【PCL点云库:下】
PCL点云库:下
- 摘要
- 点云配准
- 曲面重建
摘要
本篇博客参考《点云库PCL从入门到精通》对其中的主要内容进行了总结并对代码进行了调试,以便加深理解和记忆。
点云库PCL从入门到精通
Gitee:配套代码
点云配准
- 概述
点云配准是将【不同视角、时间、设备】得到的目标点云通过空间变换(旋转矩阵R+平移向量T)对齐到与源点云(模板点云【同一物体】)同一坐标系的过程(使得目标点云通过变换后的输出点云与源点云的距离度量最小)
- 分类
- 分类1
- 手动配准
- 依赖仪器的配准
- 自动配准
- 分类2
- 粗配准:使用点云旋转不变性,基于贪心的思路,计算复杂度较高,容易得到局部最优解
- 精配准:基于采样一致性算法,减少计算组合数
- 分类1
- 配准的一般算法流程
- 按照同样的方法,对输入点云、模板点云进行预处理、提取关键点
- 对提取的关键点计算其特征描述子
- 结合输入点云和模板点云之间位置和特征的相似度,初步估计其对应关系(找到相似特征再确定数据的重合部分)
- 点匹配(使用xyz三维坐标)
- 穷举配准
- KDTree等近邻搜索
- 有序点云:图像空间中查找
- 无序点云:索引空间中查找
- 特征匹配
- 穷举匹配
- KDTree等近邻搜索
- 估计对应关系的两种方法
- 直接对应估计(输入到模板、默认):为点云A中的每一个点搜索点云B中的对应点,确认最终对应点
- 相互对应估计:为A中的每一个点搜索B中的对应点,再为B中的每个点搜索A中的对应点,将两次对应点取交集得到最终对应点
- 点匹配(使用xyz三维坐标)
- 假设数据是有噪声的,除去对配准有影响的错误的对应点对
- 使用RANSAC估计等方法剔除不满足假设的对应关系
- NMS过滤
- 利用剩余的正确对应关系,估算刚体变换,完成配准:通过最小化错误度量(最小二乘法)估计最优变化
- PCL中的配准模块
PCL中Registration模块实现了点云相关的算法,包括确定初始对应点集合、去除错误对应点对、坐标变换、多种配准算法,依赖于common、kdtree、sample_consensus、features模块
-
迭代最近点ICP算法
- 原理
在上述配准算法流程的基础上,ICP迭代最近点算法的核心是交替变化,先设置一个初始变化(单位矩阵、零向量或粗配准提供的初始变换):1)固定变换T,优化点对应关系(最近邻寻找对应关系、剔除无效点对);2)固定对应关系,优化变换T
迭代上述2个过程,每次迭代至少不增加误差,最终收敛到局部最优
-
局限性
- 初始变换影响大
- 容易陷入局部最优
-
简单使用
#pragma once #ifndef CLOUD_REGISTRATION_HEADER#define CLOUD_REGISTRATION_HEADER#include <pcl/point_types.h> #include <pcl/point_cloud.h> #include <pcl/registration/icp.h>/* * 迭代最近点ICP算法 */ int test_icp();#endif // CLOUD_REGISTRATION_HEADER#include "cloud_registration.h"/* * 迭代最近点ICP算法 */ int test_icp() {/* 模板点云构造 */pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_in(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);cloud_in->width = 5;cloud_in->height = 1;cloud_in->is_dense = false;cloud_in->points.resize(cloud_in->width * cloud_in->height);for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud_in->points.size(); ++i){cloud_in->points[i].x = 1024 * rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);cloud_in->points[i].y = 1024 * rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);cloud_in->points[i].z = 1024 * rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);}/* 待配准点云构造 */pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_out(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);*cloud_out = *cloud_in;// 基于模板点云对待配准点云施加一个平移变换for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud_in->points.size(); ++i){cloud_out->points[i].x = cloud_in->points[i].x + 0.3f;cloud_out->points[i].y = cloud_in->points[i].y + 0.4f;cloud_out->points[i].z = cloud_in->points[i].z + 0.5f;} /* ICP迭代最近点 */pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> Final; // 配准后点云pcl::IterativeClosestPoint<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::PointXYZ> icp;icp.setInputSource(cloud_in);icp.setInputTarget(cloud_out);icp.align(Final);// hasConverged配准正确输出true std::cout << "has converged:" << icp.hasConverged() << " score: " << icp.getFitnessScore() << std::endl;std::cout << icp.getFinalTransformation() << std::endl;return 0; }- 逐帧配准(两两配准)
将所有帧点云进行刚体变换,使其与第一个点云统一到一个坐标系中。对于每帧点云通过迭代(逐渐对齐)找到最佳的刚体变换,并将变换累积到全部点云(更新到全局刚体变换)
#pragma once #ifndef CLOUD_REGISTRATION_HEADER#define CLOUD_REGISTRATION_HEADER#include <pcl/point_types.h> #include <pcl/point_cloud.h> #include <pcl/registration/icp.h> #include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> #include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h> #include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h> #include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h> #include <pcl/registration/icp_nl.h>/* * 点云逐帧配准 */ int test_pairwise_incremental_registration();#endif // CLOUD_REGISTRATION_HEADER#include "cloud_registration.h"/* * 点云逐帧配准 */ int test_pairwise_incremental_registration() {/* 点云读取 */std::vector<char*> cloud_files = {"capture0001.pcd","capture0002.pcd","capture0003.pcd"};std::vector<pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr> clouds;for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud_files.size(); i++) {// 注意此处clouds需初始化,且初始化的方式clouds.push_back(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>));if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile(cloud_files[i], *(clouds[i])) == -1){std::cout << "read cloud data failed. filename is: " << cloud_files[i] << std::endl;return -1;}} // 全局变换矩阵(累积用)Eigen::Matrix4f GlobalTransform = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity();// 当前帧对的变换矩阵Eigen::Matrix4f pairTransform;// 全局结果pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr result(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);for (size_t i = 1; i < clouds.size() ; i++){ std::cout << "第" << i + 1 << "组" << std::endl;/* 可视化 */pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer* p = new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("Pairwise Incremental Registration");p->removePointCloud("vp1_target");p->removePointCloud("vp1_source");pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> tgt_h(clouds.at(i), 0, 255, 0);pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> src_h(clouds.at(i - 1), 255, 0, 0);// 连续两两配准,相邻两帧点云p->addPointCloud(clouds.at(i), tgt_h, "vp1_target");p->addPointCloud(clouds.at(i - 1), src_h, "vp1_source");p->spin();/* 下采样【可选】 */bool downsample = true;pcl::VoxelGrid<pcl::PointXYZ> grid;pcl:: PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr src(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tgt(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);if (downsample){grid.setLeafSize(0.05, 0.05, 0.05);grid.setInputCloud(clouds[i - 1]);grid.filter(*src);grid.setInputCloud(clouds[i]);grid.filter(*tgt);}else{src = clouds[i];tgt = clouds[i - 1];}/* 计算曲面法线和曲率 */pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::PointNormal> norm_est;pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>());norm_est.setSearchMethod(tree);norm_est.setKSearch(30);pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>::Ptr points_with_normals_src(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>);norm_est.setInputCloud(src);norm_est.compute(*points_with_normals_src);pcl::copyPointCloud(*src, *points_with_normals_src);pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>::Ptr points_with_normals_tgt(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>);norm_est.setInputCloud(tgt);norm_est.compute(*points_with_normals_tgt);pcl::copyPointCloud(*tgt, *points_with_normals_tgt);/* 配准 */// 配准后的点云pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr output(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);// 创建非线性ICP对象pcl::IterativeClosestPointNonLinear<pcl::PointNormal, pcl::PointNormal> reg;// 变换收敛阈值reg.setTransformationEpsilon(1e-6);// 两个对应关系之间的最大距离:10厘米(根据数据集大小来调整)reg.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance(0.1); // 每次align()的最大迭代次数reg.setMaximumIterations(2);reg.setInputTarget(points_with_normals_tgt);// 累积变换矩阵Eigen::Matrix4f Ti = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity();// 上一次的变换矩阵Eigen::Matrix4f prev;// 最终变换矩阵Eigen::Matrix4f targetToSource;// 配准结果pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>::Ptr reg_result = points_with_normals_src;// 开始ICP迭代(外循环30次,内循环2次)for (int i = 0; i < 30; ++i){// 更新输入点云(使用上一次的结果)points_with_normals_src = reg_result;// 执行配准reg.setInputSource(points_with_normals_src);reg.align(*reg_result);// 累积变换矩阵(左乘)Ti = reg.getFinalTransformation() * Ti;// 自适应调整对应距离阈值:如果这次转换和之前转换之间的差异小于阈值,则通过减小最大对应距离来改善程序if (fabs((reg.getLastIncrementalTransformation() - prev).sum()) < reg.getTransformationEpsilon())reg.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance(reg.getMaxCorrespondenceDistance() - 0.001);prev = reg.getLastIncrementalTransformation();// 可视化当前状态pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer* p = new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("Pairwise Incremental Registration");p->removePointCloud("source");p->removePointCloud("target");pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerGenericField<pcl::PointNormal> tgt_color_handler(points_with_normals_tgt, "curvature");if (!tgt_color_handler.isCapable())std::cout<<"Cannot create curvature color handler!"<<std::endl;pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerGenericField<pcl::PointNormal> src_color_handler(points_with_normals_src, "curvature");if (!src_color_handler.isCapable())std::cout << "Cannot create curvature color handler!" << std::endl;p->addPointCloud(points_with_normals_tgt, tgt_color_handler, "target");p->addPointCloud(points_with_normals_src, src_color_handler, "source");p->spinOnce();}// 计算从Target到Source的变换矩阵targetToSource = Ti.inverse();// 将Target点云变换到Source坐标系pcl::transformPointCloud(*clouds[i], *output, targetToSource);p = new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("Pairwise Incremental Registration");p->removePointCloud("source");p->removePointCloud("target");pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> cloud_src_h(clouds[i - 1], 255, 0, 0);pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> cloud_tgt_h(output, 0, 255, 0);p->addPointCloud(clouds[i - 1], cloud_src_h, "source");p->addPointCloud(output, cloud_tgt_h, "target");p->spin();p->removePointCloud("source");p->removePointCloud("target");// 合并source到变换后的target *output += *clouds[i - 1];pairTransform = targetToSource;// 将当前结果转换到全局坐标系pcl::transformPointCloud(*output, *result , GlobalTransform);// 更新全局变换矩阵(左乘)GlobalTransform = pairTransform * GlobalTransform;}return 0; }
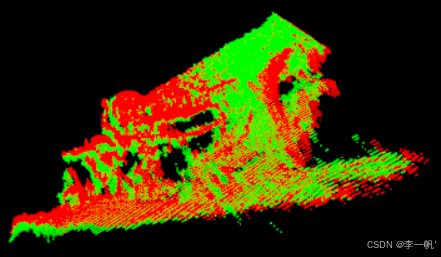
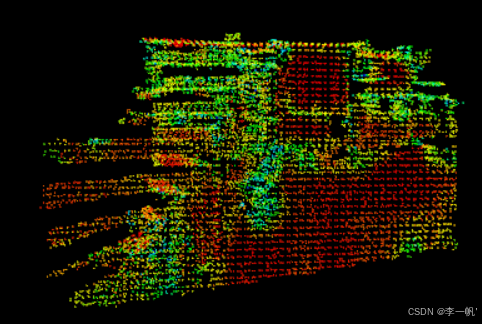
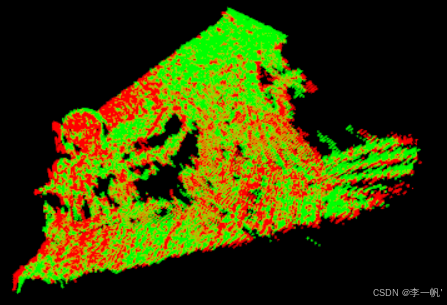
-
基于整体分布变换NDT的配准
-
算法流程
- 将目标点云划分为网格(体素),并为每个网格计算正态分布(均值和协方差)
- 通过优化源点云变换参数,使其在目标点云分布中的概率最大化
-
特点:不利于对应点的特征估计和匹配,速度更快,更鲁棒
-
实例
#pragma once #ifndef CLOUD_REGISTRATION_HEADER#define CLOUD_REGISTRATION_HEADER#include <pcl/point_types.h> #include <pcl/point_cloud.h>#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>#include <pcl/registration/ndt.h>/* * 基于正态分布的配准 */ int test_normal_distribution_transform();#endif // CLOUD_REGISTRATION_HEADER#include "cloud_registration.h"/* * 基于正态分布的配准 */ int test_normal_distribution_transform() {/* 模板点云构造 */pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_in(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);cloud_in->width = 1000;cloud_in->height = 1;cloud_in->is_dense = false;cloud_in->points.resize(cloud_in->width * cloud_in->height);for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud_in->points.size(); ++i){cloud_in->points[i].x = 1024 * rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);cloud_in->points[i].y = 1024 * rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);cloud_in->points[i].z = 0;}/* 待配准点云构造 */pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_out(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);*cloud_out = *cloud_in;// 基于模板点云对待配准点云施加一个平移变换for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud_in->points.size(); ++i){cloud_out->points[i].x = cloud_in->points[i].x + 3.0f;cloud_out->points[i].y = cloud_in->points[i].y + 4.0f;cloud_out->points[i].z = cloud_in->points[i].z + 5.0f;}/* 正态分布变换 *///初始化正态分布变换(NDT)pcl::NormalDistributionsTransform<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::PointXYZ> ndt;// ndt.setOulierRatio(0.55); // 离群值比例//设置依赖尺度NDT参数,为终止条件设置最小转换差异ndt.setTransformationEpsilon(0.01);//为More-Thuente线搜索设置最大步长ndt.setStepSize(0.1);//设置NDT网格结构的分辨率(VoxelGridCovariance)ndt.setResolution(100.0);//设置匹配迭代的最大次数ndt.setMaximumIterations(30);// 设置要配准的点云ndt.setInputSource(cloud_in);// 设置点云配准目标ndt.setInputTarget(cloud_out);// 设置初始变换Eigen::AngleAxisf init_rotation(0.6931, Eigen::Vector3f::UnitZ());Eigen::Translation3f init_translation(1.79387, 0.720047, 0);Eigen::Matrix4f init_guess = (init_translation * init_rotation).matrix();//计算需要的刚体变换以便将输入的点云匹配到目标点云pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr output_cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);ndt.align(*output_cloud, init_guess);std::cout << "Normal Distributions Transform has converged:" << ndt.hasConverged() << " score: " << ndt.getFitnessScore() << std::endl;// 使用创建的变换对未过滤的输入点云进行变换pcl::transformPointCloud(*cloud_in, *output_cloud, ndt.getFinalTransformation());/* 可视化 */pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer::Ptr viewer_final(new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("3D Viewer"));viewer_final->setBackgroundColor(255, 255, 255);viewer_final->initCameraParameters();// 对目标点云着色(红色)并可视化pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> target_color(cloud_out, 255, 0, 0);viewer_final->addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>(cloud_out, target_color, "target cloud");viewer_final->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 5, "target cloud");//对转换后的目标点云着色(绿色)并可视化pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> output_color(output_cloud, 0, 255, 0);viewer_final->addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>(output_cloud, output_color, "output cloud");viewer_final->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 5, "output cloud");while (!viewer_final->wasStopped()){viewer_final->spinOnce(100);}return 0; }
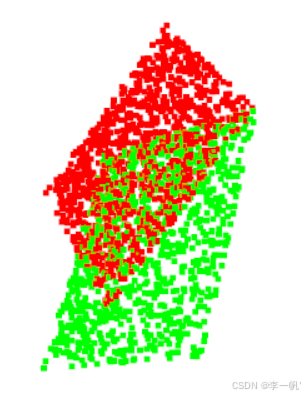
-
基于采样一致性的预对齐配准算法
- 算法流程
- 特征提取:从模板点云和目标点云中提取局部特征描述子(如FPFH)
- 特征匹配:在特征空间中找到模板点云和目标点云之间的对应关系
- 预筛选:使用各种几何约束筛选匹配对(过滤)
- RANSAC优化:在筛选后的匹配对中随机采样,计算变换矩阵并评估质量
- 迭代优化:重复上述过程直到找到最优变换
- 示例
#pragma once #ifndef CLOUD_REGISTRATION_HEADER#define CLOUD_REGISTRATION_HEADER#include <pcl/point_types.h> #include <pcl/point_cloud.h>#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h> #include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h> #include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h> #include <pcl/features/fpfh.h> #include <pcl/registration/sample_consensus_prerejective.h>/* * 基于采样一致性的变换矩阵估计 * 在场景中计算模板物体的位姿 */ int test_sample_consensus_pre_rejective();#endif // CLOUD_REGISTRATION_HEADER#include "cloud_registration.h"/* * 基于采样一致性的变换矩阵估计 * 在场景中计算模板物体的位姿 */ int test_sample_consensus_initial_alignment() {/* 点云创建与加载 */pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>::Ptr object(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>);pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>::Ptr scene(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>);if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile<pcl::PointNormal>("chef.pcd", *object) < 0 ||pcl::io::loadPCDFile<pcl::PointNormal>("rs1.pcd", *scene) < 0){pcl::console::print_error("Error loading object/scene file!\n");return -1;}/* 空间均匀下采样 */pcl::VoxelGrid<pcl::PointNormal> grid;const float leaf = 0.005f;grid.setLeafSize(leaf, leaf, leaf);grid.setInputCloud(object);grid.filter(*object);grid.setInputCloud(scene);grid.filter(*scene);/* 法线估计 */pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointNormal, pcl::PointNormal> nest;nest.setRadiusSearch(0.01);nest.setInputCloud(scene);nest.compute(*scene);/* 特征估计 */pcl::FPFHEstimation<pcl::PointNormal, pcl::PointNormal, pcl::FPFHSignature33> fest;pcl::PointCloud<pcl::FPFHSignature33>::Ptr object_features(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::FPFHSignature33>);pcl::PointCloud<pcl::FPFHSignature33>::Ptr scene_features(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::FPFHSignature33>);fest.setRadiusSearch(0.025);fest.setInputCloud(object);fest.setInputNormals(object);fest.compute(*object_features);fest.setInputCloud(scene);fest.setInputNormals(scene);fest.compute(*scene_features);/* 采样一致性配准 */pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>::Ptr object_aligned(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>);pcl::SampleConsensusPrerejective<pcl::PointNormal, pcl::PointNormal, pcl::FPFHSignature33> align;align.setInputSource(object);align.setSourceFeatures(object_features);align.setInputTarget(scene);align.setTargetFeatures(scene_features);align.setMaximumIterations(50000); // 采样一致性迭代次数align.setNumberOfSamples(3); // 创建假设所需的样本数(对应点的样本你数,正常估计位姿至少3点)align.setCorrespondenceRandomness(5); // 使用的临近特征点的数目(对应点随机度:构造对应点时并非直接选择特征匹配距离最小的,而是在N个最佳匹配点之间进行随机选择)align.setSimilarityThreshold(0.9f); // 多边形边长度相似度阈值(对于目标物体和场景上的对应点,根据它们在各自的空间里之间的欧式距离不变这一特性,筛选错误的对应点。