【网络运维】Playbook部署文件:Files模块库&JINJA2模板
部署文件到受管主机
实验环境
[furongwang@controller ~]$ mkdir web && cd web[furongwang@controller web]$ cat > ansible.cfg <<'EOF'
[defaults]
remote_user = furongwang
inventory = ./inventory[privilege_escalation]
become = True
become_user = root
become_method = sudo
become_ask_pass = False
EOF[furongwang@controller web]$ cat > inventory <<'EOF'
controller
node1
node2
node3
node4
EOF
Files模块库
红帽Ansible引擎本身内置附带了大型模块集合(模块库),为了便于整理、记录和管理这些模块,已根据文档中的功能以及在系统上安装的时间将它们分成多个组。
Files 模块库包含的模块允许您完成与Linux文件管理相关的大多数任务,如创建、复制、编辑和修改文件的权限和其他属性,下表列出了常用的Files模块库中使用的模块。
- file:设置权限、所有权、SELinux上下文以及常规文件、符号链接、硬链接和目录的时间戳等属性。此模块还可以创建或删除常规文件、符号链接、硬链接和目录。
- sefcontext,设置持久selinux上下文。
- lineinfile:确保特定行位于某个文件中,或使用反向引用正则表达式来替换现有行。
- replace:查找文件中行,一次性替换成对应内容。
- blockinfile:插入、更新或删除多行文本块。
- stat:检索文件的状态信息,类似于Linux stat命令。
- copy:将文件从本地或远程计算机复制到受管节点上的某个位置。
- synchronize:围绕rsync命令的一个程序,可加快和简化常见任务。
- fetch:用于从远程计算机获取文件到控制节点。
file 模块
示例1: 创建文件或修改文件属性
---
- hosts: node1gather_facts: notasks:- name: Touch a file and set permissionsfile:path: /tmp/testfileowner: furongwanggroup: wheelmode: "640"state: touch
mode选项: 必须使用前导0 (‘0644’ or ‘01777’) 或者引起来 (‘‘644’’ or ‘‘1777’’) 。如果直接写640,则会640当做10进制,并转换成二进制1 010 000 000,最终文件权限是-w- — --T。
示例2: 创建目录
---
- hosts: node1gather_facts: notasks:- name: create directoryfile:path: /webdevowner: apachegroup: apachemode: 0755state: directory
示例3: 删除文件
---
- hosts: node1gather_facts: notasks:- name: delete file file:path: /tmp/testfilestate: absent
sefcontext 模块
selinux库中添加默认规则。
示例:
---
- hosts: node1gather_facts: notasks:- sefcontext:target: '/samba(/.*)?'setype: samba_share_tstate: present
注意:
- sefcontext模块是修改selinux 库规则,并不会立刻应用于文件,relabel时候才会生效。
- file模块会立刻应用于文件。
lineinfile 模块
示例1:确保文件中存在特定行,没有对应文本时在最后一行加入
---
- hosts: node1gather_facts: notasks:- name: add linelineinfile:path: /tmp/testfileline: 'Add this line to file'state: present
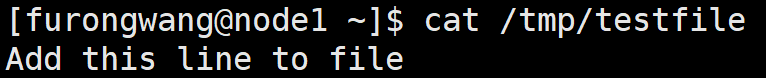
还可以在特定位置插入:
-
insertbefore,最后一个匹配到前插入
--- - hosts: node1gather_facts: notasks:- name: add linelineinfile:path: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.confline: 'Listen 82'insertbefore: 'Listen 80'state: present -
insertafter,最后一个匹配到后插入
--- - hosts: node1gather_facts: notasks:- name: add linelineinfile:path: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.confline: 'Listen 82'insertafter: 'Listen 80'state: present
示例2:替换文本行
---
- hosts: node1 gather_facts: no tasks: - name: replace linelineinfile: path: /tmp/testfileregexp: 'Add' line: 'replace'state: present
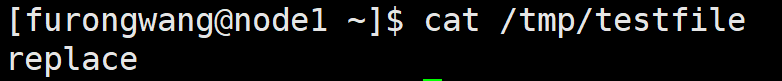
原包含Add的行“Add this line to file” 被替换。
---
- hosts: node1gather_facts: notasks:- name: add linelineinfile:path: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.confline: '#Listen 80'regexp: '^Listen 80'state: present
