【拓扑序 容斥原理】P6651 「SWTR-5」Chain|省选-
本文涉及知识点
容斥原理
C++图论 拓扑序
P6651 「SWTR-5」Chain
题目描述|
给定 nnn 个点,mmm 条边的有向无环图。不保证图连通。
qqq 次询问,每次给出 kkk 和 kkk 个互不相同的数 cic_ici,求出如果去掉这 kkk 个点,整个有向无环图将剩余多少条链。答案对 109+710^9+7109+7 取模。每次询问独立。
-
“链”的定义是:我们设一条长度为 ppp 的链的路径为 w0→w1→⋯→wp−1→wpw_0\to w_1\to\cdots\to w_{p-1}\to w_pw0→w1→⋯→wp−1→wp,则应满足 w0w_0w0 入度为 000,wpw_pwp 出度为 000。你可以将其理解为一条食物链。
-
两条链是“不同的”,当且仅当它们的长度不同,或者经过的点集不同。
-
需要特别注意的是,删去某些点后新产生的链不计入答案。 例如 1→2→3→41\to 2\to 3\to 41→2→3→4 一图中,有 111 条链 1→2→3→41\to 2\to 3\to 41→2→3→4。如果去掉 222 号点,则剩余 000 条链。
输入格式
第一行两个整数 n,mn,mn,m,分别表示点的个数和边的条数。
接下来 mmm 行,每行两个整数 u,v(u≠v)u,v(u\neq v)u,v(u=v),表示 u→vu\to vu→v 有一条有向边。
第 m+2m+2m+2 行一个整数 qqq,表示询问个数。
接下来 qqq 行:
- 每行先是一个整数 kkk,表示去掉的点的个数。
- 接下来 kkk 个整数 cic_ici,表示去掉的点的编号。
输出格式
共 qqq 行,每行表示该次询问答案对 109+710^9+7109+7 取模后的值。
输入输出样例 #1
输入 #1
7 14
3 2
4 5
2 5
2 6
3 1
3 5
3 7
3 6
6 4
1 4
6 5
1 6
7 2
7 4
7
3 2 4 6
2 4 6
2 2 5
2 1 4
0
1 4
1 6
输出 #1
1
3
0
6
13
7
5
输入输出样例 #2
输入 #2
233 1
1 2
6
0
1 10
2 10 40
1 1
1 2
2 1 2
输出 #2
232
231
230
231
231
231
说明/提示
「样例 111 说明」
DAG 如图:
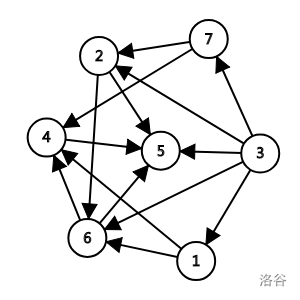
询问 111:如果去掉 2,4,62,4,62,4,6,则剩余 111 条链:3→53\to 53→5。
询问 222:如果去掉 4,64,64,6,则剩余 333 条链:3→53\to 53→5,3→2→53\to 2\to 53→2→5,3→7→2→53\to 7\to 2\to 53→7→2→5。
询问 777:如果去掉 666,则剩余 555 条链:3→53\to 53→5,3→2→53\to 2\to 53→2→5,3→7→2→53\to 7\to 2\to 53→7→2→5,3→1→4→53\to 1\to 4\to 53→1→4→5,3→7→4→53\to 7\to 4\to 53→7→4→5。
「数据范围与约定」
本题采用捆绑测试。
- Subtask 1(1 point):给定的图是一条链。
- Subtask 2(14 points):n,q≤10n,q\leq 10n,q≤10。
- Subtask 3(20 points):q≤103q\leq 10^3q≤103。
- Subtask 4(17 points):k=1k=1k=1。
- Subtask 5(18 points):k=2k=2k=2。
- Subtask 6(30 points):无特殊限制。
对于 100%100\%100% 的数据:2≤n≤2×1032\leq n\leq 2\times 10^32≤n≤2×103,1≤m≤min(n×(n−1)2,2×104)1\leq m\leq \min(\frac{n\times(n-1)}{2},2\times 10^4)1≤m≤min(2n×(n−1),2×104),1≤q≤5×1051\leq q\leq 5\times 10^51≤q≤5×105。
所有询问满足:1≤∑k≤2×1061\leq \sum k\leq 2\times 10^61≤∑k≤2×106,0≤k≤min(n,15)0\leq k\leq \min(n,15)0≤k≤min(n,15),1≤ci≤n1\leq c_i\leq n1≤ci≤n。保证 cic_ici 互不相同。
本题轻微卡常,请注意 IO 优化。
「题目来源」
Sweet Round 05 D。
idea & solution:Alex_Wei。
拓扑序 容斥原理
性质一:令原始图为G,任意合法路径的起点在G中入度为0,终点出度为0,删点和边无法影响G,故链条不会增加。
性质二:删除链条任意一点,则链条不合法。故计算初始链条数,减去删点减少的链条数。
增加超级源点0,指向所有入度为0的节点;增加超级终点N+1,所有出度为0的节点指向它。
to[x]记录0到x的方案数,from[x]记录x到N+1的方案数。cnt[x][y]表示x到y的路径数,to=cnt[0] form[i] = cnt[i][N+1]。
ans0=to[N+1]就是初始方案数。
经过x的链条数:to[x]×from[x]to[x] \times from[x]to[x]×from[x]
to[x1][x2],表示x1到x2的方案数,x1的拓扑序 > x2拓扑序>x3拓扑序。 经过x1,x2,x3的链条数:to[x1]×cnt[x1][x2]×cnt[x2][x3]×from[x3]to[x1] \times cnt[x1][x2] \times cnt[x2][x3] \times from[x3]to[x1]×cnt[x1][x2]×cnt[x2][x3]×from[x3]
直接用容斥原理的时间复杂度是:O(Q×K×2k)O(Q\times K \times 2^k)O(Q×K×2k) 超时。
容斥原理优化
对每个查询按拓扑序降序排序,即一定不会存在ci+1→ci0c_{i+1} \rightarrow c_i0ci+1→ci0
to2[i]记录0到cic_ici,且不经过c0...i−1c_{0...i-1}c0...i−1的路径数。
