Linux软件编程3.(文件IO和目录IO)
1.文件IO的概念
标准IO有缓存,文件IO无缓存,多用于硬件操作和通信。
标准IO是库函数,文件IO是系统效用。
2.系统调用与库函数
系统调用:是Linux内核中的代码,只能在Linux系统中使用
库函数:是对系统调用的封装,可以在不同的操作系统中安装并使用,库函数最终还是要调用系统调用完成对应功能
3.文件IO函数接口
3.1open打开文件
原型:int open(const char *pathname, int flags);int open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode);
功能:打开文件获得操作文件的文件描述符
参数:pathname:要打开的文件路径flags:打开文件的标志,必须包含三者之一O_RDONLYO_WRONLYO_RDWR O_CREAT 文件不存在创建(注意要给定创建文件的权限)O_TRUNC 文件存在截断为0(清0)O_APPEND 追加O_EXCL 文件存在报错
返回值:成功返回新文件描述符失败返回-1三个特殊的文件描述符:标准输入(0)、标准输出(1)、标准错误(2)。
3.2close关闭文件
注意:
有三个特殊的文件描述符:标准输入(0)、标准输出(1)、标准错误(2)
文件描述符特点:
非负整数打开并关闭文件:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>int main(void)
{int fd = 0;//0664//110110100//rw-rw-r--fd = open("a.txt", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0664);if (-1 == fd){perror("fail to open");return -1;}printf("fd = %d\n", fd);close(fd);return 0;
}3.3标准IO对应的文件IO的打开方式
| 标准IO | 文件IO |
| r | O_RDONLY |
| r+ | O_RDWR |
| w | O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC , 0664 |
| w+ | O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0664 |
| a | O_WRONLY | O_APPEND | O_CREAT, 0664 |
| a+ | O_RDWR | O_APPEND | O_CREAT, 0664 |
3.4write写入
原型:ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count);
功能:向文件描述符中写入buf指向的count个字节的数据
参数:fd:文件描述符buf:要写入的数据空间首地址count:要写入的字节数
返回值:成功返回实际写入的字节数失败返回-1
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>int main(void)
{int fd = 0;char tmpbuff[4096] = {"hello world"};ssize_t nret = 0;fd = open("a.txt", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0664);if (-1 == fd){perror("fail to open");return -1;}nret = write(fd, tmpbuff, strlen(tmpbuff));printf("实际写入:%ld\n", nret);close(fd);return 0;
}3.5read读取
原型:ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count);
功能:从文件描述符中读取count个字节放入buf指向的空间中
参数:fd:文件描述符buf:存放数据空间的首地址count:想要读取的字节数
返回值:成功返回实际读到的字节数读到文件末尾返回0 读取出错返回-1读取/usr/include/stdio.h路径下4096个字节:
#include "head.h"int main(void)
{ int fd = 0;char tmpbuff[4096] = {0};ssize_t nret = 0;fd = open("/usr/include/stdio.h", O_RDONLY);if (-1 == fd){perror("fail to open");return -1;}nret = read(fd, tmpbuff, sizeof(tmpbuff));printf("实际接收 %ld 字节, 内容:%s\n", nret, tmpbuff);close(fd);return 0;
}用read和write进行文件的拷贝:
#include "head.h"int main(void)