- 有相同行时,优先替换靠后的行。
示例3:替换成多行文本
---
- hosts: node1gather_facts: notasks:- name: add linelineinfile:path: /tmp/testfileline: |line 1line 2regexp: 'replace'state: present
replace 模块
该模块使用正则表达式匹配内容,将匹配的内容替换成指定的内容。匹配的多个地方都会被替换掉。
示例:
---
- hosts: node1gather_facts: notasks:- name: replace multi linereplace:path: /tmp/testfileregexp: '^Hello World.*'replace: 'Hello furongwang'
blockinfile 模块
示例:将文本块添加到现有文件
---
- hosts: node1gather_facts: notasks:- name: add block lines to fileblockinfile:path: /tmp/testfileblock: |line 1 in fileline 2 in fileaaline 3 in file sssstate: present
添加的内容如下,会在第一行和最后一行额外添加注释。
# BEGIN ANSIBLE MANAGED BLOCK
line 1 in file
line 2 in fileaa
line 3 in file sss
# END ANSIBLE MANAGED BLOCK
stat 模块
stat 模块检索文件的信息,类似于Linux stat命令。 参数提供检索文件属性、确定文件校验和等功能。
stat 模块返回一个包含文件状态数据的值的散列字典,允许您使用单独的变量引用各条信息。
示例:
---
- hosts: node1gather_facts: notasks:- stat:path: /tmp/testfilechecksum_algorithm: md5register: result- debug:msg: "/tmp/testfile md5 is {{ result.stat.checksum }}"- debug:var: result
copy 模块
示例1:将控制节点上文件拷贝到受管理节点,类似于Linux中scp命令。
---
- hosts: node1gather_facts: notasks:- name: copy /tmp/testfile to remote nodecopy:src: /tmp/testfiledest: /tmp
说明:此模块假定设置了force: yes,强制覆盖远程文件,类似scp命令。如果设置force: no, 则不会出现覆盖。
示例2:写入字符串到文件
---
- hosts: node1gather_facts: notasks:- name: write string into /tmp/testfilecopy:content: "hello world\n"dest: /tmp/testfile
synchronize 模块
synchronize 模块是一个围绕 rsync 工具的打包程序,它简化了playbook中的常见文件管理任务。
rsync工具必须同时安装在本地和远程主机上。默认情况下,在使用synchronize模块时, “本地主机”是同步任务的源主机, 而 “目标主机”是synchronize连接到的主机。
示例1:同步文件
---
- hosts: node1gather_facts: notasks:- name: synchronize filesynchronize:src: /tmp/testfiledest: /tmp/
示例2:同步目录
---
- hosts: node1gather_facts: noremote_user: roottasks:- name: synchronize directorysynchronize:src: /etc/sysconfigdest: /tmp/
fetch 模块
从受管节点检索文件,例如将被管理节点文件先取到控制节点,然后用于分发到其他节点。诸如SSH公钥之类的文件。
示例:
---
- hosts: node1gather_facts: notasks:- name: fetch file from remote nodefetch:src: /tmp/testfiledest: /tmp
文件保存在:/tmp/node1/tmp/testfile。
[furongwang@controller web]$ tree /tmp/node1
/tmp/node1
└── tmp└── testfile1 directory, 1 file
使用JINJA2模板部署文件
JINJA2 模板介绍
Jinja2 模板是功能强大的工具,可用于自定义要在受管节点上部署的配置文件。 创建Jinja2 模板后,可以通过template模块部署到受管节点上, 该模块支持将控制节点中的本地文件转移到受管节点。
示例1:部署web服务器,主页内容显示为Welcome to HOSTNAME。HOSTNAME为受管主机完全主机名。
playbook内容如下:
---
- name: Enable intranet serviceshosts: node1tasks:- name: ensure latest version of httpd yum:name: httpdstate: latest- name: test html page is installedtemplate: # template模块: 复制文件到受管主机时,根据jinja2语法替换src: index.html.j2 # 指定 Jinja2 模板来源dest: /var/www/html/index.html # 指定要在目标主机上创建的文件- name: httpd enabled and runningservice:name: httpdenabled: truestate: restarted
...
