C++ stack and queue
目录
1.stack
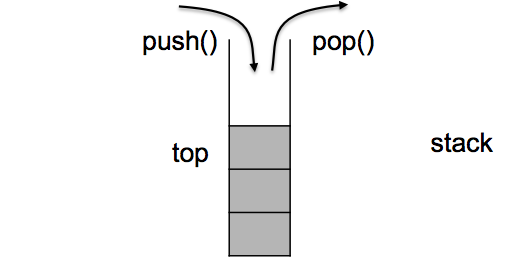
1.1 stack的介绍
1.2 stack的使用
1.3 OJ 题目
1.4 stack的模拟实现
2.queue
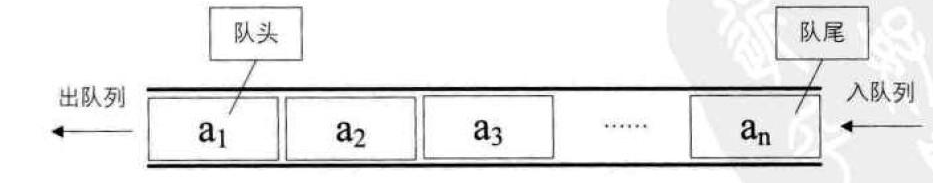
2.1 queue的介绍
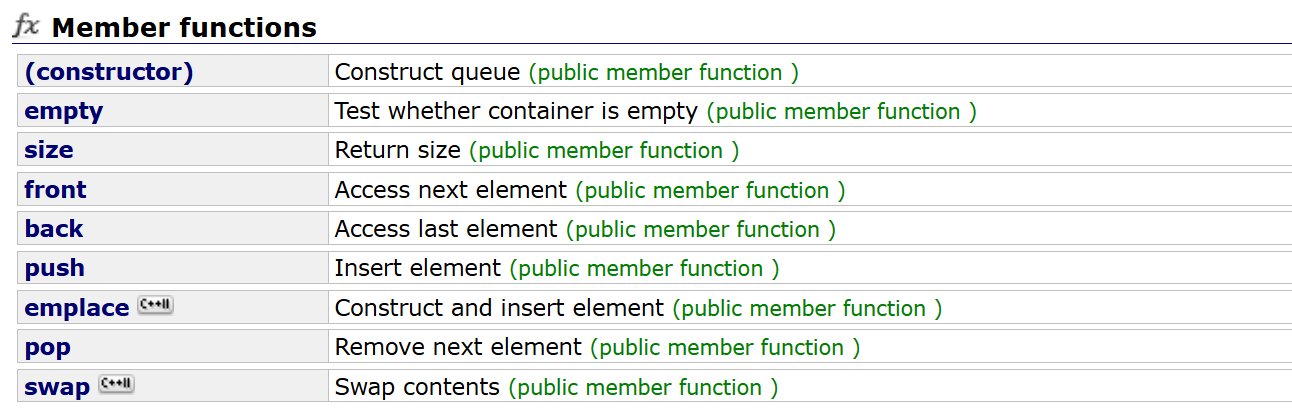
2.2 queue的使用
2.3 OJ 题目
2.4 queue的模拟实现
3.容器适配器
3.1 什么是适配器
3.2 STL标准库中stack和queue的底层结构
编辑
4.deque(双端队列)
4.1 deque的介绍
4.2 deque的使用
4.3 deque剖析
4.4 deque的缺陷
4.5 为什么选择deque作为stack和queue的底层默认容器?
