数据结构基础:链表(2)——双向链表、循环链表、内核链表
一、双向链表
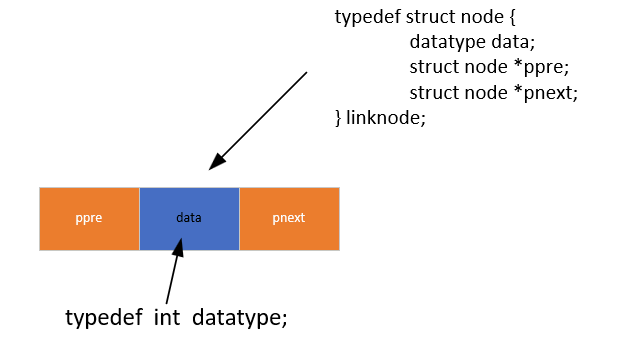
1 节点定义
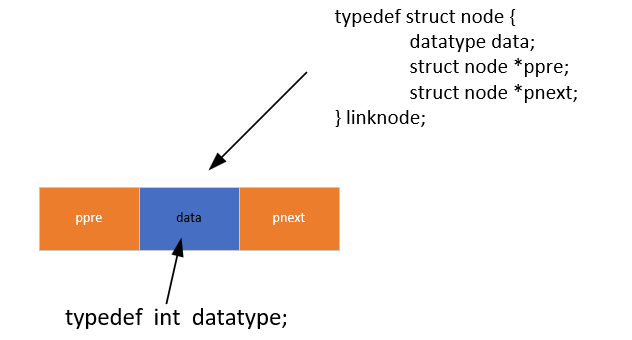
/* 节点存放数据的类型 */
typedef int datatype;/* 节点类型 */
typedef struct node
{datatype data; //存放数据空间struct node *ppre; //存放前一个节点地址struct node *pnext; //存放下一个节点地址
}linknode;2 空链表的创建
(双向链表的创建基本思想与单向链表是一致的。可拿单向链表【上一篇文章中有写】作为参考)
- 申请节点空间
- 对pnext和ppre赋值为NULL
- 返回空白节点地址即可
linknode *create_empty_linklist(void)
{linknode *ptmpnode = NULL;ptmpnode = malloc(sizeof(linknode));if (NULL == ptmpnode){perror("fail to malloc");return NULL;}ptmpnode->ppre = NULL;ptmpnode->pnext = NULL;return ptmpnode;
}双向链表和单向链表在操作上的方法基本一致,只有头插法和链表删除有较大区别
3 链表的头插法(与单向链表不同)
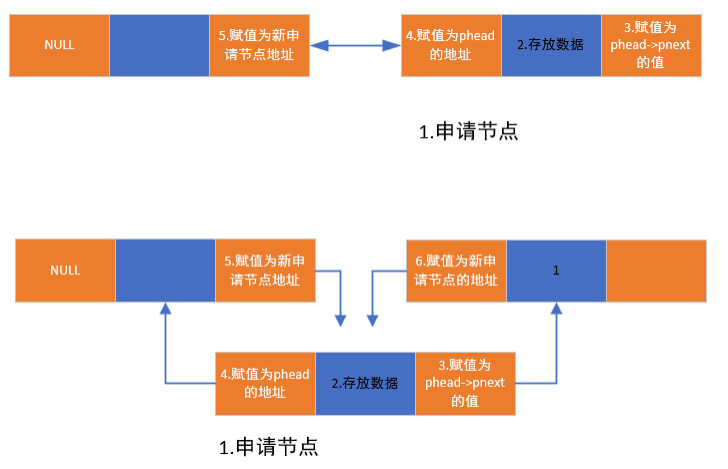
步骤:
- 申请节点
- 存放数据
- pnext赋值为phead->pnext
- ppre赋值为phead的地址
- phead->pnext赋值为新申请节点地址
- 如果有后一个节点,需要让后一个节点的ppre指向该节点
/* 头插法 */
int insert_head_linklist(linknode *phead, datatype tmpdata)
{linknode *ptmpnode = NULL;ptmpnode = malloc(sizeof(linknode));if (NULL == ptmpnode){perror("fail to malloc");return -1;}ptmpnode->data = tmpdata;ptmpnode->pnext = phead->pnext;ptmpnode->ppre = phead;phead->pnext = ptmpnode;if (ptmpnode->pnext != NULL){ptmpnode->pnext->ppre = ptmpnode;}return 0;
}4 链表的遍历(参考单向链表)
/* 链表的遍历 */
int show_linklist(linknode *phead)
{linknode *ptmpnode = NULL;ptmpnode = phead->pnext;while (ptmpnode != NULL){printf("%d ", ptmpnode->data);ptmpnode = ptmpnode->pnext;}printf("\n");return 0;
}5 链表的查找(参考单向链表)
/* 链表的查找 */
linknode *find_linklist(linknode *phead, datatype tmpdata)
{linknode *ptmpnode = NULL;ptmpnode = phead->pnext;while (ptmpnode != NULL){if (ptmpnode->data == tmpdata){return ptmpnode;}ptmpnode = ptmpnode->pnext;}return NULL;
}6 链表的修改(参考单向链表)
/* 链表的修改 */
int update_linklist(linknode *phead, datatype olddata, datatype newdata)
{linknode *ptmpnode = NULL;ptmpnode = phead->pnext;while (ptmpnode != NULL){if (ptmpnode->data == olddata){ptmpnode->data = newdata;}ptmpnode = ptmpnode->pnext;}return 0;
}
7 链表的删除(与单向链表不同)
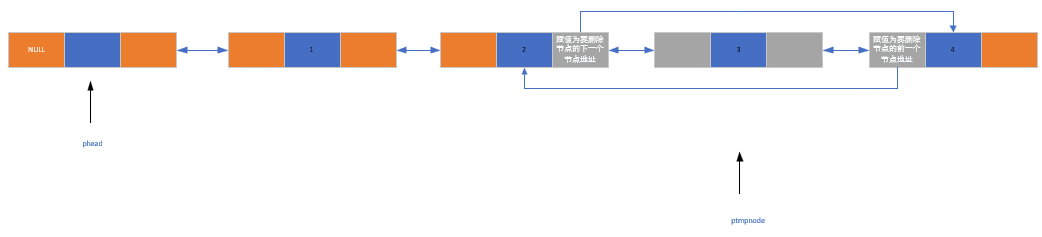
步骤:
- 找到要删除的节点
- 让删除节点的前一个节点的pnext指向要删除节点的后一个节点
- 让伤处节点的后一个节点的ppre指向要删除节点的前一个节点
- 将要删除的节点释放掉
/* 链表的删除 */
int delete_linklist(linknode *phead, datatype tmpdata)
{linknode *ptmpnode = NULL;linknode *pfreenode = NULL;ptmpnode = phead->pnext;while (ptmpnode != NULL){if (ptmpnode->data == tmpdata){ptmpnode->ppre->pnext = ptmpnode->pnext;if (ptmpnode->pnext != NULL){ptmpnode->pnext->ppre = ptmpnode->ppre;}pfreenode = ptmpnode;ptmpnode = ptmpnode->pnext;free(pfreenode);}else{ptmpnode = ptmpnode->pnext;}}return 0;
}8 链表的销毁(参考单向链表)
/* 链表的销毁 */
int destroy_linklist(linknode **pphead)
{linknode *ptmpnode = NULL;linknode *pfreenode = NULL;ptmpnode = *pphead;pfreenode = ptmpnode;while (ptmpnode != NULL){ptmpnode = ptmpnode->pnext;free(pfreenode);pfreenode = ptmpnode;}*pphead = NULL;return 0;
}9 链表的尾插法(与单向链表不同)
步骤:
- 申请节点
- 将节点的pnext赋值为NULL
- 找到链表最后一个节点
- 将节点的ppre赋值为最后一个节点地址
- 将最后一个节点的pnext赋值为新申请节点
/* 尾插法 */
int insert_tail_linklist(linknode *phead, datatype tmpdata)
{linknode *ptmpnode = NULL;linknode *plastnode = NULL;ptmpnode = malloc(sizeof(linknode));if (NULL == ptmpnode){perror("fail to malloc");return -1;}plastnode = phead;while (plastnode->pnext != NULL){plastnode = plastnode->pnext;}ptmpnode->data = tmpdata;ptmpnode->pnext = NULL;ptmpnode->ppre = plastnode;plastnode->pnext = ptmpnode;return 0;
}二、循环链表
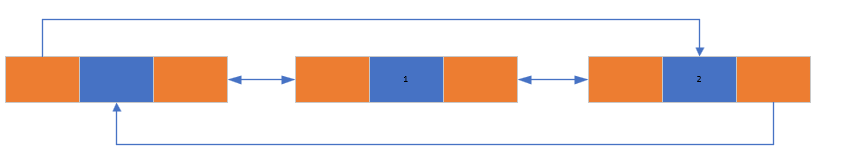
1 循环链表的特点
- 头结点的ppre指向链表最后一个节点
- 最后节点的pnext指向第一个节点
2 节点的定义(参考双向链表)
/* 节点存放数据的类型 */
typedef int datatype;/* 节点类型 */
typedef struct node
{datatype data; //存放数据空间struct node *ppre; //存放前一个节点地址struct node *pnext; //存放下一个节点地址
}linknode;3 链表创建
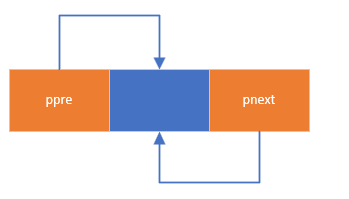
- 申请节点
- pnext和ppre都指向自己
/* 创建空链表 */
linknode *create_empty_linklist(void)
{linknode *ptmpnode = NULL;ptmpnode = malloc(sizeof(linknode));if (NULL == ptmpnode){perror("fail to malloc");return NULL;}ptmpnode->pnext = ptmpnode->ppre = ptmpnode;return ptmpnode;
}4 链表的头插法
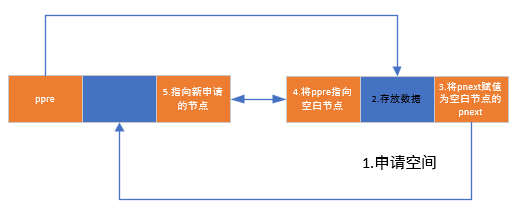
步骤:
- 申请节点空间
- 存放数据
- 将pnext指向空白节点的pnext
- 将ppre指向空白节点
