SpringAop源码详解
Spring AOP 源码详解
在实际开发过程中,会有需要用到自动事务管理,自动日志打印等需求,那么通过一个注解或者配置,实现自动对类进行功能增强就非常有必要。Spring Aop就提供了这样的功能,实现对目标类的成员方法进行增强
SpringAop和AspectJ二者的关系
1、AspectJ是一个面向切面的Java框架,他定义了一套切面语言,如@Aspect、@Before、@AfterReturning、@AfterThrowing、@After、@Around等,还提供了强大的切面表达式,如(如@PointCut execution(* com.example.service..(…))),提供了强大的切面解析框架。
2、SpringAop提供了创建代理的能力,Spring定义了两个重要的核心接口,Advisor(PointCut+Advice通知)的组合,定义了在哪个类哪个方法增强哪个方法及增强逻辑,Advice是一个包含通知逻辑的拦截器,等同于AspectJ里的@Before等注解的实际类型。
同时Spring通过ProxyFactory代理工厂来创建目标类型的代理,可以选择(CglibAopProxy\JdkAopProxy)两种代理,我们一般在启动类配置@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass =true) // 强制使用CGLIB代理 不需要接口 生成被代理类的子类
代理工厂类:DefaultAopProxyFactory.java
/*** 决定是JDK动态代理 还是CGLIB* config.isProxyTargetClass() ->* 最关键的开关(由 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true)控制) 是否开启CGLIB 默认值false* @param config the AOP configuration in the form of an* AdvisedSupport object* @return* @throws AopConfigException*/@Overridepublic AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();if (targetClass == null) {throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");}if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);}return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);}else {return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);}}这样两个组件的分工协作实现了完整的AOP功能
SpringAop增强的过程
1、创建代理的入口
有循环依赖的类和正常的类,AOP代理生成位置不一样。
有循环依赖,代理生成位置在获取早期bean引用的方法里:
protected Object getEarlyBeanReference(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object bean) {Object exposedObject = bean;if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {if (bp instanceof SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;exposedObject = ibp.getEarlyBeanReference(exposedObject, beanName);}}}return exposedObject;
}
这里会有一个BeanPostPorcessor,AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator,类里面的getEarlyBeanReference方法用来获取早期引用,如果有代理就要增强后返回。
// 进行代理增强@Overridepublic Object getEarlyBeanReference(Object bean, String beanName) {Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);this.earlyProxyReferences.put(cacheKey, bean);// 代理生成的核心方法return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);}
没有循环依赖
代理生成的位置在调用完初始化方法,后置处理器里
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)throws BeansException {Object result = existingBean;for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);if (current == null) {return result;}result = current;}return result;
}
这里有一个BeanPostProcessor,AbstractAutoProxyCreator,这个类和上面的类是父子关系,调用的方法也一样,可以看到,最终都是调用wrapIfNecessary方法来创建代理
/*** Create a proxy with the configured interceptors if the bean is* identified as one to proxy by the subclass.* @see #getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean*/@Overridepublic Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {if (bean != null) {Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) {return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);}}return bean;}
2、获取切面类,判断当前目标类需不需要代理,(切面类不需要代理,没有切入规则的类不需要代理),上面两个生成代理方法的里面都有个关键逻辑
if (isInfrastructureClass(beanClass) || shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)) {this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);return null;}
isInfrastructureClass(beanClass)用来判断当前类是不是切面的子类
shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)
就是关键的解析切面类,判断切入规则
AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.class@Overrideprotected boolean shouldSkip(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {// TODO: Consider optimization by caching the list of the aspect namesList<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();for (Advisor advisor : candidateAdvisors) {if (advisor instanceof AspectJPointcutAdvisor &&((AspectJPointcutAdvisor) advisor).getAspectName().equals(beanName)) {return true;}}return super.shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName);}
findCandidateAdvisors() 就是查找所有的切面类
AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.classprotected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() {// Add all the Spring advisors found according to superclass rules.List<Advisor> advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors();// Build Advisors for all AspectJ aspects in the bean factory.if (this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder != null) {advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors());}return advisors;}
buildAspectJAdvisors() 方法进行真正的切面解析
/*** 寻找当前bean工厂注解了AspectJ注解的类,并返回aop切面列表代表他们*/public List<Advisor> buildAspectJAdvisors() {List<String> aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;if (aspectNames == null) {synchronized (this) {aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;if (aspectNames == null) {List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();aspectNames = new ArrayList<>();String[] beanNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(this.beanFactory, Object.class, true, false);for (String beanName : beanNames) {if (!isEligibleBean(beanName)) {continue;} // 逐个扫描beanFactory中的bean,如果有aspect注解就扫描切面Class<?> beanType = this.beanFactory.getType(beanName, false);if (beanType == null) {continue;}// isAspect 方法判断是不是有Aspect注解if (this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType)) {aspectNames.add(beanName);AspectMetadata amd = new AspectMetadata(beanType, beanName);if (amd.getAjType().getPerClause().getKind() == PerClauseKind.SINGLETON) {MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =new BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);List<Advisor> classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory);if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {this.advisorsCache.put(beanName, classAdvisors);}else {this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);}advisors.addAll(classAdvisors);}else {// Per target or per this.if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Bean with name '" + beanName +"' is a singleton, but aspect instantiation model is not singleton");}MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =new PrototypeAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));}}}this.aspectBeanNames = aspectNames;return advisors;}}}if (aspectNames.isEmpty()) {return Collections.emptyList();}List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();for (String aspectName : aspectNames) {List<Advisor> cachedAdvisors = this.advisorsCache.get(aspectName);if (cachedAdvisors != null) {advisors.addAll(cachedAdvisors);}else {MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = this.aspectFactoryCache.get(aspectName);advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));}}return advisors;}
getAdvisors方法用于获取当前注解有@Aspect的切面类的详细细腻
@Overridepublic List<Advisor> getAdvisors(MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory) {Class<?> aspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();String aspectName = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectName();validate(aspectClass);// We need to wrap the MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory with a decorator// so that it will only instantiate once.MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory =new LazySingletonAspectInstanceFactoryDecorator(aspectInstanceFactory);List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();for (Method method : getAdvisorMethods(aspectClass)) {AspectJPrecedenceComparator.getAspectDeclarationOrder(Advisor).Advisor advisor = getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, 0, aspectName);if (advisor != null) {advisors.add(advisor);}}// If it's a per target aspect, emit the dummy instantiating aspect.if (!advisors.isEmpty() && lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated()) {Advisor instantiationAdvisor = new SyntheticInstantiationAdvisor(lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory);advisors.add(0, instantiationAdvisor);}// Find introduction fields.for (Field field : aspectClass.getDeclaredFields()) {Advisor advisor = getDeclareParentsAdvisor(field);if (advisor != null) {advisors.add(advisor);}}return advisors;}
上面的接口返回 List,即所有声明的通知方法列表,封装成Advisor。
