SQL复杂查询
DQL:数据查询语言
常见的查询条件:
比较查询
范围查询
分组查询
结果排序
结果分页
模糊查询
子查询
连接查询
条件语句 | 简介 |
= != > < >= <= 比较运算 | 列名 运算符 值 |
between 开始 and 结束 | 范围 id between 2 and 4 |
in /not in | 成员 id in (2,4) |
and | && | 逻辑与 查询结果必须满足==所有==条件 |
or | || | 逻辑或 查询结果满足任意==一个==条件 |
not | ! | 逻辑非 查询所有不满足条件的结果 |
is null | 查询结果为空的值 |
is not null | 查询结果不为空的值 |
order by | 排序 order by id 逆序从大到小使用desc |
like | 模糊查询 name like "%三%" % 表示任意个任意值 |
电商案例:
1.登录
mysql -uroot -p → 输入密码2.创建库
create database 库名;3.进入库
use 库名;4.创建表
(1)用户表
create table users (id int primary key auto_increment,username varchar(50) not null,age int,gender enum('男', '女', '未知'),city varchar(50),register_time datetime default current_timestamp);查看用户表结构
desc users;(2)商品表
create table products (id int primary key auto_increment,name varchar(100) not null,category varchar(50) not null,price decimal(10,2) not null check (price > 0),stock int not null default 0 check (stock >= 0));查看商品表结构
desc products;(3)订单表
create table orders (id int primary key auto_increment,user_id int not null,product_id int not null,quantity int not null check (quantity > 0),total_amount decimal(10,2) not null check (total_amount > 0),status enum('待付款', '已付款', '已发货', '已完成', '已取消') default '待付款',create_time datetime default current_timestamp,-- 外键关联foreign key (user_id) references users(id),foreign key (product_id) references products(id));查看订单表结构
desc orders;5.插入数据
(1)插入用户数据
insert into users (username, age, gender, city, register_time) values('张三', 28, '男', '北京', '2023-01-15 09:30:00'),('李四', 22, '女', '上海', '2023-02-20 14:15:00'),('王五', 35, '男', '广州', '2023-03-05 10:00:00'),('赵六', 19, '女', '北京', '2023-04-18 16:45:00'),('孙七', 42, '男', '深圳', '2023-05-10 11:20:00');查看用户表数据
select * from users;(2)插入商品数据
insert into products (name, category, price, stock) values('iphone 14', '手机', 5999.00, 50),('华为matebook', '电脑', 6999.00, 30),('小米手环', '智能设备', 199.00, 100),('nike运动鞋', '服装', 699.00, 80),('机械键盘', '电脑配件', 299.00, 60);查看商品表数据
