0807 IO线程的同步互斥
Part 1.梳理思维导图
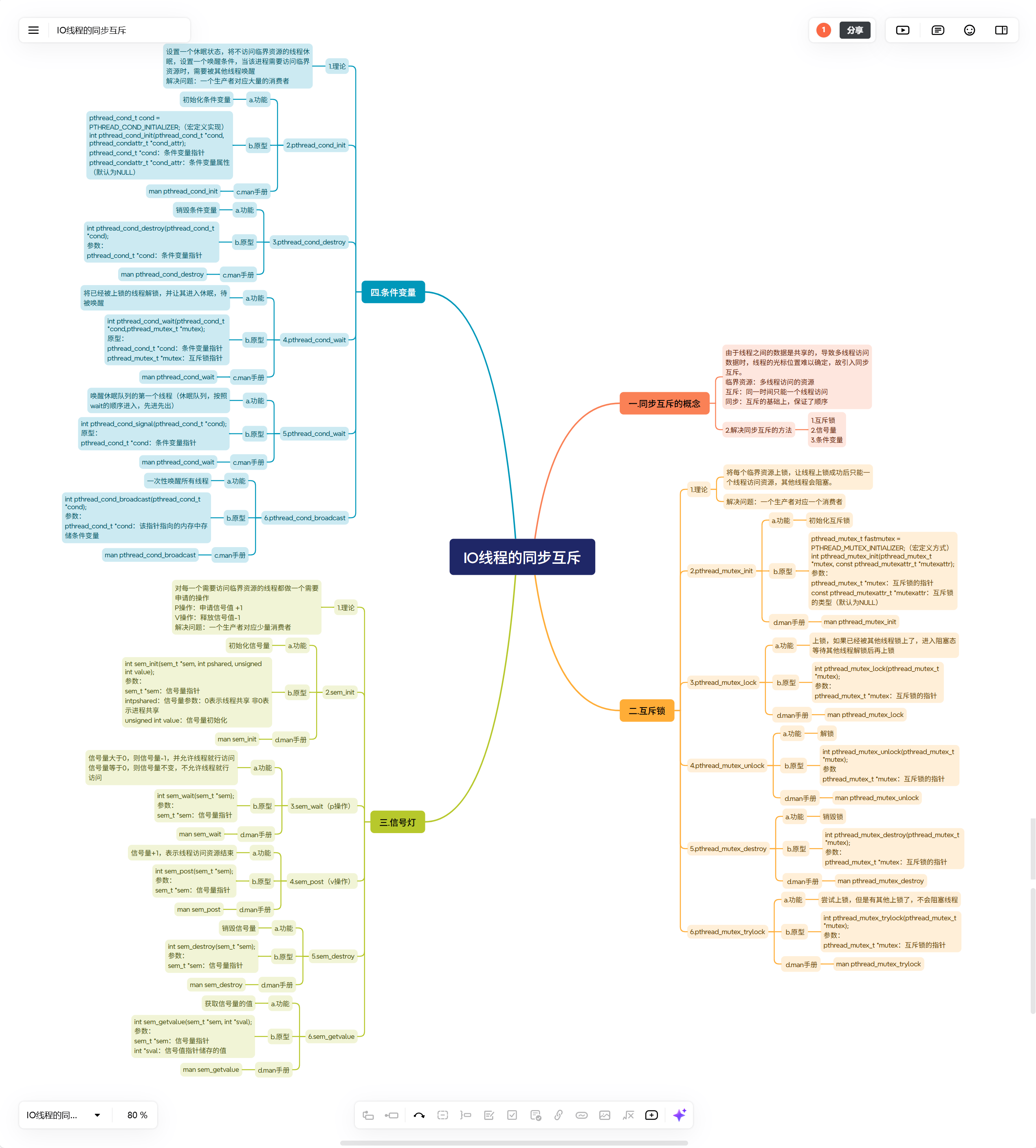
一.同步互斥的概念
由于线程之间的数据是共享的,导致多线程访问数据时,线程的光标位置难以确定,故引入同步互斥。
临界资源:多线程访问的资源
互斥:同一时间只能一个线程访问
同步:互斥的基础上,保证了顺序
2.解决同步互斥的方法
1.互斥锁
2.信号量
3.条件变量
二.互斥锁
1.理论
将每个临界资源上锁,让线程上锁成功后只能一个线程访问资源,其他线程会阻塞。
解决问题:一个生产者对应一个消费者
2.pthread_mutex_init
a.功能
初始化互斥锁
b.原型
pthread_mutex_t fastmutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;(宏定义方式)
int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *mutex, const pthread_mutexattr_t *mutexattr);
参数:
pthread_mutex_t *mutex:互斥锁的指针
const pthread_mutexattr_t *mutexattr:互斥锁的类型(默认为NULL)
c.例子
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;//宏定义d.man手册
man pthread_mutex_init
3.pthread_mutex_lock
a.功能
上锁,如果已经被其他线程锁上了,进入阻塞态等待其他线程解锁后再上锁
b.原型
int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
参数:
pthread_mutex_t *mutex:互斥锁的指针
c.例子
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
void *callback1(void *arg)
{ while(1){pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);//上锁a += 20;printf("a = %d\n",a);}pthread_exit(NULL);
}
d.man手册
man pthread_mutex_lock
4.pthread_mutex_unlock
a.功能
解锁
b.原型
int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
参数
pthread_mutex_t *mutex:互斥锁的指针
c.例子
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
void *callback1(void *arg)
{ while(1){pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);a += 20;printf("a = %d\n",a);pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);//解锁}pthread_exit(NULL);
}
d.man手册
man pthread_mutex_unlock
5.pthread_mutex_destroy
a.功能
销毁锁
b.原型
int pthread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
参数:
pthread_mutex_t *mutex:互斥锁的指针
c.例子
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
void *callback1(void *arg)
{ while(1){pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);a += 20;printf("a = %d\n",a);pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);//解锁}pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{pthread_t thread1;if(0 != pthread_create(&thread1,NULL,callback1,NULL)){printf("thread1 pthread_create error\n");return -1;}pthread_join(thread1,NULL); pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);//销毁锁return 0;
}
d.man手册
man pthread_mutex_destroy
6.pthread_mutex_trylock
a.功能
尝试上锁,但是有其他上锁了,不会阻塞线程
b.原型
int pthread_mutex_trylock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
参数:
pthread_mutex_t *mutex:互斥锁的指针
c.man手册
man pthread_mutex_trylock
