platform总线注册流程分析
我们以前了解过知识点:平台总线设备、驱动、设备驱动自动匹配;设备模型keyset/kobject;总线流程分析等。 这里我们继续看一个知识点 平台总线的注册流程分析。
文章目录
- 前言
- 参考资料
- 一、platform_bus_init 方法
- 启动位置-方法分析
- early_platform_cleanup();
- bus_register
- 思考bus_register
- 结构体platform_bus_type
- 二、platform_match 分析
- pdev->driver_override 匹配方式
- 源码解析
- 如何设置 driver_override
- 注意事项
- of_driver_match_device匹配方式-设备树匹配
- 匹配机制详解
- 基本匹配流程
- 关键数据结构
- 匹配优先级规则
- 典型驱动示例
- 设备树节点示例
- 匹配过程图示
- acpi_driver_match_device 匹配方式
- platform_match_id 匹配方式
- 源码分析
- 典型驱动中的使用示例
- 驱动和设备名字匹配方式-strcmp(pdev->name, drv->name)
- 基本匹配原理
- 关键数据结构
- 平台设备结构 (platform_device)
- 平台驱动结构 (platform_driver)
- 典型使用场景
- 三、platform_match 实际使用示例
- 设备树匹配示例
- ID表匹配示例
- 性能考虑
- 总结
前言
通过了解设备模型 相关知识点:设备模型keyset/kobject;总线流程分析等来进一步了解平台总线注册流程。
同步之前的platform 总线相关知识点串联起来。
参考资料
迅为设备模型资料参考](https://blog.csdn.net/beijingxunwei/category_12551484.html)
注册一个自己的总线
在总线目录下创建属性文件
驱动-注册自己的总线并创建属性文件
总线注册流程理论分析实验
linux bus_register过程
Linux设备驱动模型简述(源码剖析)
驱动-总线bus注册流程分析
platform总线注册流程实例分析实验
驱动-平台总线-platform设备注册platform驱动注册篇
驱动-平台总线-probe
