C++ unordered_map 和 unordered_set 的使用
C++ unordered_map 和 unordered_set 的使用
文章目录
- C++ unordered_map 和 unordered_set 的使用
- 一、unordered_set的使用
- 1.1 unordered_set类的介绍
- 1.2 unordered_set和set的使用差异
- 1.3 unordered_set的功能
- 1.3.1 unordered_set的初始化
- 1.3.2 unordered_set的迭代器
- 1.3.3 unordered_set的常见成员函数
- 1.4 unordered_multiset
- 二、unordered_map的使用
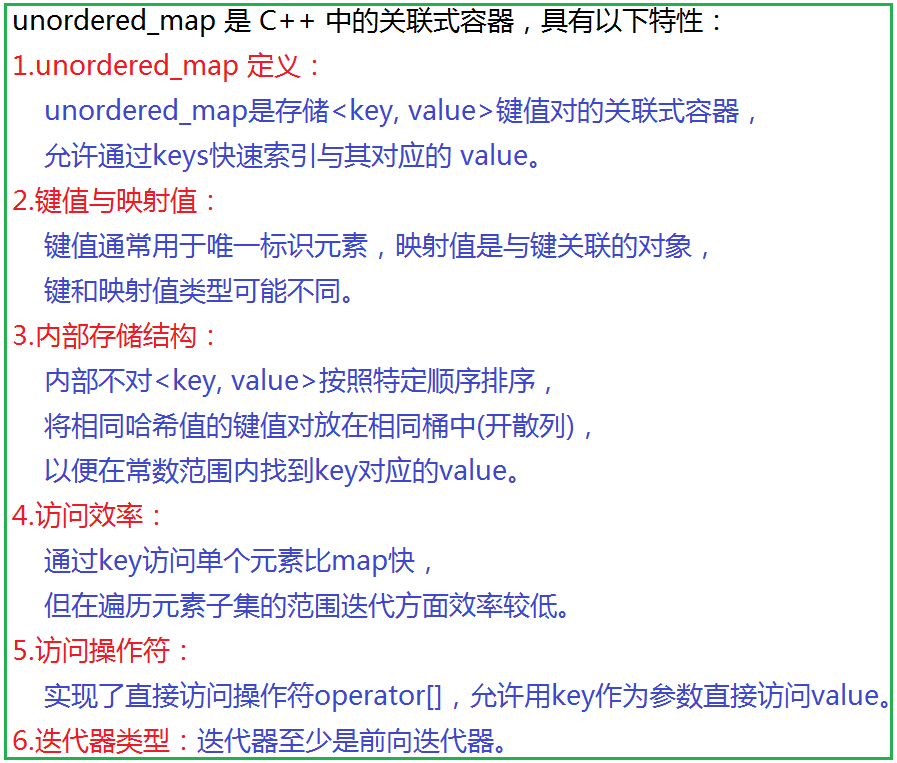
- 2.1 unordered_map类的介绍
- 2.2 unordered_map和map的使用差异
- 2.3 unordered_map的功能
- 2.3.1 unordered_map的初始化
- 2.3.2 unordered_map的迭代器
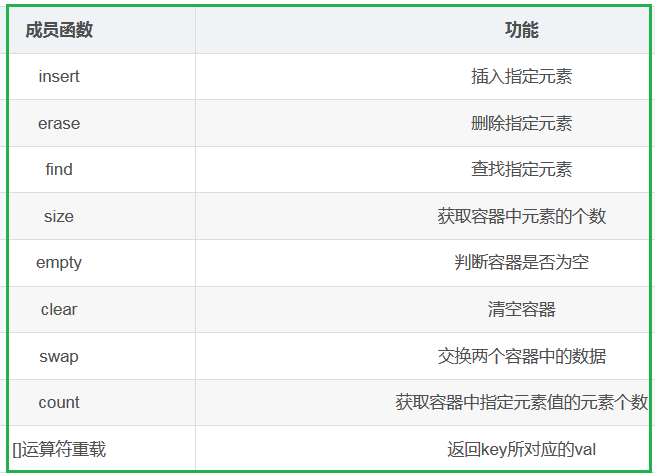
- 2.3.3 unordered_map的常见成员函数
- 2.4 unordered_multimap
- 三、源代码总结
- 3.1 unordered_set.cpp
- 3.2 unordered_map.cpp
- 3.3 Test.cpp
unordered的意思是无序的!