三.信号灯
1.理论
对每一个需要访问临界资源的线程都做一个需要申请的操作
P操作:申请信号值 +1
V操作:释放信号值-1
解决问题:一个生产者对应少量消费者
2.sem_init
a.功能
初始化信号量
b.原型
int sem_init(sem_t *sem, int pshared, unsigned int value);
参数:
sem_t *sem:信号量指针
int pshared:信号量参数:0表示线程共享 非0表示进程共享
unsigned int value:信号量初始化
c.例子
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{sem_t sem;//创建信号量semsem_init(&sem,0,4);//初始化sem
}d.man手册
man sem_init
3.sem_wait(p操作)
a.功能
信号量大于0,则信号量-1,并允许线程就行访问
信号量等于0,则信号量不变,不允许线程就行访问
b.原型
int sem_wait(sem_t *sem);
参数:
sem_t *sem:信号量指针
c.例子
void *callback1(void *arg)
{ while(1){sem_wait(&sem); //p操作printf("生产\n");sleep(1);} pthread_exit(NULL);
}
d.man手册
man sem_wait
4.sem_post(v操作)
a.功能
信号量+1,表示线程访问资源结束
b.原型
int sem_post(sem_t *sem);
参数:
sem_t *sem:信号量指针
c.例子
void *callback1(void *arg)
{ while(1){sem_wait(&sem); printf("生产\n");sleep(1);sem_post(&sem);} pthread_exit(NULL);
}
d.man手册
man sem_post
5.sem_destroy
a.功能
销毁信号量
b.原型
int sem_destroy(sem_t *sem);
参数:
sem_t *sem:信号量指针
c.例子
#include<myhead.h>sem_t sem;void *callback1(void *arg)
{ while(1){sem_wait(&sem); printf("生产\n");sleep(1);sem_post(&sem);} pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{pthread_t thread1;sem_init(&sem,0,1);if(0 != pthread_create(&thread1,NULL,callback1,NULL)){printf("thread1 pthread_create error\n");return -1;}pthread_join(thread1,NULL); sem_destroy(&sem);//销毁信号值return 0;
}
d.man手册
man sem_destroy
6.sem_getvalue
a.功能
获取信号量的值
b.原型
int sem_getvalue(sem_t *sem, int *sval);
参数:
sem_t *sem:信号量指针
int *sval:信号值指针储存的值
c.man手册
man sem_getvalue
四.条件变量
1.理论
设置一个休眠状态,将不访问临界资源的线程休眠,设置一个唤醒条件,当该进程需要访问临界资源时,需要被其他线程唤醒
解决问题:一个生产者对应大量的消费者
2.pthread_cond_init
a.功能
初始化条件变量
b.原型
pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;(宏定义实现)
int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *cond, pthread_condattr_t *cond_attr);
pthread_cond_t *cond:条件变量指针
pthread_condattr_t *cond_attr:条件变量属性(默认为NULL)
c.例子
pthread_cong_t cond;//定义条件变量
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{pthread_cond_init(&cond,NULL);//初始化
}d.man手册
man pthread_cond_init
3.pthread_cond_destroy
a.功能
销毁条件变量
b.原型
int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond);
参数:
pthread_cond_t *cond:条件变量指针
c.例子
pthread_cong_t cond;//定义条件变量
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{pthread_cond_init(&cond,NULL);pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);//销毁
}d.man手册
man pthread_cond_destroy
4.pthread_cond_wait