- 将空白节点的pnext指向新申请节点
- 将后续节点的ppre指向新申请节点
/* 头插法 */
int insert_head_linklist(linknode *phead, datatype tmpdata)
{linknode *ptmpnode = NULL;ptmpnode = malloc(sizeof(linknode));if (NULL == ptmpnode){perror("fail to malloc");return -1;}ptmpnode->data = tmpdata;ptmpnode->pnext = phead->pnext;ptmpnode->ppre = phead;ptmpnode->pnext->ppre = ptmpnode;ptmpnode->ppre->pnext = ptmpnode;return 0;
}5 链表的尾插法
/* 尾插法 */
int insert_tail_linklist(linknode *phead, datatype tmpdata) {linknode *ptmpnode = NULL;ptmpnode = malloc(sizeof(linknode));if (NULL == ptmpnode) {perror("fail to malloc");return -1;}ptmpnode->data = tmpdata;ptmpnode->pnext = phead;ptmpnode->ppre = phead->ppre;ptmpnode->pnext->ppre = ptmpnode;ptmpnode->ppre->pnext = ptmpnode;return 0;
}
- 申请节点空间并存放数据
- 将新节点的
pnext指向头节点,ppre指向头节点的ppre(即原最后一个节点)- 调整原最后一个节点的
pnext和头节点的ppre,使新节点插入到链表尾部
6 链表的遍历
- 从 head->next 开始遍历,循环条件为当前节点不等于头节点,依次访问每个节点的数据。
7 链表的查找(参考双向链表)
/* 链表的查找 */
linknode *find_linklist(linknode *phead, datatype tmpdata) {linknode *ptmpnode = NULL;ptmpnode = phead->pnext;while (ptmpnode != phead) {if (ptmpnode->data == tmpdata) {return ptmpnode;}ptmpnode = ptmpnode->pnext;}return NULL;
}
- 从 head->next 开始遍历,循环条件为当前节点不等于头节点,若找到与目标数据匹配的节点,返回该节点地址,否则返回 NULL
8 链表的修改(参考双向链表)
/* 链表的修改 */
int update_linklist(linknode *phead, datatype olddata, datatype newdata) {linknode *ptmpnode = NULL;ptmpnode = phead->pnext;while (ptmpnode != phead) {if (ptmpnode->data == olddata) {ptmpnode->data = newdata;}ptmpnode = ptmpnode->pnext;}return 0;
}
- 从 head->next 开始遍历,循环条件为当前节点不等于头节点,找到数据与旧值匹配的节点,将其数据修改为新值。
9 链表的删除(参考双向链表)
/* 链表的删除 */
int delete_linklist(linknode *phead, datatype tmpdata) {linknode *ptmpnode = NULL;linknode *pfreenode = NULL;ptmpnode = phead->pnext;while (ptmpnode != phead) {if (ptmpnode->data == tmpdata) {ptmpnode->ppre->pnext = ptmpnode->pnext;ptmpnode->pnext->ppre = ptmpnode->ppre;pfreenode = ptmpnode;ptmpnode = ptmpnode->pnext;free(pfreenode);} else {ptmpnode = ptmpnode->pnext;}}return 0;
}
- 从 head->next 开始遍历,循环条件为当前节点不等于头节点,找到数据匹配的节点。