该值越接近1,去除的对应关系减少,增加了排除错误的风险。align.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance(2.5f * 0.005); // 判断是否为内点的距离阈值(判断假设的变换矩阵,变换后的点云和目标点云的距离应小于阈值align.setInlierFraction(0.25f); // 接受位姿假设所需的内点比例(内点数在输入点云数中的比例高于该阈值,则认为假设变换有效,一般高于25%被认为是收敛的)align.align(*object_aligned);/* 显示结果 */if (align.hasConverged()){Eigen::Matrix4f transformation = align.getFinalTransformation();pcl::console::print_info(" | %6.3f %6.3f %6.3f | \n", transformation(0, 0), transformation(0, 1), transformation(0, 2));pcl::console::print_info("R = | %6.3f %6.3f %6.3f | \n", transformation(1, 0), transformation(1, 1), transformation(1, 2));pcl::console::print_info(" | %6.3f %6.3f %6.3f | \n", transformation(2, 0), transformation(2, 1), transformation(2, 2));pcl::console::print_info("\n");pcl::console::print_info("t = < %0.3f, %0.3f, %0.3f >\n", transformation(0, 3), transformation(1, 3), transformation(2, 3));pcl::console::print_info("\n");pcl::console::print_info("Inliers: %i/%i\n", align.getInliers().size(), object->size());// Show alignmentpcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer visu("translation estimation");int v1(0), v2(0);visu.createViewPort(0, 0, 0.5, 1, v1);visu.createViewPort(0.5, 0, 1, 1, v2);visu.setBackgroundColor(255, 255, 255, v1);visu.addPointCloud(scene, pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointNormal>(scene, 0.0, 255.0, 0.0), "scene", v1);visu.addPointCloud(object_aligned, pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointNormal>(object_aligned, 0.0, 0.0, 255.0), "object_aligned", v1);visu.addPointCloud(object, pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointNormal>(object, 0.0, 255.0, 0.0), "object_before_aligned", v2);visu.addPointCloud(scene, pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointNormal>(scene, 0.0, 0.0, 255.0), "scene_v2", v2);visu.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 3, "scene");visu.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 3, "object_aligned");visu.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 3, "object_before_aligned");visu.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 3, "scene_v2");visu.spin();}else{std::cout<<"Alignment failed!\n";return -1;}return 0; }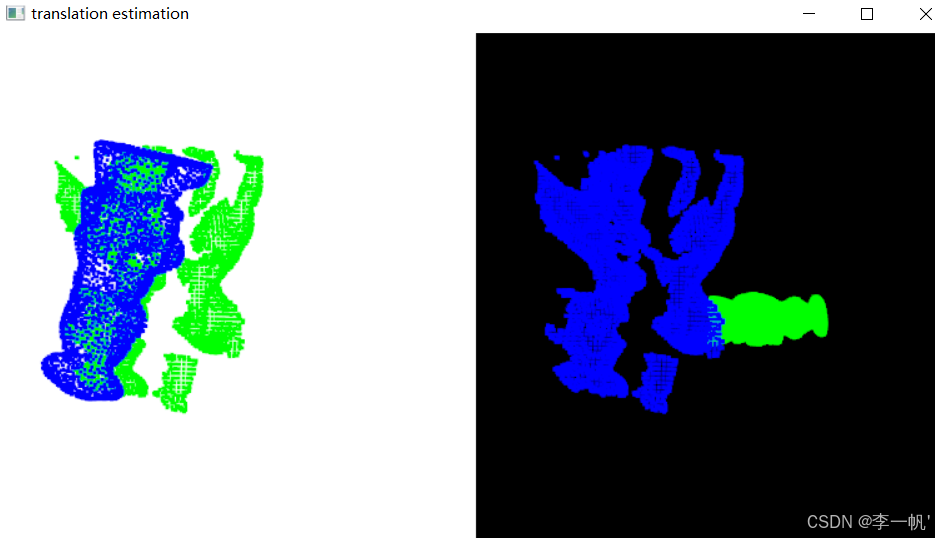
-
基于采样一致性的SAC-IA配准算法
- 与SampleConsensusPrerejective的相同点
- 都基于RANSAC框架
- 都需要先提取特征描述子(如FPFH)
- 都适用于初始位置未知的配准问题
- 都能处理含有噪声和异常值的情况
- 与SampleConsensusPrerejective的不同点
特性 SampleConsensusInitialAlignment (SAC-IA) SampleConsensusPrerejective 主要目的 初始粗配准 精细配准 算法复杂度 相对较低 更高,有更多优化步骤 处理阶段 通常作为ICP的前置步骤 可以直接作为最终配准 匹配策略 简单特征匹配 加入几何一致性的预筛选 参数数量 较少 更多可调参数 计算速度 较快 较慢但更精确 重叠要求 需要较高重叠度 能处理更低重叠度 内点处理 基本RANSAC策略 更复杂的内点评估 - 示例
#pragma once #ifndef CLOUD_REGISTRATION_HEADER#define CLOUD_REGISTRATION_HEADER#include <pcl/point_types.h> #include <pcl/point_cloud.h>#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> #include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h> #include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>#include <pcl/features/fpfh.h> #include <pcl/registration/ia_ransac.h> #include <pcl/filters/passthrough.h>/* * 基于采样一致性的SAC-IA配准算法 */ int test_sample_consensus_initial_alignment();#endif // CLOUD_REGISTRATION_HEADERclass FeatureCloud {private:// Point cloud datapcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr xyz_;pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals_;pcl::PointCloud<pcl::FPFHSignature33>::Ptr features_;pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr search_method_xyz_;// Parametersfloat normal_radius_;float feature_radius_; public:FeatureCloud() :search_method_xyz_(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>),normal_radius_(0.02f),feature_radius_(0.02f){}~FeatureCloud() {}void setInputCloud(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr xyz){xyz_ = xyz;processInput();}void loadInputCloud(const std::string& pcd_file){xyz_ = pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);pcl::io::loadPCDFile(pcd_file, *xyz_);processInput();}pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr getPointCloud() const{return (xyz_);}pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr getSurfaceNormals() const{return (normals_);}pcl::PointCloud<pcl::FPFHSignature33>::Ptr getLocalFeatures() const{return (features_);}protected:// Compute the surface normals and local featuresvoid processInput(){computeSurfaceNormals();computeLocalFeatures();}// Compute the surface normalsvoid computeSurfaceNormals(){normals_ = pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> norm_est;norm_est.setInputCloud(xyz_);norm_est.setSearchMethod(search_method_xyz_);norm_est.setRadiusSearch(normal_radius_);norm_est.compute(*normals_);}// Compute the local feature descriptorsvoid computeLocalFeatures(){features_ = pcl::PointCloud<pcl::FPFHSignature33>::Ptr(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::FPFHSignature33>);pcl::FPFHEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal, pcl::FPFHSignature33> fpfh_est;fpfh_est.setInputCloud(xyz_);fpfh_est.setInputNormals(normals_);fpfh_est.setSearchMethod(search_method_xyz_);fpfh_est.setRadiusSearch(feature_radius_);fpfh_est.compute(*features_);} };class TemplateAlignment { public:// A struct for storing alignment resultsstruct Result{float fitness_score;Eigen::Matrix4f final_transformation;EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW};TemplateAlignment() :min_sample_distance_(0.05f),max_correspondence_distance_(0.01f * 0.01f),nr_iterations_(500){// Intialize the parameters in the Sample Consensus Intial Alignment (SAC-IA) algorithmsac_ia_.setMinSampleDistance(min_sample_distance_);sac_ia_.