在文件目录下创建 index.html.j2 ,内容如下:
Welcome to {{ ansible_fqdn }}
剧本执行完成后,index.html内容如下:
Welcome to node1.furongwang.cloud
template模块,与copy模块类似,允许指定已部署文件的所有者(拥有该文件的用户) 、组、权限和 SELinux上下文 。
示例2:推送 ssh 服务配置文件。 sshd_config.j2内容如下:
# {{ ansible_managed }}
# DO NOT MAKE LOCAL MODIFICATIONS TO THIS FILE AS THEY WILL BE LOST
Port {{ ssh_port }}
ListenAddress {{ ansible_facts['default_ipv4']['address'] }}HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_key
HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ecdsa_key
HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ed25519_key
SyslogFacility AUTHPRIV
PermitRootLogin {{ root_allowed }}
AllowGroups {{ groups_allowed }}AuthorizedKeysFile /etc/.rht_authorized_keys .ssh/authorized_keys
PasswordAuthentication {{ passwords_allowed }}
playbook 参考
---
- name: config sshd servicehosts: node1vars:ssh_port: 1022root_allowed: "yes"groups_allowed: wheelpasswords_allowed: "yes"ansible_managed: "Ansible managed"tasks:- name: config sshd servicetemplate:src: sshd_config.j2dest: /root/sshd_config
Jinja2 模板语法
Jinja2 模板由多个元素组成:数据、变量和表达式。在呈现Jinja2模板时, 这些变量和表达式被替换为对应的值。模板中使用的变量可以在playbook的vars部分中指定,也可以使用受管主机FACTS。
变量和逻辑表达式置于分隔符之间:
- {{ EXPR }},用于装载表达式,比如变量,运算表达式,比较表达式。
- {% EXPR %},用于装载控制语句,比如if,for等。
- {# #},用于装载注释,模板文件中的注释不会包含在最终生成文件中。
for 语句
Jinja2使用for语句来提供循环功能。
示例1:
---
- name: test templatehosts: node1vars:users:- tom- jack- Snoopy- lucytasks:- name: test templatetemplate:src: testfile.j2dest: /tmp/testfile
...
testfile.j2内容如下:
{% for user in users %}
{{ user }}
{% endfor %}
for用于声明循环,{% endfor %} 表示结束。user变量会遍历users变量中所有值。
生成的/tmp/testfile内容如下:
tom
jack
Snoopy
lucy
示例2: testfile.j2内容如下
{# for statement #}
{% for user in users %}
{{ loop.index }} - {{ user }}
{% endfor %}
loop.index代表当前循环的索引号,从1开始到最后循环体的数量。例如循环体有12个,那么loop.index代表1,2,3,…,12。
生成的/tmp/testfile内容如下:
1 - tom
2 - jack
3 - Snoopy
4 - lucy
示例3: 部署myhosts
创建 playbook:
-
使用模板文件hosts.j2在dev主机组中的主机上生成文件/etc/myhosts。
-
hosts.j2内容如下:
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6 -
针对每个受管节点包含一行内容:
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain610.1.8.10 controller.furongwang.cloud controller 10.1.8.11 node1.furongwang.cloud node1 10.1.8.12 node2.furongwang.cloud node2 10.1.8.13 node3.furongwang.cloud node3 10.1.8.14 node4.furongwang.cloud node4注:清单主机名称的显示顺序不重要。
inventory 内容如下:
[controllers]
controller[dev]
node1[test]
node2[prod]
node3
node4
答案如下:
---