{FILE *fp1 = NULL;FILE *fp2 = NULL;char src[256] = {0};char dst[256] = {0};char tmpbuff[4060] ={0};printf("请输入要拷贝的文件名:");m_fgets(src);printf("请输入目的文件名:");m_fgets(dst);char a[4096]={0};ssize_t nret;fp1 = open(src, O_RDONLY);if (NULL == fp1){perror("fail to open1");return -1;}fp2 = open (dst,O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC ,0664);if (NULL == fp2){perror("fail to open2");return -1;}while (nret = read(fp1,tmpbuff,sizeof(tmpbuff))) {write(fp2,tmpbuff,nret); }close(fp1);close(fp2);return 0;
}3.6lseek文件描述符偏移量的定位
原型:off_t lseek(int fd, off_t offset, int whence);
功能:重新定位流的偏移量
参数:fd:文件描述符offset:偏移量whence:SEEK_SETSEEK_CURSEEK_END
返回值:成功返回偏移量失败返回-1偏移打印并获取当前偏移量
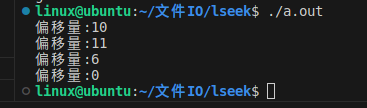
#include "head.h"int main(void)
{int fd = 0;char ch = 0;off_t len = 0;fd = open("a.txt", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT, 0664);if (-1 == fd){perror("fail to open");return -1;}len = lseek(fd, 10, SEEK_SET);printf("偏移量:%ld\n", len);ch = 'a';write(fd, &ch, 1);len = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_CUR);printf("偏移量:%ld\n", len);len = lseek(fd, -5, SEEK_CUR);printf("偏移量:%ld\n", len);ch = 'b';write(fd, &ch, 1);len = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_SET);printf("偏移量:%ld\n", len);ch = 'c';write(fd, &ch, 1); close(fd);return 0;
}
3.7文件IO与标准IO互相转换的函数
| 函数接口 | 功能 |
| fileno | 根据文件流指针获得文件描述符 |
| fdopen | 根据已经打开的文件描述符获得文件流指针 |
| feof | 判断文件流指针是否到达末尾 |
| ferror | 判断文件流指针是否出错 |
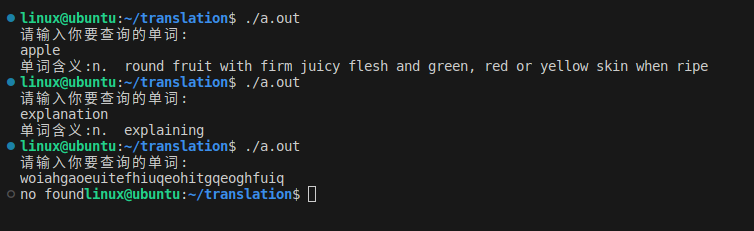
小项目:单词查找
需要从dict.txt文本文件中查找从终端输入的单词,并输出其意思。

#include"head.h"
int main(void)
{char in_put_word[256] = {0};char tmpbuff[1024] = {0}; char word[256] = {0};char explanation[256] = {0};int a = 0;printf("请输入你要查询的单词:\n");gets(in_put_word);in_put_word[strlen(in_put_word)]= '\0';FILE *fp = NULL;fp = fopen("dict.txt", "r");if (NULL == fp){perror("fail to fopen");return -1;}while(1){ if(fgets(tmpbuff, sizeof(tmpbuff), fp) == NULL){printf("no found\n");break;}//将fgets读到的内容分割,前半部分为255个字节的内容,遇到空格截止存在word中//后半部分读取255个字节内容,遇到\n截止,存在explanation中sscanf(tmpbuff, "%255s %255[^\n]", word, explanation);if(strcmp(in_put_word, word) == 0){printf("单词含义:%s\n",explanation);a = 1;break;}}fclose(fp);return 0;
}
4.目录IO
4.1操作方式
1)打开目录文件 2)读取目录文件中的目录项 3)关闭目录文件
4.2函数接口
4.2.1opendir打开目录流获得目录流指针
原型:DIR *opendir(const char *name);功能:打开目录流获得目录流指针参数:name:目录文件的路径返回值:成功返回目录流指针失败返回NULL4.2.2closedir关闭目录流指针
原型:int closedir(DIR *dirp);
功能:关闭目录流指针4.2.3readdir读取并返回下一个目录项的信息
原型:struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dirp);
功能:读取并返回下一个目录项的信息
参数:dirp:目录流指针