Linux在线源码
为什么参考资料总是把以前的知识点拉出来,是为了让知识更有层次和体系。 新知识和旧知识串联起来。
一、platform_bus_init 方法
platform_bus_init 是 Linux 内核中初始化平台总线(platform bus)的核心函数。平台总线是 Linux 设备驱动模型中用于连接没有物理总线的设备(通常是 SoC 上的集成设备)的虚拟总线。
启动位置-方法分析
在 /source/drivers/base/init.c 中启动的
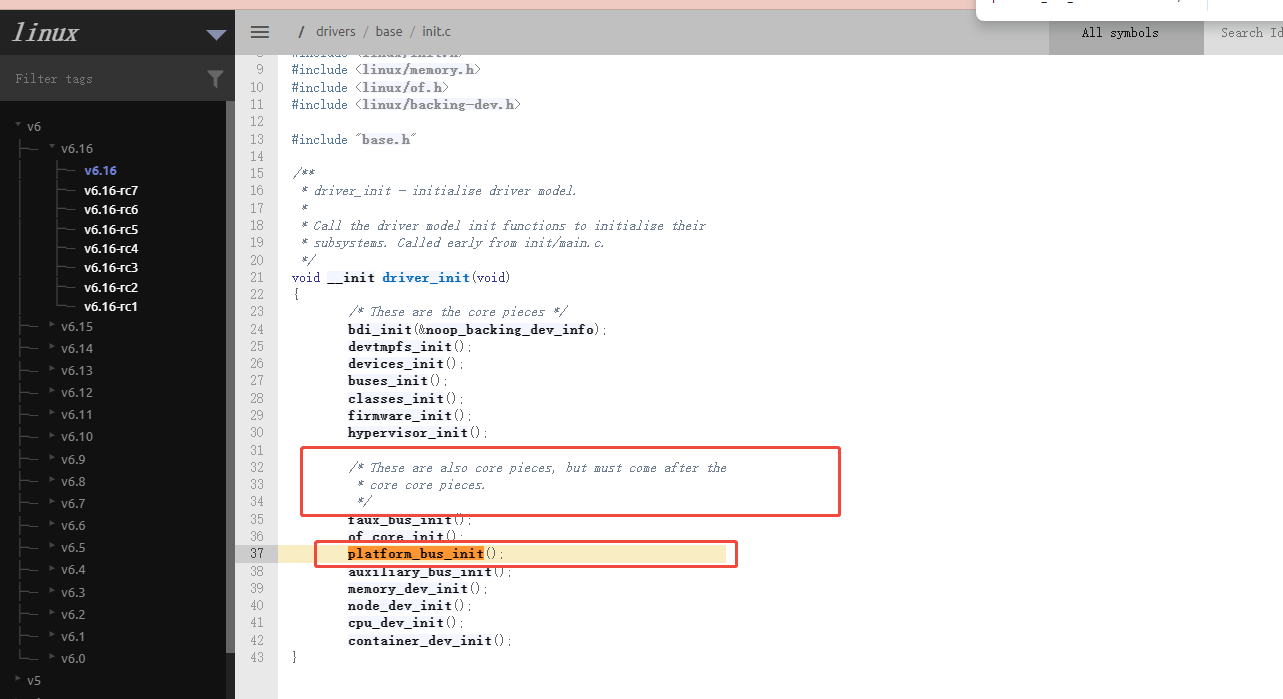
源码
int __init platform_bus_init(void)
{int error;early_platform_cleanup();error = device_register(&platform_bus);if (error) {put_device(&platform_bus);return error;}error = bus_register(&platform_bus_type);if (error)device_unregister(&platform_bus);return error;
}
early_platform_cleanup();
初始化资源管理,清理早期注册的平台设备,确保没有冲突。 这里不是我们讨论的核心目标,我们看看下面的方法
bus_register
这个不就是我们上一篇 驱动-总线bus注册流程分析 的知识点嘛。 看源码:
error = bus_register(&platform_bus_type);
我们讨论的核心重点就是 platform_bus_type 类型。 我们在 驱动-注册自己的总线并创建属性文件 篇中分简单使用并分析过这个api,简单了解了bus_type 结构体。
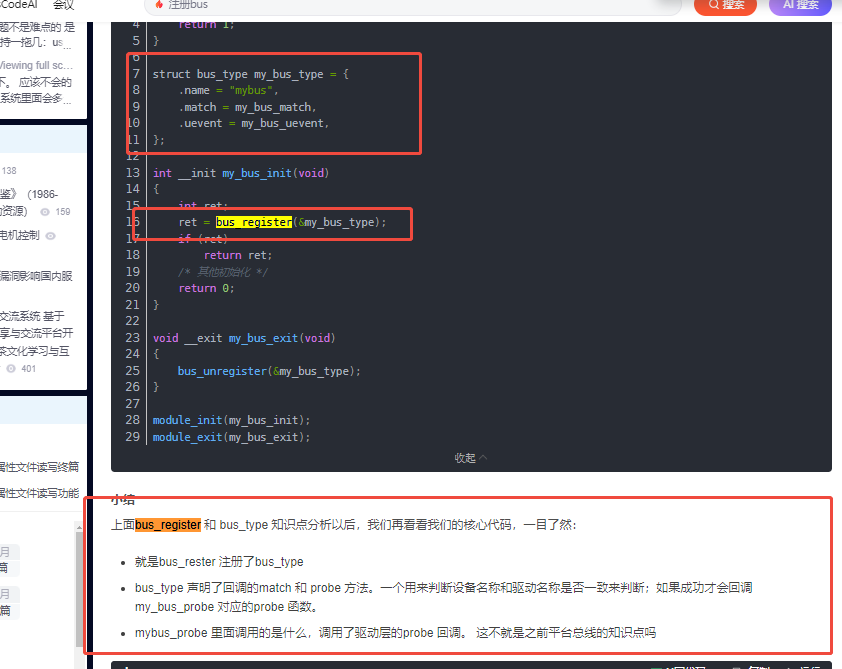
那我们就继续看看 platform_bus_type 结构体
思考bus_register
按照上一篇的知识点 驱动-注册自己的总线并创建属性文件 那么在/sys/bus 下面就应该有 platform_bus_type对应name 的结构体。
const struct bus_type platform_bus_type = {.name = "platform",.....