- name: /etc/myhosts is up to datehosts: alltasks:- name: Deploy /etc/myhoststemplate:src: hosts.j2dest: /etc/myhostswhen: inventory_hostname in groups.dev
文件目录下创建 hosts.j2,内容如下:
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6{% for server in groups.all %}
{{ hostvars[server].ansible_default_ipv4.address }} {{ hostvars[server].ansible_fqdn }} {{ hostvars[server].ansible_hostname }}
{% endfor %}
说明:
- hostvars是magic 变量,通过该变量引用其他受管主机facts。
- [server]不能使用单引号,因为server作为变量处理,替换为all中主机。
- play 必须针对所有主机执行,收集所有主机facts,因为模版需要引用所有主机的facts。
- 只部署到dev主机组,使用when语句。groups.dev是magic变量,该变量获取dev主机组中主机清单。
示例4: num 变量引用方括号中列表
{% for num in [3,1,7,8,2] %}
{{ num }}
{% endfor %}
生成的文件内容如下:
3
1
7
8
2
示例5: range(3)代表 0 1 2,循环三次。
{% for num in range(3) %}
{{ num }}
{% endfor %}
生成的文件内容如下:
0
1
2
示例6: range(1,4,2),从1开始,到4结束,步长2。
{% for num in range(1,4,2) %}
{{ num }}
{% endfor %}
生成的文件内容如下:
1
3
if 语句
Jinja2使用if语句来提供条件控制。如果满足某些条件, 则在部署文件中放置一行。if语句判断条件同ansible中when语句。
示例1: 只要变量finished不是假值,那么输出finished变量值。
{% if finished %}
{{ finished }}
{% endif %}
示例2: 如果PORT定义了端口,那么使用该值,否则使用默认3306。
{% if PORT is defined %}
bind-address=0.0.0.0:{{ PORT }}
{% else %}
bind-address=0.0.0.0:3306
{% endif %}
示例3:
{% if 条件1 %}
...
{% elif 条件2 %}
...
{% elif 条件n %}
...
{% else %}
...
{% endif %}
{% elif 条件N %}可以多次使用。
示例4: for和if配合使用
{% for num in [7,1,5,3,9] if num>3 %}
{{ num }}
{% endfor %}
等同于:
{% for num in [7,1,5,3,9] %}
{% if num>3 %}
{{ num }}
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}
生成的文件内容如下:
7
5
9
表达式
示例1:
{{ 1 == 1 }}
{{ 2 != 2 }}
{{ 2 > 1 }}
{{ 2 >= 1 }}
{{ 2 < 1 }}
{{ 2 <= 1 }}
生成的文件内容如下:
True
False
True
True
False
False
示例2:
jinja2 test
{{ (2 > 1) or (1 > 2) }}
{{ (2 > 1) and (1 > 2) }}
{{ not true }}
{{ not True }}
{{ not false }}
{{ not False }}
生成的文件内容如下:
jinja2 test
True
False
False
False
True
True
示例3:
{{ 3 + 2 }}
{{ 3 - 4 }}
{{ 3 * 5 }}
{{ 2 ** 3 }}
{{ 7 / 5 }}
{{ 7 // 5 }}
{{ 17 % 5 }}
生成的文件内容如下:
5
-1
15
8
1.4
1
2
示例4:
jinja2 test
{{ 1 in [1,2,3,4] }}
{{ 1 not in [1,2,3,4] }}
生成的文件内容如下:
jinja2 test
True
False
模版注释
{# #},用于装载注释,模板文件中的注释不会包含在最终生成文件中。
示例:
{# 此处是注释 #}
{% for num in [7,1,5,3,9] %}
{% if num>3 %}
{{ num }}
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}
生成的文件内容如下:
7
5
9
ansible_managed 变量
为避免系统管理员修改Ansible部署的文件,最好在模板顶部包含注释,指示不应手动编辑该文件。
在/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg配置文件[defaults]块中有如下默认配置:
[defaults]
ansible_managed = Ansible managed
可使用ansible_managed变量来引用“Ansible managed” 字符串。
要想在jinja2 模板内,使用ansible_managed变量代表的字符串,使用下列语法:
{{ ansible_managed }}