4.6 STL标准库中对于stack和queue的模拟实现
4.6.1 stack.h
4.6.2 queue.h
5.priority_queue
5.1 priority_queue介绍
5.1.2 priority_queue的使用
5.2 仿函数介绍(简单)
5.3 priority_queue 模拟实现
5.3.1 priority_queue.h
5.4 OJ 使用
5.5 test.cpp
1.stack
1.1 stack的介绍
堆栈是一种容器适配器,专门设计用于在后进先出环境(后进先出)中运行,其中元素仅从容器的一端插入和提取。
cplusplus.com/reference/stack/stack/?kw=stack
1.2 stack的使用
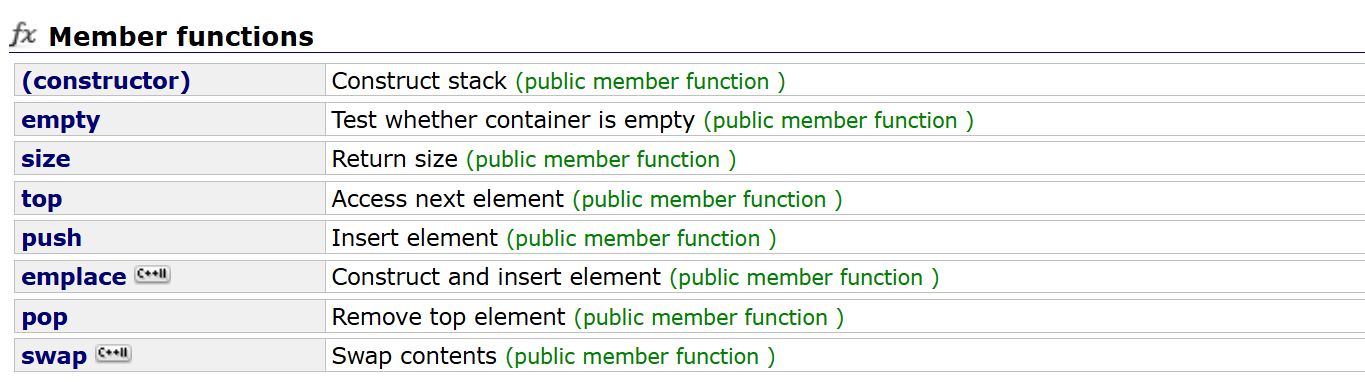
前文中也接触过过Stack和queue,有了stl提供的Stack和queue,我们就不再需要自己实现栈和队列,大大方便了我们利用Stack和queue解决问题。
1.3 OJ 题目
155. 最小栈 - 力扣(LeetCode)
借助两个栈实现最小栈
class MinStack {
public:MinStack() {}void push(int val) {_st.push(val);if(_minst.empty() || val <= _minst.top()){_minst.push(val);}}void pop() {if(_st.top() == _minst.top()){_minst.pop();}_st.pop();}int top() {return _st.top();}int getMin() {return _minst.top();}private:stack<int> _st;stack<int> _minst;
};/*** Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:* MinStack* obj = new MinStack();* obj->push(val);* obj->pop();* int param_3 = obj->top();* int param_4 = obj->getMin();*/栈的压入、弹出序列_牛客题霸_牛客网
class Solution {
public:/*** 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可** * @param pushV int整型vector * @param popV int整型vector * @return bool布尔型*/bool IsPopOrder(vector<int>& pushV, vector<int>& popV) {size_t popi=0;stack<int> st;for(auto& e : pushV){st.push(e);while(!st.empty() && st.top() == popV[popi]){st.pop();popi++;}}return st.empty();}