下面是上面方法内部方法解析,反射拿到所有声明的方法,提取出来带有切面通知注解的方法,如@Before,返回列表
private List<Method> getAdvisorMethods(Class<?> aspectClass) {final List<Method> methods = new ArrayList<>();ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(aspectClass, method -> {// Exclude pointcuts 排除pointCutif (AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(method, Pointcut.class) == null) {methods.add(method);}}, ReflectionUtils.USER_DECLARED_METHODS);if (methods.size() > 1) {methods.sort(METHOD_COMPARATOR);}return methods;}
把拿到的切面通知方法method封装成Advisor类,后面
public Advisor getAdvisor(Method candidateAdviceMethod, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory,int declarationOrderInAspect, String aspectName) {validate(aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut = getPointcut(candidateAdviceMethod, aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());if (expressionPointcut == null) {return null;}return new InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(expressionPointcut, candidateAdviceMethod,this, aspectInstanceFactory, declarationOrderInAspect, aspectName);}
Advisor 类里封装了两个组件,一个PointCut->AspectJExpressionPointcut ,代表切入点的表达式,另一个是切入点的通知逻辑,包含通知方法.Method 类型的candidateAdviceMethod方法,最终封装成一个完整的通知实例对象,就是这个类
InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl
可以看到这个类的接口,通知接口,后续会用到,主要还是记住这个接口InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisor这个接口的最终父接口就是Advisor,顶层的通知接口
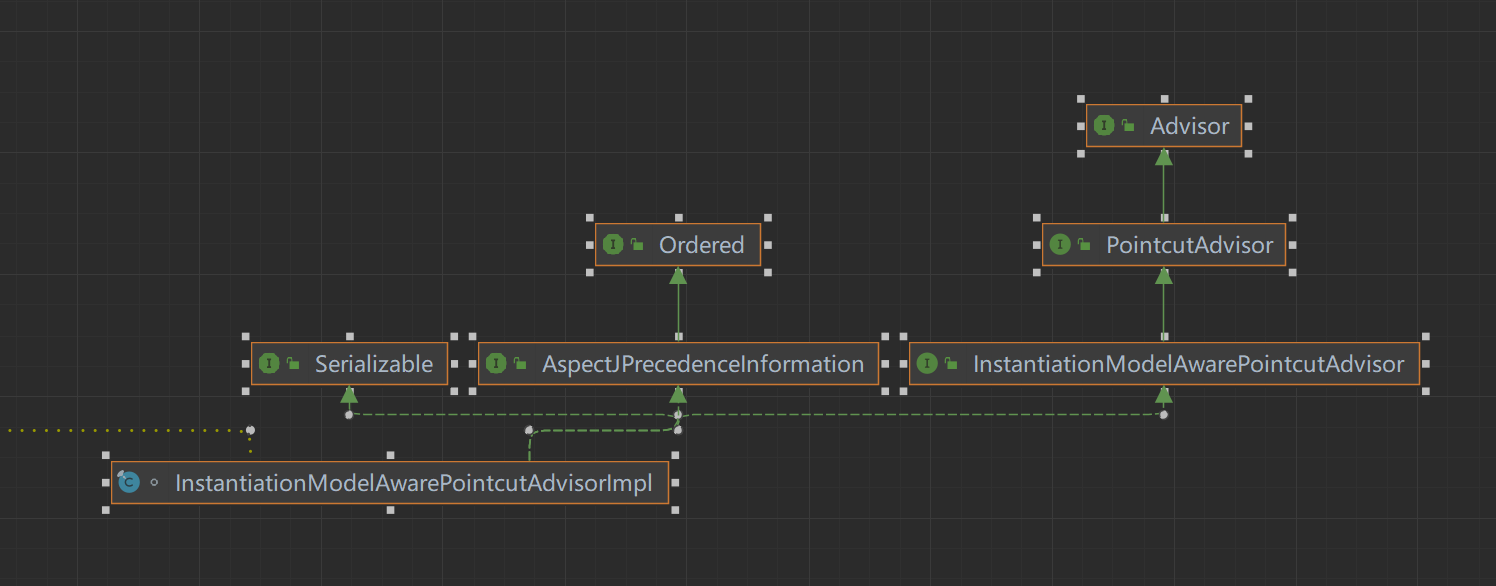
这里会缓存当前类的解析结果,后续再进来就不用再重新走获取逻辑了this指针是指向AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator,这个类就是处理AOP的,在容器内单例存在,长久保存
this.advisorsCache.put(beanName, classAdvisors)
上面拿到的List<Advisor 所有通知,.
检查 Advisor类型:if (advisor instanceof AspectJPointcutAdvisor)
筛选出通过 AspectJ 注解风格(如 @Before, @After等)定义的 Advisor(实际类型是 InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl)
匹配切面名称:((AspectJPointcutAdvisor) advisor).getAspectName().equals(beanName)
取出当前 Advisor所属的切面名称 (即 @Aspect注解类在 Spring 容器中的 bean name),检查它是否与当前正在处理的 bean 的名称 (beanName) 相同。
for (Advisor advisor : candidateAdvisors) {if (advisor instanceof AspectJPointcutAdvisor &&((AspectJPointcutAdvisor) advisor).getAspectName().equals(beanName)) {return true;}}
如果找到匹配(即当前 beanName是一个切面 bean 的名称),则 return true;
含义:当前 bean 是一个切面,应跳过代理创建,不对其进行代理。
到这里,protected boolean shouldSkip(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) 方法就基本完成了,主要是判断是不是要代理当前类,还同时做了所有切面类的解析和注册。
接下来判断,已经那到的切面类是不是能对当前目标类进行代理,代理规则判断
public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) {if (candidateAdvisors.isEmpty()) {return candidateAdvisors;}List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new ArrayList<>();for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor && canApply(candidate, clazz)) {eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);}}boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty();for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {// already processedcontinue;}if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) {eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);}}return eligibleAdvisors;}
这里canApply pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)方法判断切面是不是匹配当前类
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null");if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) {return false;}MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher();if (methodMatcher == MethodMatcher.TRUE) {// No need to iterate the methods if we're matching any method anyway...return true;}}
切入点类型会保存匹配的类型和方法
public class AnnotationMatchingPointcut implements Pointcut {private final ClassFilter classFilter;private final MethodMatcher methodMatcher;获取到匹配的切面,那么就要增强,走创建代理逻辑
// Create proxy if we have advice. 为目标bean获取通知和切面Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);Object proxy = createProxy(bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());return proxy;}
这里通过proxyFactory代理工厂拿到代理生成器
protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName,@Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);}// 生成代理的工厂ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);if (proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {// Explicit handling of JDK proxy targets (for introduction advice scenarios)if (Proxy.isProxyClass(beanClass)) {// Must allow for introductions; can't just set interfaces to the proxy's interfaces only.for (Class<?> ifc : beanClass.getInterfaces()) {proxyFactory.addInterface(ifc);}}}else {// No proxyTargetClass flag enforced, let's apply our default checks...if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);}else {evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);}}Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);}return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());}
默认用的是默认代理工厂 DefaultAopProxyFactory.java,可以看到config.isProxyTargetClass()就是从配置获取是否用CGLIB代理,@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass =true)
还结合是否有接口,判断走jdk代理还是cglib
@Overridepublic AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();if (targetClass == null) {throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");}if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);}return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);}else {return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);}}
我们这里走的是CGLIB代理,所有用的是CglibAopProxy.java来创建代理类
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Creating CGLIB proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());}try {Class<?> rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();Assert.state(rootClass != null, "Target class must be available for creating a CGLIB proxy");Class<?> proxySuperClass = rootClass;if (rootClass.getName().contains(ClassUtils.CGLIB_CLASS_SEPARATOR)) {proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass();Class<?>[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces();for (Class<?> additionalInterface : additionalInterfaces) {this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface);}}// Validate the class, writing log messages as necessary.validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader);// Configure CGLIB Enhancer...Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer();if (classLoader != null) {enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader);if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader &&((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) {enhancer.setUseCache(false);}}enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareGeneratorStrategy(classLoader));Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass);Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length];for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) {types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass();}// fixedInterceptorMap only populated at this point, after getCallbacks call aboveenhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter(this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset));enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);// Generate the proxy class and create a proxy instance.return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks);}catch (CodeGenerationException | IllegalArgumentException ex) {throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of " + this.advised.getTargetClass() +": Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",ex);}catch (Throwable ex) {// TargetSource.getTarget() failedthrow new AopConfigException("Unexpected AOP exception", ex);}}
可以看到这里使用Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer();创建代理,他主要有两个属性要设置,superClass,被代理类,callbacks,这个是一系列MethodInterceptor的实现类,通过内部intercept方法实现代理
看一下他是怎么创建回调拦截器数组的,这里是生成了一串拦截器,按顺序执行