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance(max_correspondence_distance_);sac_ia_.setMaximumIterations(nr_iterations_);}~TemplateAlignment() {}// Set the given cloud as the target to which the templates will be alignedvoid setTargetCloud(FeatureCloud& target_cloud){target_ = target_cloud;sac_ia_.setInputTarget(target_cloud.getPointCloud());sac_ia_.setTargetFeatures(target_cloud.getLocalFeatures());}// Add the given cloud to the list of template cloudsvoid addTemplateCloud(FeatureCloud& template_cloud){templates_.push_back(template_cloud);}// Align the given template cloud to the target specified by setTargetCloud ()void align(FeatureCloud& template_cloud, TemplateAlignment::Result& result){sac_ia_.setInputSource(template_cloud.getPointCloud());sac_ia_.setSourceFeatures(template_cloud.getLocalFeatures());pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> registration_output;sac_ia_.align(registration_output);result.fitness_score = (float)sac_ia_.getFitnessScore(max_correspondence_distance_);result.final_transformation = sac_ia_.getFinalTransformation();}// Align all of template clouds set by addTemplateCloud to the target specified by setTargetCloud ()void alignAll(std::vector<TemplateAlignment::Result, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Result> >& results){results.resize(templates_.size());for (size_t i = 0; i < templates_.size(); ++i){align(templates_[i], results[i]);}}// Align all of template clouds to the target cloud to find the one with best alignment scoreint findBestAlignment(TemplateAlignment::Result& result){// Align all of the templates to the target cloudstd::vector<Result, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Result> > results;alignAll(results);// Find the template with the best (lowest) fitness scorefloat lowest_score = std::numeric_limits<float>::infinity();int best_template = 0;for (size_t i = 0; i < results.size(); ++i){const Result& r = results[i];if (r.fitness_score < lowest_score){lowest_score = r.fitness_score;best_template = (int)i;}}// Output the best alignmentresult = results[best_template];return (best_template);}private:// A list of template clouds and the target to which they will be alignedstd::vector<FeatureCloud> templates_;FeatureCloud target_;// The Sample Consensus Initial Alignment (SAC-IA) registration routine and its parameterspcl::SampleConsensusInitialAlignment<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::FPFHSignature33> sac_ia_;float min_sample_distance_;float max_correspondence_distance_;int nr_iterations_; };/* * 基于采样一致性的SAC-IA配准算法 */ int test_sample_consensus_initial_alignment() {/* 加载模板点云 */std::vector<FeatureCloud> object_templates;std::ifstream input_stream("face_registration/object_templates.txt");object_templates.resize(0);std::string pcd_filename;while (input_stream.good()){std::getline(input_stream, pcd_filename);if (pcd_filename.empty() || pcd_filename.at(0) == '#') // Skip blank lines or commentscontinue;FeatureCloud template_cloud;template_cloud.loadInputCloud(pcd_filename);object_templates.push_back(template_cloud);}input_stream.close();/* 加载目标点云 */pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);pcl::io::loadPCDFile("face_registration/person.pcd", *cloud);/* 直通滤波,对目标点云进行过滤 */const float depth_limit = 1.0;pcl::PassThrough<pcl::PointXYZ> pass;pass.setInputCloud(cloud);pass.setFilterFieldName("z");pass.setFilterLimits(0, depth_limit);pass.filter(*cloud);/* 目标点云下采样 */const float voxel_grid_size = 0.005f;pcl::VoxelGrid<pcl::PointXYZ> vox_grid;vox_grid.setInputCloud(cloud);vox_grid.setLeafSize(voxel_grid_size, voxel_grid_size, voxel_grid_size);vox_grid.filter(*cloud);/* 配准 */FeatureCloud target_cloud;target_cloud.setInputCloud(cloud);TemplateAlignment template_align;for (size_t i = 0; i < object_templates.size(); ++i){template_align.addTemplateCloud(object_templates[i]);}template_align.setTargetCloud(target_cloud);// 寻找最好的配准变换TemplateAlignment::Result best_alignment;int best_index = template_align.findBestAlignment(best_alignment);const FeatureCloud& best_template = object_templates[best_index];/* 打印结果 */// The alignment fitness score values less than 0.00002 are goodprintf("Best fitness score: %f\n", best_alignment.fitness_score);Eigen::Matrix3f rotation = best_alignment.final_transformation.block<3, 3>(0, 0);Eigen::Vector3f translation = best_alignment.final_transformation.block<3, 1>(0, 3);printf("\n");printf(" | %6.3f %6.3f %6.3f | \n", rotation(0, 0), rotation(0, 1), rotation(0, 2));printf("R = | %6.3f %6.3f %6.3f | \n", rotation(1, 0), rotation(1, 1), rotation(1, 2));printf(" | %6.3f %6.3f %6.3f | \n", rotation(2, 0), rotation(2, 1), rotation(2, 2));printf("\n");printf("t = < %0.3f, %0.3f, %0.3f >\n", translation(0), translation(1), translation(2));return 0; } - 与SampleConsensusPrerejective的相同点
- 算法流程
-