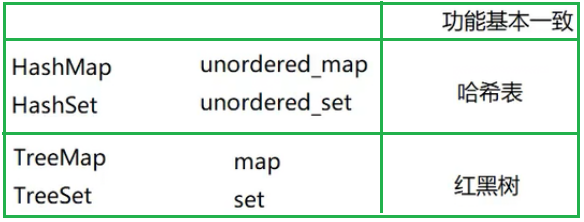
一、unordered_set的使用
1.1 unordered_set类的介绍
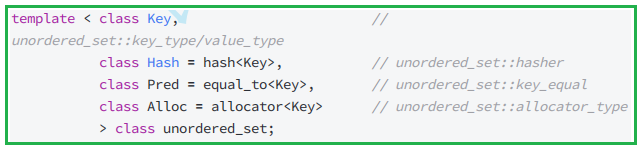


1.2 unordered_set和set的使用差异



以下代码是对于 set 和 unordered_set 的测试
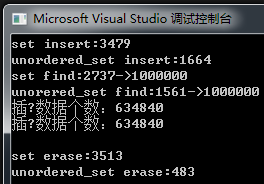
代码如下(示例):
#include<unordered_set>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
#include<iostream>
#include<time.h>
using namespace std;
int test_set2()
{const size_t N = 1000000;unordered_set<int> us;set<int> s;vector<int> v;v.reserve(N);srand(time(0));for (size_t i = 0; i < N; ++i){//v.push_back(rand()); // N⽐较⼤时,重复值⽐较多v.push_back(rand() + i); // 重复值相对少//v.push_back(i); // 没有重复,有序}// 21:15size_t begin1 = clock();for (auto e : v){s.insert(e);}size_t end1 = clock();cout << "set insert:" << end1 - begin1 << endl;size_t begin2 = clock();us.reserve(N);for (auto e : v){us.insert(e);}size_t end2 = clock();cout << "unordered_set insert:" << end2 - begin2 << endl;int m1 = 0;size_t begin3 = clock();for (auto e : v){auto ret = s.find(e);if (ret != s.end()){++m1;}}size_t end3 = clock();cout << "set find:" << end3 - begin3 << "->" << m1 << endl;int m2 = 0;size_t begin4 = clock();for (auto e : v){auto ret = us.find(e);if (ret != us.end()){++m2;}}size_t end4 = clock();cout << "unorered_set find:" << end4 - begin4 << "->" << m2 << endl;cout << "插⼊数据个数:" << s.size() << endl;cout << "插⼊数据个数:" << us.size() << endl << endl;size_t begin5 = clock();for (auto e : v){s.erase(e);}size_t end5 = clock();cout << "set erase:" << end5 - begin5 << endl;size_t begin6 = clock();for (auto e : v){us.erase(e);}size_t end6 = clock();cout << "unordered_set erase:" << end6 - begin6 << endl << endl;return 0;
}
int main()
{test_set2();return 0;
}
1.3 unordered_set的功能
unordered_set与STL其他大多数容器一样,为了支持所有类型,是一个类模版
1.3.1 unordered_set的初始化
unordered_set初始化会调用构造函数,构造函数重载了一下几种构造方式
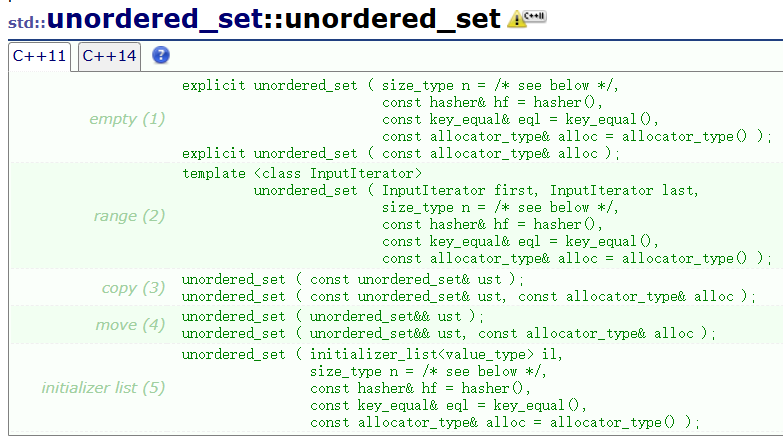
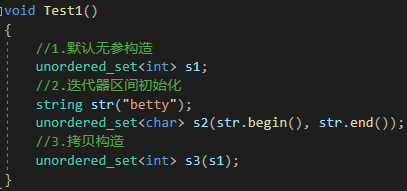
1.3.2 unordered_set的迭代器
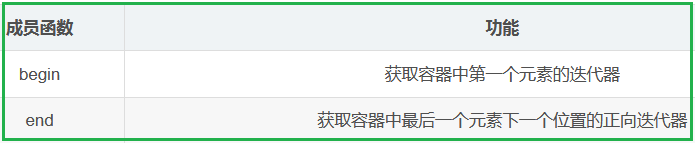