返回值:成功返回包含目录项信息结构体指针失败返回NULL读到文件末尾返回NULLstruct dirent {ino_t d_ino; /* Inode number:通过inode找到文件对应的磁盘空
间位置 */off_t d_off; /* Not an offset; see below */unsigned short d_reclen; /* Length of this record */unsigned char d_type; /* Type of file; not supportedby all filesystem types:文件类型 */char d_name[256]; /* Null-terminated filename: 文件名*/};返回输入路径文件的属性:
#include "head.h"int main(void)
{DIR *dp = NULL;struct dirent *pp = NULL;char filepath[256] = {0};printf("请输入路径:\n");m_fgets(filepath);dp = opendir(filepath);if (NULL == dp){perror("fail to opendir");return -1;}while (1){pp = readdir(dp);if (NULL == pp){break;}if ('.' == pp->d_name[0]){continue;}switch (pp->d_type){case DT_BLK:printf("块设备文件");break;case DT_CHR:printf("字符设备文件");break;case DT_DIR:printf("目录文件");break;case DT_FIFO:printf("管道文件");break;case DT_LNK:printf("链接文件");break;case DT_REG:printf("普通文件");break;case DT_SOCK:printf("套接字文件");break;}printf("\t\t%s\t\t%s/%s\n", pp->d_name, filepath, pp->d_name);}closedir(dp);return 0;
}4.2.4getcwd获得当前工作目录的绝对路径
原型:char *getcwd(char *buf, size_t size);
功能:获得当前工作目录的绝对路径
参数:buf:存放路径字符串空间首地址size:最多存放字符串的大小
返回值:成功返回包含字符串空间的首地址失败返回NULL示例:
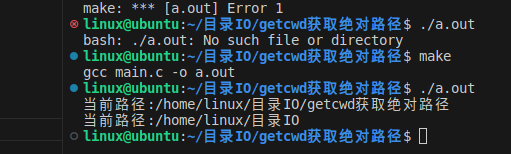
#include "head.h"int main(void)
{char tmpbuff[4096] = {0};FILE *fp = NULL;getcwd(tmpbuff, sizeof(tmpbuff));printf("当前路径:%s\n", tmpbuff);mkdir("tmp", 0777);rmdir("tmp");chdir("..");getcwd(tmpbuff, sizeof(tmpbuff));printf("当前路径:%s\n", tmpbuff);fclose(fopen("file.txt", "w"));return 0;
} 
深度有限遍历所有文件并打印路径:
#include "head.h"void listdir(char *dirpath)
{DIR *dp = NULL;struct dirent *pp = NULL;char tmpbuff[4096] = {0};dp = opendir(dirpath);if (NULL == dp){perror("fail to opendir");printf("failed:%s\n", dirpath);return;}while (1){pp = readdir(dp);if (NULL == pp){break;}if ('.' == pp->d_name[0]){continue;}sprintf(tmpbuff, "%s/%s", dirpath, pp->d_name);printf("%s\n", tmpbuff);if (pp->d_type == DT_DIR){listdir(tmpbuff);}}closedir(dp);return;
}int main(void)
{listdir("/home/linux");return 0;
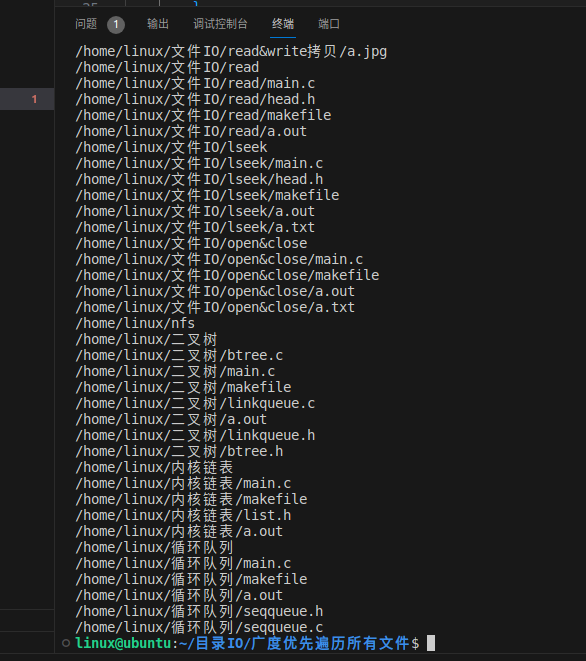
}广度优先遍历所有文件并打印路径:
#include "head.h" // 包含自定义头文件 head.h(可能包含通用定义或函数声明)
#include "linkqueue.h" // 包含链式队列的实现头文件void listdir(char *dirpath) // 定义遍历目录的函数,参数为目录路径