to2[0]=to[c0]to2[1]=to[c1]−to2[0]∗cnt[c0][c1]⋯to2[i]=to[ci]−to2[0]×cnt[c0][ci]−to2[1]×cnt[c1][ci]−⋯−to2[i−1]×cnt[ci−1][ci]to2[0] = to[c_0] \\ to2[1] = to[c_1] - to2[0]*cnt[c_0][c_1]\\ \cdots \\ to2[i] = to[c_i] - to2[0]\times cnt[c_0][c_i] - to2[1]\times cnt[c_1][c_i] - \cdots - to2[i-1]\times cnt[c_{i-1}][c_i]to2[0]=to[c0]to2[1]=to[c1]−to2[0]∗cnt[c0][c1]⋯to2[i]=to[ci]−to2[0]×cnt[c0][ci]−to2[1]×cnt[c1][ci]−⋯−to2[i−1]×cnt[ci−1][ci]
f(i) 表示经过i的链条数,g(i,j)表示先后经过i,j的链条数。
删除i,j后的链条数位:
ans1 - f(i) -f(j) + g(i,j)+g(j,i)
di,jd_{i,j}di,j表示 0⋯i⋯j⋯N+10 \cdots i \cdots j \cdots N+10⋯i⋯j⋯N+1的链条数,因为无环,故不存在拓扑序小的指向拓扑序大的,故di,j和dj,i至少有一个位0d_{i,j}和d_{j,i}至少有一个位0di,j和dj,i至少有一个位0。
如果di,j和dj,i都为0d_{i,j}和d_{j,i}都为0di,j和dj,i都为0
代码
核心代码
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include<map>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
#include<unordered_set>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<functional>
#include<queue>
#include <stack>
#include<iomanip>
#include<numeric>
#include <math.h>
#include <climits>
#include<assert.h>
#include<cstring>
#include<list>#include <bitset>
using namespace std;template<class T1, class T2>
std::istream& operator >> (std::istream& in, pair<T1, T2>& pr) {in >> pr.first >> pr.second;return in;
}template<class T1, class T2, class T3 >
std::istream& operator >> (std::istream& in, tuple<T1, T2, T3>& t) {in >> get<0>(t) >> get<1>(t) >> get<2>(t);return in;
}template<class T1, class T2, class T3, class T4 >
std::istream& operator >> (std::istream& in, tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4>& t) {in >> get<0>(t) >> get<1>(t) >> get<2>(t) >> get<3>(t);return in;
}template<class T1, class T2, class T3, class T4,class T5 >
std::istream& operator >> (std::istream& in, tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4,T5>& t) {in >> get<0>(t) >> get<1>(t) >> get<2>(t) >> get<3>(t) >> get<4>(t);return in;
}template<class T1, class T2, class T3, class T4, class T5,class T6 >
std::istream& operator >> (std::istream& in, tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5,T6>& t) {in >> get<0>(t) >> get<1>(t) >> get<2>(t) >> get<3>(t) >> get<4>(t) >>get<5>(t);return in;
}template<class T = int>
vector<T> Read() {int n;cin >> n;vector<T> ret(n);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {cin >> ret[i];}return ret;
}
template<class T = int>
vector<T> ReadNotNum() {vector<T> ret;T tmp;while (cin >> tmp) {ret.emplace_back(tmp);if ('\n' == cin.get()) { break; }}return ret;
}template<class T = int>
vector<T> Read(int n) {vector<T> ret(n);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {cin >> ret[i];}return ret;
}template<int N = 1'000'000>
class COutBuff
{
public:COutBuff() {m_p = puffer;}template<class T>void write(T x) {int num[28], sp = 0;if (x < 0)*m_p++ = '-', x = -x;if (!x)*m_p++ = 48;while (x)num[++sp] = x % 10, x /= 10;while (sp)*m_p++ = num[sp--] + 48;AuotToFile();}void writestr(const char* sz) {strcpy(m_p, sz);m_p += strlen(sz);AuotToFile();}inline void write(char ch){*m_p++ = ch;AuotToFile();}inline void ToFile() {fwrite(puffer, 1, m_p - puffer, stdout);m_p = puffer;}~COutBuff() {ToFile();}