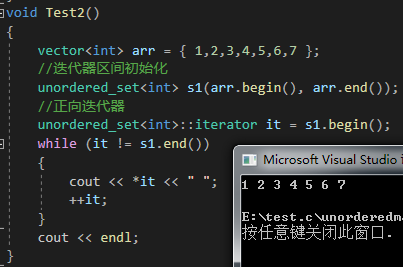
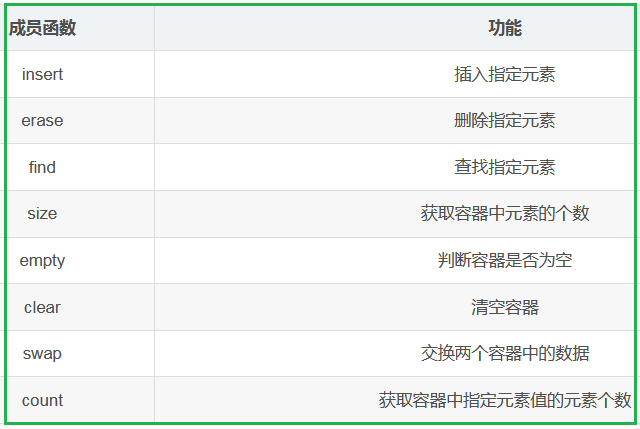
1.3.3 unordered_set的常见成员函数
1.4 unordered_multiset
unordered_multiset的使用方式与unordered_set基本一致
本质的区别在于unordered_multiset允许键值冗余,即可存储重复元素
unordered_multiset和find返回底层哈希表中第一个找到的键值val的元素迭代器
二、unordered_map的使用
2.1 unordered_map类的介绍
2.2 unordered_map和map的使用差异



2.3 unordered_map的功能
unordered_map与STL其他大多数容器一样,为了支持所有类型,所以是一个类模版
2.3.1 unordered_map的初始化
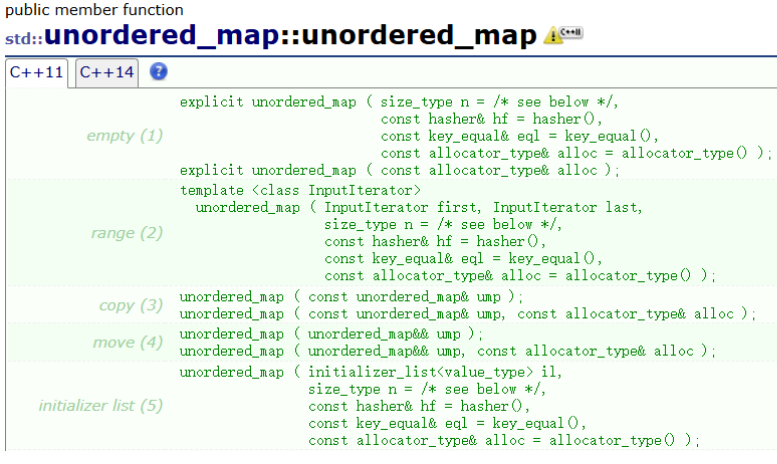
unordered_map初始化会调用构造函数,其构造函数分别重载了一下几种方式
2.3.2 unordered_map的迭代器
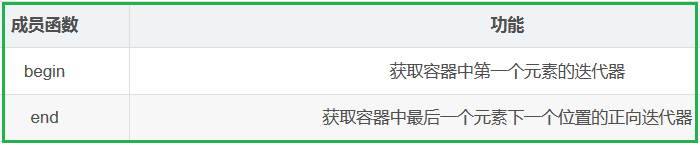
2.3.3 unordered_map的常见成员函数
unordered_map和unordered_set的成员函数类似,只不过多了一个 [ ] 运算符重载
2.4 unordered_multimap
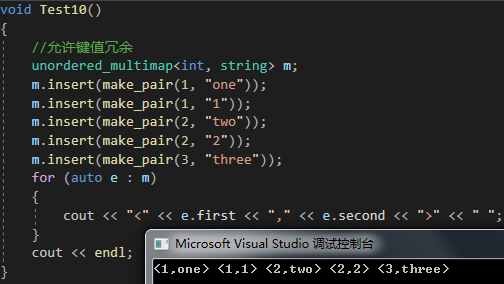
unordered_multimap的使用方式与unordered_map基本一致
唯一的区别在于 unordered_multimap 允许键值冗余,即可存储重复元素


三、源代码总结
3.1 unordered_set.cpp
代码如下(示例):
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<unordered_set>
#include<unordered_map>
void Test1()
{//1.默认无参构造unordered_set<int> s1;//2.迭代器区间初始化string str("betty");unordered_set<char> s2(str.begin(), str.end());//3.拷贝构造unordered_set<int> s3(s1);
}
void Test2()
{vector<int> arr = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 };//迭代器区间初始化unordered_set<int> s1(arr.begin(), arr.end());//正向迭代器unordered_set<int>::iterator it = s1.begin();while (it != s1.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;
}void Test3()
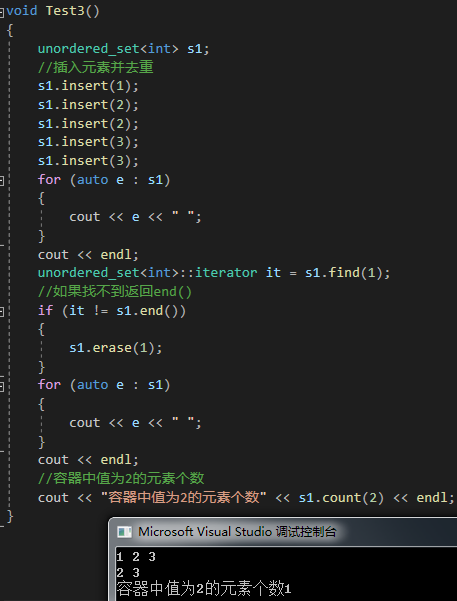
{unordered_set<int> s1;//插入元素并去重s1.insert(1);s1.insert(2);s1.insert(2);s1.insert(3);s1.insert(3);for (auto e : s1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;unordered_set<int>::iterator it = s1.find(1);//如果找不到返回end()if (it != s1.end()){s1.erase(1);}for (auto e : s1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;//容器中值为2的元素个数cout << "容器中值为2的元素个数" << s1.count(2) << endl;
}void Test4()
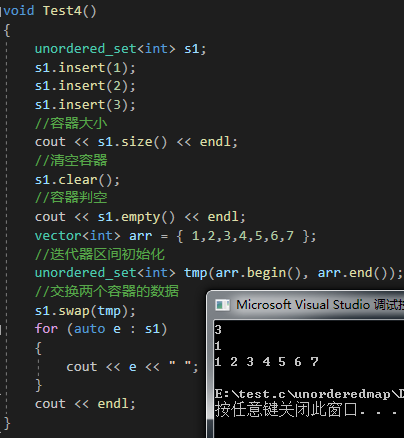
