Linux 723 磁盘配额 限制用户写入 quota;snap快照原理
磁盘配额quota
限制用户对磁盘使用
vim /etc/fstab
usrquota,grpquota
[root@web caozx26]# vim /etc/fstab
[root@web caozx26]# cat /etc/fstab#
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Sat Apr 19 17:11:28 2025
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
# See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info
#
/dev/mapper/centos-root / xfs defaults 0 0
UUID=0671af2f-69a1-4a84-bb51-ceb937bc1a92 /boot xfs defaults 0 0
/dev/mapper/centos-swap swap swap defaults 0 0
/dev/sdb2 /u2 ext4 defaults,usrquota,grpquota 0 0
/dev/sdd6 swap swap defaults 0 0
/tmp/swapfile swap swap defaults,pir=1 0 0
/dev/vg7/lv7 /u7 ext4 defaults,usrquota,grpquota 0 0umoun /u7
mount -a
mount |grep u7
[root@web caozx26]# umount /u7
[root@web caozx26]# mount -a
[root@web caozx26]# mount |grep u7
/dev/mapper/vg7-lv7 on /u7 type ext4 (rw,relatime,quota,usrquota,grpquota,data=ordered)
[root@web caozx26]# ll /u7
总用量 16
drwx------ 2 root root 16384 7月 20 20:18 lost+foundquotacheck -aucg
ll /u7
quotaon -a
edquota -u kefu2
[root@web caozx26]# quotacheck -acug
[root@web caozx26]# ll /u7
总用量 32
-rw------- 1 root root 6144 7月 23 23:08 aquota.group
-rw------- 1 root root 6144 7月 23 23:08 aquota.user
drwx------ 2 root root 16384 7月 20 20:18 lost+found
[root@web caozx26]# quotaon -a
[root@web caozx26]# edquota -u kefu2
[root@web caozx26]# quota -uvs kefu2
Disk quotas for user kefu2 (uid 1023):Filesystem space quota limit grace files quota limit grace/dev/sdb2 0K 0K 0K 0 0 0
/dev/mapper/vg7-lv70K 10240K 12288K 0 10 15测试
[root@web caozx26]# setfacl -m u:kefu2:rwx /u7
[root@web caozx26]# su - kefu2
上一次登录:三 7月 23 23:14:04 CST 2025pts/0 上
[kefu2@web ~]$ ll -d /u7
drwxrwxr-x+ 3 root root 4096 7月 23 23:08 /u7
[kefu2@web ~]$ cd /u7
[kefu2@web u7]$ ll
总用量 32
-rw------- 1 root root 6144 7月 23 23:08 aquota.group
-rw------- 1 root root 7168 7月 23 23:08 aquota.user
drwx------ 2 root root 16384 7月 20 20:18 lost+found
[kefu2@web u7]$ touch file{1..8}
[kefu2@web u7]$ ls
aquota.group aquota.user file1 file2 file3 file4 file5 file6 file7 file8 lost+found
[kefu2@web u7]$ touch file{9..11}
dm-7: warning, user file quota exceeded.
[kefu2@web u7]$ ll
总用量 32
-rw------- 1 root root 7168 7月 23 23:08 aquota.group
-rw------- 1 root root 7168 7月 23 23:08 aquota.user
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kefu2 kefu2 0 7月 23 23:52 file1
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kefu2 kefu2 0 7月 23 23:52 file10
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kefu2 kefu2 0 7月 23 23:52 file11
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kefu2 kefu2 0 7月 23 23:52 file2
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kefu2 kefu2 0 7月 23 23:52 file3
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kefu2 kefu2 0 7月 23 23:52 file4
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kefu2 kefu2 0 7月 23 23:52 file5
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kefu2 kefu2 0 7月 23 23:52 file6
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kefu2 kefu2 0 7月 23 23:52 file7
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kefu2 kefu2 0 7月 23 23:52 file8
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kefu2 kefu2 0 7月 23 23:52 file9
drwx------ 2 root root 16384 7月 20 20:18 lost+found
[kefu2@web u7]$ touch file{12..16}
dm-7: write failed, user file limit reached.
touch: 无法创建"file16": 超出磁盘限额
[kefu2@web u7]$ rm -f file *
rm: 无法删除"aquota.group": 不允许的操作
rm: 无法删除"aquota.user": 不允许的操作
rm: 无法删除"lost+found": 是一个目录
[kefu2@web u7]$ rm -f file*
[kefu2@web u7]$ ls
aquota.group aquota.user lost+found
[kefu2@web u7]$ dd if=/dev/zero of=/u7/file1 bs=1M count=11
dm-7: warning, user block quota exceeded.
记录了11+0 的读入
记录了11+0 的写出
11534336字节(12 MB)已复制,0.0178305 秒,647 MB/秒
[kefu2@web u7]$ ls
aquota.group aquota.user file1 lost+found
[kefu2@web u7]$ dd if=/dev/zero of=/u7/file2 bs=2M count=1
dm-7: write failed, user block limit reached.
dd: 写入"/u7/file2" 出错: 超出磁盘限额
记录了1+0 的读入
记录了0+0 的写出
1048576字节(1.0 MB)已复制,0.00197683 秒,530 MB/秒问题
[root@web caozx26]# df -h
文件系统 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点
devtmpfs 470M 0 470M 0% /dev
tmpfs 487M 0 487M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 487M 39M 448M 8% /run
tmpfs 487M 0 487M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/centos-root 17G 17G 618M 97% /
/dev/sda1 1014M 172M 843M 17% /boot
/dev/sr0 4.4G 4.4G 0 100% /mnt
tmpfs 98M 12K 98M 1% /run/user/42
tmpfs 98M 0 98M 0% /run/user/0
/dev/mapper/vg7-lv7 2.1G 6.0M 2.0G 1% /u7
/dev/mapper/vg_mysql-lv_mysql 7.8G 1.2G 6.2G 17% /usr/local/mysql
/dev/mapper/vg1-lv1 1.5G 35M 1.4G 3% /uc1
/dev/mapper/vg1-lv1--snap 1.5G 4.6M 1.4G 1% /mmt/lv1-snap
/dev/sdb2 976M 2.6M 907M 1% /u2
[root@web caozx26]# pvdisplay /dev/sdb2
WARNING: Ignoring duplicate config value: snapshot_autoextend_percentWARNING: Device for PV r1noGN-Dn5A-udh3-qROp-C2Tj-HSil-AMqIZX not found or rejected by a filter.Couldn't find device with uuid r1noGN-Dn5A-udh3-qROp-C2Tj-HSil-AMqIZX.Failed to find physical volume "/dev/sdb2".