private:inline void AuotToFile() {if (m_p - puffer > N - 100) {ToFile();}}char puffer[N], * m_p;
};template<int N = 1'000'000>
class CInBuff
{
public:inline CInBuff() {}inline CInBuff<N>& operator>>(char& ch) {FileToBuf();ch = *S++;return *this;}inline CInBuff<N>& operator>>(int& val) {FileToBuf();int x(0), f(0);while (!isdigit(*S))f |= (*S++ == '-');while (isdigit(*S))x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (*S++ ^ 48);val = f ? -x : x; S++;//忽略空格换行 return *this;}inline CInBuff& operator>>(long long& val) {FileToBuf();long long x(0); int f(0);while (!isdigit(*S))f |= (*S++ == '-');while (isdigit(*S))x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (*S++ ^ 48);val = f ? -x : x; S++;//忽略空格换行return *this;}template<class T1, class T2>inline CInBuff& operator>>(pair<T1, T2>& val) {*this >> val.first >> val.second;return *this;}template<class T1, class T2, class T3>inline CInBuff& operator>>(tuple<T1, T2, T3>& val) {*this >> get<0>(val) >> get<1>(val) >> get<2>(val);return *this;}template<class T1, class T2, class T3, class T4>inline CInBuff& operator>>(tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4>& val) {*this >> get<0>(val) >> get<1>(val) >> get<2>(val) >> get<3>(val);return *this;}template<class T = int>inline CInBuff& operator>>(vector<T>& val) {int n;*this >> n;val.resize(n);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {*this >> val[i];}return *this;}template<class T = int>vector<T> Read(int n) {vector<T> ret(n);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {*this >> ret[i];}return ret;}template<class T = int>vector<T> Read() {vector<T> ret;*this >> ret;return ret;}
private:inline void FileToBuf() {const int canRead = m_iWritePos - (S - buffer);if (canRead >= 100) { return; }if (m_bFinish) { return; }for (int i = 0; i < canRead; i++){buffer[i] = S[i];//memcpy出错 }m_iWritePos = canRead;buffer[m_iWritePos] = 0;S = buffer;int readCnt = fread(buffer + m_iWritePos, 1, N - m_iWritePos, stdin);if (readCnt <= 0) { m_bFinish = true; return; }m_iWritePos += readCnt;buffer[m_iWritePos] = 0;S = buffer;}int m_iWritePos = 0; bool m_bFinish = false;char buffer[N + 10], * S = buffer;
};class CNeiBo
{
public:static vector<vector<int>> Two(int n, const vector<pair<int, int>>& edges, bool bDirect, int iBase = 0){vector<vector<int>> vNeiBo(n);for (const auto& [i1, i2] : edges){vNeiBo[i1 - iBase].emplace_back(i2 - iBase);if (!bDirect){vNeiBo[i2 - iBase].emplace_back(i1 - iBase);}}return vNeiBo;}static vector<vector<int>> Two(int n, const vector<vector<int>>& edges, bool bDirect, int iBase = 0){vector<vector<int>> vNeiBo(n);for (const auto& v : edges){vNeiBo[v[0] - iBase].emplace_back(v[1] - iBase);if (!bDirect){vNeiBo[v[1] - iBase].emplace_back(v[0] - iBase);}}return vNeiBo;}static vector<vector<std::pair<int, int>>> Three(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, bool