机器学习 决策树案例电信用户流失
目录
一.分类树案例
1.利用pandas库读取数据并划分特征集X与结果集y
2.由于类别1的数据较少我们采用过采样的方法使数据平衡
3.划分训练集(80%)和测试集(30%)
4.遍历参数组合,结合交叉验证根据recall值大小选择最优参数
5.用交叉验证得到的最优参数创建模型
6.模型训练评估
7.通过调整阈值来进一步提高召回率
8.完整呈现代码
二.回归树案例
1.只有一列特征数据
2.多列特征数据
一.分类树案例
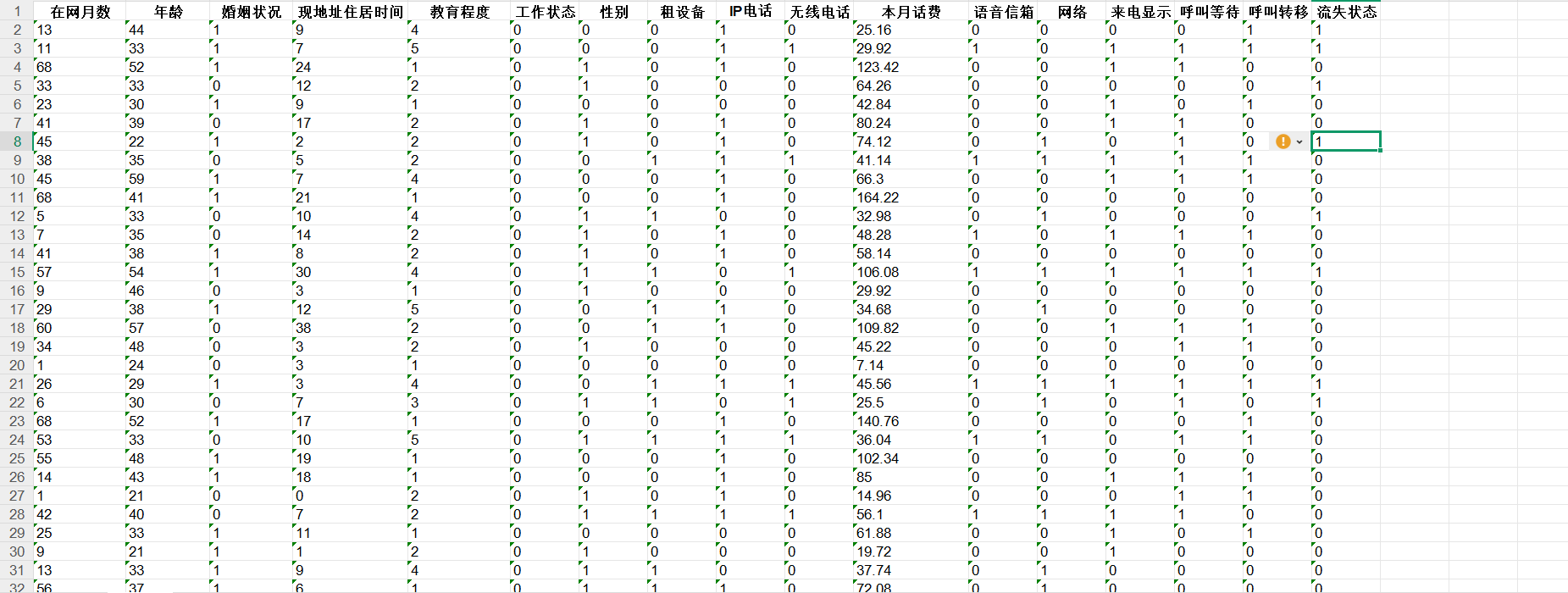
数据集包含600行17列,目标为预测客户是否会流失(分类问题)。其中0:446条,1:154条
电信客户流失数据.xlsx部分内容如下:
1.利用pandas库读取数据并划分特征集X与结果集y
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, cross_val_score
data = pd.read_excel('电信客户流失数据.xlsx')
X=data.iloc[:,:-1]
y=data.iloc[:,-1]2.由于类别1的数据较少我们采用过采样的方法使数据平衡
from imblearn.over_sampling import SMOTE
oversample=SMOTE(random_state=0)#保证数据拟合效果,随机种子
os_x_train,os_y_train=oversample.fit_resample(X,y)3.划分训练集(80%)和测试集(30%)
train_x,test_x,train_y,test_y=train_test_split(os_x_train,os_y_train,test_size=0.3,random_state=100)
4.遍历参数组合,结合交叉验证根据recall值大小选择最优参数
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
max_depths=[4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
min_samples_splits=[2,3,4,5,6,7]
min_samples_leafs=range(2,7)
max_leaf_nodes=range(2,7)
score_last=0
scores=[]
global best_depth
global best_split
global best_leaf
global best_node
for i in max_depths:for j in min_samples_splits:for k in min_samples_leafs:for m in max_leaf_nodes:dtr = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='gini',max_depth=i,min_samples_split=j,min_samples_leaf=k,max_leaf_nodes=m,random_state=100)score=cross_val_score(dtr,train_x,train_y,cv=7,scoring='recall')score_avg=sum(score)/len(score)if score_avg > score_last:best_depth = ibest_split = jbest_leaf = kbest_node=mscore_last = score_avgscores.append(score_avg)print('max_depths=',i,' min_samples_splits=',j,' min_samples_leafs=',k,'max_leaf_nodes=',m,'recall= ',score_avg)
print('交叉验证完成.....................')