select * from products;(3)插入订单数据
insert into orders (user_id, product_id, quantity, total_amount, status, create_time) values(1, 1, 1, 5999.00, '已完成', '2023-06-01 10:30:00'),(1, 3, 2, 398.00, '已完成', '2023-06-15 15:45:00'),(2, 4, 1, 699.00, '已完成', '2023-06-05 09:15:00'),(3, 2, 1, 6999.00, '已发货', '2023-06-20 11:20:00'),(4, 5, 1, 299.00, '待付款', '2023-06-25 16:30:00'),(5, 1, 1, 5999.00, '已取消', '2023-06-18 14:00:00'),(2, 3, 1, 199.00, '已完成', '2023-06-10 10:00:00'),(3, 5, 2, 598.00, '已完成', '2023-06-08 13:25:00');查看订单表数据
select * from orders;6.查询
基础格式:select 查询字段 from 表名 where 条件;
基础比较
= | 等于 | select * from users where gender = '男'; |
!=/<> | 不等于 | select * from products where category != '服装'; |
>/< | 大于/小于 | select * from orders where total_amount > 2000; |
>=/<= | 大于等于/小于等于 | select * from users where age <= 30; |
范围匹配
between(比囤) ... and ... | 在指定范围内(包含边界) | select * from products where price between 500 and 5000; |
in (...) | 匹配列表中的任意值 | select * from users where city in ('广州', '深圳'); |
not in (...) | 不匹配列表中的值 | select * from orders where status not in ('已取消', '待付款'); |
模糊查询
like | 模糊匹配,`%`匹配任意字符,`_`匹配单个字符 | select * from products where name like '华为%'; select * from users where username like '_三%'; |
空值判断
is null | 字段值为null | select * from users where age is null; |
is not null | 字段值不为null | select * from products where stock is not null; |
逻辑组合
and | 同时满足多个条件 | select * from orders where status = '已完成' and quantity > 1; |
or | 满足任意一个条件 | select * from users where age < 20 or gender = '未知'; |
not | 条件取反 | select * from products where not price < 100; |
分组查询
关键字:group by
示例:select user_id,sum(total_amount) from orders group by user_id
having sum(total_amount)>5000;
统计每个用户的总订单金额,并筛选出总金额超过 5000 的用户
having 在这里用于过滤分组后的聚合结果(与 where 不同,where 用于分组前过滤行)。