基于VFH描述子聚类识别与位姿估计
聚类:3D点的集合,通常代表一个特殊目标或场景的一部分,由分割或提取算法获得
目标:根据各个聚类的场景(模板点云)及其对应的位姿,从一组聚类中查询与用户输入场景最近似的候选集。将识别问题抽象为近邻估计问题
训练阶段:给定只包含一个物体的场景,估计该物体的位姿(采集设备旋转物体,获得不同视角下点云的VFH描述子、保存不同视角的点云,并基于此建立KDTree)
测试阶段:从给定场景分割提取聚类、对每个聚类从当前视角计算其VFH描述子、利用VFH描述子在训练阶段建立的KDTree中搜索候选集
- 交互式多深度摄像头标定
多个深度摄像头一起使用时,存在全局标定问题。即将多个深度摄像头(深度相机位置固定)获取的点云数据配准在一个全局坐标系中
-
曲面重建
-
曲面重建的方法分类
- 插值法:完全通过原始数据点得到重建曲面
- 逼近法:用分片线性曲面或其他形式来逼近原始数据,从而使得产生的平面是原始点集的一个逼近
-
曲面的表现形式
- 参数曲面重建
- 隐式曲面重建
- 变形曲面重建
- 细分曲面重建
- 分片线性曲面重建
-
PCL的曲面重建模块和相关理论基础
-
PCL surface模块:实现了点云曲面重建的基于算法与数据结构。包括如点云平滑、重采样、建立凸包、三角化、泊松重建、MC重建、Ear Clipping等算法
-
凸包算法:凸包(Convex Hull)是计算机图形学中的概念,常用于二维的面积计算和三维的体积估计。在一个实数向量空间V中,对于给定集合X,所有包含X的凸集的交集S被称为X的凸包。.在二维欧式空间中,凸包可以想象为一条刚好包着所有点的橡皮圈。最常用的凸包算法是Graham扫描法和Jarvis步进法。PCL的凸包计算是对第三方库qhull的封装。
-
Ear Clipping算法:多边形的一个顶点,和它邻近的两个顶点组成一个三角形,如果该三角形内部不存在该多边形的其他顶点,就可以将该形成的三角形当作一个Ear。沿着顶点切下该Ear,每切一次,就能得到一个三角形和少了一个顶点的多边形。重复上述操作,直到该多边形只剩3个顶点。这样,这个多边形就被完全分解为了三角形
-
贪婪投影三角化算法:将三维点通过法线投影到某一平面,然后基于Delaunay的空间区域增长算法(该算法选取一个样本三角片作为初始曲面,不断扩张曲面边界,最后形成一张完整的三角网格曲面)对投影点进行平面内的三角化,从而获得各点的连接关系。最后,根据投影点云的连接关系确定各原始三维点间的拓扑关系,所得三角网格即为重建得到的曲面模型(该算法需假设曲面光滑,点云密度变换均匀,不能在三角化的同时对曲面进行平滑和孔洞修复)
-
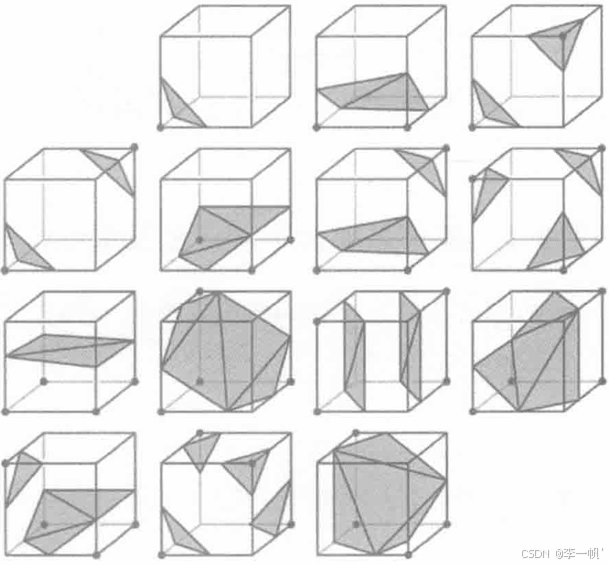
移动立方体算法:找出所有与等值面相交的体素,再分布找出每个体素与等值面相交的交面,这些交面连在一起即使所求曲面。为了确定体素中等值面的剖分方式,因此要为所求等值面规定一个极限值,然后对体素的八个顶点进行分类(2^8=256种组合,除去对称性,则有15种),来判断顶点位于等值面内还是等值面外,再根据顶点分类结果确定等值面的剖分方式(求得等值面与体素边界的交点,即等值点)若体素很小,则可以假定函数沿体素边界线性变化,根据该假设可以用线性插值计算等值面与体素边界的交点。连接等值点形成三角形或多边形,再将三角形或多边形连接,即可得到等值面(所求曲面)
- 若顶点的数据值大于等值面的阈值,则定义该顶点位于等值面之内
- 若顶点的数据值小于等值面的阈值,则定义该顶点位于等值面之外
- 若一个体素的部分顶点的数据值大于等值面的阈值,另一些小于等值面的阈值,那么等值面必通过该体素
-
泊松曲面重建:泊松曲面重建法是一种基于隐式函数的三角网格重建算法,该类方法通过对点云数据进行最优化的插值处理来获得近似曲面。其算法输入是包含法线的点云集,假设所有点位于或邻近一个未知模型的表面。算法目标是估计模型的指示函数和提取等值面,再基于指示函数和等值面利用MC算法完成曲面重建,最终输出为曲面模型数据
-
-
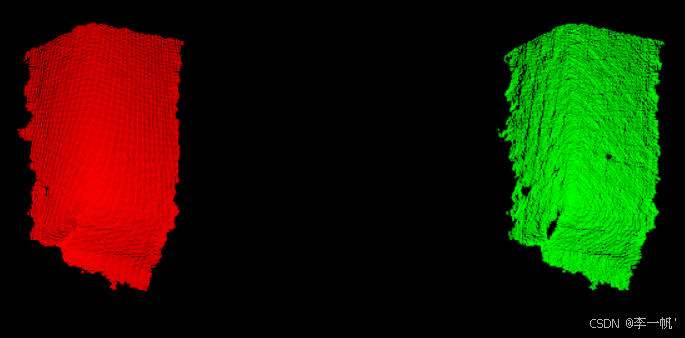
基于移动最小二乘法MLS的法线估计、点云平滑、数据重采样
- 数据重采样的意义
对于包含测量误差(尤其是小目标)的数据直接用于曲面重建,可能会造成重建的表面不光滑或有漏洞。此外,多个扫描点扫描结果配置后的数据直接用于曲面重建可能会在某块区域出现重叠的两个曲面。重采样可以对上述两个问题进行解决。重采样后的点云数据法线方向更加一致,曲率特征间的方差减小
- 实例
#pragma once #ifndef CLOUD_SURFACE_REBUILD_HEADER #define CLOUD_SURFACE_REBUILD_HEADER#include <pcl/point_cloud.h> #include <pcl/point_types.h> #include <pcl/search/kdtree.h> #include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> #include <pcl/visualization/cloud_viewer.h> #include <pcl/filters/filter.h>#include <pcl/surface/mls.h>/* * 基于移动最小二乘法的法线估计、点云平滑、数据重采样 */ int test_mls_resampling();#endif // !CLOUD_SURFACE_REBUILD_HEADER#include "cloud_surface_rebuild.h"/* * 基于移动最小二乘法的法线估计、点云平滑、数据重采样 */ int test_mls_resampling() {/* 点云创建与读取 */pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>());pcl::io::loadPCDFile("milk.pcd", *cloud);std::vector<int> indices;pcl::removeNaNFromPointCloud(*cloud, *cloud, indices);/* MLS法线估计、点云平滑 */pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>::Ptr mls_points (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>);// MLS估计器pcl::MovingLeastSquares<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::PointNormal> mls;// 参数设置pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>);mls.setComputeNormals(true);mls.setInputCloud(cloud);// 设置点云平滑的方式mls.setPolynomialOrder(2);mls.setSearchMethod(tree);mls.setSearchRadius(0.03);// 曲面重建mls.process(*mls_points);/* 可视化 */pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer::Ptr visual(new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer);visual->setBackgroundColor(255, 255, 255);int v1(1);visual->createViewPort(0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 1.0, v1);int v2(2);visual->createViewPort(0.5, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, v2);pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> origin_handler (cloud,255,0,0);visual->addPointCloud(cloud, origin_handler, "cloud",v1);pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointNormal> output_handler(mls_points, 0, 255, 0);visual->addPointCloud(mls_points, output_handler, "mls_points",v2);visual->spin();return 0; }
-
在平面模型上构建凸(凹)多边形
从点云中提取平面模型 → 将滤波后的点云投影到平面模型 → 为投影后的点云计算其对应的2D凸(凹)多边形
#pragma once #ifndef CLOUD_SURFACE_REBUILD_HEADER #define CLOUD_SURFACE_REBUILD_HEADER#include <pcl/point_cloud.h> #include <pcl/point_types.h> #include <pcl/search/kdtree.h> #include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> #include <pcl/visualization/cloud_viewer.h> #include <pcl/filters/filter.h>#include <pcl/ModelCoefficients.h> #include <pcl/segmentation/sac_segmentation.h> #include <pcl/filters/project_inliers.h> #include <pcl/surface/concave_hull.h>/* * 在平面模型上构建凸(凹)多边形 */ int test_concave_hull_2d();#endif // !CLOUD_SURFACE_REBUILD_HEADER#include "cloud_surface_rebuild.h"/* * 在平面模型上构建凸(凹)多边形 */ int test_concave_hull_2d() {/* 点云的读取和构造 */pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);pcl::PCDReader reader;reader.read("milk.pcd", *cloud);std::vector<int> indices;pcl::removeNaNFromPointCloud(*cloud, *cloud, indices);/* 平面模型估计 */pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients(new pcl::ModelCoefficients);// 存储点云分割后的结果pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers(new pcl::PointIndices);pcl::SACSegmentation<pcl::PointXYZ> seg;// 设置优化系数【可选】seg.setOptimizeCoefficients(true);seg.