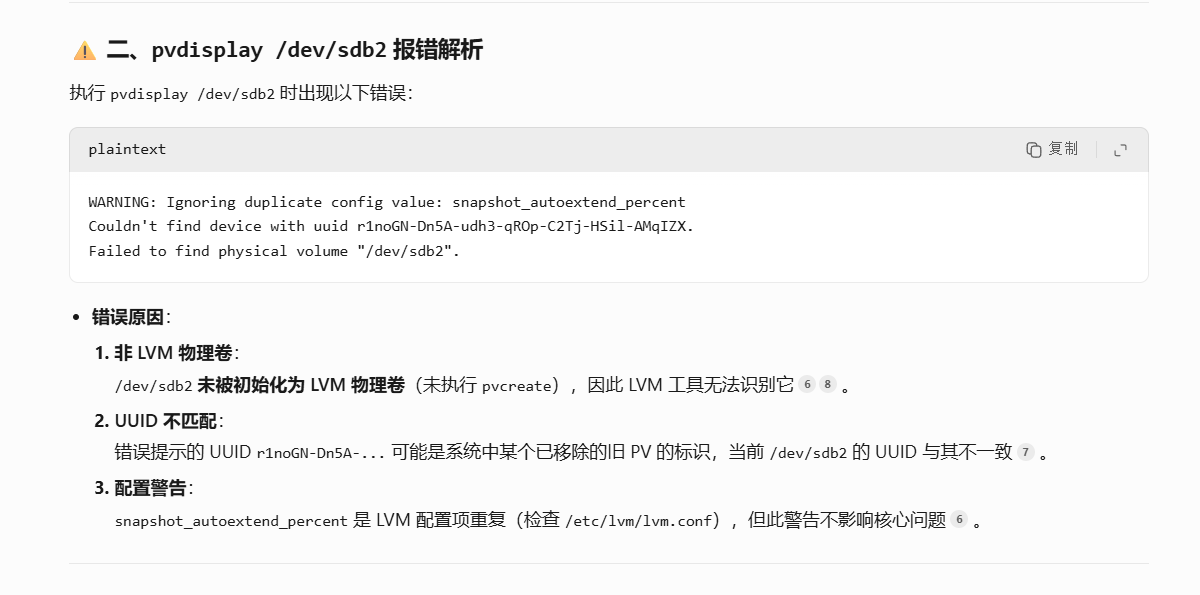
[root@web caozx26]# pvs
WARNING: Ignoring duplicate config value: snapshot_autoextend_percentWARNING: Device for PV r1noGN-Dn5A-udh3-qROp-C2Tj-HSil-AMqIZX not found or rejected by a filter.Couldn't find device with uuid r1noGN-Dn5A-udh3-qROp-C2Tj-HSil-AMqIZX.PV VG Fmt Attr PSize PFree/dev/sda2 centos lvm2 a-- <19.00g 0/dev/sdb5 vg01 lvm2 a-- 1020.00m 724.00m/dev/sdb6 vg01 lvm2 a-- 1020.00m 0/dev/sdb7 vg01 lvm2 a-- 1020.00m 40.00m/dev/sdb8 vg01 lvm2 a-- 1020.00m 0/dev/sdc1 vg_mysql lvm2 a-- <2.00g 0/dev/sdc2 vg_mysql lvm2 a-- <2.00g 0/dev/sdc5 vg_mysql lvm2 a-- <2.00g 0/dev/sdc6 vg_mysql lvm2 a-- <2.00g 0/dev/sdc7 vg_mysql lvm2 a-- 896.00m 880.00m/dev/sdd1 vg1 lvm2 a-- <2.00g <2.00g/dev/sdd2 vg1 lvm2 a-- <2.00g 376.00m/dev/sdd5 vg2 lvm2 a-- <2.00g <2.00g/dev/sdd7 vg7 lvm2 a-- <2.00g 0/dev/sdd8 vg7 lvm2 a-- <2.00g 708.00m[unknown] vg2 lvm2 a-m <2.00g <2.00g
[root@web caozx26]# lvs
WARNING: Ignoring duplicate config value: snapshot_autoextend_percentWARNING: Device for PV r1noGN-Dn5A-udh3-qROp-C2Tj-HSil-AMqIZX not found or rejected by a filter.Couldn't find device with uuid r1noGN-Dn5A-udh3-qROp-C2Tj-HSil-AMqIZX.LV VG Attr LSize Pool Origin Data% Meta% Move Log Cpy%Sync Convertroot centos -wi-ao---- <17.00gswap centos -wi-ao---- 2.00glv01 vg01 -wi-a----- <3.09glv02 vg01 -wi-a----- 120.00mlv03 vg01 -wi-a----- 36.00mlv1 vg1 owi-aor-r- 1.50g 100.00lv1-snap vg1 swi-aos--- 128.00m lv1 23.59lv7 vg7 -wi-ao---- <2.10glv8 vg7 -wi-a----- 1.20glv_mysql vg_mysql -wi-ao---- 8.00g
[root@web caozx26]# blkid /dev/sdb2
/dev/sdb2: UUID="faacf3c9-5c84-4fae-a3d2-f323d9cbc0ef" TYPE="ext4"
[root@web u2]# ls
aquota.group aquota.user lost+found
[root@web u2]# cd aquota.group
bash: cd: aquota.group: 不是目录
[root@web u2]# ls aquota.group
aquota.group
[root@web u2]# ll -d
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 7月 23 22:00 .
[root@web u2]# ls -d
.
[root@web u2]# ll
总用量 32
-rw------- 1 root root 6144 7月 23 22:00 aquota.group
-rw------- 1 root root 7168 7月 23 22:00 aquota.user
drwx------ 2 root root 16384 7月 13 21:58 lost+found
[root@web u2]# ls -l /u2