};
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(platform_bus_type);
结构体platform_bus_type
const struct bus_type platform_bus_type = {.name = "platform",.dev_groups = platform_dev_groups,.match = platform_match,.uevent = platform_uevent,.probe = platform_probe,.remove = platform_remove,.shutdown = platform_shutdown,.dma_configure = platform_dma_configure,.dma_cleanup = platform_dma_cleanup,.pm = &platform_dev_pm_ops,
};
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(platform_bus_type);
这里其实没有什么特别要讲的,都是一些基本的知识点回调方法等。 那么我们核心看看匹配流程match
二、platform_match 分析
直接上源码:
/*** platform_match - bind platform device to platform driver.* @dev: device.* @drv: driver.** Platform device IDs are assumed to be encoded like this:* "<name><instance>", where <name> is a short description of the type of* device, like "pci" or "floppy", and <instance> is the enumerated* instance of the device, like '0' or '42'. Driver IDs are simply* "<name>". So, extract the <name> from the platform_device structure,* and compare it against the name of the driver. Return whether they match* or not.*/
static int platform_match(struct device *dev, const struct device_driver *drv)
{struct platform_device *pdev = to_platform_device(dev);struct platform_driver *pdrv = to_platform_driver(drv);/* When driver_override is set, only bind to the matching driver */if (pdev->driver_override)return !strcmp(pdev->driver_override, drv->name);/* Attempt an OF style match first */if (of_driver_match_device(dev, drv))return 1;/* Then try ACPI style match */if (acpi_driver_match_device(dev, drv))return 1;/* Then try to match against the id table */if (pdrv->id_table)return platform_match_id(pdrv->id_table, pdev) != NULL;/* fall-back to driver name match */return (strcmp(pdev->name, drv->name) == 0);
}
这里最核心的知识点是搞清楚具体的匹配流程和优先级,这样自己做platform 总线的时候,设备驱动匹配流程才更加熟练。
pdev->driver_override 匹配方式
实现了 驱动覆盖(driver override) 机制,它允许强制指定某个设备使用特定的驱动,而不遵循常规的匹配规则。
源码解析
条件判断:if (pdev->driver_override)
-
检查平台设备
pdev的driver_override成员是否被设置(非 NULL) -
driver_override 是一个字符串指针,用于存储用户指定的驱动名称
字符串比较:!strcmp(pdev->driver_override, drv->name)
- 比较设备指定的驱动名称(driver_override)与当前驱动的名称(
drv->name) strcmp()返回 0 表示字符串相等,! 操作符将结果转换为布尔值- 如果名称匹配则返回 true(1),否则返回 false(0)
如何设置 driver_override
用户空间可以通过 sysfs 设置 driver_override:
# 强制设备使用"my_driver"驱动
echo "my_driver" > /sys/bus/platform/devices/device-name/driver_override# 绑定设备到驱动
echo device-name > /sys/bus/platform/drivers/my_driver/bind# 清除覆盖设置
echo "" > /sys/bus/platform/devices/device-name/driver_override
注意事项
- 匹配优先级:
driver_override的检查优先级最高,会覆盖其他所有匹配规则 - 安全性:只有具有足够权限的用户才能修改此属性
of_driver_match_device匹配方式-设备树匹配
上源码
/*** of_driver_match_device - Tell if a driver's of_match_table matches a device.* @drv: the device_driver structure to test* @dev: the device structure to match against*/
static inline int of_driver_match_device(struct device *dev,const struct device_driver *drv)
{return of_match_device(drv->of_match_table, dev) != NULL;
}/*** of_match_device - Tell if a struct device matches an of_device_id list* @matches: array of of device match structures to search in* @dev: the of device structure to match against** Used by a driver to check whether an platform_device present in the* system is in its list of supported devices.*/
const struct of_device_id *of_match_device(const struct of_device_id *matches,const struct device *dev)
{if (!matches || !dev->of_node || dev->of_node_reused)return NULL;return of_match_node(matches, dev->of_node);
}of_driver_match_device 是 Linux 内核中用于Open Firmware (Device Tree)设备与驱动匹配的核心函数,属于设备树(Device Tree)驱动模型的关键部分。
of_match_node 的内部实现会:
- 遍历驱动的
of_match_table数组 - 对每个条目,与设备节点的
compatible属性进行比较 - 使用strcmp进行字符串匹配
匹配机制详解
基本匹配流程
- 获取设备节点:从设备结构中获取关联的设备树节点(
dev->of_node) - 获取驱动匹配表:从驱动结构中获取
of_match_table - 字符串匹配:将设备节点的compatible属性与驱动of_match_table中的字符串进行比对