private Callback[] getCallbacks(Class<?> rootClass) throws Exception {// Parameters used for optimization choices...boolean exposeProxy = this.advised.isExposeProxy();boolean isFrozen = this.advised.isFrozen();boolean isStatic = this.advised.getTargetSource().isStatic();// Choose an "aop" interceptor (used for AOP calls).Callback aopInterceptor = new DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(this.advised);// Choose a "straight to target" interceptor. (used for calls that are// unadvised but can return this). May be required to expose the proxy.Callback targetInterceptor;if (exposeProxy) {targetInterceptor = (isStatic ?new StaticUnadvisedExposedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) :new DynamicUnadvisedExposedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource()));}else {targetInterceptor = (isStatic ?new StaticUnadvisedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) :new DynamicUnadvisedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource()));}// Choose a "direct to target" dispatcher (used for// unadvised calls to static targets that cannot return this).Callback targetDispatcher = (isStatic ?new StaticDispatcher(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) : new SerializableNoOp());Callback[] mainCallbacks = new Callback[] {aopInterceptor, // for normal advicetargetInterceptor, // invoke target without considering advice, if optimizednew SerializableNoOp(), // no override for methods mapped to thistargetDispatcher, this.advisedDispatcher,new EqualsInterceptor(this.advised),new HashCodeInterceptor(this.advised)};Callback[] callbacks;// If the target is a static one and the advice chain is frozen,// then we can make some optimizations by sending the AOP calls// direct to the target using the fixed chain for that method.if (isStatic && isFrozen) {Method[] methods = rootClass.getMethods();Callback[] fixedCallbacks = new Callback[methods.length];this.fixedInterceptorMap = new HashMap<>(methods.length);// TODO: small memory optimization here (can skip creation for methods with no advice)for (int x = 0; x < methods.length; x++) {Method method = methods[x];List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, rootClass);fixedCallbacks[x] = new FixedChainStaticTargetInterceptor(chain, this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget(), this.advised.getTargetClass());this.fixedInterceptorMap.put(method, x);}// Now copy both the callbacks from mainCallbacks// and fixedCallbacks into the callbacks array.callbacks = new Callback[mainCallbacks.length + fixedCallbacks.length];System.arraycopy(mainCallbacks, 0, callbacks, 0, mainCallbacks.length);System.arraycopy(fixedCallbacks, 0, callbacks, mainCallbacks.length, fixedCallbacks.length);this.fixedInterceptorOffset = mainCallbacks.length;}else {callbacks = mainCallbacks;}return callbacks;}第一个就放了默认的拦截器,要记住这个很重要
Callback aopInterceptor = new DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(this.advised);
后续调用目标方法主要是通过这个拦截器进入增强方法,
DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(this.advised)
这里的this.advised 也就是proxyFactory.advised ,是我们上面解析过的,附一张代理工厂类图
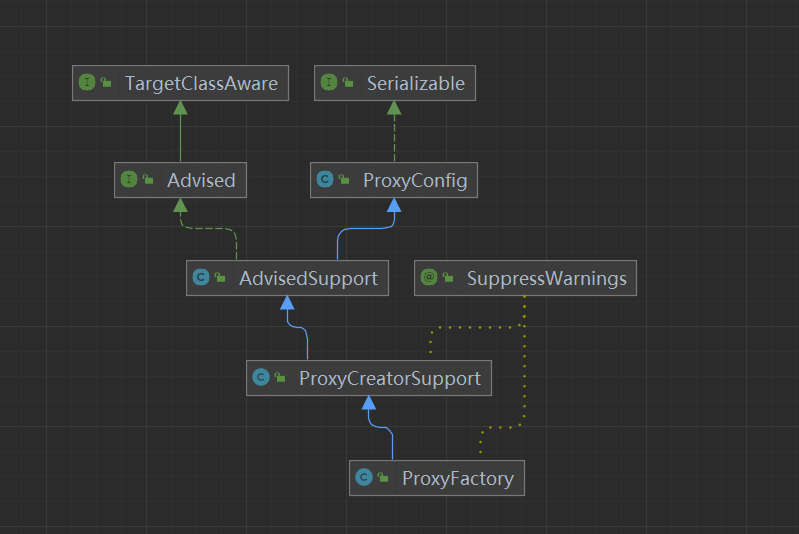
// 生成代理的工厂ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
// 这里其实是把目标类匹配的通知拦截器列表给到代理工厂,方便后面使用
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
//代理工厂是ProxyCreatorSupport 的子类
public class ProxyFactory extends ProxyCreatorSupport ;
//创建代理生成器,传入代理工厂本身,这里用的父类接收,实际上我们看到,创建代理生成器,会把这个代理工厂配置都作为构造参数 new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();if (targetClass == null) {throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");}if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);}return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);}else {return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);}}上面设置完成,这是设置最终代理创建的方法,
protected Object createProxyClassAndInstance(Enhancer enhancer, Callback[] callbacks) {enhancer.setInterceptDuringConstruction(false);enhancer.setCallbacks(callbacks);return (this.constructorArgs != null && this.constructorArgTypes != null ?enhancer.create(this.constructorArgTypes, this.constructorArgs) :enhancer.create());}最终返回给容器一个Proxy代理类实例
结束
到这里一个完整的代理创建就完成了,很复杂,但是梳理清楚后也没那么难,最关键的还是创建代理,也是核心
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();enhancer.setSuperclass(EatService.class);enhancer.setCallback(new MyMethodInvocate());// 设置回调方法 代理方法 MethodIntercept拦截器EatService eat = (EatService) enhancer.create(); // 创建代理类