总用量 32
-rw------- 1 root root 6144 7月 23 22:00 aquota.group
-rw------- 1 root root 7168 7月 23 22:00 aquota.user
drwx------ 2 root root 16384 7月 13 21:58 lost+found
[root@web u2]#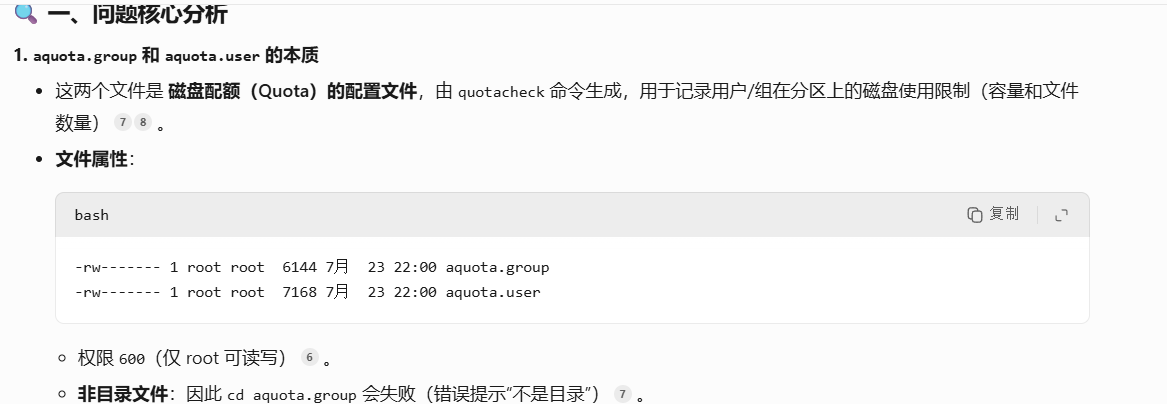
[root@web u2]# setenforce 0
setenforce: SELinux is disabled
[root@web u2]# sudo quota -u kefu /u2
Disk quotas for user kefu (uid 1022): no limited resources used
quota: user /u2 does not exist.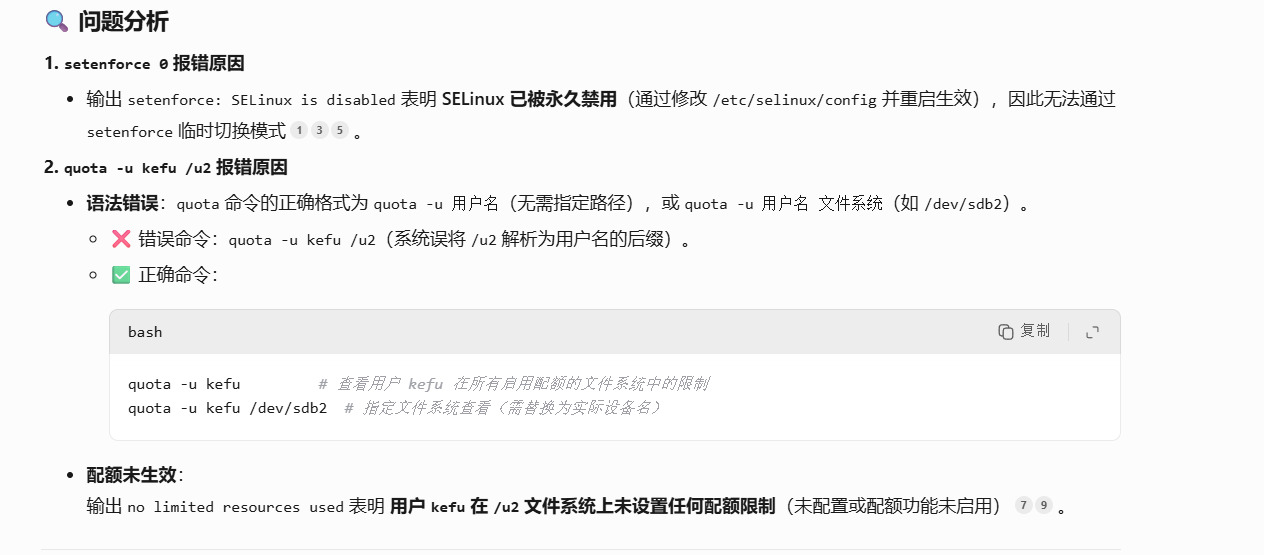
[root@web u2]# quota -u kefu
Disk quotas for user kefu (uid 1022): no limited resources used
[root@web u2]# mount |grep /u2
/dev/sdb2 on /u2 type ext4 (rw,relatime,quota,usrquota,grpquota,data=ordered)
[root@web caozx26]# mount |grep u7
/dev/mapper/vg7-lv7 on /u7 type ext4 (rw,relatime,quota,usrquota,grpquota,data=ordered)
[root@web caozx26]# ll /u7
总用量 16
drwx------ 2 root root 16384 7月 20 20:18 lost+found
[root@web caozx26]# quotacheck -acug
quotacheck: Quota for users is enabled on mountpoint /u2 so quotacheck might damage the file.
Please turn quotas off or use -f to force checking.
[root@web caozx26]# ll /u7
总用量 16
drwx------ 2 root root 16384 7月 20 20:18 lost+found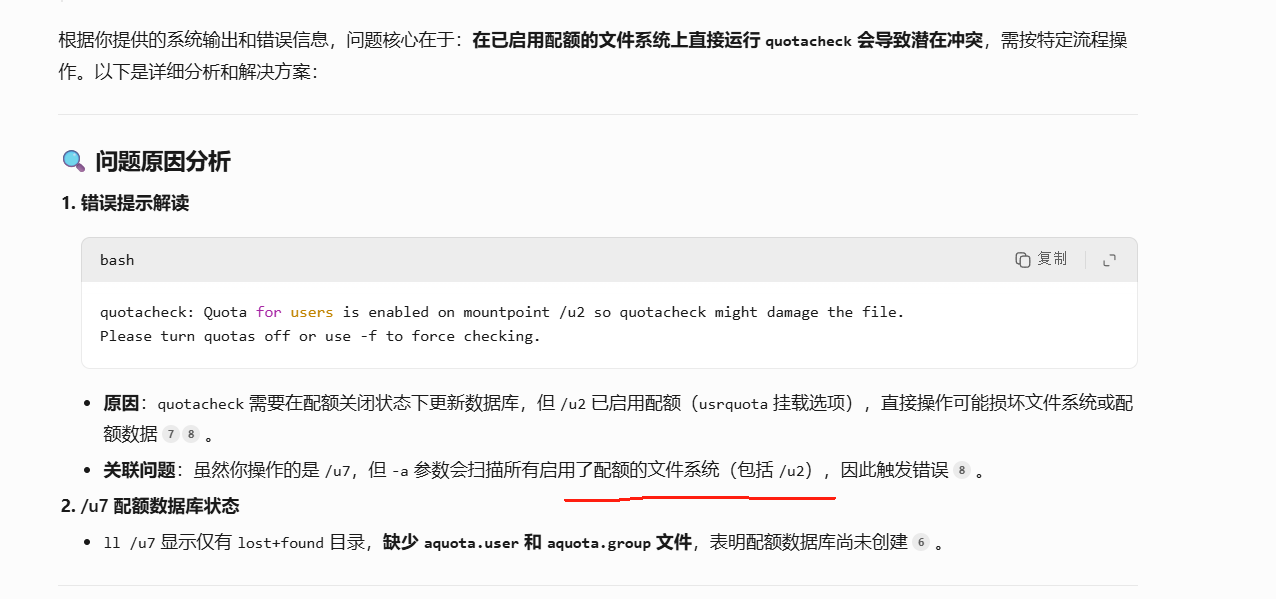
[root@web caozx26]# vim /etc/fstab
[root@web caozx26]# cat /etc/fstab#
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Sat Apr 19 17:11:28 2025
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
# See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info
#
/dev/mapper/centos-root / xfs defaults 0 0
UUID=0671af2f-69a1-4a84-bb51-ceb937bc1a92 /boot xfs defaults 0 0
/dev/mapper/centos-swap swap swap defaults 0 0
/dev/sdb2 /u2 ext4 defaults 0 0
/dev/sdd6 swap swap defaults 0 0
/tmp/swapfile swap swap defaults,pir=1 0 0
/dev/vg7/lv7 /u7 ext4 defaults,usrquota,grpquota 0 0
[root@web caozx26]# mount -a
[root@web caozx26]# mount |grep u7
/dev/mapper/vg7-lv7 on /u7 type ext4 (rw,relatime,quota,usrquota,grpquota,data=ordered)
[root@web caozx26]# quotacheck -acug
quotacheck: Quota for users is enabled on mountpoint /u2 so quotacheck might damage the file.
Please turn quotas off or use -f to force checking.
