LLM—— 基于 MCP 协议(SSE 模式)的工具调用实践
在上一篇博客中,我们介绍了 基于 MCP 协议(Stdio 模式)的工具调用实践。本文我们将聚焦于MCP协议(SSE模式)的工具调用实践,了解SSE模式下,客户端与服务端的交互方式,并通过实际的案例加深对该模式下交互的体验,那就让我们开始吧!
一、什么是 MCP 的 SSE 模式?
MCP 提供了统一的工具注册、结构化参数传输和调用机制,而 SSE(Server-Sent Events) 是一种基于 HTTP 的、用于服务器向客户端单向推送事件的通信机制。
使用 MCP SSE 模式的好处:
- ✅ 使用 HTTP 建立连接,适合公网 / 跨网络部署
- ✅ 使用 SSE 从服务器向客户端推送异步响应
- ✅ 支持分布式架构,工具运行在远程容器或服务中
典型场景:远程工具服务注册在某台服务器上,客户端通过 HTTP+SSE 长连接进行调用,实现跨主机 / 跨区域的 Agent 工具执行系统。
二、示例项目
项目包含服务端(工具注册)与客户端(工具调用)两部分,使用HTTP + SSE 长连接进行通信。
服务端(注册工具并提供 SSE 连接)
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCPmcp = FastMCP("MyServer", host="127.0.0.1", port=8050)@mcp.tool()
def say_hello(name: str) -> str:return f"Hello, {name}! Nice to meet you!"@mcp.tool()
def add(a: int, b: int) -> int:return a + bif __name__ == "__main__":mcp.run(transport="sse")
- MCP 会监听
/sse路由,提供 Server-Sent Event 长连接 - 所有工具通过
@mcp.tool()装饰器注册,具备参数/类型/描述信息
客户端(连接远程服务并调用工具)
import asynciofrom mcp import ClientSession
from mcp.client.sse import sse_clientasync def main():# Connect to the server using SSEasync with sse_client("http://localhost:8050/sse") as (read_stream, write_stream):async with ClientSession(read_stream, write_stream) as session:# Initialize the connectionawait session.initialize()# List avaliable toolstools_result = await session.list_tools()print("Available tools:")for tool in tools_result.tools:print(f"- {tool.name}: {tool.description}")# Call our calculator toolresult = await session.call_tool("add", arguments={"a": 1, "b": 2})print(f"1 + 2 = {result.content[0].text}")if __name__ == "__main__":asyncio.run(main())
- 客户端使用
aiohttp发起 SSE 连接 ClientSession支持工具发现、函数调用等能力
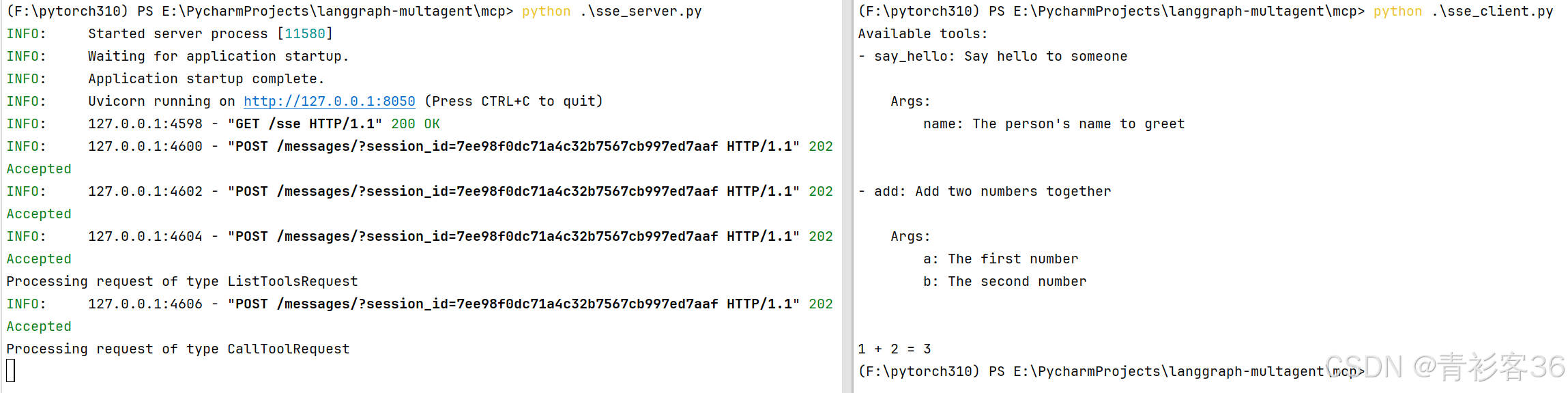
运行结果:
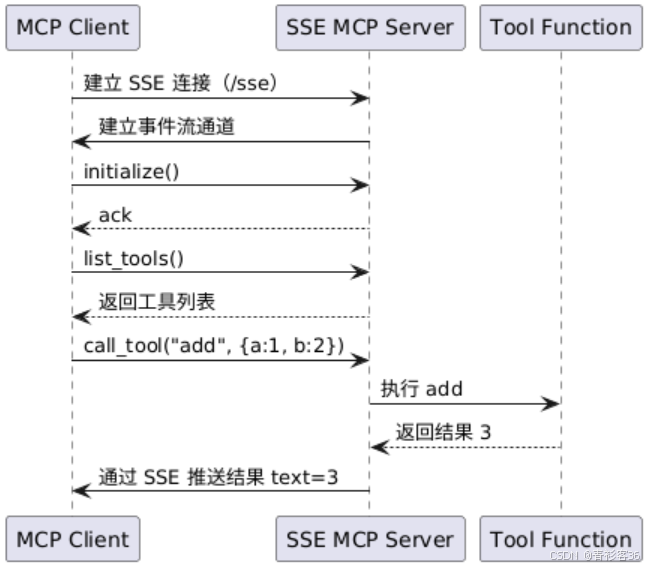
交互流程时序图
三、总结
MCP 协议结合 SSE 模式,为构建可远程部署、异步交互、安全解耦的工具调用系统提供了完整的底层能力:
- 模型通过标准 HTTP 建立连接
- 工具通过结构化参数远程调用
- 服务器通过 SSE 通道推送返回结果
- 非常适合构建远程智能体、插件化执行平台和 LLM 工具桥接系统
如果你正在开发一个跨网络的智能工具执行系统,或希望将 LLM 系统与现有微服务桥接,那么MCP将是一个非常值得选择的选项。