a.功能
将已经被上锁的线程解锁,并让其进入休眠,待被唤醒
b.原型
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *cond,pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
原型:
pthread_cond_t *cond:条件变量指针
pthread_mutex_t *mutex:互斥锁指针
c.例子
pthread_cong_t cond;//定义条件变量
pthread_mutex_t mutex;//定义互斥锁
void *callback1(void *arg)
{ while(1){pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&mutex);//解锁休眠printf("生产\n");sleep(1);} pthread_exit(NULL);
}int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{pthread_cond_init(&cond,NULL);//初始化if(0 != pthread_create(&thread1,NULL,callback1,NULL)){printf("thread1 pthread_create error\n");return -1;}pthread_join(callback1,NULL);pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);//销毁
}
d.man手册
man pthread_cond_wait
5.pthread_cond_wait
a.功能
唤醒休眠队列的第一个线程(休眠队列,按照wait的顺序进入,先进先出)
b.原型
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);
原型:
pthread_cond_t *cond:条件变量指针
c.例子
pthread_cong_t cond;//定义条件变量
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;//定义并初始化互斥锁
void *callback1(void *arg)
{ while(1){sleep(1);printf("生产\n");pthread_cond_signal(&cond);} pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void *callback2(void *arg)
{ while(1){pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);//上锁pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&mutex);//解锁休眠printf("%ld:消费\n",pthread_self());pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);//解锁} pthread_exit(NULL);
}int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{pthread_cond_init(&cond,NULL);//初始化if(0 != pthread_create(&thread1,NULL,callback1,NULL)){printf("thread1 pthread_create error\n");return -1;}pthread_t thread2[5];for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){if(0 != pthread_create(&thread2[i],NULL,callback2,NULL)){printf("thread2 pthread_create error\n");return -1;} }pthread_join(thread1,NULL);for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){pthread_join(thread2[i],NULL);}pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);//销毁条件变量pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);//销毁锁return 0;
}
全流程即是:
1.先睡一下具有唤醒条件的线程1
2.线程2上锁,并且解锁进入休眠,并进入休眠队列排队,并阻塞cpu换线程运行
3.如果cpu换到线程1,线程一执行,并唤醒休眠队列第一个,自己阻塞,并运行唤醒的队列
d.man手册
man pthread_cond_wait
6.pthread_cond_broadcast
a.功能
一次性唤醒所有线程
b.原型
int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond);
参数:
pthread_cond_t *cond:该指针指向的内存中存储条件变量
c.man手册
man pthread_cond_broadcast