[root@web caozx26]# quota -uvs kefu2
Disk quotas for user kefu2 (uid 1023):Filesystem space quota limit grace files quota limit grace/dev/sdb2 0K 0K 0K 0 0 0
/dev/mapper/vg7-lv70K 10240K 12288K 0 10 15
[root@web caozx26]# su - kefu2
[kefu2@web ~]$ dd if=/dev/zero of=test99 bs=1M count=11
记录了11+0 的读入
记录了11+0 的写出
11534336字节(12 MB)已复制,0.00745521 秒,1.5 GB/秒
[kefu2@web ~]$ dd if=/dev/zero of=test99 bs=1M count=13
记录了13+0 的读入
记录了13+0 的写出
13631488字节(14 MB)已复制,0.0136268 秒,1.0 GB/秒
[kefu2@web ~]$ ls
test99
[kefu2@web ~]$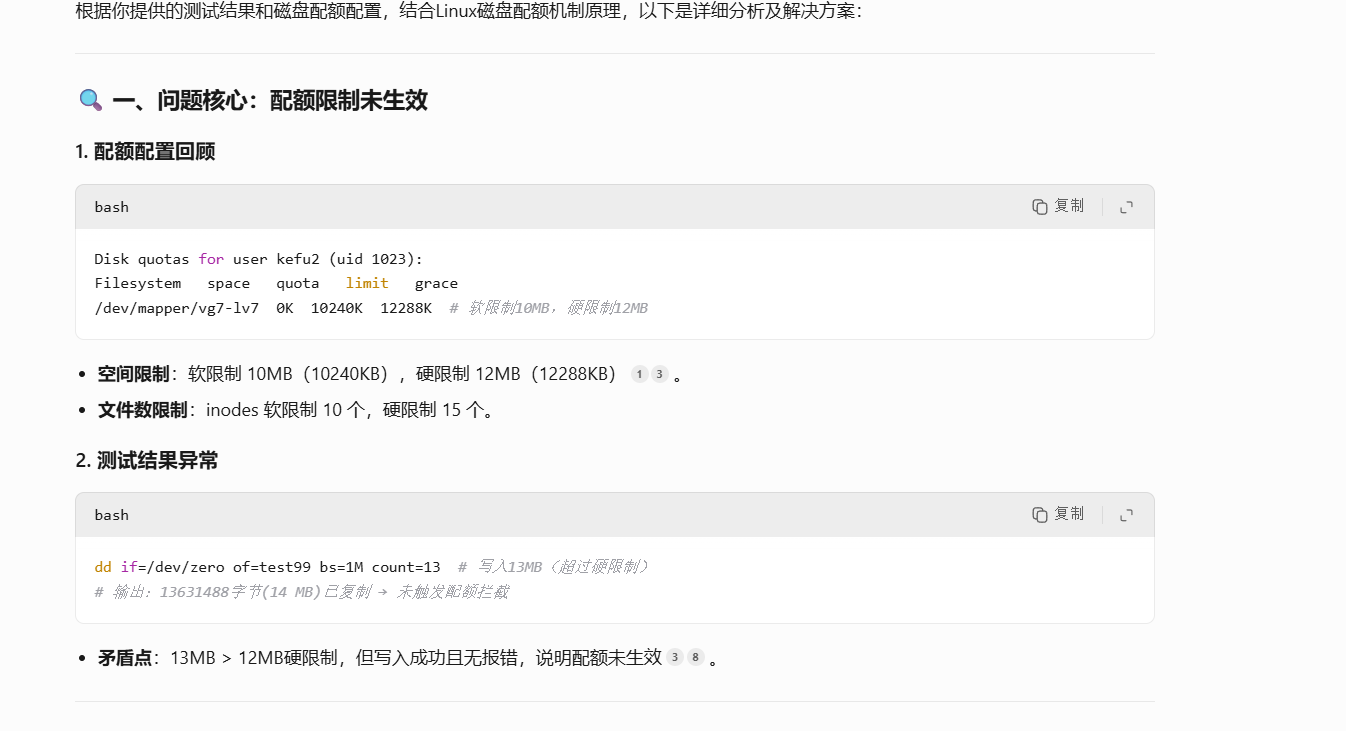
记录

root@192.168.235.20's password:┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐│ • MobaXterm 20.0 • ││ (SSH client, X-server and networking tools) ││ ││ ➤ SSH session to root@192.168.235.20 ││ • SSH compression : ✘ ││ • SSH-browser : ✔ ││ • X11-forwarding : ✔ (remote display is forwarded through SSH) ││ • DISPLAY : ✔ (automatically set on remote server) ││ ││ ➤ For more info, ctrl+click on help or visit our website │└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘Last login: Tue Jul 22 19:17:27 2025 from 192.168.235.1
[root@web ~]# cat /etc/lvm/lvm.conf
# This is an example configuration file for the LVM2 system.
# It contains the default settings that would be used if there was no
# /etc/lvm/lvm.conf file.
#
# Refer to 'man lvm.conf' for further information including the file layout.
#
# Refer to 'man lvm.conf' for information about how settings configured in
# this file are combined with built-in values and command line options to
# arrive at the final values used by LVM.
#
# Refer to 'man lvmconfig' for information about displaying the built-in
# and configured values used by LVM.
#
# If a default value is set in this file (not commented out), then a
# new version of LVM using this file will continue using that value,
# even if the new version of LVM changes the built-in default value.
#
# To put this file in a different directory and override /etc/lvm set
# the environment variable LVM_SYSTEM_DIR before running the tools.
#
# N.B. Take care that each setting only appears once if uncommenting
# example settings in this file.# Configuration section config.
# How LVM configuration settings are handled.
config {# Configuration option config/checks.# If enabled, any LVM configuration mismatch is reported.# This implies checking that the configuration key is understood by# LVM and that the value of the key is the proper type. If disabled,# any configuration mismatch is ignored and the default value is used# without any warning (a message about the configuration key not being# found is issued in verbose mode only).checks = 1# Configuration option config/abort_on_errors.# Abort the LVM process if a configuration mismatch is found.abort_on_errors = 0# Configuration option config/profile_dir.# Directory where LVM looks for configuration profiles.profile_dir = "/etc/lvm/profile"
}# Configuration section devices.
# How LVM uses block devices.
devices {# Configuration option devices/dir.# Directory in which to create volume group device nodes.# Commands also accept this as a prefix on volume group names.# This configuration option is advanced.dir = "/dev"# Configuration option devices/scan.# Directories containing device nodes to use with LVM.# This configuration option is advanced.scan = [ "/dev" ]# Configuration option devices/obtain_device_list_from_udev.# Obtain the list of available devices from udev.# This avoids opening or using any inapplicable non-block devices or# subdirectories found in the udev directory. Any device node or# symlink not managed by udev in the udev directory is ignored. This# setting applies only to the udev-managed device directory; other# directories will be scanned fully. LVM needs to be compiled with# udev support for this setting to apply.obtain_device_list_from_udev = 1# Configuration option devices/external_device_info_source.# Select an external device information source.# Some information may already be available in the system and LVM can# use this information to determine the exact type or use of devices it# processes. Using an existing external device information source can# speed up device processing as LVM does not need to run its own native# routines to acquire this information. For example, this information# is used to drive LVM filtering like MD component detection, multipath# component detection, partition detection and others.## Accepted values:# none# No external device information source is used.# udev# Reuse existing udev database records. Applicable only if LVM is# compiled with udev support.#external_device_info_source = "none"# Configuration option devices/preferred_names.# Select which path name to display for a block device.# If multiple path names exist for a block device, and LVM needs to# display a name for the device, the path names are matched against# each item in this list of regular expressions. The first match is# used. Try to avoid using undescriptive /dev/dm-N names, if present.# If no preferred name matches, or if preferred_names are not defined,# the following built-in preferences are applied in order until one# produces a preferred name:# Prefer names with path prefixes in the order of:# /dev/mapper, /dev/disk, /dev/dm-*, /dev/block.# Prefer the name with the least number of slashes.# Prefer a name that is a symlink.# Prefer the path with least value in lexicographical order.## Example# preferred_names = [ "^/dev/mpath/", "^/dev/mapper/mpath", "^/dev/[hs]d" ]#preferred_names = [ "^/dev/mpath/", "^/dev/mapper/mpath", "^/dev/[hs]d" ]# Configuration option devices/filter.# Limit the block devices that are used by LVM commands.# This is a list of regular expressions used to accept or reject block# device path names. Each regex is delimited by a vertical bar '|'# (or any character) and is preceded by 'a' to accept the path, or# by 'r' to reject the path. The first regex in the list to match the# path is used, producing the 'a' or 'r' result for the device.# When multiple path names exist for a block device, if any path name# matches an 'a' pattern before an 'r' pattern, then the device is# accepted. If all the path names match an 'r' pattern first, then the# device is rejected. Unmatching path names do not affect the accept# or reject decision. If no path names for a device match a pattern,# then the device is accepted. Be careful mixing 'a' and 'r' patterns,# as the combination might produce unexpected results (test changes.)# Run vgscan after changing the filter to regenerate the cache.# See the use_lvmetad comment for a special case regarding filters.## Example# Accept every block device:# filter = [ "a|.*/|" ]# Reject the cdrom drive:# filter = [ "r|/dev/cdrom|" ]# Work with just loopback devices, e.g. for testing:# filter = [ "a|loop|", "r|.*|" ]# Accept all loop devices and ide drives except hdc:# filter = [ "a|loop|", "r|/dev/hdc|", "a|/dev/ide|", "r|.*|" ]# Use anchors to be very specific:# filter = [ "a|^/dev/hda8$|", "r|.*/|" ]## This configuration option has an automatic default value.# filter = [ "a|.*/|" ]# Configuration option devices/global_filter.# Limit the block devices that are used by LVM system components.# Because devices/filter may be overridden from the command line, it is# not suitable for system-wide device filtering, e.g. udev and lvmetad.# Use global_filter to hide devices from these LVM system components.# The syntax is the same as devices/filter. Devices rejected by# global_filter are not opened by LVM.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# global_filter = [ "a|.*/|" ]# Configuration option devices/cache_dir.# Directory in which to store the device cache file.# The results of filtering are cached on disk to avoid rescanning dud# devices (which can take a very long time). By default this cache is# stored in a file named .cache. It is safe to delete this file; the# tools regenerate it. If obtain_device_list_from_udev is enabled, the# list of devices is obtained from udev and any existing .cache file# is removed.cache_dir = "/etc/lvm/cache"# Configuration option devices/cache_file_prefix.