};150. 逆波兰表达式求值 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public:int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) {stack<int> s;for (size_t i = 0; i < tokens.size(); ++i){string& str = tokens[i];// str为数字if (!("+" == str || "-" == str || "*" == str || "/" == str)){s.push(atoi(str.c_str()));}else{// str为操作符int right = s.top();s.pop();int left = s.top();s.pop();switch (str[0]){case '+':s.push(left + right);break;case '-':s.push(left - right);break;case '*':s.push(left * right);break;case '/':// 题目说明了不存在除数为0的情况s.push(left / right);break;}}}return s.top();}
};232. 用栈实现队列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class MyQueue {
public:MyQueue() {}void push(int x) {_push.push(x);}int pop() {if(_pop.empty()){while(!_push.empty()){int front = _push.top();_pop.push(front);_push.pop();} }int x = _pop.top();_pop.pop();return x;}int peek() {if(_pop.empty()){while(!_push.empty()){int front = _push.top();_pop.push(front);_push.pop();}}return _pop.top();}bool empty() {return _push.empty() && _pop.empty();}private:stack<int> _push;stack<int> _pop;
};/*** Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:* MyQueue* obj = new MyQueue();* obj->push(x);* int param_2 = obj->pop();* int param_3 = obj->peek();* bool param_4 = obj->empty();*/1.4 stack的模拟实现
#include<vector>
namespace sy
{template<class T>class stack{public:stack() {}void push(const T& x) { _c.push_back(x); }void pop() { _c.pop_back(); }T& top() { return _c.back(); }const T& top()const { return _c.back(); }size_t size()const { return _c.size(); }bool empty()const { return _c.empty(); }private:std::vector<T> _c;};
}2.queue
2.1 queue的介绍
2.2 queue的使用
2.3 OJ 题目
102. 二叉树的层序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {vector<vector<int>> vv;int levelsize=0;//当前层数个数,控制数据一层一层出queue<TreeNode*> q;if(root){q.push(root);levelsize=1;}while(!q.empty()){vector<int> v;while(levelsize--){TreeNode* front= q.front();v.push_back(front->val);q.pop();if(front->left){q.push(front->left);}if(front->right){q.push(front->right);}}//当前层出完,下一层都进队列了,队列的size就是下一层的数据levelsize=q.size();vv.push_back(v);}return vv;}
};225. 用队列实现栈 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class MyStack {
public:MyStack() {}void push(int x) {if(!q1.empty()){q1.push(x);}else{q2.push(x);}}int pop() {int top;if (!q1.empty()) {// 将q1中除最后一个元素外的所有元素转移到q2while (q1.size() > 1) {q2.push(q1.front());q1.pop();}top = q1.front();q1.pop();}else {// 将q2中除最后一个元素外的所有元素转移到q1while (q2.size() > 1) {q1.push(q2.front());q2.pop();}top = q2.front();q2.pop();}return top;
