Thread 中的 run() 方法 和 start() 方法的
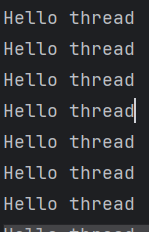
此时调用 run() 方法,仍属于单线程状况。其结果只会调用 MyThread 类中的 run() 方法。
class MyThread extends Thread {//继承 Thread 重写 runpublic void run() {while (true) {System.out.println("Hello Thread");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}
}
public class Demo1{public static void main(String[] args) {MyThread t1 = new MyThread();t1.run();while (true) {System.out.println("Hello Main");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}
}
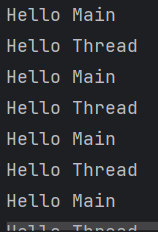
更改代码将 run 改为 start 后可发现交替打印 Hellow Thread 和 Hello Main 。说明调用 start 方法后会新开辟一个线程并执行 run 方法
class MyThread extends Thread {//继承 Thread 重写 runpublic void run() {while (true) {System.out.println("Hello Thread");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}
}
public class Demo1{public static void main(String[] args) {MyThread t1 = new MyThread();t1.start();while (true) {System.out.println("Hello Main");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}
}