自然语言翻译--seq2seq
一、简单介绍
1.1seq2seq简单定义
Seq2Seq(Sequence to Sequence)是一种深度学习模型结构,用于将一个序列映射为另一个序列,常用于机器翻译、语音识别、文本摘要、对话系统等任务。
1.2模型结构介绍
该模型是基于encoder和decoder框架的神经网络模型。
encoder是编码器,主要负责将序列编码为固定长度的隐藏状态,简单理解可以理解为它负责将每个词变为向量并压缩为一个上下文向量。
decoder是解码器,它根据编码器encoder的隐藏状态逐步生成目标序列,简单理解为输出序列。
模型结构: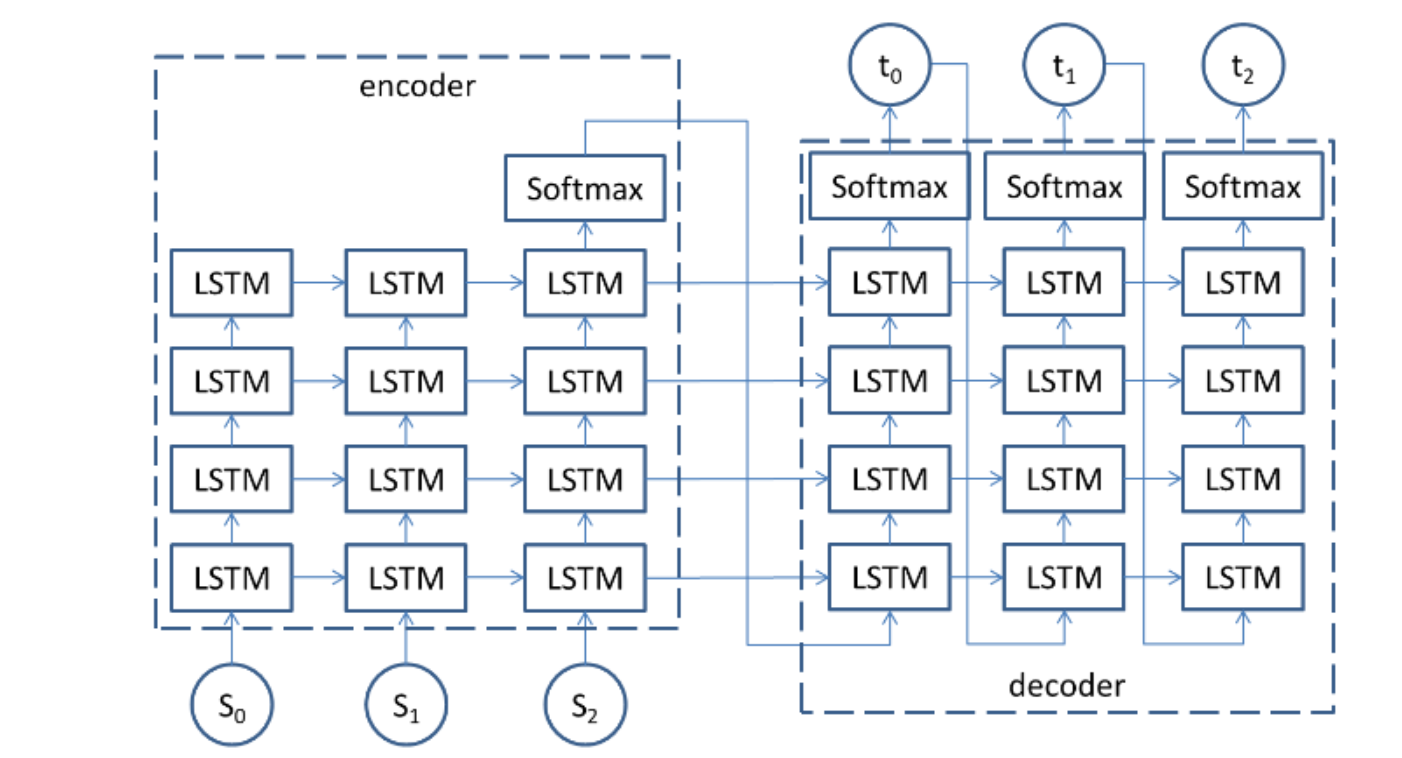
1.3工作流程
(1)输入序列;
(2)encoder编码----压缩向量;
(3)decoder编码----生成序列;
(4)训练方式----强制教学teacher forcing;
二、搭建seq2seq
2.1数据预处理
我们要把文本处理成计算机能看懂的数据--词向量,并将文本进行分词、去重、映射、填充,最后构建数据加载器。
代码参考:
"""
数据处理步骤:1. 构建词表3. 批量加载4. 序列转索引5. 填充最终结果 得到数据加载器[tensor([[15, 8, 5, 2, 0],[14, 3, 12, 7, 2]]), tensor([[ 1, 7, 4, 13, 0],[ 1, 3, 11, 8, 6]]), tensor([[ 7, 4, 13, 2, 0],[ 3, 11, 8, 6, 2]])]
torch.Size([2, 5])2. 词嵌入 放到模型去做
"""import torch# 数据预处理# 简单的英语到法语的句子对示例
pairs = [["i am a student", "我 是 一个 学生"],["he is a teacher", "他 是 一个 老师"],["she loves apples", "她 喜欢 苹果"],["we are friends", "我们 是 朋友"]
]# 第一步 构建词汇表
def build_vocab(sentences):vocab = set()for sentence in sentences:for word in sentence.split(' '):vocab.add(word)#集合不能用appendword2idx = {word: idx for idx, word in enumerate(vocab, start=3)}word2idx['<PAD>'] = 0 # 填充符word2idx['<SOS>'] = 1 # 开始符word2idx['<EOS>'] = 2 # 结束符idx2word = {idx: word for word, idx in word2idx.items()}return word2idx, idx2word# 为英语和法语句子构建词汇表
eng_sentences = [pair[0] for pair in pairs]
fra_sentences = [pair[1] for pair in pairs]
eng_word2idx, eng_idx2word = build_vocab(eng_sentences)
fra_word2idx, fra_idx2word = build_vocab(fra_sentences)# 第二步:将句子转换为索引序列
def sentence_to_indices(sentence, word2idx,flag = False):if flag == 1:return [word2idx['<SOS>']] + [word2idx[word] for word in sentence.split(' ')]elif flag == 2:return [word2idx[word] for word in sentence.split(' ')] + [word2idx['<EOS>']]return [word2idx[word] for word in sentence.split(' ')] + [word2idx['<EOS>']] # 句尾添加结束符input_seqs = [sentence_to_indices(pair[0], eng_word2idx) for pair in pairs]
target_inputs = [sentence_to_indices(pair[1], fra_word2idx,flag=1) for pair in pairs]
target_labels = [sentence_to_indices(pair[1], fra_word2idx,flag=2) for pair in pairs]
print(target_inputs)
print(target_labels)