# A prefix used before the .cache file name. See devices/cache_dir.cache_file_prefix = ""# Configuration option devices/write_cache_state.# Enable/disable writing the cache file. See devices/cache_dir.write_cache_state = 1# Configuration option devices/types.# List of additional acceptable block device types.# These are of device type names from /proc/devices, followed by the# maximum number of partitions.## Example# types = [ "fd", 16 ]## This configuration option is advanced.# This configuration option does not have a default value defined.# Configuration option devices/sysfs_scan.# Restrict device scanning to block devices appearing in sysfs.# This is a quick way of filtering out block devices that are not# present on the system. sysfs must be part of the kernel and mounted.)sysfs_scan = 1# Configuration option devices/scan_lvs.# Scan LVM LVs for layered PVs, allowing LVs to be used as PVs.# When 1, LVM will detect PVs layered on LVs, and caution must be# taken to avoid a host accessing a layered VG that may not belong# to it, e.g. from a guest image. This generally requires excluding# the LVs with device filters. Also, when this setting is enabled,# every LVM command will scan every active LV on the system (unless# filtered), which can cause performance problems on systems with# many active LVs. When this setting is 0, LVM will not detect or# use PVs that exist on LVs, and will not allow a PV to be created on# an LV. The LVs are ignored using a built in device filter that# identifies and excludes LVs.scan_lvs = 0# Configuration option devices/multipath_component_detection.# Ignore devices that are components of DM multipath devices.multipath_component_detection = 1# Configuration option devices/md_component_detection.# Ignore devices that are components of software RAID (md) devices.md_component_detection = 1# Configuration option devices/fw_raid_component_detection.# Ignore devices that are components of firmware RAID devices.# LVM must use an external_device_info_source other than none for this# detection to execute.fw_raid_component_detection = 0# Configuration option devices/md_chunk_alignment.# Align PV data blocks with md device's stripe-width.# This applies if a PV is placed directly on an md device.md_chunk_alignment = 1# Configuration option devices/default_data_alignment.# Default alignment of the start of a PV data area in MB.# If set to 0, a value of 64KiB will be used.# Set to 1 for 1MiB, 2 for 2MiB, etc.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# default_data_alignment = 1# Configuration option devices/data_alignment_detection.# Detect PV data alignment based on sysfs device information.# The start of a PV data area will be a multiple of minimum_io_size or# optimal_io_size exposed in sysfs. minimum_io_size is the smallest# request the device can perform without incurring a read-modify-write# penalty, e.g. MD chunk size. optimal_io_size is the device's# preferred unit of receiving I/O, e.g. MD stripe width.# minimum_io_size is used if optimal_io_size is undefined (0).# If md_chunk_alignment is enabled, that detects the optimal_io_size.# This setting takes precedence over md_chunk_alignment.data_alignment_detection = 1# Configuration option devices/data_alignment.# Alignment of the start of a PV data area in KiB.# If a PV is placed directly on an md device and md_chunk_alignment or# data_alignment_detection are enabled, then this setting is ignored.# Otherwise, md_chunk_alignment and data_alignment_detection are# disabled if this is set. Set to 0 to use the default alignment or the# page size, if larger.data_alignment = 0# Configuration option devices/data_alignment_offset_detection.# Detect PV data alignment offset based on sysfs device information.# The start of a PV aligned data area will be shifted by the# alignment_offset exposed in sysfs. This offset is often 0, but may# be non-zero. Certain 4KiB sector drives that compensate for windows# partitioning will have an alignment_offset of 3584 bytes (sector 7# is the lowest aligned logical block, the 4KiB sectors start at# LBA -1, and consequently sector 63 is aligned on a 4KiB boundary).# pvcreate --dataalignmentoffset will skip this detection.data_alignment_offset_detection = 1# Configuration option devices/ignore_suspended_devices.# Ignore DM devices that have I/O suspended while scanning devices.# Otherwise, LVM waits for a suspended device to become accessible.# This should only be needed in recovery situations.ignore_suspended_devices = 0# Configuration option devices/ignore_lvm_mirrors.# Do not scan 'mirror' LVs to avoid possible deadlocks.# This avoids possible deadlocks when using the 'mirror' segment type.# This setting determines whether LVs using the 'mirror' segment type# are scanned for LVM labels. This affects the ability of mirrors to# be used as physical volumes. If this setting is enabled, it is# impossible to create VGs on top of mirror LVs, i.e. to stack VGs on# mirror LVs. If this setting is disabled, allowing mirror LVs to be# scanned, it may cause LVM processes and I/O to the mirror to become# blocked. This is due to the way that the mirror segment type handles# failures. In order for the hang to occur, an LVM command must be run# just after a failure and before the automatic LVM repair process# takes place, or there must be failures in multiple mirrors in the# same VG at the same time with write failures occurring moments before# a scan of the mirror's labels. The 'mirror' scanning problems do not# apply to LVM RAID types like 'raid1' which handle failures in a# different way, making them a better choice for VG stacking.ignore_lvm_mirrors = 1# Configuration option devices/disable_after_error_count.# Number of I/O errors after which a device is skipped.# During each LVM operation, errors received from each device are# counted. If the counter of a device exceeds the limit set here,# no further I/O is sent to that device for the remainder of the# operation. Setting this to 0 disables the counters altogether.disable_after_error_count = 0# Configuration option devices/require_restorefile_with_uuid.# Allow use of pvcreate --uuid without requiring --restorefile.require_restorefile_with_uuid = 1# Configuration option devices/pv_min_size.# Minimum size in KiB of block devices which can be used as PVs.# In a clustered environment all nodes must use the same value.# Any value smaller than 512KiB is ignored. The previous built-in# value was 512.pv_min_size = 2048# Configuration option devices/issue_discards.# Issue discards to PVs that are no longer used by an LV.# Discards are sent to an LV's underlying physical volumes when the LV# is no longer using the physical volumes' space, e.g. lvremove,# lvreduce. Discards inform the storage that a region is no longer# used. Storage that supports discards advertise the protocol-specific# way discards should be issued by the kernel (TRIM, UNMAP, or# WRITE SAME with UNMAP bit set). Not all storage will support or# benefit from discards, but SSDs and thinly provisioned LUNs# generally do. If enabled, discards will only be issued if both the# storage and kernel provide support.issue_discards = 0# Configuration option devices/allow_changes_with_duplicate_pvs.# Allow VG modification while a PV appears on multiple devices.# When a PV appears on multiple devices, LVM attempts to choose the# best device to use for the PV. If the devices represent the same# underlying storage, the choice has minimal consequence. If the# devices represent different underlying storage, the wrong choice# can result in data loss if the VG is modified. Disabling this# setting is the safest option because it prevents modifying a VG# or activating LVs in it while a PV appears on multiple devices.# Enabling this setting allows the VG to be used as usual even with# uncertain devices.allow_changes_with_duplicate_pvs = 1# Configuration option devices/allow_mixed_block_sizes.# Allow PVs in the same VG with different logical block sizes.# When allowed, the user is responsible to ensure that an LV is# using PVs with matching block sizes when necessary.allow_mixed_block_sizes = 1
}# Configuration section allocation.