}int top() {if(!q1.empty()){return q1.back();}else{return q2.back();}}bool empty() {return q1.empty() && q2.empty();}private:queue<int> q1;queue<int> q2;
};/*** Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:* MyStack* obj = new MyStack();* obj->push(x);* int param_2 = obj->pop();* int param_3 = obj->top();* bool param_4 = obj->empty();*/2.4 queue的模拟实现
#include <list>
namespace sy
{template<class T>class queue{public:queue() {}void push(const T& x) { _c.push_back(x); }void pop() { _c.pop_front(); }T& back() { return _c.back(); }const T& back()const { return _c.back(); }T& front() { return _c.front(); }const T& front()const { return _c.front(); }size_t size()const { return _c.size(); }bool empty()const { return _c.empty(); }private:std::list<T> _c;};
}3.容器适配器
3.1 什么是适配器
3.2 STL标准库中stack和queue的底层结构

4.deque(双端队列)
4.1 deque的介绍
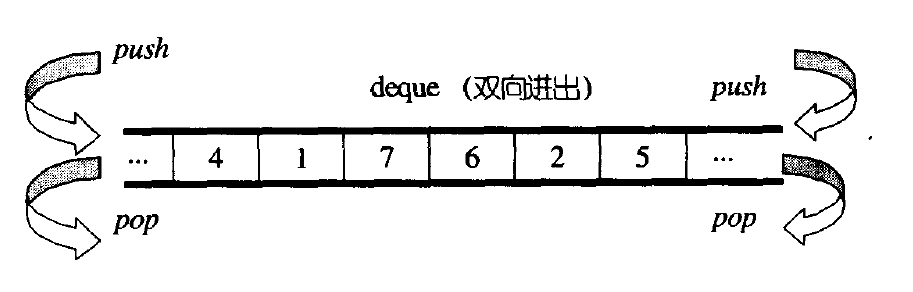
4.2 deque的使用
deque - C++ Reference
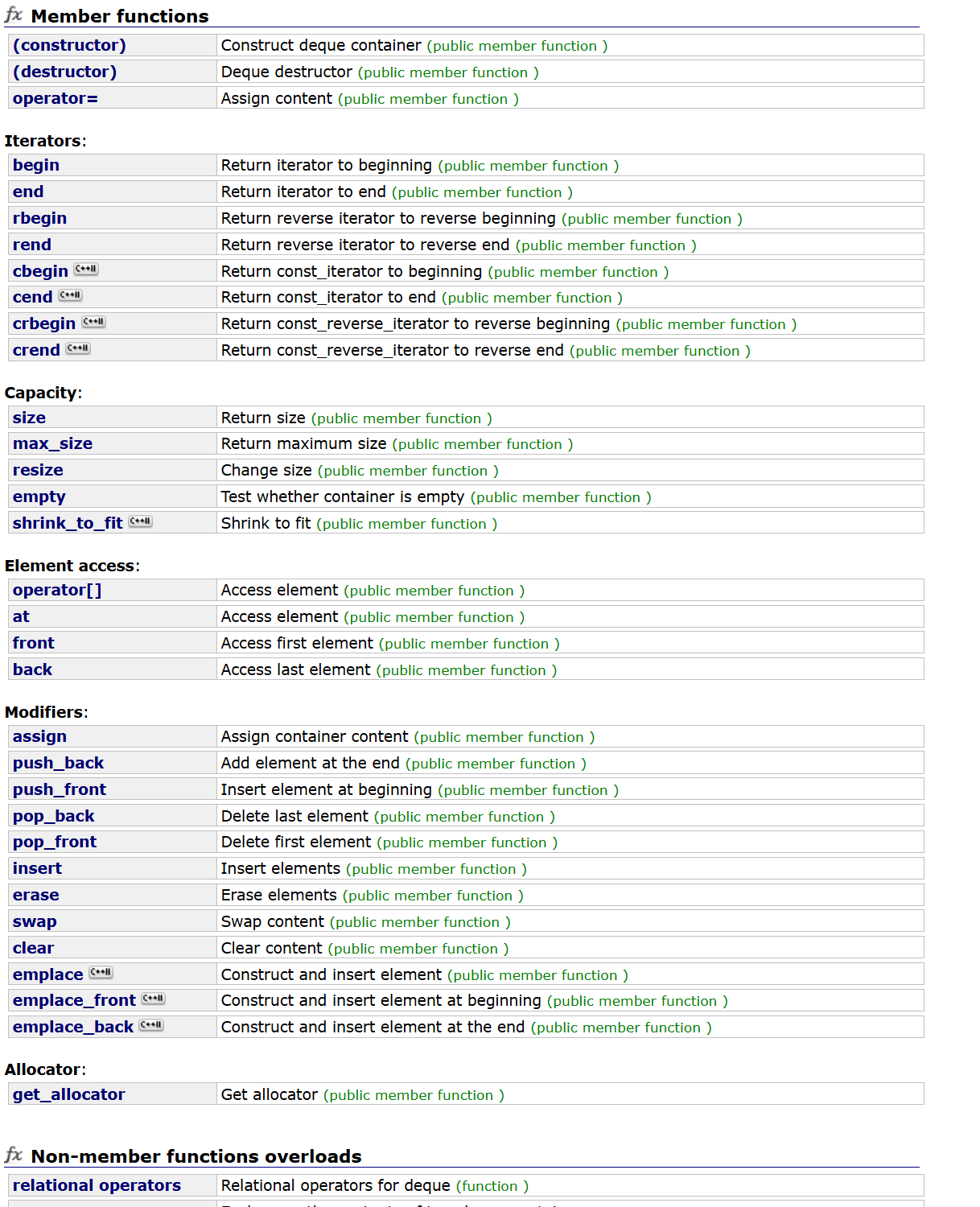
和之前学过的string,vector相关接口类似。

4.3 deque剖析
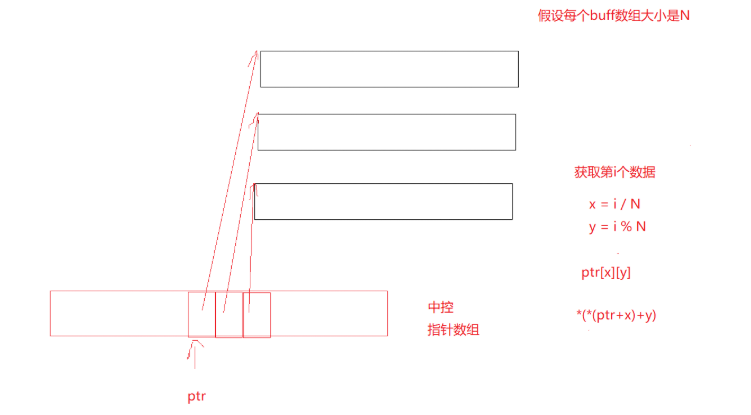
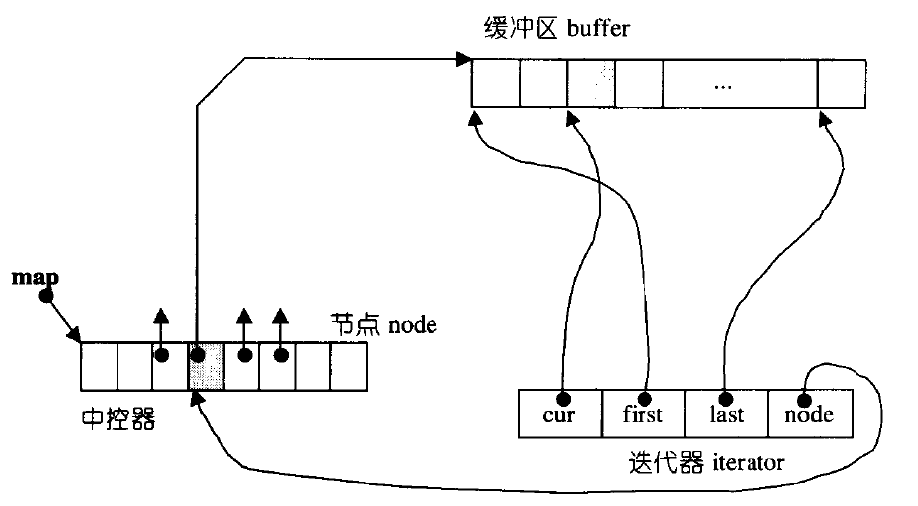
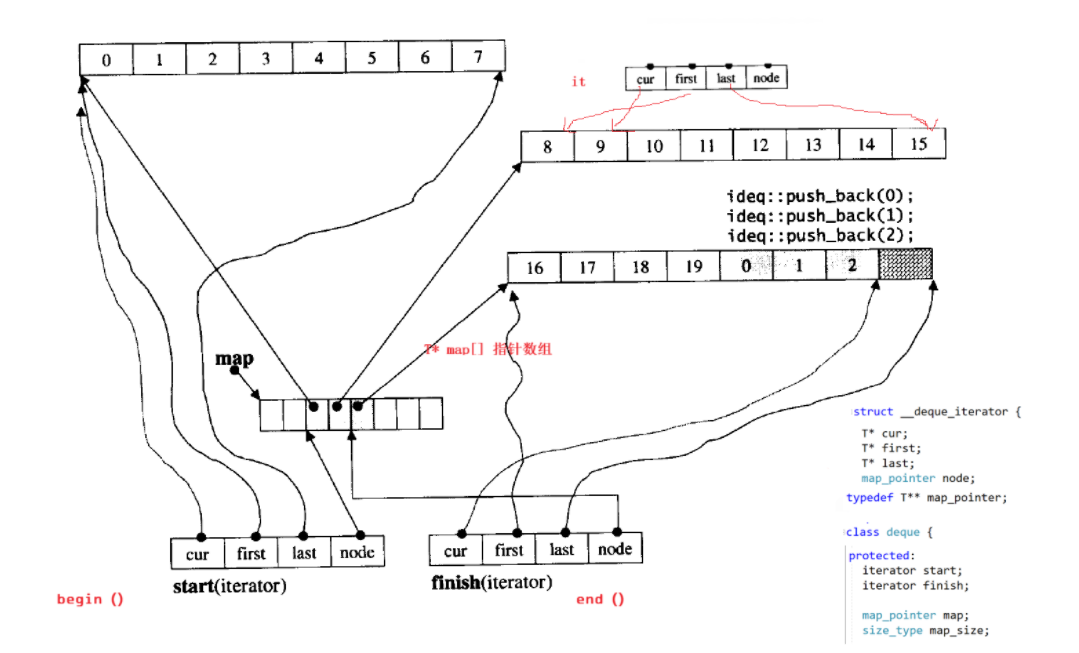
4.4 deque的缺陷
4.5 为什么选择deque作为stack和queue的底层默认容器?