- 调整该节点前一个节点的
pnext和后一个节点的ppre,释放该节点空间。
10 链表的销毁(参考双向链表)
/* 链表的销毁 */
int destroy_linklist(linknode **pphead) {linknode *ptmpnode = NULL;linknode *pfreenode = NULL;ptmpnode = (*pphead)->pnext;pfreenode = ptmpnode;while (ptmpnode != *pphead) {ptmpnode = ptmpnode->pnext;free(pfreenode);pfreenode = ptmpnode;}free(*pphead);*pphead = NULL;return 0;
}
- 遍历链表,释放除头节点外的所有节点,最后释放头节点,并将头节点指针置为 NULL。
三、内核链表
1 概念
- 是 Linux 内核中使用的一种链表结构。
- 与普通链表不同,普通链表的节点中包含数据,而内核链表是数据中包含链表节点,因此使用同一种结构可以存储不同类型的数据。
2 结构描述
/* 内核链表中的节点类型 */
struct list_head {struct list_head *next;struct list_head *prev;
};
- 节点结构包含
next和prev指针,分别指向后一个和前一个节点。
3 常用操作及宏定义
- 初始化空白头结点:
INIT_LIST_HEAD(head),使头节点的next和prev都指向自身。- 头插法:
list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head),将新节点插入到链表头部。- 尾插法:
list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head),将新节点插入到链表尾部。- 按指定顺序插入:
list_add_order(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head, int (*compare)(struct list_head *, struct list_head *)),根据比较函数指定的顺序插入节点。- 将节点移出所属的链表:
list_del(struct list_head *old),移除节点并做特殊标记。- 将节点移出所属的链表并初始化:
list_del_init(struct list_head *old),移除节点后将其初始化为指向自身。- 将节点移动到另一个链表的头部:
list_move(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)。- 将节点移动到另一个链表的尾部:
list_move_tail(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)。- 判断链表是否为空:
list_empty(struct list_head *head),若头节点的next指向自身则为空。- 链表拼接相关:
__list_splice、list_splice、list_splice_init、__list_append、list_append、list_append_init等,用于将一个链表的元素拼接到另一个链表的前面或后面。- 判断节点位置:
list_is_last判断当前节点是否为最后一个节点;list_is_singular判断链表是否只有一个节点。- 节点替换:
list_replace用新节点替换旧节点;list_replace_init替换后初始化旧节点。- 链表左旋:
list_rotate_left将链表左旋。- 数据元素地址相关宏:
list_entry根据链表节点地址找到数据元素首地址;list_first_entry、list_last_entry分别找到第一个和最后一个数据元素地址;list_next_entry、list_prev_entry找到下一个和上一个数据元素地址等。- 遍历相关宏:
list_for_each遍历链表节点元素地址;list_for_each_entry等遍历所有数据元素首地址,部分宏支持在遍历过程中修改数据元素指针。
可以参考list.h中关于内核链表的常见操作
/*
Copyright (c) 2008-2012 Red Hat, Inc. <http://www.redhat.com>
This file is part of GlusterFS.
