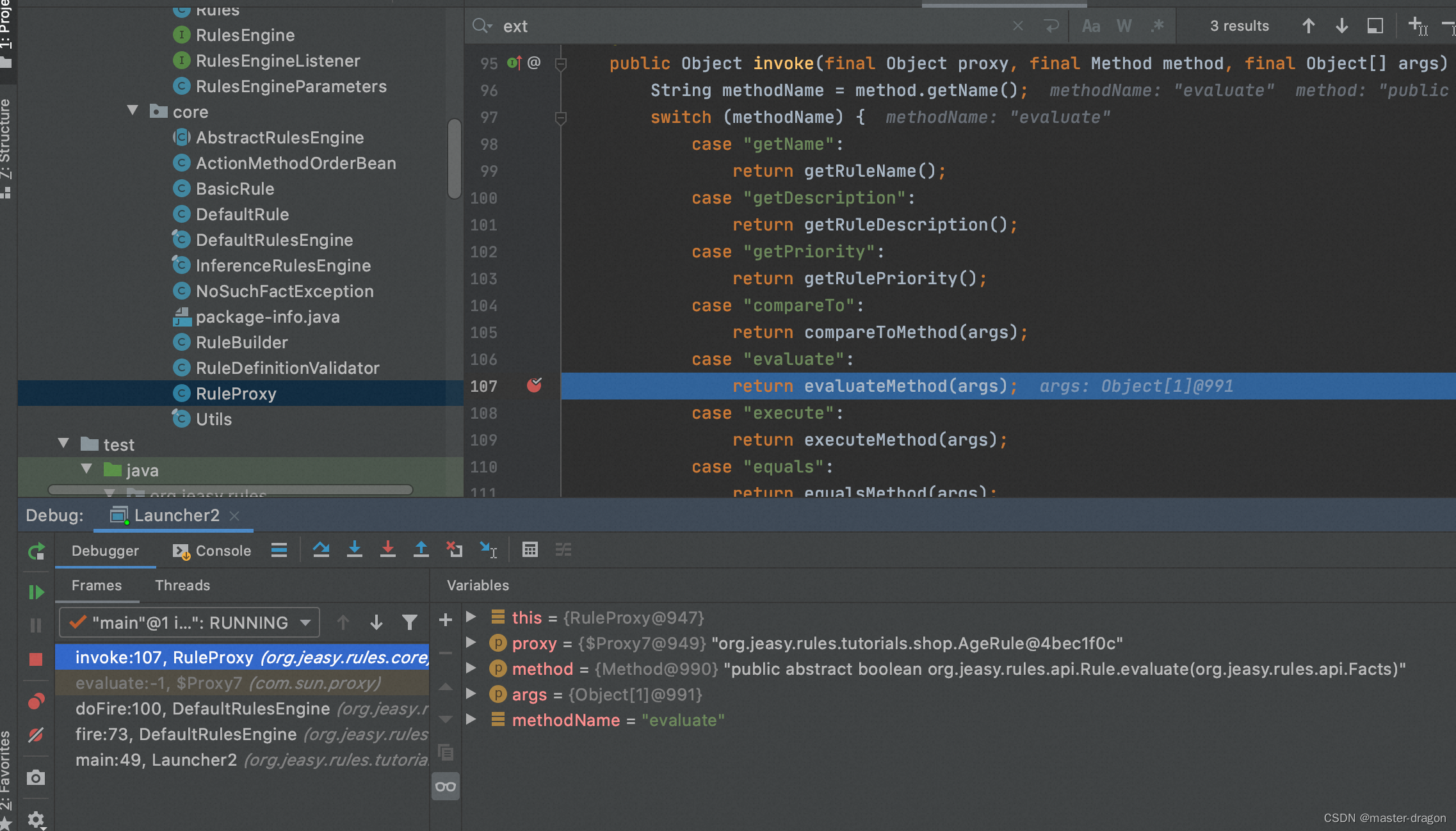
private Object evaluateMethod(final Object[] args) throws IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {Facts facts = (Facts) args[0];Method conditionMethod = getConditionMethod();try {List<Object> actualParameters = getActualParameters(conditionMethod, facts);return conditionMethod.invoke(target, actualParameters.toArray()); // validated upfront} catch (NoSuchFactException e) {LOGGER.warn("Rule '{}' has been evaluated to false due to a declared but missing fact '{}' in {}",getTargetClass().getName(), e.getMissingFact(), facts);return false;} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {LOGGER.warn("Types of injected facts in method '{}' in rule '{}' do not match parameters types",conditionMethod.getName(), getTargetClass().getName(), e);return false;}
}
规则执行监听器
在规则执行的过程中,可以做各种操作。可以看成规则的扩展点
/*** A listener for rule execution events.** @author Mahmoud Ben Hassine (mahmoud.benhassine@icloud.com)*/
public interface RuleListener {/*** Triggered before the evaluation of a rule.** @param rule being evaluated* @param facts known before evaluating the rule* @return true if the rule should be evaluated, false otherwise*/default boolean beforeEvaluate(Rule rule, Facts facts) {return true;}/*** Triggered after the evaluation of a rule.** @param rule that has been evaluated* @param facts known after evaluating the rule* @param evaluationResult true if the rule evaluated to true, false otherwise*/default void afterEvaluate(Rule rule, Facts facts, boolean evaluationResult) { }/*** Triggered on condition evaluation error due to any runtime exception.** @param rule that has been evaluated* @param facts known while evaluating the rule* @param exception that happened while attempting to evaluate the condition.*/default void onEvaluationError(Rule rule, Facts facts, Exception exception) { }/*** Triggered before the execution of a rule.** @param rule the current rule* @param facts known facts before executing the rule*/default void beforeExecute(Rule rule, Facts facts) { }/*** Triggered after a rule has been executed successfully.** @param rule the current rule* @param facts known facts after executing the rule*/default void onSuccess(Rule rule, Facts facts) { }/*** Triggered after a rule has failed.** @param rule the current rule* @param facts known facts after executing the rule* @param exception the exception thrown when attempting to execute the rule*/default void onFailure(Rule rule, Facts facts, Exception exception) { }}
回顾规则执行和监听器的执行过程
// 1. 条件执行前
triggerListenersBeforeEvaluate(rule, facts);
try {evaluationResult = rule.evaluate(facts);
} catch(Exception e){// 2. 条件执行失败triggerListenersOnEvaluationError(rule, facts, exception);
}if (evaluationResult) {// 3. 条件执行后(条件满足)triggerListenersAfterEvaluate(rule, facts, true);try {// 4. 动作执行前triggerListenersBeforeExecute(rule, facts);rule.execute(facts);// 5. 动作执行后triggerListenersOnSuccess(rule, facts);} catch (Exception exception) {// 6. 条件执行失败triggerListenersOnFailure(rule, exception, facts);}
}else{// 3. 条件执行后(条件不满足)triggerListenersAfterEvaluate(rule, facts, false);
}
扩展
- Java Expression Language (JEXL) :表达式语言引擎
https://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-jexl/apidocs/org/apache/commons/jexl3/JexlEngine.html
-
MVEL:一个功能强大的基于Java应用程序的表达式语言。
-
SpEL:Spring表达式语言
name: adult rule
description: when age is greater than 18, then mark as adult
priority: 1
condition: "#{ ['person'].age > 18 }"
actions:- "#{ ['person'].setAdult(true) }"