{unordered_set<int> s1;s1.insert(1);s1.insert(2);s1.insert(3);//容器大小cout << s1.size() << endl;//清空容器s1.clear();//容器判空cout << s1.empty() << endl;vector<int> arr = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 };//迭代器区间初始化unordered_set<int> tmp(arr.begin(), arr.end());//交换两个容器的数据s1.swap(tmp);for (auto e : s1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;
}void Test5()
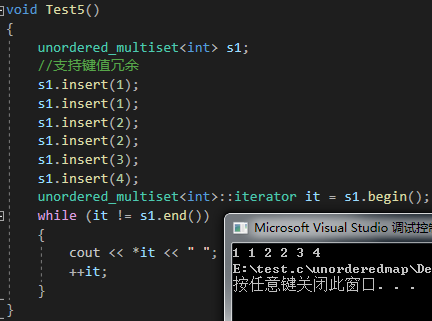
{unordered_multiset<int> s1;//支持键值冗余s1.insert(1);s1.insert(1);s1.insert(2);s1.insert(2);s1.insert(3);s1.insert(4);unordered_multiset<int>::iterator it = s1.begin();while (it != s1.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}
}
void Test6()
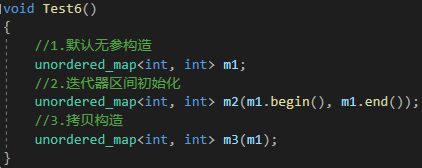
{//1.默认无参构造unordered_map<int, int> m1;//2.迭代器区间初始化unordered_map<int, int> m2(m1.begin(), m1.end());//3.拷贝构造unordered_map<int, int> m3(m1);
}
void Test7()
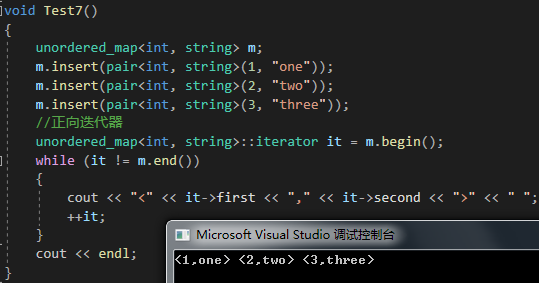
{unordered_map<int, string> m;m.insert(pair<int, string>(1, "one"));m.insert(pair<int, string>(2, "two"));m.insert(pair<int, string>(3, "three"));//正向迭代器unordered_map<int, string>::iterator it = m.begin();while (it != m.end()){cout << "<" << it->first << "," << it->second << ">" << " ";++it;}cout << endl;
}
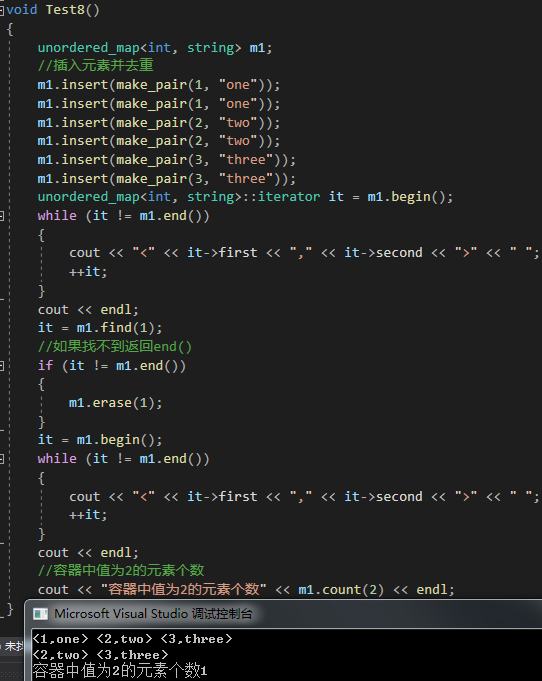
void Test8()
{unordered_map<int, string> m1;//插入元素并去重m1.insert(make_pair(1, "one"));m1.insert(make_pair(1, "one"));m1.insert(make_pair(2, "two"));m1.insert(make_pair(2, "two"));m1.insert(make_pair(3, "three"));m1.insert(make_pair(3, "three"));unordered_map<int, string>::iterator it = m1.begin();while (it != m1.end()){cout << "<" << it->first << "," << it->second << ">" << " ";++it;}cout << endl;it = m1.find(1);//如果找不到返回end()if (it != m1.end()){m1.erase(1);}it = m1.begin();while (it != m1.end()){cout << "<" << it->first << "," << it->second << ">" << " ";++it;}cout << endl;//容器中值为2的元素个数cout << "容器中值为2的元素个数" << m1.count(2) << endl;
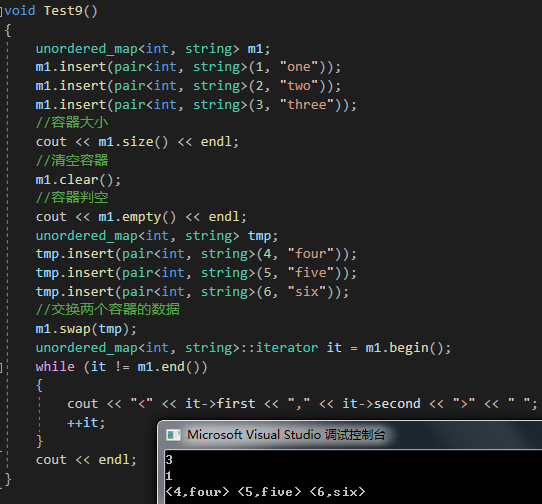
}void Test9()