聚合筛选
having | 对分组结果筛选(需配合group by) | select user_id, sum(total_amount) from orders group by user_id having sum(amount) > 5000; |
常用聚合函数
函数名 | 简介 |
count() | 查询数量或次数 |
max() | 最大值 |
min() | 最小值 |
avg() | 平均值 |
sum() | 求和 |
select count(*) from products;select avg(price) from products;select max(price) from products;select min(price) from products;select sum(price) from products;子查询
子查询是指嵌套在另一个 sql 语句中的查询语句。它就像一个 “查询中的查询”,主要用于辅助外层查询筛选数据、生成条件或提供数据。
exists | 子查询有结果则成立 | select * from users where exists (select 1 from orders where user_id = users.id); |
not exists | 子查询无结果则成立 | select * from products where not exists (select 1 from orders where product_id = products.id); |
去重
distinct | 筛选唯一值 | select distinct city from users; |
排序(order by)
必须放在where之后,limit之前
可指定多个排序字段,用逗号分隔
字符串按字典顺序排序,日期按时间先后排序
order by 字段 asc | 按指定字段升序排列(默认) | select * from products order by price asc; |
order by 字段 desc | 按指定字段降序排列 | select * from orders order by create_time desc; |
多字段排序 | 先按第一个字段排,再按第二个字段排 | select * from users order by city asc, age desc; |
分页(limit)
语法格式:limit [offset,] row_count,offset可选(默认0)
分页查询通常需要配合order by使用,否则分页结果可能不稳定
计算第n页数据(每页显示m条)的公式:limit (n-1)*m, m
limit 条数 | 只返回前n条记录 | select * from products order by price desc limit 5; |
limit 起始位置, 条数 | 从指定位置开始返回n条记录(起始从0开始) | select * from orders order by id limit 10, 5; --第11-15条记录 跳过数,查询数 |
分页公式 | 第n页(每页m条):limit (n-1)*m, m | select * from users limit 20, 10; --第3页,每页10条 |
连接查询(难点)
连接查询用于根据表之间的关联关系(通常是外键)从多个表中获取数据。
常见的连接类型包括:
(1)内连接 JOIN
(2)外连接
①左(外)连接
②右(外)连接
(3)联合查询
1.内连接(INNER JOIN)
只返回两个表中匹配条件的记录,是最常用的连接方式。
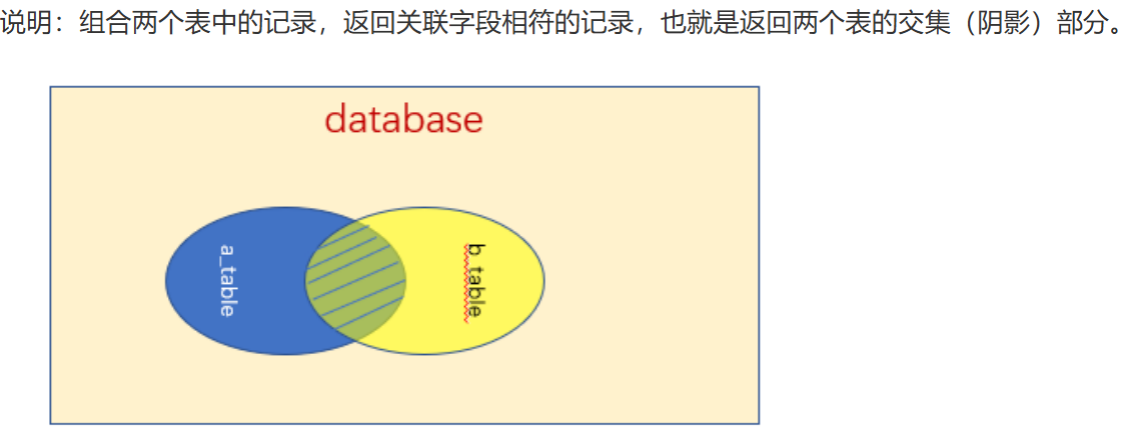
查询所有订单的用户和商品信息
AS 起别名, 可以省略
selecto.id as 订单id,u.username as 用户名,p.name as 商品名称,o.total_amount as 总金额from orders oinner join users u on o.user_id = u.idinner join products p on o.product_id = p.id;笛卡尔查询(交叉连接): 将所有表中的所有内容都会排列组合一次,不加关联条件时会产生。