4.6 STL标准库中对于stack和queue的模拟实现
4.6.1 stack.h
#pragma once
#include<deque>
namespace sy
{template<class T, class Container = deque<T>>class stack{public:void push(const T& x){_con.push_back(x);}void pop(){_con.pop_back();}const T& top() const{return _con.back();}size_t size() const{return _con.size();}bool empty() const{return _con.empty();}private:Container _con;};
}4.6.2 queue.h
#pragma once
#include<deque>namespace sy
{template<class T, class Container = deque<T>>class queue{public:void push(const T& x){_con.push_back(x);}void pop(){_con.pop_front();}const T& front() const{return _con.front();}const T& back() const{return _con.back();}size_t size() const{return _con.size();}bool empty() const{return _con.empty();}private:Container _con;};
}
5.priority_queue
5.1 priority_queue介绍
cplusplus.com/reference/queue/priority_queue/#google_vignette
priority_queue 是 C++ 标准库中的一种容器适配器,基于堆数据结构实现,用于高效管理具有优先级的元素。默认情况下,元素按从大到小的顺序排列(大顶堆),但可以通过自定义比较器调整排序方式。
- 底层实现:通常基于 vector 或 deque 实现,使用堆算法维护优先级。
- 时间复杂度:插入和删除操作的时间复杂度为 O(log n),访问顶部元素为 O(1)。
- 默认排序:
std::less<T>导致大顶堆(最大值在顶部),可通过std::greater<T>改为小顶堆。
5.1.2 priority_queue的使用
priority_queue - C++ Reference
 如果在priority_queue中放自定义类型的数据,用户需要在自定义类型中提供> 或者< 的重载。
如果在priority_queue中放自定义类型的数据,用户需要在自定义类型中提供> 或者< 的重载。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <functional> // greater算法的头文件
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1): _year(year), _month(month), _day(day){}bool operator<(const Date& d)const{return (_year < d._year) ||(_year == d._year && _month < d._month) ||(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day);}bool operator>(const Date& d)const{return (_year > d._year) ||(_year == d._year && _month > d._month) ||(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day);}friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d){_cout << d._year << "-" << d._month << "-" << d._day;return _cout;}
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};
void TestPriorityQueue()
{// 大堆,需要用户在自定义类型中提供<的重载priority_queue<Date> q1;q1.push(Date(2025, 10, 29));q1.push(Date(2025, 10, 28));q1.push(Date(2025, 10, 30));cout << q1.top() << endl;// 如果要创建小堆,需要用户提供>的重载priority_queue<Date, vector<Date>, greater<Date>> q2;q2.push(Date(2025, 10, 29));q2.push(Date(2025, 10, 28));q2.push(Date(2025, 10, 30));cout << q2.top() << endl;
}int main()
{TestPriorityQueue();return 0;
}
//运行结果:
//2025 - 10 - 30
//2025 - 10 - 285.2 仿函数介绍(简单)
仿函数:本质是一个类,这个类重载operator(),它的对象可以像函数一样使用,使用时候需要包含<functional>。
template<class T>
class Less
{
public:bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y){return x < y;}
};template<class T>
class Greater
{
public:bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y){return x > y;}
};5.2.1 使用