# exit()# 第三步: 填充序列到相同长度
def pad_sequences(sequences, max_len, padding_value=0):# 思想是先创建全零的张量 然后将真实数据赋值给创建的全零张量padded_sequences = torch.zeros((len(sequences), max_len), dtype=torch.long)for i, seq in enumerate(sequences):padded_sequences[i, :len(seq)] = torch.tensor(seq, dtype=torch.long)return padded_sequences# 找到最长句子的长度用于填充
input_max_len = max([len(seq) for seq in input_seqs])
target_max_len = max([len(seq) for seq in target_inputs])
target_max_len2 = max([len(seq) for seq in target_labels])input_seqs_padded = pad_sequences(input_seqs, input_max_len)
target_input_padded = pad_sequences(target_inputs, target_max_len)
target_label_padded = pad_sequences(target_labels, target_max_len2)from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, TensorDataset
import torch.utils.data as Data
# 第四步:创建数据加载器
batch_size = 2# 定义自定义数据集类 MyDataSet
class MyDataSet(Data.Dataset):def __init__(self, enc_inputs, dec_inputs, dec_outputs):super(MyDataSet, self).__init__() # 调用父类的初始化方法self.enc_inputs = enc_inputs # 初始化编码器输入数据self.dec_inputs = dec_inputs # 初始化解码器输入数据self.dec_outputs = dec_outputs # 初始化解码器输出数据def __len__(self):return self.enc_inputs.shape[0] # 返回数据集样本数量def __getitem__(self, idx):return self.enc_inputs[idx], self.dec_inputs[idx], self.dec_outputs[idx] # 获取指定索引处的样本数据# 创建 DataLoader 对象 loader,用于批量加载数据
dataloader = Data.DataLoader(MyDataSet(input_seqs_padded,target_input_padded, target_label_padded), # 自定义数据集对象作为数据源batch_size=batch_size, # 每个批次的样本数量shuffle=True # 是否打乱数据集顺序,True 表示打乱
)# 假设 input_size 和 output_size 是词汇表的大小
input_size = len(eng_word2idx)
output_size = len(fra_word2idx)
hidden_size = 256
num_layers = 1
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')if __name__ == '__main__':# 拿一个批次的数据看看for batch in dataloader:print(batch)print(batch[0].shape)break
2.2encoder
定义encoder类,实现encoder功能,压缩向量,返回隐藏状态。
代码参考:
import torch
from torch import nn
"""
英文--> 中文
encoder 英文
"""
class Encoder(nn.Module):def __init__(self, vocab_size, hidden_size):""":param vocab_size: 英文词表大小:param hidden_size: 词嵌入隐藏大小和LSTM隐藏层大小一致"""super(Encoder, self).__init__()# 词嵌入层self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, hidden_size)# 调用模型LSTMself.lstm = nn.LSTM(hidden_size, hidden_size)def forward(self, x):""":param x: [5,2]:return: [b,seq,hidden_size]"""# 词嵌入层x = self.embedding(x)# 调用模型LSTM 需要的数据格式(seq_len,batch_size,input_size)output, (h_t, c_t) = self.lstm(x)return output, (h_t, c_t)if __name__ == '__main__':encoder = Encoder(vocab_size=10, hidden_size=256)x = torch.randint(0, 9, (2, 5))print(x)output, (h_t, c_t) = encoder(x)print(output.shape)print(h_t.shape)print(c_t.shape)2.3decoder