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE);seg.setMethodType(pcl::SAC_RANSAC);// 设置距离阈值,与估计平面模型距离小于阈值的点均被视为内点seg.setDistanceThreshold(0.01);seg.setInputCloud(cloud);seg.segment(*inliers, *coefficients);/* 点云投影 */pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_projected(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);pcl::ProjectInliers<pcl::PointXYZ> proj;proj.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE);proj.setInputCloud(cloud);proj.setModelCoefficients(coefficients);proj.filter(*cloud_projected);/* 凸(凹)多边形构建 */pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_hull(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);pcl::ConcaveHull<pcl::PointXYZ> chull;chull.setInputCloud(cloud_projected);chull.setAlpha(0.1);chull.reconstruct(*cloud_hull);/* 可视化 */pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer::Ptr visual(new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer);visual->setBackgroundColor(255, 255, 255);int v1(1);visual->createViewPort(0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 1.0, v1);int v2(2);visual->createViewPort(0.5, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, v2);pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> origin_handler(cloud, 255, 0, 0);visual->addPointCloud(cloud, origin_handler, "cloud", v1);pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> output_handler(cloud_hull, 0, 255, 0);visual->addPointCloud(cloud_hull, output_handler, "cloud_hull", v2);visual->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 8, "cloud_hull", v2);visual->spin();return 0; }
-
基于贪婪投影三角化的曲面重建
-
理论介绍:处理一系列可以使网格“生长扩大”的点(边缘点),延申这些点直到所有符合几何正确性和拓扑正确性的点都被连上
- 将有向点云投影到某一平面内
- 在平面内对投影进行三角化
- 根据平面内三维点的拓扑连接关系获得一个三角格曲面模型
-
优点:可以处理来自一个或多个扫描仪得到的且有多个连接处的散乱点云
-
局限性:更适用于采样点表面光滑且密度变化较均匀的情况
-
示例
#pragma once #ifndef CLOUD_SURFACE_REBUILD_HEADER #define CLOUD_SURFACE_REBUILD_HEADER#include <pcl/point_cloud.h> #include <pcl/point_types.h> #include <pcl/search/kdtree.h> #include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> #include <pcl/visualization/cloud_viewer.h> #include <pcl/filters/filter.h>#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h> #include <pcl/surface/gp3.h>/* * 基于贪婪投影三角化的曲面重建 */ int greedy_projection_triangulation();#endif // !CLOUD_SURFACE_REBUILD_HEADER#include "cloud_surface_rebuild.h" /* * 基于贪婪投影三角化的曲面重建 */ int greedy_projection_triangulation() {/* 点云的读取和构造 */pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);pcl::PCDReader reader;reader.read("milk.pcd", *cloud);std::vector<int> indices;pcl::removeNaNFromPointCloud(*cloud, *cloud, indices);/* 法线估计 */pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> n;pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>);tree->setInputCloud(cloud);n.setInputCloud(cloud);n.setSearchMethod(tree);n.setKSearch(20);n.compute(*normals);/* 点云合并 */pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>::Ptr cloud_with_normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>);pcl::concatenateFields(*cloud, *normals, *cloud_with_normals);/* 贪婪投影三角化 */pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointNormal>::Ptr tree_with_normal(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointNormal>);tree_with_normal->setInputCloud(cloud_with_normals);pcl::GreedyProjectionTriangulation<pcl::PointNormal> gp3;pcl::PolygonMesh triangles;// 设置三角化后每个三角形的最大可能边长gp3.setSearchRadius(0.25);// 控制搜索邻域大小,定义了可搜索邻域的个数,一般取值为50-100// gp3.setMaximumNearestNeighbors();// 控制搜索邻域大小,规定了搜索邻域的最远距离,一般为2.5-3gp3.setMu(2.5);// 设置三角化后每个三角形的最小角度数,此处取10gp3.setMinimumAngle(M_PI / 18); // 设置三角化后每个三角形的最大角度数,此处取120gp3.setMaximumAngle(2 * M_PI / 3);// 为了处理边缘或者角太过尖锐及其一个表面的两条边太过接近的情况,规定某些法线的方向偏离指定角度,该点就不连接到样本点上gp3.setMaximumSurfaceAngle(M_PI / 4);// 为了处理边缘或者角太过尖锐及其一个表面的两条边太过接近的情况,保证法线朝向一致gp3.setNormalConsistency(false);gp3.setSearchMethod(tree_with_normal);gp3.setInputCloud(cloud_with_normals);gp3.reconstruct(triangles);std::vector<int> parts = gp3.getPartIDs();std::vector<int> states = gp3.getPointStates();/* 可视化 */pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer::Ptr viewer(new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer);int v1(1);viewer->createViewPort(0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 1.0, v1);int v2(2);viewer->createViewPort(0.5, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, v2);viewer->initCameraParameters();viewer->setBackgroundColor(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> origin_handler(cloud, 255, 0, 0);viewer->addPointCloud(cloud, origin_handler, "cloud", v1);viewer->addPolygonMesh(triangles, "triangles", v2);viewer->spin();return 0; }
-
-
基于B样条曲线的曲面重建
-
算法流程
- 利用PCA对B样条曲面进行初始化,该步骤假设输入的点云数据有两个主要方向
- 对初始化后的B样条曲面进行拟合和迭代优化
- 利用圆来初始化B样条曲线(该步骤假设点云是紧致的,即没有空间分离的聚类)
- 对初始化的B样条曲线进行拟合
- 对上述用B样条曲线裁剪后的B样条曲面进行三角化,得到最终拟合的曲面
-
PCL安装设置:安装编译时需设置开启BUID_surface_on_nurbs,可开启USE_UMFPACK(用于快速求解大型稀疏线性方程组,如不开启则使用Eigen进行求解,速度慢于UMFPACK)
-
示例