bDirect, int iBase = 0){vector<vector<std::pair<int, int>>> vNeiBo(n);for (const auto& v : edges){vNeiBo[v[0] - iBase].emplace_back(v[1] - iBase, v[2]);if (!bDirect){vNeiBo[v[1] - iBase].emplace_back(v[0] - iBase, v[2]);}}return vNeiBo;}static vector<vector<std::pair<int, int>>> Three(int n, const vector<tuple<int, int, int>>& edges, bool bDirect, int iBase = 0){vector<vector<std::pair<int, int>>> vNeiBo(n);for (const auto& [u, v, w] : edges){vNeiBo[u - iBase].emplace_back(v - iBase, w);if (!bDirect){vNeiBo[v - iBase].emplace_back(u - iBase, w);}}return vNeiBo;}static vector<vector<int>> Mat(vector<vector<int>>& neiBoMat){vector<vector<int>> neiBo(neiBoMat.size());for (int i = 0; i < neiBoMat.size(); i++){for (int j = i + 1; j < neiBoMat.size(); j++){if (neiBoMat[i][j]){neiBo[i].emplace_back(j);neiBo[j].emplace_back(i);}}}return neiBo;}
};class CDGTopSort
{
public:template <class T = vector<int> >CDGTopSort(const vector<T>& vNeiBo) :m_vDeg(vNeiBo.size()), m_neiBo(vNeiBo) {const int N = vNeiBo.size();m_backNeiBo.resize(N);for (int cur = 0; cur < N; cur++){m_vDeg[cur] = vNeiBo[cur].size();for (const auto& next : vNeiBo[cur]){m_backNeiBo[next].emplace_back(cur);}}}void Init() {auto Add = [&](int i) {if (0 != m_vDeg[i]) { return; }m_que.emplace(i);};for (int i = 0; i < m_vDeg.size(); i++){Add(i);}while (m_que.size()){const int cur = m_que.front(); m_que.pop();if (!OnDo(cur)) { continue; }for (const auto& next : m_backNeiBo[cur]){m_vDeg[next]--;Add(next);}};}queue<int> m_que;vector<int> m_vDeg;vector<int> m_vSort;
protected:const vector<vector<int>>& m_neiBo;vector<vector<int>> m_backNeiBo;virtual bool OnDo(int cur) {m_vSort.emplace_back(cur);return true;};
};template<long long MOD = 1000000007, class T1 = int, class T2 = long long>
class C1097Int
{
public:C1097Int(T1 iData = 0) :m_iData(iData% MOD){}C1097Int(T2 llData) :m_iData(llData% MOD) {}C1097Int operator+(const C1097Int& o)const{return C1097Int(((T2)m_iData + o.m_iData) % MOD);}C1097Int& operator+=(const C1097Int& o){m_iData = ((T2)m_iData + o.m_iData) % MOD;return *this;}C1097Int& operator-=(const C1097Int& o){m_iData = ((T2)MOD + m_iData - o.m_iData) % MOD;return *this;}C1097Int operator-(const C1097Int& o)const{return C1097Int(((T2)MOD + m_iData - o.m_iData) % MOD);}C1097Int operator*(const C1097Int& o)const{return((T2)m_iData * o.m_iData) % MOD;}C1097Int& operator*=(const C1097Int& o){m_iData = ((T2)m_iData * o.m_iData) % MOD;return *this;}C1097Int operator/(const C1097Int& o)const{return *this * o.PowNegative1();}C1097Int& operator/=(const C1097Int& o){*this *= o.PowNegative1();return *this;}bool operator==(const C1097Int& o)const{return m_iData == o.m_iData;}bool operator<(const C1097Int& o)const{return m_iData < o.m_iData;}C1097Int pow(T2 n)const{C1097Int iRet = (T1)1, iCur = *this;while (n){if (n & 1){iRet *= iCur;}iCur *= iCur;n >>= 1;}return iRet;}C1097Int PowNegative1()const{return pow(MOD - 2);}T1 ToInt()const{return ((T2)m_iData + MOD) % MOD;}