print('best_depth=',best_depth,'best_split=',best_split,'best_leaf=',best_leaf,'max_leaf_nodes=',best_node,'max_recall= ',max(scores))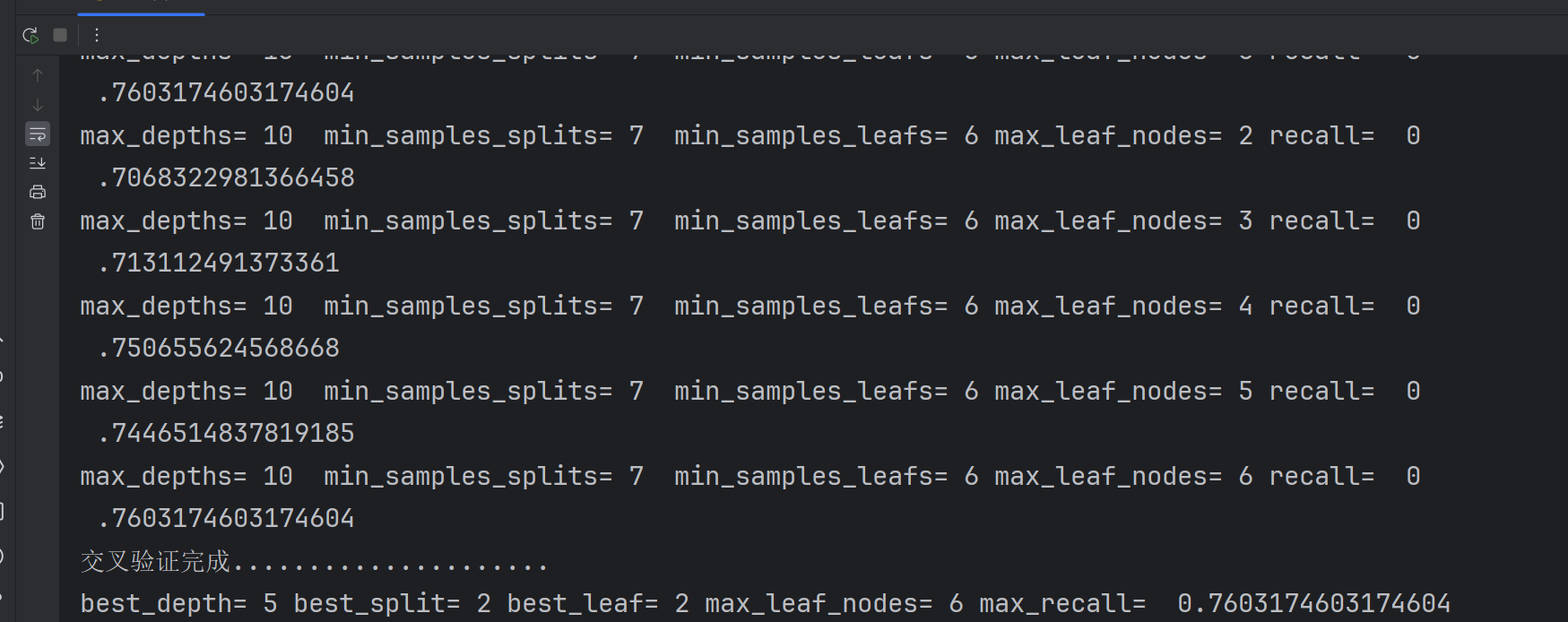
5.用交叉验证得到的最优参数创建模型
dtr=DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=best_depth,min_samples_split=best_split,min_samples_leaf=best_leaf,max_leaf_nodes=best_node,random_state=100)6.模型训练评估
打印出自测报告与测试报告
dtr.fit(train_x,train_y)
self_predited = dtr.predict(train_x)
from sklearn import metrics
print('==========自测报告============')
print(metrics.classification_report(train_y,self_predited))
print('==========测试报告============')
test_predicted =dtr.predict(test_x)
print(metrics.classification_report(test_y,test_predicted))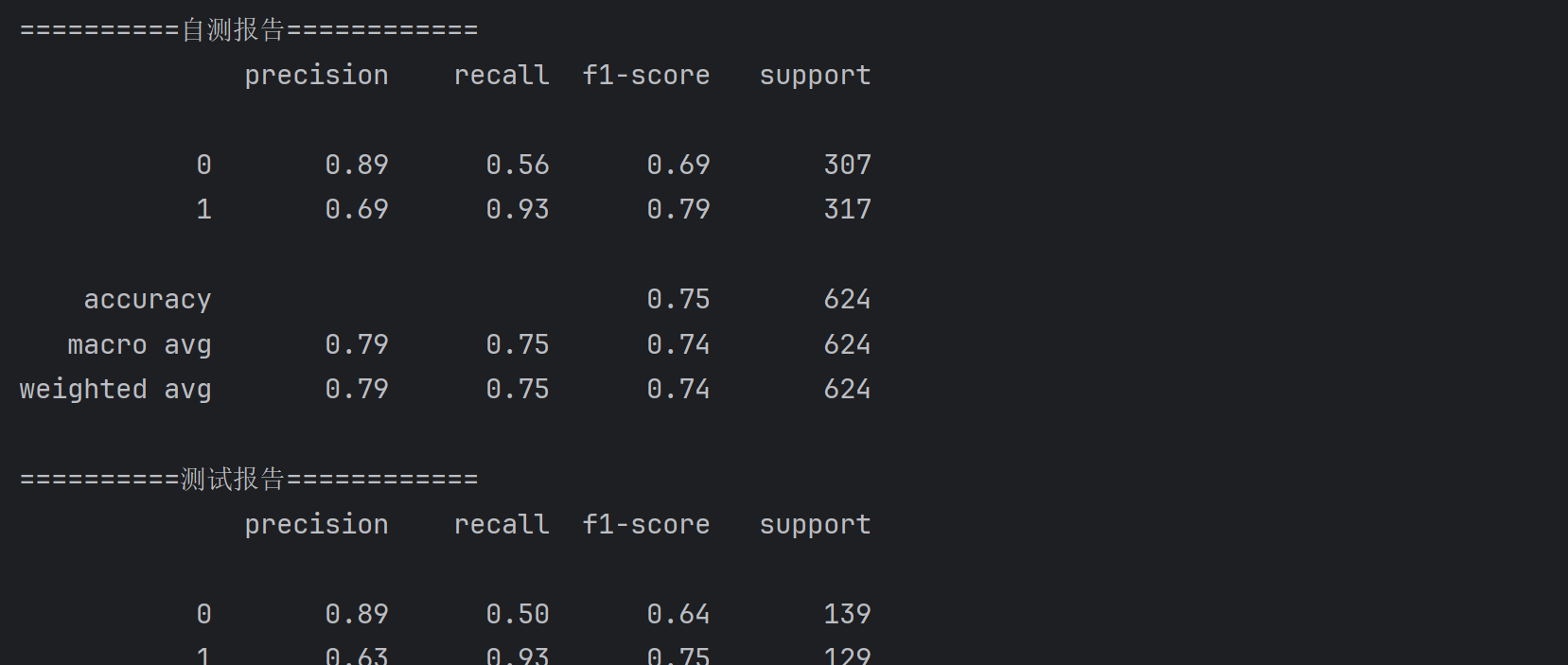
7.通过调整阈值来进一步提高召回率
thresholds=[0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4,0.5,0.6,0.7,0.8,0.9]
recalls=[]
for i in thresholds:predicted_proba=dtr.predict_proba(test_x)predicted_proba=pd.DataFrame(predicted_proba)predicted_proba= predicted_proba.drop([0],axis=1)predicted_proba[predicted_proba[1]>i]=1predicted_proba[predicted_proba[1]<=i]=0recall=metrics.recall_score(test_y,predicted_proba)recalls.append(recall)
best_th=thresholds[np.argmax(recalls)]
print('最佳阈值为{},recall={}'.format(best_th,max(recalls)))8.完整呈现代码
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, cross_val_score
data = pd.read_excel('电信客户流失数据.xlsx')
X=data.iloc[:,:-1]
y=data.iloc[:,-1]from imblearn.over_sampling import SMOTE
oversample=SMOTE(random_state=0)#保证数据拟合效果,随机种子