This file is licensed to you under your choice of the GNU Lesser
General Public License, version 3 or any later version (LGPLv3 or
later), or the GNU General Public License, version 2 (GPLv2), in all
cases as published by the Free Software Foundation.
*/#ifndef _LLIST_H
#define _LLIST_H/* 内核链表中的节点类型 */
struct list_head {
struct list_head *next;
struct list_head *prev;
};/* 初始化空白头结点 */
#define INIT_LIST_HEAD(head) do { \
(head)->next = (head)->prev = head; \
} while (0)/* 头插法 */
static inline void
list_add (struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{
new->prev = head;
new->next = head->next;
new->prev->next = new;
new->next->prev = new;/* 尾插法 */
static inline void
list_add_tail (struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{
new->next = head;
new->prev = head->prev;
new->prev->next = new;
new->next->prev = new;
}/* 按指定顺序插入 *//* This function will insert the element to the list in a order.
Order will be based on the compare function provided as a input.
If element to be inserted in ascending order compare should return:
0: if both the arguments are equal
>0: if first argument is greater than second argument
<0: if first argument is less than second argument */
static inline void
list_add_order (struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head,
int (*compare)(struct list_head *, struct list_head *))
{
struct list_head *pos = head->prev;
while ( pos != head ) {
if (compare(new, pos) >= 0)
break;
/* Iterate the list in the reverse order. This will
have
better efficiency if the elements are inserted in
the
ascending order */
pos = pos->prev;
}
list_add (new, pos);
}/* 将节点移出所属的链表 */
static inline void
list_del (struct list_head *old)
{
old->prev->next = old->next;
old->next->prev = old->prev;
old->next = (void *)0xbabebabe;
old->prev = (void *)0xcafecafe;
}/* 将节点移出所属的链表,并初始化 */
static inline void
list_del_init (struct list_head *old)
{old->prev->next = old->next;
old->next->prev = old->prev;
old->next = old;
old->prev = old;
}/* 将节点移动到另一个链表的头部 */
static inline void
list_move (struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
{
list_del (list);
list_add (list, head);
}/* 将节点移动到另一个链表的尾部 */
static inline void
list_move_tail (struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
{
list_del (list);
list_add_tail (list, head);
}/* 判断链表是否为空 */
static inline int
list_empty (struct list_head *head)
{
return (head->next == head);
}/* 将list链表所有元素拼到head链表的前面 */
static inline void
__list_splice (struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
{
(list->prev)->next = (head->next);
(head->next)->prev = (list->prev);
(head)->next = (list->next);
(list->next)->prev = (head);
}/* 将list链表所有元素拼到head链表的前面 */
static inline void
list_splice (struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
{
if (list_empty (list))
return;
__list_splice (list, head);
}/* 将list链表所有元素拼到head链表的前面,并初始化list头结点 *//* Splice moves @list to the head of the list at @head. */static inline void
list_splice_init (struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
{if (list_empty (list))
return;
__list_splice (list, head);
INIT_LIST_HEAD (list);
}/* 将list链表所有元素追加到head链表的后面 */
static inline void
__list_append (struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
{
(head->prev)->next = (list->next);
(list->next)->prev = (head->prev);
(head->prev) = (list->prev);
(list->prev)->next = head;
}/* 将list链表所有元素追加到head链表的后面 */
static inline void
list_append (struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
{
if (list_empty (list))
return;
__list_append (list, head);
}/* 将list链表所有元素追加到head链表的后面,并初始化list */
/* Append moves @list to the end of @head */static inline void
list_append_init (struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
{
if (list_empty (list))
return;
__list_append (list, head);
INIT_LIST_HEAD (list);
}/* 判断当前节点是否为最后一个节点 */
static inline int
list_is_last (struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
{
return (list->next == head);
}/* 判断链表是否只有一个节点 */
static inline int
list_is_singular(struct list_head *head)
{
return !list_empty(head) && (head->next == head->prev);
}/* 将旧节点用新节点替换 */
/**
* list_replace - replace old entry by new one* @old : the element to be replaced
* @new : the new element to insert
*
* If @old was empty, it will be overwritten.