#pragma once #ifndef CLOUD_SURFACE_REBUILD_HEADER #define CLOUD_SURFACE_REBUILD_HEADER#include <pcl/point_cloud.h> #include <pcl/point_types.h> #include <pcl/search/kdtree.h> #include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> #include <pcl/visualization/cloud_viewer.h> #include <pcl/filters/filter.h>#include <pcl/surface/on_nurbs/fitting_surface_tdm.h> #include <pcl/surface/on_nurbs/fitting_curve_2d_asdm.h> #include <pcl/surface/on_nurbs/triangulation.h>/* * 基于B样条曲线的曲面重建 */ int test_bspline_fitting();#endif // !CLOUD_SURFACE_REBUILD_HEADER#include "cloud_surface_rebuild.h" /* * 基于B样条曲线的曲面重建 */ int test_bspline_fitting() {/* 点云读取构建 */pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);// pcl::PCLPointCloud2是PCL中的通用点云存储形式,可以表示任意类型的点云(无论点类型是PointXYZ、PointXYZRGB还是自定义类型)// 直接使用某种特定类型的点云去读取文件数据可能会导致字段不匹配或数据丢失,因此可使用PCLPointCloud2读入再做中转pcl::PCLPointCloud2 cloud2;if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile("milk.pcd", cloud2) == -1)throw std::runtime_error(" PCD file not found.");fromPCLPointCloud2(cloud2, *cloud);/* 初始化可视化对象 */pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("3d viewer");viewer.setBackgroundColor(255, 255, 255);viewer.setSize(800, 600);pcl::on_nurbs::NurbsDataSurface data;PointCloud2Vector3d(cloud, data.interior);pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> handler(cloud, 0, 255, 0);viewer.addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>(cloud, handler, "cloud_cylinder");// B样条曲面模型多项式的阶数,阶数的数值最少为2(对应点线性)且不能大于控制点个数,其对应的次数degree为order-1(因此本例为2次多项式)unsigned order(3);// 拟合优化迭代的次数(每次迭代时添加控制点的个数,这样每次迭代的参数方向上控制点的个数呈2倍增长)unsigned refinement(4);// 完成拟合优化后的迭代次数unsigned iterations(10);// 在每个参数方向上控制点的采样点个数,用于对拟合得到的B样条曲面进行三角化unsigned mesh_resolution(128);// 拟合相关参数pcl::on_nurbs::FittingSurface::Parameter params;// 描述曲面本身的平滑性params.interior_smoothness = 0.2;// 优化时用到的权重参数params.interior_weight = 1.0;// 曲面边界的平滑性(用pcl::on_nurbs::NurbsDataSurface::boundary声明定义的边界)params.boundary_smoothness = 0.2;// 优化时的边界权重,大于0则会尽量将拟合的边界向定义靠近params.boundary_weight = 0.0;// 初始化B样条曲面,利用静态函数构造局部坐标系,该坐标轴的轴方向由PCA得到的主向量决定,原点位置用点云的重心确定// 为了估计B样条曲面的空间域,在PCA的第一、第二方向组成的平面上,构造包围盒。该包围盒用于初始化带有最少控制点的B样条曲面(一般这些控制点无法足够好地趋近点云的几何形状,需要通过逐步增加控制点同时缩小拟合曲面与点云数据的距离)ON_NurbsSurface nurbs = pcl::on_nurbs::FittingSurface::initNurbsPCABoundingBox(order, &data);// 利用输入点云和初始B样条曲面对表面填充类进行初始化pcl::on_nurbs::FittingSurface fit(&data, nurbs);// 设置是否打印调试信息fit.setQuiet(true);// 用于可视化的曲面模型pcl::PolygonMesh mesh;pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr mesh_cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);std::vector<pcl::Vertices> mesh_vertices;// on_nurbs::Triangulation可以将ON_NurbsSurface和PolygonMesh进行转换用于可视化pcl::on_nurbs::Triangulation::convertSurface2PolygonMesh(fit.m_nurbs, mesh, mesh_resolution);viewer.addPolygonMesh(mesh, "mesh_nurbs");std::cout << "Before refine" << endl;viewer.spin();/* 控制点插入:在两个参数方向上增加控制点,并同时对B样条曲面进行拟合使其趋近最终解 */for (unsigned i = 0; i < refinement; i++){// 设置在参数方向0上增加控制点优化fit.refine(0);// 设置在参数方向1上增加控制点优化【可选】fit.refine(1);fit.assemble(params);fit.solve();pcl::on_nurbs::Triangulation::convertSurface2Vertices(fit.m_nurbs, mesh_cloud, mesh_vertices, mesh_resolution);viewer.updatePolygonMesh<pcl::PointXYZ>(mesh_cloud, mesh_vertices, "mesh_nurbs");// viewer.spinOnce(1000);std::cout << "refine: " << i << endl;}/* 以最终优化确定的控制点数量进行多次迭代拟合求解 */for (unsigned i = 0; i < iterations; i++){fit.assemble(params);fit.solve();pcl::on_nurbs::Triangulation::convertSurface2Vertices(fit.m_nurbs, mesh_cloud, mesh_vertices, mesh_resolution);viewer.updatePolygonMesh<pcl::PointXYZ>(mesh_cloud, mesh_vertices, "mesh_nurbs");// viewer.spinOnce(1000);std::cout << "iterations: " << i << endl;}/* 为了进一步去除拟合结果中超出形状本身的部分,需对其进行裁剪:首先投影点云数据到B样条曲面的参数域上,在该二维空间进行带权重B样条曲线拟合,由此创建出闭合修剪曲线,该修剪曲线近似包含所有点*/pcl::on_nurbs::FittingCurve2dAPDM::FitParameter curve_params;// 距离阈值:如果曲线的支撑域到最近数据点的距离大于该阈值,则添加控制点curve_params.addCPsAccuracy = 5e-2;// 不进行控制点插入时的内部迭代优化次数curve_params.addCPsIteration = 3;// 允许的最大控制点个数curve_params.maxCPs = 200;// 曲线的平均拟合精度curve_params.accuracy = 1e-3;// 最大迭代次数curve_params.iterations = 100;// 每一个支撑域内控制点个数curve_params.param.closest_point_resolution = 0;// 最近点对应的权重curve_params.param.closest_point_weight = 1.0;// 外点的最近点的阈值,拟合时不考虑远离曲线的外点的距离值大于该阈值的点curve_params.param.closest_point_sigma2 = 0.1;// 内点的最近点的阈值,拟合时不考虑远离曲线的内点的距离值大于该阈值的点curve_params.param.interior_sigma2 = 0.00001;// 平滑凹凸性,该值使得曲线向内或向外,0没有作用、<0向内凹、>0向外凹curve_params.param.smooth_concavity = 1.0;// 平滑项权重curve_params.param.smoothness = 1.0;printf(" curve fitting ...\n");pcl::on_nurbs::NurbsDataCurve2d curve_data;curve_data.interior = data.interior_param;// 设置进行带权重的B样条曲线拟合curve_data.interior_weight_function.push_back(true);ON_NurbsCurve curve_nurbs = pcl::on_nurbs::FittingCurve2dAPDM::initNurbsCurve2D(order, curve_data.interior);// 用最小的控制点个数表示的一个圆来初始化该拟合曲线,其圆心为投影后点云的重心,半径为距离圆心最远的点pcl::on_nurbs::FittingCurve2dASDM curve_fit(&curve_data, curve_nurbs);curve_fit.setQuiet (false);// 曲线拟合curve_fit.fitting(curve_params);// 可视化// visualizeCurve(curve_fit.m_nurbs, fit.m_nurbs, viewer);// 完成对B样条曲面的三角化pcl::on_nurbs::Triangulation::convertTrimmedSurface2PolygonMesh(fit.m_nurbs, curve_fit.m_nurbs, mesh, mesh_resolution);viewer.removePolygonMesh("mesh_nurbs");viewer.addPolygonMesh(mesh, "mesh_nurbs");viewer.spin();/* 保持B样条曲面模型曲面*//*if ( fit.m_nurbs.IsValid() ){ONX_Model model;ONX_Model_Object& surf = model.m_object_table.AppendNew();surf.m_object = new ON_NurbsSurface(fit.m_nurbs);surf.m_bDeleteObject = true;surf.m_attributes.m_layer_index = 1;surf.m_attributes.m_name = "surface";ONX_Model_Object& curv = model.m_object_table.AppendNew();curv.m_object = new ON_NurbsCurve(curve_fit.m_nurbs);curv.m_bDeleteObject = true;curv.m_attributes.m_layer_index = 2;curv.m_attributes.m_name = "trimming curve";model.Write(file_3dm.c_str());printf(" model saved: %s\n", file_3dm.c_str());}*/return 0; } -