os_x_train,os_y_train=oversample.fit_resample(X,y)train_x,test_x,train_y,test_y=train_test_split(os_x_train,os_y_train,test_size=0.3,random_state=100)from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
max_depths=[4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
min_samples_splits=[2,3,4,5,6,7]
min_samples_leafs=range(2,7)
max_leaf_nodes=range(2,7)
score_last=0
scores=[]
global best_depth
global best_split
global best_leaf
global best_node
for i in max_depths:for j in min_samples_splits:for k in min_samples_leafs:for m in max_leaf_nodes:dtr = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='gini',max_depth=i,min_samples_split=j,min_samples_leaf=k,max_leaf_nodes=m,random_state=100)score=cross_val_score(dtr,train_x,train_y,cv=7,scoring='recall')score_avg=sum(score)/len(score)if score_avg > score_last:best_depth = ibest_split = jbest_leaf = kbest_node=mscore_last = score_avgscores.append(score_avg)print('max_depths=',i,' min_samples_splits=',j,' min_samples_leafs=',k,'max_leaf_nodes=',m,'recall= ',score_avg)
print('交叉验证完成.....................')
print('best_depth=',best_depth,'best_split=',best_split,'best_leaf=',best_leaf,'max_leaf_nodes=',best_node,'max_recall= ',max(scores))
dtr=DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=best_depth,min_samples_split=best_split,min_samples_leaf=best_leaf,max_leaf_nodes=best_node,random_state=100)
dtr.fit(train_x,train_y)
self_predited = dtr.predict(train_x)
from sklearn import metrics