# How LVM selects space and applies properties to LVs.
allocation {# Configuration option allocation/cling_tag_list.# Advise LVM which PVs to use when searching for new space.# When searching for free space to extend an LV, the 'cling' allocation# policy will choose space on the same PVs as the last segment of the# existing LV. If there is insufficient space and a list of tags is# defined here, it will check whether any of them are attached to the# PVs concerned and then seek to match those PV tags between existing# extents and new extents.## Example# Use the special tag "@*" as a wildcard to match any PV tag:# cling_tag_list = [ "@*" ]# LVs are mirrored between two sites within a single VG, and# PVs are tagged with either @site1 or @site2 to indicate where# they are situated:# cling_tag_list = [ "@site1", "@site2" ]## This configuration option does not have a default value defined.# Configuration option allocation/maximise_cling.# Use a previous allocation algorithm.# Changes made in version 2.02.85 extended the reach of the 'cling'# policies to detect more situations where data can be grouped onto# the same disks. This setting can be used to disable the changes# and revert to the previous algorithm.maximise_cling = 1# Configuration option allocation/use_blkid_wiping.# Use blkid to detect existing signatures on new PVs and LVs.# The blkid library can detect more signatures than the native LVM# detection code, but may take longer. LVM needs to be compiled with# blkid wiping support for this setting to apply. LVM native detection# code is currently able to recognize: MD device signatures,# swap signature, and LUKS signatures. To see the list of signatures# recognized by blkid, check the output of the 'blkid -k' command.use_blkid_wiping = 1# Configuration option allocation/wipe_signatures_when_zeroing_new_lvs.# Look for and erase any signatures while zeroing a new LV.# The --wipesignatures option overrides this setting.# Zeroing is controlled by the -Z/--zero option, and if not specified,# zeroing is used by default if possible. Zeroing simply overwrites the# first 4KiB of a new LV with zeroes and does no signature detection or# wiping. Signature wiping goes beyond zeroing and detects exact types# and positions of signatures within the whole LV. It provides a# cleaner LV after creation as all known signatures are wiped. The LV# is not claimed incorrectly by other tools because of old signatures# from previous use. The number of signatures that LVM can detect# depends on the detection code that is selected (see# use_blkid_wiping.) Wiping each detected signature must be confirmed.# When this setting is disabled, signatures on new LVs are not detected# or erased unless the --wipesignatures option is used directly.wipe_signatures_when_zeroing_new_lvs = 1# Configuration option allocation/mirror_logs_require_separate_pvs.# Mirror logs and images will always use different PVs.# The default setting changed in version 2.02.85.mirror_logs_require_separate_pvs = 0# Configuration option allocation/raid_stripe_all_devices.# Stripe across all PVs when RAID stripes are not specified.# If enabled, all PVs in the VG or on the command line are used for# raid0/4/5/6/10 when the command does not specify the number of# stripes to use.# This was the default behaviour until release 2.02.162.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# raid_stripe_all_devices = 0# Configuration option allocation/cache_pool_metadata_require_separate_pvs.# Cache pool metadata and data will always use different PVs.cache_pool_metadata_require_separate_pvs = 0# Configuration option allocation/cache_metadata_format.# Sets default metadata format for new cache.## Accepted values:# 0 Automatically detected best available format# 1 Original format# 2 Improved 2nd. generation format## This configuration option has an automatic default value.# cache_metadata_format = 0# Configuration option allocation/cache_mode.# The default cache mode used for new cache.## Accepted values:# writethrough# Data blocks are immediately written from the cache to disk.# writeback# Data blocks are written from the cache back to disk after some# delay to improve performance.## This setting replaces allocation/cache_pool_cachemode.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# cache_mode = "writethrough"# Configuration option allocation/cache_policy.# The default cache policy used for new cache volume.# Since kernel 4.2 the default policy is smq (Stochastic multiqueue),# otherwise the older mq (Multiqueue) policy is selected.# This configuration option does not have a default value defined.# Configuration section allocation/cache_settings.# Settings for the cache policy.# See documentation for individual cache policies for more info.# This configuration section has an automatic default value.# cache_settings {# }# Configuration option allocation/cache_pool_chunk_size.# The minimal chunk size in KiB for cache pool volumes.# Using a chunk_size that is too large can result in wasteful use of# the cache, where small reads and writes can cause large sections of# an LV to be mapped into the cache. However, choosing a chunk_size# that is too small can result in more overhead trying to manage the# numerous chunks that become mapped into the cache. The former is# more of a problem than the latter in most cases, so the default is# on the smaller end of the spectrum. Supported values range from# 32KiB to 1GiB in multiples of 32.# This configuration option does not have a default value defined.# Configuration option allocation/cache_pool_max_chunks.# The maximum number of chunks in a cache pool.# For cache target v1.9 the recommended maximumm is 1000000 chunks.# Using cache pool with more chunks may degrade cache performance.# This configuration option does not have a default value defined.# Configuration option allocation/thin_pool_metadata_require_separate_pvs.# Thin pool metdata and data will always use different PVs.thin_pool_metadata_require_separate_pvs = 0# Configuration option allocation/thin_pool_zero.# Thin pool data chunks are zeroed before they are first used.# Zeroing with a larger thin pool chunk size reduces performance.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# thin_pool_zero = 1# Configuration option allocation/thin_pool_discards.# The discards behaviour of thin pool volumes.## Accepted values:# ignore# nopassdown# passdown## This configuration option has an automatic default value.# thin_pool_discards = "passdown"# Configuration option allocation/thin_pool_chunk_size_policy.# The chunk size calculation policy for thin pool volumes.## Accepted values:# generic# If thin_pool_chunk_size is defined, use it. Otherwise, calculate# the chunk size based on estimation and device hints exposed in# sysfs - the minimum_io_size. The chunk size is always at least# 64KiB.# performance# If thin_pool_chunk_size is defined, use it. Otherwise, calculate# the chunk size for performance based on device hints exposed in# sysfs - the optimal_io_size. The chunk size is always at least# 512KiB.## This configuration option has an automatic default value.# thin_pool_chunk_size_policy = "generic"# Configuration option allocation/thin_pool_chunk_size.# The minimal chunk size in KiB for thin pool volumes.# Larger chunk sizes may improve performance for plain thin volumes,# however using them for snapshot volumes is less efficient, as it# consumes more space and takes extra time for copying. When unset,# lvm tries to estimate chunk size starting from 64KiB. Supported# values are in the range 64KiB to 1GiB.# This configuration option does not have a default value defined.# Configuration option allocation/physical_extent_size.# Default physical extent size in KiB to use for new VGs.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# physical_extent_size = 4096
}# Configuration section log.