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <functional> // greater算法的头文件
using namespace std;
void TestPriorityQueue()
{// 默认情况下,创建的是大堆,其底层按照小于号比较vector<int> v{ 3,2,7,6,0,4,1,9,8,5 };priority_queue<int> q1;for (auto& e : v)q1.push(e);cout << q1.top() << endl;//9// 如果要创建小堆,将第三个模板参数换成greater比较方式priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> q2(v.begin(), v.end());cout << q2.top() << endl;//0// 如果要创建大堆,将第三个模板参数换成less比较方式//priority_queue<int, vector<int>, less<int>> q2(v.begin(), v.end());}int main()
{TestPriorityQueue();return 0;
}5.3 priority_queue 模拟实现
5.3.1 priority_queue.h
#pragma once#include<vector>template<class T>
class Less
{
public:bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y){return x < y;}
};template<class T>
class Greater
{
public:bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y){return x > y;}
};namespace sy
{// 默认是大堆template<class T, class Container = vector<T>, class Compare = Less<T>>class priority_queue{public:void AdjustUp(int child){Compare com;int parent = (child - 1) / 2;while (child > 0){//if (_con[parent] < _con[child])if (com(_con[parent], _con[child])){swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);child = parent;parent = (child - 1) / 2;}else{break;}}}void push(const T& x){_con.push_back(x);AdjustUp(_con.size() - 1);}void AdjustDown(int parent){// 先假设左孩子小size_t child = parent * 2 + 1;Compare com;while (child < _con.size()) // child >= n说明孩子不存在,调整到叶子了{// 找出小的那个孩子//if (child + 1 < _con.size() && _con[child] < _con[child + 1])if (child + 1 < _con.size() && com(_con[child], _con[child + 1])){++child;}//if (_con[parent] < _con[child])if (com(_con[parent], _con[child])){swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);parent = child;child = parent * 2 + 1;}else{break;}}}void pop(){swap(_con[0], _con[_con.size() - 1]);_con.pop_back();AdjustDown(0);}const T& top(){return _con[0];}size_t size() const{return _con.size();}bool empty() const{return _con.empty();}private:Container _con;};
}5.4 OJ 使用
215. 数组中的第K个最大元素 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public:
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k)
{// 将数组中的元素先放入优先级队列中priority_queue<int> p(nums.begin(), nums.end());// 将优先级队列中前k-1个元素删除掉for(int i= 0; i < k-1; ++i){p.pop();}return p.top();}
};主持人调度(二)_牛客题霸_牛客网
class Solution
{
public:int minmumNumberOfHost(int n, vector<vector<int> >& startEnd) {sort(startEnd.begin(), startEnd.end());priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> heap; // 创建⼀个⼩根堆heap.push(startEnd[0][1]); // 先把第⼀个区间放进去for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) // 处理剩下的区间{int a = startEnd[i][0], b = startEnd[i][1];if(a >= heap.top()) // 没有重叠{heap.pop();heap.push(b);}else // 有重叠{heap.push(b); // 重新安排⼀个⼈}}return heap.size();}