{linknode *plinkqueue = NULL; // 初始化队列指针char tmppath[256] = {0}; // 临时存储出队的目录路径(缓冲区大小256字节)char filepath[1024] = {0}; // 存储完整文件路径(缓冲区大小1024字节)DIR *dp = NULL; // 目录流指针struct dirent *pp = NULL; // 目录条目指针plinkqueue = create_empty_linkqueue(); // 创建空队列enter_linkqueue(plinkqueue, dirpath); // 将初始目录路径入队while (!is_empty_linkqueue(plinkqueue)) // 循环直到队列为空{quit_linkqueue(plinkqueue, tmppath); // 从队头取出一个目录路径到 tmppathdp = opendir(tmppath); // 尝试打开目录if (NULL == dp) // 打开失败处理{perror("fail to opendir"); // 打印错误信息printf("%s\n", tmppath); // 输出失败路径return; // 直接返回(可能需改为 continue 以继续处理其他目录)}while (1) // 循环读取目录条目{pp = readdir(dp); // 读取下一个目录条目if (NULL == pp) // 如果条目为空(遍历完毕){break; // 退出循环}if ('.' == pp->d_name[0]) // 跳过隐藏文件(以 . 开头){continue;}sprintf(filepath, "%s/%s", tmppath, pp->d_name); // 拼接完整路径printf("%s\n", filepath); // 打印路径if (pp->d_type == DT_DIR) // 如果是子目录{enter_linkqueue(plinkqueue, filepath); // 将子目录路径入队}}closedir(dp); // 关闭当前目录流(原代码遗漏,需补充)}destroy_linkqueue(&plinkqueue); // 销毁队列释放内存return; // 函数结束
}int main(void)
{listdir("/home/linux"); // 从 /home/linux 开始遍历目录return 0; // 程序正常退出
}均可实现以下效果:
4.2.5chdir切换当前的工作路径
原型:int chdir(const char *path);
功能:切换当前的工作路径
参数:path:要切换的路径
返回值:成功返回0失败返回-14.2.6mkdir创建目录文件
原型:int mkdir(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);
功能:创建目录文件
r:读权限,决定用户是否能够查看目录下所有文件名
w:写权限,决定用户是否能够在目录下新建文件
x:执行权限,决定用户是否能够进入目录4.2.7rmdir删除目录文件
原型:int rmdir(const char *pathname);
功能:删除目录文件5.时间相关的函数接口
5.1时间类型分类
5.2函数接口
5.2.1time
原型:time_t time(time_t *tloc);
功能:返回1970-1-1日到现在的秒数
参数:存放秒数空间的首地址
返回值:成功返回秒数失败返回-15.2.2localtime
原型:struct tm *localtime(const time_t *timep);
功能:将秒数转换为结构体时间
参数:timep:1970-1-1到现在的秒数
返回值:成功返回包含时间的结构体指针失败返回NULLstruct tm {int tm_sec; /* Seconds (0-60) */int tm_min; /* Minutes (0-59) */int tm_hour; /* Hours (0-23) */int tm_mday; /* Day of the month (1-31) */int tm_mon; /* Month (0-11) */int tm_year; /* Year - 1900 */int tm_wday; /* Day of the week (0-6, Sunday = 0) */int tm_yday; /* Day in the year (0-365, 1 Jan = 0) */int tm_isdst; /* Daylight saving time */};5.2.3mktime
原型:time_t mktime(struct tm *tm);
功能:
将结构体时间转换为time_t类型的时间
参数:
tm:结构体时间的首地址
返回值:
成功返回time_t时间
失败返回-1 5.2.4ctime
原型:char *ctime(const time_t *timep);
功能:
将time_t时间转换为字符串时间应用:
#include "head.h"int main(void)
{time_t t;time_t ret;struct tm *ptm = NULL;char *pstr = NULL;// time(&t);t = time(NULL);printf("t = %ld\n", t);ptm = localtime(&t);printf("%04d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d\n", ptm->tm_year+1900, ptm->tm_mon+1, ptm->tm_mday, ptm->tm_hour, ptm->tm_min, ptm->tm_sec);ret = mktime(ptm);printf("ret = %ld\n", ret);pstr = ctime(&ret);printf("pstr = %s\n", pstr);return 0;
}