# How LVM log information is reported.
log {# Configuration option log/report_command_log.# Enable or disable LVM log reporting.# If enabled, LVM will collect a log of operations, messages,# per-object return codes with object identification and associated# error numbers (errnos) during LVM command processing. Then the# log is either reported solely or in addition to any existing# reports, depending on LVM command used. If it is a reporting command# (e.g. pvs, vgs, lvs, lvm fullreport), then the log is reported in# addition to any existing reports. Otherwise, there's only log report# on output. For all applicable LVM commands, you can request that# the output has only log report by using --logonly command line# option. Use log/command_log_cols and log/command_log_sort settings# to define fields to display and sort fields for the log report.# You can also use log/command_log_selection to define selection# criteria used each time the log is reported.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# report_command_log = 0# Configuration option log/command_log_sort.# List of columns to sort by when reporting command log.# See <lvm command> --logonly --configreport log -o help# for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# command_log_sort = "log_seq_num"# Configuration option log/command_log_cols.# List of columns to report when reporting command log.# See <lvm command> --logonly --configreport log -o help# for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# command_log_cols = "log_seq_num,log_type,log_context,log_object_type,log_object_name,log_object_id,log_object_group,log_object_group_id,log_message,log_errno,log_ret_code"# Configuration option log/command_log_selection.# Selection criteria used when reporting command log.# You can define selection criteria that are applied each# time log is reported. This way, it is possible to control the# amount of log that is displayed on output and you can select# only parts of the log that are important for you. To define# selection criteria, use fields from log report. See also# <lvm command> --logonly --configreport log -S help for the# list of possible fields and selection operators. You can also# define selection criteria for log report on command line directly# using <lvm command> --configreport log -S <selection criteria># which has precedence over log/command_log_selection setting.# For more information about selection criteria in general, see# lvm(8) man page.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# command_log_selection = "!(log_type=status && message=success)"# Configuration option log/verbose.# Controls the messages sent to stdout or stderr.verbose = 0# Configuration option log/silent.# Suppress all non-essential messages from stdout.# This has the same effect as -qq. When enabled, the following commands# still produce output: dumpconfig, lvdisplay, lvmdiskscan, lvs, pvck,# pvdisplay, pvs, version, vgcfgrestore -l, vgdisplay, vgs.# Non-essential messages are shifted from log level 4 to log level 5# for syslog and lvm2_log_fn purposes.# Any 'yes' or 'no' questions not overridden by other arguments are# suppressed and default to 'no'.silent = 0# Configuration option log/syslog.# Send log messages through syslog.syslog = 1# Configuration option log/file.# Write error and debug log messages to a file specified here.# This configuration option does not have a default value defined.# Configuration option log/overwrite.# Overwrite the log file each time the program is run.overwrite = 0# Configuration option log/level.# The level of log messages that are sent to the log file or syslog.# There are 6 syslog-like log levels currently in use: 2 to 7 inclusive.# 7 is the most verbose (LOG_DEBUG).level = 0# Configuration option log/indent.# Indent messages according to their severity.indent = 1# Configuration option log/command_names.# Display the command name on each line of output.command_names = 0# Configuration option log/prefix.# A prefix to use before the log message text.# (After the command name, if selected).# Two spaces allows you to see/grep the severity of each message.# To make the messages look similar to the original LVM tools use:# indent = 0, command_names = 1, prefix = " -- "prefix = " "# Configuration option log/activation.# Log messages during activation.# Don't use this in low memory situations (can deadlock).activation = 0# Configuration option log/debug_classes.# Select log messages by class.# Some debugging messages are assigned to a class and only appear in# debug output if the class is listed here. Classes currently# available: memory, devices, io, activation, allocation, lvmetad,# metadata, cache, locking, lvmpolld. Use "all" to see everything.debug_classes = [ "memory", "devices", "io", "activation", "allocation", "lvmetad", "metadata", "cache", "locking", "lvmpolld", "dbus" ]
}# Configuration section backup.
# How LVM metadata is backed up and archived.
# In LVM, a 'backup' is a copy of the metadata for the current system,
# and an 'archive' contains old metadata configurations. They are
# stored in a human readable text format.
backup {# Configuration option backup/backup.# Maintain a backup of the current metadata configuration.# Think very hard before turning this off!backup = 1# Configuration option backup/backup_dir.# Location of the metadata backup files.# Remember to back up this directory regularly!backup_dir = "/etc/lvm/backup"# Configuration option backup/archive.# Maintain an archive of old metadata configurations.# Think very hard before turning this off.archive = 1# Configuration option backup/archive_dir.# Location of the metdata archive files.# Remember to back up this directory regularly!archive_dir = "/etc/lvm/archive"# Configuration option backup/retain_min.# Minimum number of archives to keep.retain_min = 10# Configuration option backup/retain_days.# Minimum number of days to keep archive files.retain_days = 30
}# Configuration section shell.
# Settings for running LVM in shell (readline) mode.
shell {# Configuration option shell/history_size.# Number of lines of history to store in ~/.lvm_history.history_size = 100
}# Configuration section global.