*/
static inline void list_replace(struct list_head *old,
struct list_head *new)
{
new->next = old->next;
new->next->prev = new;
new->prev = old->prev;
new->prev->next = new;
}/* 将旧节点用新节点替换,并初始化旧节点 */
static inline void list_replace_init(struct list_head *old,
struct list_head *new)
{
list_replace(old, new);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(old);
}/* 内核链表左旋 */
/**
* list_rotate_left - rotate the list to the left
* @head: the head of the list
*/
static inline void list_rotate_left (struct list_head *head)
{
struct list_head *first;
if (!list_empty (head)) {
first = head->next;
list_move_tail (first, head);
}
}/* 根据链表节点地址找到数据元素首地址 */
#define list_entry(ptr, type, member) \
((type *)((char *)(ptr)-(unsigned long)(&((type *)0)->member)))/* 找到第一个数据元素地址 */
#define list_first_entry(ptr, type, member) \
list_entry((ptr)->next, type, member)/* 找到最后一个数据元素地址 */
#define list_last_entry(ptr, type, member) \
list_entry((ptr)->prev, type, member)/* 找到下一个数据元素地址 */
#define list_next_entry(pos, member) \
list_entry((pos)->member.next, typeof(*(pos)), member)/* 找到上一个数据元素地址 */
#define list_prev_entry(pos, member) \
list_entry((pos)->member.prev, typeof(*(pos)), member)/* 遍历链表节点元素地址 */
#define list_for_each(pos, head)
\
for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next)/* 遍历所有数据元素首地址 */
#define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) \
for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member); \
&pos->member != (head); \
pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member))/* 遍历所有数据元素首地址(可以在遍历过程中修改数据元素指针) */
#define list_for_each_entry_safe(pos, n, head, member) \
for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member), \
n = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member); \
&pos->member != (head); \
pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.next, typeof(*n), member))/* 倒着遍历所有数据元素首地址 */
#define list_for_each_entry_reverse(pos, head, member)
\
for (pos = list_entry((head)->prev, typeof(*pos), member); \
&pos->member != (head); \
pos = list_entry(pos->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member))/* 倒着遍历所有数据元素首地址(可以在遍历过程中修改数据元素指针) */
#define list_for_each_entry_safe_reverse(pos, n, head, member)
\
for (pos = list_entry((head)->prev, typeof(*pos), member), \
n = list_entry(pos->member.prev, typeof(*pos), member); \
&pos->member != (head); \
pos = n, n = list_entry(n->member.prev, typeof(*n), member))/*
* This list implementation has some advantages, but one disadvantage:
you
* can't use NULL to check whether you're at the head or tail. Thus,
the
* address of the head has to be an argument for these macros.
*//* 获得下一个数据元素空间首地址,如果没有返回NULL */
#define list_next(ptr, head, type, member) \
(((ptr)->member.next == head) ? NULL \
: list_entry((ptr)->member.next, type,
member))/* 获得上一个数据元素空间首地址,如果没有返回NULL */
#define list_prev(ptr, head, type, member) \
(((ptr)->member.prev == head) ? NULL \
: list_entry((ptr)->member.prev, type,
member))#endif /* _LLIST_H */