{unordered_map<int, string> m1;m1.insert(pair<int, string>(1, "one"));m1.insert(pair<int, string>(2, "two"));m1.insert(pair<int, string>(3, "three"));//容器大小cout << m1.size() << endl;//清空容器m1.clear();//容器判空cout << m1.empty() << endl;unordered_map<int, string> tmp;tmp.insert(pair<int, string>(4, "four"));tmp.insert(pair<int, string>(5, "five"));tmp.insert(pair<int, string>(6, "six"));//交换两个容器的数据m1.swap(tmp);unordered_map<int, string>::iterator it = m1.begin();while (it != m1.end()){cout << "<" << it->first << "," << it->second << ">" << " ";++it;}cout << endl;
}
void Test10()
{//允许键值冗余unordered_multimap<int, string> m;m.insert(make_pair(1, "one"));m.insert(make_pair(1, "1"));m.insert(make_pair(2, "two"));m.insert(make_pair(2, "2"));m.insert(make_pair(3, "three"));for (auto e : m){cout << "<" << e.first << "," << e.second << ">" << " ";}cout << endl;
}int main()
{Test10();
}3.2 unordered_map.cpp
代码如下(示例):
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<unordered_set>
#include<unordered_map>
void Test1()
{//1.默认无参构造unordered_set<int> s1;//2.迭代器区间初始化string str("betty");unordered_set<char> s2(str.begin(), str.end());//3.拷贝构造unordered_set<int> s3(s1);
}
void Test2()
{vector<int> arr = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 };//迭代器区间初始化unordered_set<int> s1(arr.begin(), arr.end());//正向迭代器unordered_set<int>::iterator it = s1.begin();while (it != s1.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;
}void Test3()
{unordered_set<int> s1;//插入元素并去重s1.insert(1);s1.insert(2);s1.insert(2);s1.insert(3);s1.insert(3);for (auto e : s1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;unordered_set<int>::iterator it = s1.find(1);//如果找不到返回end()if (it != s1.end()){s1.erase(1);}for (auto e : s1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;//容器中值为2的元素个数cout << "容器中值为2的元素个数" << s1.count(2) << endl;
}void Test4()
{unordered_set<int> s1;s1.insert(1);s1.insert(2);s1.insert(3);//容器大小cout << s1.size() << endl;//清空容器s1.clear();//容器判空cout << s1.empty() << endl;vector<int> arr = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 };//迭代器区间初始化unordered_set<int> tmp(arr.begin(), arr.end());//交换两个容器的数据s1.swap(tmp);for (auto e : s1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;