关键数据结构
驱动端 - struct of_device_id (定义在 include/linux/mod_devicetable.h)
struct of_device_id {char name[32];char type[32];char compatible[128];const void *data;
};
设备端 - 设备树节点的compatible属性,格式通常为:
compatible = "manufacturer,model", "generic-model";
匹配优先级规则
of_driver_match_device 按照以下顺序进行匹配:
- 精确匹配:检查设备树节点是否有与驱动
of_match_table完全相同的compatible字符串 - 通配符匹配:支持省略厂商前缀的匹配(只比较"model"部分)
- 级联匹配:检查多个
compatible字符串(设备树可以指定多个兼容设备)
典型驱动示例
static const struct of_device_id my_driver_of_match[] = {{ .compatible = "abc,xyz-device" },{ .compatible = "def,xyz-device" },{ /* 结束标记 */ },
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of, my_driver_of_match);static struct platform_driver my_driver = {.driver = {.name = "my-device",.of_match_table = my_driver_of_match,},.probe = my_probe,.remove = my_remove,
};
哈哈哈,这个不就是之前的知识点嘛
platform总线注册流程实例分析实验
驱动-平台总线-platform设备注册platform驱动注册篇
设备树节点示例
匹配的设备树节点:
device@12340000 {compatible = "abc,xyz-device", "generic-xyz-device";reg = <0x12340000 0x1000>;interrupts = <0 45 4>;
};
匹配过程图示
驱动端of_match_table:[0] { .compatible = "abc,xyz-device" }[1] { .compatible = "def,xyz-device" }[2] { .compatible = "xyz-device" }[3] { /* 结束 */ }设备树节点:compatible = "abc,xyz-device", "generic-xyz";匹配过程:1. 尝试匹配"abc,xyz-device"与驱动表[0] - 成功2. 返回匹配的of_device_id结构体指针
acpi_driver_match_device 匹配方式
这种方式我们暂未接触过,暂不分析
platform_match_id 匹配方式
这段代码是 Linux 内核平台设备驱动匹配机制的核心部分,用于通过平台驱动的 id_table 来匹配平台设备。
源码分析
/* 接着尝试匹配平台的ID表 */
if (pdrv->id_table)return platform_match_id(pdrv->id_table, pdev) != NULL;
这段代码表示:
- 首先检查驱动是否定义了
id_table(pdrv->id_table是否非 NULL) - 如果定义了,则调用
platform_match_id()函数进行匹配 - 如果匹配成功(返回非 NULL),则返回 true(1),否则返回 false(0)
典型驱动中的使用示例
static const struct platform_device_id my_driver_ids[] = {{ "device_v1", 0 },{ "device_v2", (kernel_ulong_t)&v2_config },{ "", 0 },
};static struct platform_driver my_driver = {.driver = {.name = "my-driver",},.id_table = my_driver_ids,.probe = my_probe,.remove = my_remove,
};
驱动和设备名字匹配方式-strcmp(pdev->name, drv->name)
在 Linux 内核的平台设备驱动模型中,strcmp(pdev->name, drv->name 是最基础也是最直接的设备与驱动匹配方式。这是 platform_match 函数中的最后一道匹配逻辑,当前面所有匹配方式(如 driver_override、设备树匹配、id_table 匹配)都失败时,内核会回退到这种简单的名称匹配方式
基本匹配原理
return (strcmp(pdev->name, drv->name) == 0);这段代码:
- 比较平台设备名称 (
pdev->name) 和平台驱动名称 (drv->name) - 使用标准 C 库函数
strcmp进行字符串比较 - 当两个名称完全相同时返回 true(匹配成功),否则返回 false
关键数据结构
平台设备结构 (platform_device)
struct platform_device {const char *name; // 设备名称// ... 其他成员
};
平台驱动结构 (platform_driver)
struct platform_driver {struct device_driver driver;// ... 其他成员
};struct device_driver {const char *name; // 驱动名称// ... 其他成员
};
典型使用场景
简单设备驱动:没有复杂变体,一对一匹配的设备
/* 设备 */
static struct platform_device my_device = {.name = "my_device",// ...
};/* 驱动 */
static struct platform_driver my_driver = {.driver = {.name = "my_device", // 必须与设备名一致},.probe = my_probe,// ...
};
三、platform_match 实际使用示例
设备树匹配示例
驱动中定义:
static const struct of_device_id my_driver_of_match[] = {{ .compatible = "vendor,my-device" },{ /* sentinel */ }
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of, my_driver_of_match);static struct platform_driver my_driver = {.driver = {.name = "my-device",.of_match_table = my_driver_of_match,},.probe = my_probe,.remove = my_remove,
};
设备树中定义:
my_device: my-device@1234 {compatible = "vendor,my-device";reg = <0x1234 0x100>;
};
ID表匹配示例
驱动中定义:
static const struct platform_device_id my_driver_ids[] = {{ "my-device", 0 },{ "my-device-v2", 1 },{ "", 0 },
};static struct platform_driver my_driver = {.driver = {.name = "my-device",},.id_table = my_driver_ids,.probe = my_probe,.remove = my_remove,
};
性能考虑
platform_match 函数在内核初始化或模块加载时会被频繁调用,因此其实现需要高效。匹配顺序也是基于性能考虑设计的:
- 设备树匹配优先,因为现代嵌入式系统广泛使用设备树
- ACPI 匹配次之,主要用于x86体系
- ID表匹配适用于传统平台设备
- 名称匹配作为最后回退方案
总结
虽然是一个platform_bus_init 案例分析,分析到了平台总线匹配规则,但是还是从这个里面延伸了好多知识点,也对以前知识点进行了温习,知道所以然。 这个对理解设备模型也很有帮助的。