};5.5 test.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<list>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;#include"Stack.h"
#include"Queue.h"
#include"PriorityQueue.h"int main()
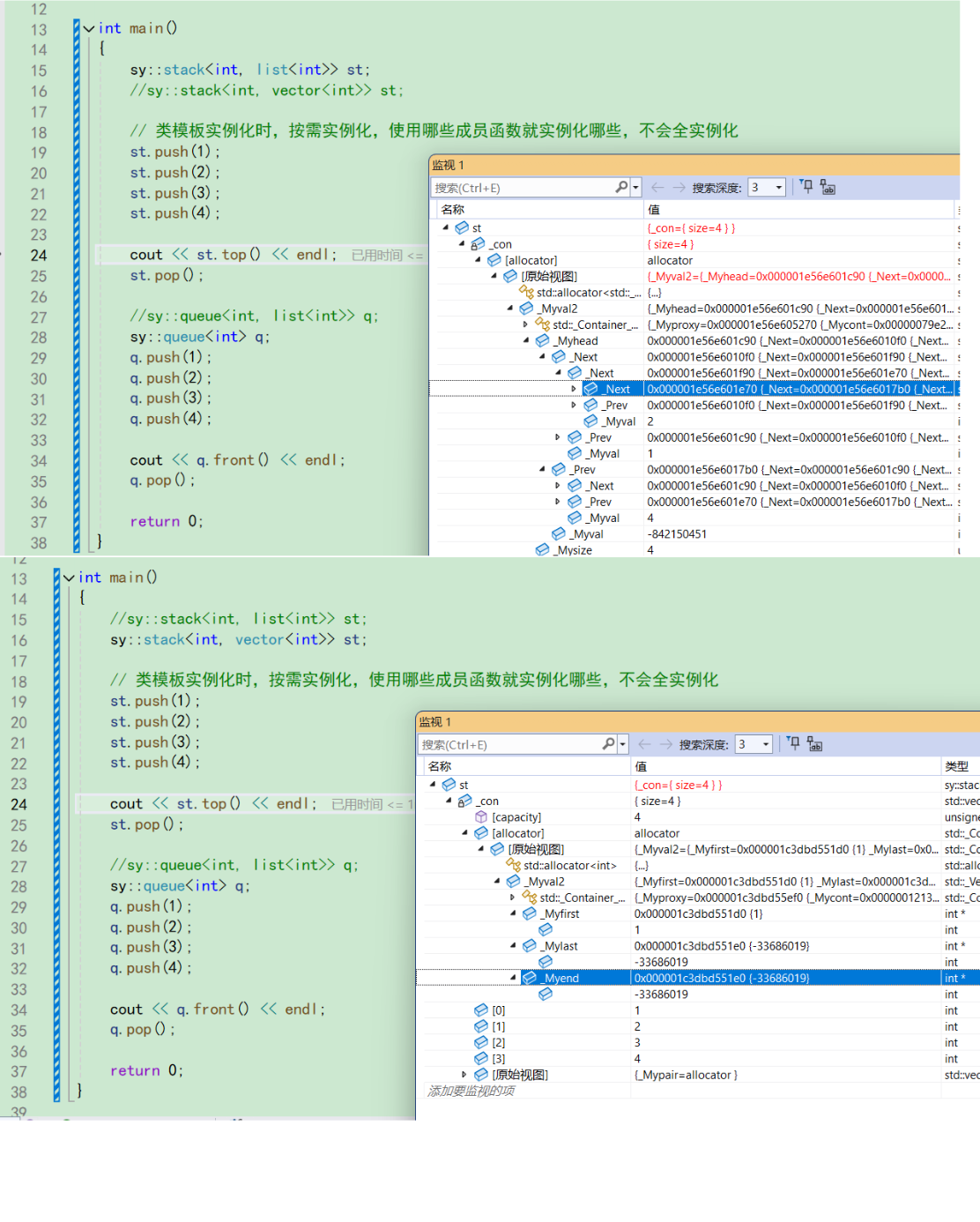
{//sy::stack<int, list<int>> st;sy::stack<int, vector<int>> st;// 类模板实例化时,按需实例化,使用哪些成员函数就实例化哪些,不会全实例化st.push(1);st.push(2);st.push(3);st.push(4);cout << st.top() << endl;st.pop();//sy::queue<int, list<int>> q;sy::queue<int> q;q.push(1);q.push(2);q.push(3);q.push(4);cout << q.front() << endl;q.pop();return 0;
}void test_op1()
{srand(time(0));const int N = 1000000;deque<int> dq;vector<int> v;for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i){auto e = rand() + i;v.push_back(e);dq.push_back(e);}int begin1 = clock();sort(v.begin(), v.end());int end1 = clock();int begin2 = clock();sort(dq.begin(), dq.end());int end2 = clock();printf("vector:%d\n", end1 - begin1);printf("deque:%d\n", end2 - begin2);
}void test_op2()
{srand(time(0));const int N = 1000000;deque<int> dq1;deque<int> dq2;for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i){auto e = rand() + i;dq1.push_back(e);dq2.push_back(e);}int begin1 = clock();sort(dq1.begin(), dq1.end());int end1 = clock();int begin2 = clock();// 拷贝到vectorvector<int> v(dq2.begin(), dq2.end());sort(v.begin(), v.end());dq2.assign(v.begin(), v.end());int end2 = clock();printf("deque sort:%d\n", end1 - begin1);printf("deque copy vector sort, copy back deque:%d\n", end2 - begin2);
}int main()
{test_op2();return 0;
}int main()
{//priority_queue<int> pq;sy::priority_queue<int, vector<int>, Greater<int>> pq;//sy::priority_queue<int> pq;pq.push(4);pq.push(1);pq.push(5);pq.push(7);pq.push(9);while (!pq.empty()){cout << pq.top() << " ";pq.pop();}cout << endl;return 0;
}//仿函数:本质是一个类,这个类重载operator(),他的对象可以像函数一样使用
//template<class T>
//class Less
//{
//public:
// bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
// {
// return x < y;
// }
//};
//
//template<class T>
//class Greater
//{
//public:
// bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
// {
// return x > y;
// }
//};//< 升序//> 降序
template<class Compare>
void BubbleSort(int* a, int n, Compare com)
{for (int j = 0; j < n; j++){// 单趟int flag = 0;for (int i = 1; i < n - j; i++){//if (a[i] < a[i - 1])if (com(a[i], a[i - 1])){swap(a[i - 1], a[i]);flag = 1;}}if (flag == 0){break;}}
}int main()
{Less<int> LessFunc;Greater<int> GreaterFunc;// 函数对象cout << LessFunc(1, 2) << endl; cout << LessFunc.operator()(1, 2) << endl;int a[] = { 9,1,2,5,7,4,6,3 };BubbleSort(a, 8, LessFunc);BubbleSort(a, 8, GreaterFunc);BubbleSort(a, 8, Less<int>());BubbleSort(a, 8, Greater<int>());return 0;
}
//运行结果
//1
//1