}void Test5()
{unordered_multiset<int> s1;//支持键值冗余s1.insert(1);s1.insert(1);s1.insert(2);s1.insert(2);s1.insert(3);s1.insert(4);unordered_multiset<int>::iterator it = s1.begin();while (it != s1.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}
}
void Test6()
{//1.默认无参构造unordered_map<int, int> m1;//2.迭代器区间初始化unordered_map<int, int> m2(m1.begin(), m1.end());//3.拷贝构造unordered_map<int, int> m3(m1);
}
void Test7()
{unordered_map<int, string> m;m.insert(pair<int, string>(1, "one"));m.insert(pair<int, string>(2, "two"));m.insert(pair<int, string>(3, "three"));//正向迭代器unordered_map<int, string>::iterator it = m.begin();while (it != m.end()){cout << "<" << it->first << "," << it->second << ">" << " ";++it;}cout << endl;
}
void Test8()
{unordered_map<int, string> m1;//插入元素并去重m1.insert(make_pair(1, "one"));m1.insert(make_pair(1, "one"));m1.insert(make_pair(2, "two"));m1.insert(make_pair(2, "two"));m1.insert(make_pair(3, "three"));m1.insert(make_pair(3, "three"));unordered_map<int, string>::iterator it = m1.begin();while (it != m1.end()){cout << "<" << it->first << "," << it->second << ">" << " ";++it;}cout << endl;it = m1.find(1);//如果找不到返回end()if (it != m1.end()){m1.erase(1);}it = m1.begin();while (it != m1.end()){cout << "<" << it->first << "," << it->second << ">" << " ";++it;}cout << endl;//容器中值为2的元素个数cout << "容器中值为2的元素个数" << m1.count(2) << endl;
}void Test9()
{unordered_map<int, string> m1;m1.insert(pair<int, string>(1, "one"));m1.insert(pair<int, string>(2, "two"));m1.insert(pair<int, string>(3, "three"));//容器大小cout << m1.size() << endl;//清空容器m1.clear();//容器判空cout << m1.empty() << endl;unordered_map<int, string> tmp;tmp.insert(pair<int, string>(4, "four"));tmp.insert(pair<int, string>(5, "five"));tmp.insert(pair<int, string>(6, "six"));//交换两个容器的数据m1.swap(tmp);unordered_map<int, string>::iterator it = m1.begin();while (it != m1.end()){cout << "<" << it->first << "," << it->second << ">" << " ";++it;}cout << endl;