private:T1 m_iData = 0;;
};class Solution {
public:vector<int> Ans(int N, vector<pair<int, int>>& edge, vector<vector<int>>& que) {N += 2;vector<vector<int>> neiBo(N);{vector<int> inDeg(N), outDeg(N);for (const auto& [u, v] : edge) {neiBo[u].emplace_back(v);inDeg[v]++;outDeg[u]++;}for (int i = 1; i + 1 < N; i++){if (0 == inDeg[i]) { neiBo[0].emplace_back(i); }if (0 == outDeg[i]) { neiBo[i].emplace_back(N - 1); }}}CDGTopSort topSort(neiBo);topSort.Init();vector < vector<C1097Int<>>> cnt(N, vector<C1097Int<>>(N));for (const auto& u : topSort.m_vSort) {cnt[u][u] = 1;for (const auto& v : neiBo[u]) {for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {cnt[u][i] += cnt[v][i];}}}C1097Int<> ans0 = cnt[0][N - 1];vector<int> vNodeToSort(N);for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {vNodeToSort[topSort.m_vSort[i]] = i;}vector<C1097Int<>> to2;vector<int> ans;for (auto& v : que) {to2.clear();sort(v.begin(), v.end(), [&](const int i1, const int i2) {return vNodeToSort[i1] > vNodeToSort[i2]; });C1097Int<> cur;for (const auto& i : v) {C1097Int biTo2 = cnt[0][i];for (int j = 0; j < to2.size(); j++) {biTo2 -= cnt[v[j]][i] * to2[j];}to2.emplace_back(biTo2);cur += biTo2 * cnt[i].back();}ans.emplace_back((ans0 - cur).ToInt());}return ans;}
};int main() {
#ifdef _DEBUGfreopen("a.in", "r", stdin);
#endif // DEBUGios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(nullptr); cout.tie(nullptr); int N,M,Q ;cin >> N >> M ;auto edge = Read<pair<int, int>>(M);cin >> Q;vector<vector<int>> que(Q);for (int i = 0; i < Q; i++) {que[i] = Read<int>();}
#ifdef _DEBUGprintf("N=%d",N);Out(edge, ",edge=");Out(que, ",que=");
#endif // DEBUGauto res = Solution().Ans(N,edge,que);for (const auto& i : res){cout << i << "\n";}return 0;
}
单元测试
int N, K;vector<pair< int, int>> edge;vector<vector<int>> que;TEST_METHOD(TestMethod11){N = 7, edge = { {3,2},{4,5},{2,5},{2,6},{3,1},{3,5},{3,7},{3,6},{6,4},{1,4},{6,5},{1,6},{7,2},{7,4} }, que = { {2,4,6},{4,6},{2,5},{1,4},{},{4},{6} };auto res = Solution().Ans(N, edge, que);AssertV({ 1,3,0,6,13,7,5 }, res);}TEST_METHOD(TestMethod12){N = 233, edge = { {1,2} }, que = { {},{10},{10,40},{1},{2},{1,2} };auto res = Solution().Ans(N, edge, que);AssertV({ 232,231,230,231,231,231 }, res);}

扩展阅读
| 我想对大家说的话 |
|---|
| 工作中遇到的问题,可以按类别查阅鄙人的算法文章,请点击《算法与数据汇总》。 |
| 学习算法:按章节学习《喜缺全书算法册》,大量的题目和测试用例,打包下载。重视操作 |
| 有效学习:明确的目标 及时的反馈 拉伸区(难度合适) 专注 |
| 员工说:技术至上,老板不信;投资人的代表说:技术至上,老板会信。 |
| 闻缺陷则喜(喜缺)是一个美好的愿望,早发现问题,早修改问题,给老板节约钱。 |
| 子墨子言之:事无终始,无务多业。也就是我们常说的专业的人做专业的事。 |
| 如果程序是一条龙,那算法就是他的是睛 |
| 失败+反思=成功 成功+反思=成功 |
视频课程
先学简单的课程,请移步CSDN学院,听白银讲师(也就是鄙人)的讲解。
https://edu.csdn.net/course/detail/38771
如何你想快速形成战斗了,为老板分忧,请学习C#入职培训、C++入职培训等课程
https://edu.csdn.net/lecturer/6176
测试环境
操作系统:win7 开发环境: VS2019 C++17
或者 操作系统:win10 开发环境: VS2022 C++17
如无特殊说明,本算法用**C++**实现。