print('==========自测报告============')
print(metrics.classification_report(train_y,self_predited))
print('==========测试报告============')
test_predicted =dtr.predict(test_x)
print(metrics.classification_report(test_y,test_predicted))thresholds=[0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4,0.5,0.6,0.7,0.8,0.9]
recalls=[]
for i in thresholds:predicted_proba=dtr.predict_proba(test_x)predicted_proba=pd.DataFrame(predicted_proba)predicted_proba= predicted_proba.drop([0],axis=1)predicted_proba[predicted_proba[1]>i]=1predicted_proba[predicted_proba[1]<=i]=0recall=metrics.recall_score(test_y,predicted_proba)recalls.append(recall)
best_th=thresholds[np.argmax(recalls)]
print('最佳阈值为{},recall={}'.format(best_th,max(recalls)))
#绘制决策树
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.tree import plot_tree
fig,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(32,32))
plot_tree(dtr,filled=True,ax=ax)
plt.show()二.回归树案例
1.只有一列特征数据
数据data.csv内容如下:
完整代码如下:
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressordata = pd.read_csv('data.csv')
X=data[['广告投入']]
y=data[['销售额']]dtr = DecisionTreeRegressor()
dtr.fit(X,y)
predicted=dtr.predict(X)
print(dtr.score(X,y))
2.多列特征数据
只需划分好特征数据与结果数据即可,照常训练
完整代码如下:
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressordata = pd.read_csv('data.csv')data = pd.read_csv('多元线性回归.csv',encoding='gbk')
X=data.iloc[:,:-1]
y=data.iloc[:,-1]
dtr = DecisionTreeRegressor()
dtr.fit(X,y)
predicted=dtr.predict(X)
print(dtr.score(X,y))