}
void Test10()
{//允许键值冗余unordered_multimap<int, string> m;m.insert(make_pair(1, "one"));m.insert(make_pair(1, "1"));m.insert(make_pair(2, "two"));m.insert(make_pair(2, "2"));m.insert(make_pair(3, "three"));for (auto e : m){cout << "<" << e.first << "," << e.second << ">" << " ";}cout << endl;
}int main()
{Test10();
}3.3 Test.cpp
代码如下(示例):
#include<unordered_set>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
#include<iostream>
#include<time.h>
using namespace std;
int test_set2()
{const size_t N = 1000000;unordered_set<int> us;set<int> s;vector<int> v;v.reserve(N);srand(time(0));for (size_t i = 0; i < N; ++i){//v.push_back(rand()); // N⽐较⼤时,重复值⽐较多v.push_back(rand() + i); // 重复值相对少//v.push_back(i); // 没有重复,有序}// 21:15size_t begin1 = clock();for (auto e : v){s.insert(e);}size_t end1 = clock();cout << "set insert:" << end1 - begin1 << endl;size_t begin2 = clock();us.reserve(N);for (auto e : v){us.insert(e);}size_t end2 = clock();cout << "unordered_set insert:" << end2 - begin2 << endl;int m1 = 0;size_t begin3 = clock();for (auto e : v){auto ret = s.find(e);if (ret != s.end()){++m1;}}size_t end3 = clock();cout << "set find:" << end3 - begin3 << "->" << m1 << endl;int m2 = 0;size_t begin4 = clock();for (auto e : v){auto ret = us.find(e);if (ret != us.end()){++m2;}}size_t end4 = clock();cout << "unorered_set find:" << end4 - begin4 << "->" << m2 << endl;cout << "插⼊数据个数:" << s.size() << endl;cout << "插⼊数据个数:" << us.size() << endl << endl;size_t begin5 = clock();for (auto e : v){s.erase(e);}size_t end5 = clock();cout << "set erase:" << end5 - begin5 << endl;size_t begin6 = clock();for (auto e : v){us.erase(e);}size_t end6 = clock();cout << "unordered_set erase:" << end6 - begin6 << endl << endl;return 0;
}
//int main()
//{
// test_set2();
// return 0;
//}