定义decoder类,实现decoder功能,生成目标序列,返回输出结果。
代码参考:
from torch import nnclass Decoder(nn.Module):def __init__(self, vocab_size, hidden_size):""":param vocab_size: 解码器的词表大小 输入输出统一:param hidden_size: 隐藏层大小"""super(Decoder, self).__init__()# 词嵌入self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, hidden_size)# 调用模型self.lstm = nn.LSTM(hidden_size, hidden_size)# 输出头 【b,s,h]--->[b,s,输出的词表大小】self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_size, vocab_size)def forward(self, x, hidden):""":param x: 输入数据格式(1,batch_size):param hidden: 拿到编码器ct ht:return:"""# 词嵌入 [b,s]--->[b,s,h]x = self.embedding(x)output, _ = self.lstm(x, hidden)# 输出头 [s,b,h]--->[b,s,h]output = self.fc(output.squeeze(0))return output2.4seq2seq
基于构建好的encoder和decoder,搭建seq2seq模型。
代码参考:
import random
import torch
from torch import nnclass Seq2seq(nn.Module):def __init__(self, encoder, decoder,device):super(Seq2seq, self).__init__()self.encoder = encoderself.decoder = decoderself.device = devicedef forward(self, enc_inputs, dec_inputs, dec_outputs, output_size, teacher_forcing_ratio=0.6):""":param enc_inputs: 编码器输入数据 【序列,批次】:param dec_inputs: 解码器输入数据 【序列,批次】:return:"""batch_size = enc_inputs.shape[1]target_len = dec_outputs.shape[0]# 初始化解码器的输出结果 形状 【序列,批次,词表大小】outputs = torch.zeros(target_len, batch_size, output_size).to(self.device)# 获取编码器的输出结果output, hidden_state = self.encoder(enc_inputs)# 获取解码器的第一个输入结果 SOS标识符dec_input = dec_inputs[0, :]# 解码每个时间步for t in range(0, target_len):dec_output = self.decoder(dec_input.unsqueeze(0), hidden_state)outputs[t] = dec_output# 训练 强制教学 模型推理结果和真实值混用flag = random.random() < teacher_forcing_ratiotop = dec_output.argmax(dim=1)dec_input = dec_outputs[t] if flag else topreturn outputsif __name__ == '__main__':from encoder import *from decoder import *from deal_data import *encoder = Encoder(input_size, hidden_size).to(device)decoder = Decoder(output_size, hidden_size).to(device)seq2seq = Seq2seq(encoder, decoder,device).to(device)for enc_input, dec_input, dec_output in dataloader:enc_input = enc_input.transpose(0, 1).to(device)dec_input = dec_input.transpose(0, 1).to(device)dec_output = dec_output.transpose(0, 1).to(device)outputs = seq2seq(enc_input, dec_input, dec_output, output_size)print(outputs.shape)break