select o.id as 订单id,u.username as 用户名,p.name as 商品名称,o.quantity as 购买数量,o.total_amount as 总金额,o.create_time as 下单时间from orders oinner join users u inner join products p;对关联的结果,进行查询
selecto.id as 订单id,u.username as 用户名,p.name as 商品名称,o.quantity as 购买数量,o.total_amount as 总金额,o.create_time as 下单时间from orders oinner join users u on o.user_id = u.idinner join products p on o.product_id = p.idwhere o.status = '已完成'order by o.create_time desc;左(外)连接(LEFT JOIN)
以左侧的表为基准,获取所有的数据,右表显示匹配到的数据,匹配不到的显示NULL
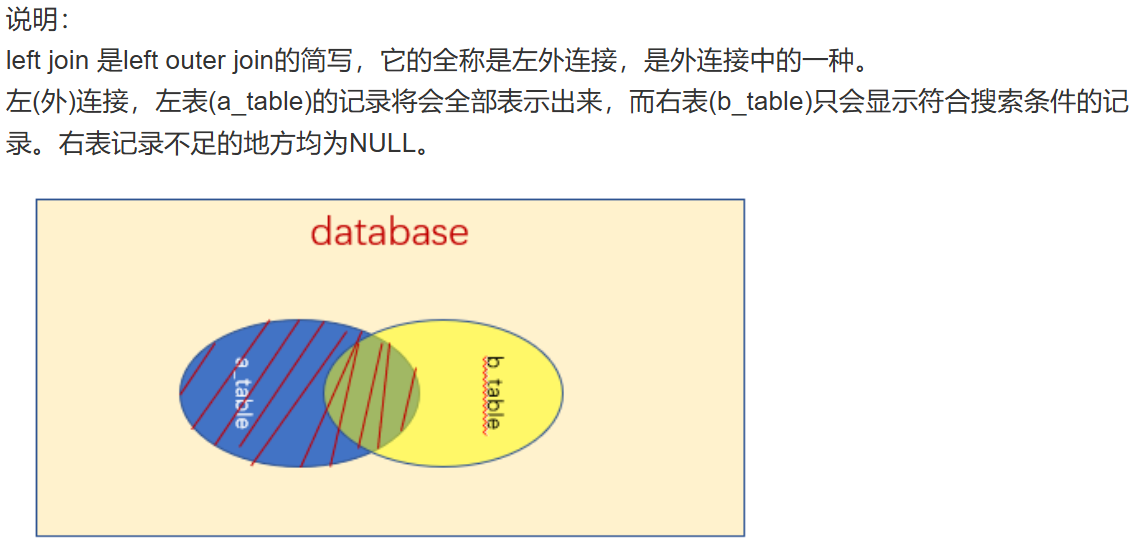
查询所有用户及其订单情况(包括没有订单的用户)
selectu.username as 用户名,count(o.id) as 订单数,ifnull(sum(o.total_amount), 0) as 总消费from users u left join orders o on u.id = o.user_idgroup by u.id, u.username;右连接(RIGHT JOIN)
与左连接相反,返回右表所有记录,以及左表中匹配条件的记录。
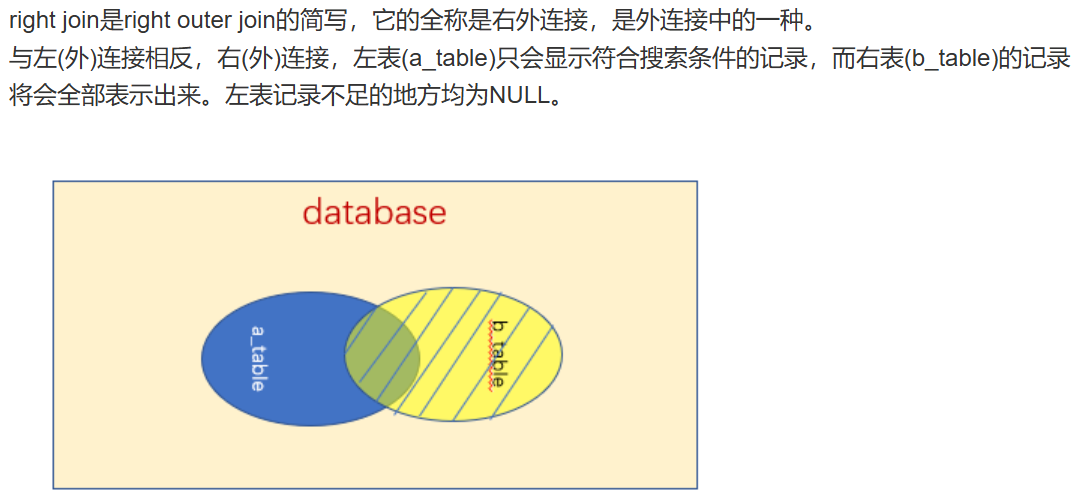
有商品及其被购买情况(包括未被购买的商品)
selectp.name as 商品名称,ifnull(sum(o.quantity), 0) as 销售总量from orders oright join products p on o.product_id = p.idgroup by p.id, p.name;自连接(SELF JOIN)
将表与自身进行连接,通常用于处理表中存在层级关系或关联关系的数据。
查询和"张三"同城市的用户
select u2.username, u2.cityfrom users u1join users u2 on u1.city = u2.citywhere u1.username = '张三' and u2.username != '张三';联合查询(UNION)
联合查询用于将多个SELECT语句的结果集合并为一个结果集,要求各查询的列数和数据类型必须一致。
UNION:合并去重
合并结果集并自动去除重复记录。
查询价格低于200的商品和年龄小于25的用户
select '商品' as 类型, name as 名称, '价格低' as 描述
from products
where price < 200
union
select '用户' as 类型, username as 名称, '年龄小' as 描述
from users
where age < 25;
UNION ALL:合并不去重
合并结果集但保留重复记录(效率比UNION高)。
查询已完成和已取消的订单,区分显示
SELECT '已完成订单' AS 订单类型, id AS 订单ID, create_time AS 时间
FROM orders
WHERE status = '已完成'
UNION ALL
SELECT '已取消订单' AS 订单类型, id AS 订单ID, create_time AS 时间
FROM orders
WHERE status = '已取消'
ORDER BY 时间;
连接查询与联合查询的区别
特征 | 连接查询(JOIN) | 联合查询(UNION) |
作用 | 横向关联多个表的数据 | 纵向合并多个查询的结果集 |
表关系 | 基于表间关联条件(如外键) | 无关联要求,但列结构需一致 |
结果集结构 | 列数为各表列数之和 | 列数与各查询的列数相同 |
使用场景 | 需要同时展示多个表的关联信息 | 需要合并多个相似结构的查询结果 |