三、训练和测试
将创建好的模型进行训练,利用训练好的模型进行测试。注意,测试的语句也需要进行处理之后才能放进模型进行推理预测。
代码参考:
import torchfrom encoder import *
from decoder import *
from deal_data import *
from seq2seq import Seq2seqencoder = Encoder(input_size, hidden_size).to(device)
decoder = Decoder(output_size, hidden_size).to(device)
seq2seq = Seq2seq(encoder, decoder, device).to(device)# 优化器和损失函数
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(seq2seq.parameters(), lr=0.001)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(ignore_index=0)for epoch in range(10):for enc_input, dec_input, dec_output in dataloader:enc_input = enc_input.transpose(0, 1).to(device)dec_input = dec_input.transpose(0, 1).to(device)dec_output = dec_output.transpose(0, 1).to(device)# 梯度清零optimizer.zero_grad()outputs = seq2seq(enc_input, dec_input, dec_output, output_size)# 模型预测出来的形状 [batch_size, seq_len, output_size]---> [batch_size * seq_len, output_size]# 真实标签的形状 [batch_size, seq_len]---> [batch_size * seq_len] view 要求连续数据loss = criterion(outputs.reshape(-1, output_size), dec_output.reshape(-1))loss.backward()optimizer.step()print('Epoch:', epoch, 'Loss:', loss.item())# 翻译函数
def translate(sentence, seq2seq):# 数据处理sentence = sentence_to_indices(sentence, eng_word2idx)# 升维度 以及 转换为张量sentence = torch.LongTensor(sentence).unsqueeze(1).to(device)# 编码器output, hidden = seq2seq.encoder(sentence)# 解码器result =[]max_len = 200 # 限定输出长度# 初始化第一个输入单词input = torch.LongTensor([[fra_word2idx['<SOS>']]]).to(device)# 解码每个输出结果for i in range(max_len):output = seq2seq.decoder(input, hidden)# 获取预测结果index = output.argmax(dim=-1)# 翻译为中文word = fra_idx2word[index.item()]if word == '<EOS>':breakelse:result.append(word)input = index.unsqueeze(0)return ' '.join(result)if __name__ == '__main__':# 测试while True:sentence = input('请输入要翻译的句子:')if sentence == 'q':breakelse:seq2seq.eval()print(translate(sentence, seq2seq))
四、小结
seq2seq由encoder和decoder搭建而成,主要用于文本处理,自然语言翻译。
encoder负责将序列变成固定长度的向量;
decoder负责将encoder传过来的隐藏状态信息转为目标序列。