# Miscellaneous global LVM settings.
global {# Configuration option global/umask.# The file creation mask for any files and directories created.# Interpreted as octal if the first digit is zero.umask = 077# Configuration option global/test.# No on-disk metadata changes will be made in test mode.# Equivalent to having the -t option on every command.test = 0# Configuration option global/units.# Default value for --units argument.units = "r"# Configuration option global/si_unit_consistency.# Distinguish between powers of 1024 and 1000 bytes.# The LVM commands distinguish between powers of 1024 bytes,# e.g. KiB, MiB, GiB, and powers of 1000 bytes, e.g. KB, MB, GB.# If scripts depend on the old behaviour, disable this setting# temporarily until they are updated.si_unit_consistency = 1# Configuration option global/suffix.# Display unit suffix for sizes.# This setting has no effect if the units are in human-readable form# (global/units = "h") in which case the suffix is always displayed.suffix = 1# Configuration option global/activation.# Enable/disable communication with the kernel device-mapper.# Disable to use the tools to manipulate LVM metadata without# activating any logical volumes. If the device-mapper driver# is not present in the kernel, disabling this should suppress# the error messages.activation = 1# Configuration option global/fallback_to_lvm1.# Try running LVM1 tools if LVM cannot communicate with DM.# This option only applies to 2.4 kernels and is provided to help# switch between device-mapper kernels and LVM1 kernels. The LVM1# tools need to be installed with .lvm1 suffices, e.g. vgscan.lvm1.# They will stop working once the lvm2 on-disk metadata format is used.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# fallback_to_lvm1 = 1# Configuration option global/format.# The default metadata format that commands should use.# The -M 1|2 option overrides this setting.## Accepted values:# lvm1# lvm2## This configuration option has an automatic default value.# format = "lvm2"# Configuration option global/format_libraries.# Shared libraries that process different metadata formats.# If support for LVM1 metadata was compiled as a shared library use# format_libraries = "liblvm2format1.so"# This configuration option does not have a default value defined.# Configuration option global/segment_libraries.# This configuration option does not have a default value defined.# Configuration option global/proc.# Location of proc filesystem.# This configuration option is advanced.proc = "/proc"# Configuration option global/etc.# Location of /etc system configuration directory.etc = "/etc"# Configuration option global/locking_type.# Type of locking to use.## Accepted values:# 0# Turns off locking. Warning: this risks metadata corruption if# commands run concurrently.# 1# LVM uses local file-based locking, the standard mode.# 2# LVM uses the external shared library locking_library.# 3# LVM uses built-in clustered locking with clvmd.# This is incompatible with lvmetad. If use_lvmetad is enabled,# LVM prints a warning and disables lvmetad use.# 4# LVM uses read-only locking which forbids any operations that# might change metadata.# 5# Offers dummy locking for tools that do not need any locks.# You should not need to set this directly; the tools will select# when to use it instead of the configured locking_type.# Do not use lvmetad or the kernel device-mapper driver with this# locking type. It is used by the --readonly option that offers# read-only access to Volume Group metadata that cannot be locked# safely because it belongs to an inaccessible domain and might be# in use, for example a virtual machine image or a disk that is# shared by a clustered machine.#locking_type = 1# Configuration option global/wait_for_locks.# When disabled, fail if a lock request would block.wait_for_locks = 1# Configuration option global/fallback_to_clustered_locking.# Attempt to use built-in cluster locking if locking_type 2 fails.# If using external locking (type 2) and initialisation fails, with# this enabled, an attempt will be made to use the built-in clustered# locking. Disable this if using a customised locking_library.fallback_to_clustered_locking = 1# Configuration option global/fallback_to_local_locking.# Use locking_type 1 (local) if locking_type 2 or 3 fail.# If an attempt to initialise type 2 or type 3 locking failed, perhaps# because cluster components such as clvmd are not running, with this# enabled, an attempt will be made to use local file-based locking# (type 1). If this succeeds, only commands against local VGs will# proceed. VGs marked as clustered will be ignored.fallback_to_local_locking = 1# Configuration option global/locking_dir.# Directory to use for LVM command file locks.# Local non-LV directory that holds file-based locks while commands are# in progress. A directory like /tmp that may get wiped on reboot is OK.locking_dir = "/run/lock/lvm"# Configuration option global/prioritise_write_locks.# Allow quicker VG write access during high volume read access.# When there are competing read-only and read-write access requests for# a volume group's metadata, instead of always granting the read-only# requests immediately, delay them to allow the read-write requests to# be serviced. Without this setting, write access may be stalled by a# high volume of read-only requests. This option only affects# locking_type 1 viz. local file-based locking.prioritise_write_locks = 1# Configuration option global/library_dir.# Search this directory first for shared libraries.# This configuration option does not have a default value defined.# Configuration option global/locking_library.# The external locking library to use for locking_type 2.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# locking_library = "liblvm2clusterlock.so"# Configuration option global/abort_on_internal_errors.# Abort a command that encounters an internal error.# Treat any internal errors as fatal errors, aborting the process that# encountered the internal error. Please only enable for debugging.abort_on_internal_errors = 0# Configuration option global/metadata_read_only.# No operations that change on-disk metadata are permitted.# Additionally, read-only commands that encounter metadata in need of# repair will still be allowed to proceed exactly as if the repair had# been performed (except for the unchanged vg_seqno). Inappropriate# use could mess up your system, so seek advice first!metadata_read_only = 0# Configuration option global/mirror_segtype_default.# The segment type used by the short mirroring option -m.# The --type mirror|raid1 option overrides this setting.## Accepted values:# mirror# The original RAID1 implementation from LVM/DM. It is# characterized by a flexible log solution (core, disk, mirrored),# and by the necessity to block I/O while handling a failure.# There is an inherent race in the dmeventd failure handling logic# with snapshots of devices using this type of RAID1 that in the# worst case could cause a deadlock. (Also see# devices/ignore_lvm_mirrors.)# raid1# This is a newer RAID1 implementation using the MD RAID1# personality through device-mapper. It is characterized by a# lack of log options. (A log is always allocated for every# device and they are placed on the same device as the image,# so no separate devices are required.) This mirror# implementation does not require I/O to be blocked while# handling a failure. This mirror implementation is not# cluster-aware and cannot be used in a shared (active/active)# fashion in a cluster.#mirror_segtype_default = "raid1"# Configuration option global/raid10_segtype_default.# The segment type used by the -i -m combination.# The --type raid10|mirror option overrides this setting.# The --stripes/-i and --mirrors/-m options can both be specified# during the creation of a logical volume to use both striping and# mirroring for the LV. There are two different implementations.## Accepted values:# raid10# LVM uses MD's RAID10 personality through DM. This is the# preferred option.# mirror# LVM layers the 'mirror' and 'stripe' segment types. The layering# is done by creating a mirror LV on top of striped sub-LVs,# effectively creating a RAID 0+1 array. The layering is suboptimal# in terms of providing redundancy and performance.#raid10_segtype_default = "raid10"# Configuration option global/sparse_segtype_default.# The segment type used by the -V -L combination.# The --type snapshot|thin option overrides this setting.# The combination of -V and -L options creates a sparse LV. There are# two different implementations.## Accepted values:# snapshot# The original snapshot implementation from LVM/DM. It uses an old# snapshot that mixes data and metadata within a single COW# storage volume and performs poorly when the size of stored data# passes hundreds of MB.# thin# A newer implementation that uses thin provisioning. It has a# bigger minimal chunk size (64KiB) and uses a separate volume for# metadata. It has better performance, especially when more data# is used. It also supports full snapshots.#sparse_segtype_default = "thin"# Configuration option global/lvdisplay_shows_full_device_path.# Enable this to reinstate the previous lvdisplay name format.# The default format for displaying LV names in lvdisplay was changed# in version 2.02.89 to show the LV name and path separately.# Previously this was always shown as /dev/vgname/lvname even when that# was never a valid path in the /dev filesystem.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# lvdisplay_shows_full_device_path = 0# Configuration option global/use_aio.# Use async I/O when reading and writing devices.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# use_aio = 1# Configuration option global/use_lvmetad.# Use lvmetad to cache metadata and reduce disk scanning.# When enabled (and running), lvmetad provides LVM commands with VG# metadata and PV state. LVM commands then avoid reading this# information from disks which can be slow. When disabled (or not# running), LVM commands fall back to scanning disks to obtain VG# metadata. lvmetad is kept updated via udev rules which must be set# up for LVM to work correctly. (The udev rules should be installed# by default.) Without a proper udev setup, changes in the system's# block device configuration will be unknown to LVM, and ignored# until a manual 'pvscan --cache' is run. If lvmetad was running# while use_lvmetad was disabled, it must be stopped, use_lvmetad# enabled, and then started. When using lvmetad, LV activation is# switched to an automatic, event-based mode. In this mode, LVs are# activated based on incoming udev events that inform lvmetad when# PVs appear on the system. When a VG is complete (all PVs present),# it is auto-activated. The auto_activation_volume_list setting# controls which LVs are auto-activated (all by default.)# When lvmetad is updated (automatically by udev events, or directly# by pvscan --cache), devices/filter is ignored and all devices are# scanned by default. lvmetad always keeps unfiltered information# which is provided to LVM commands. Each LVM command then filters# based on devices/filter. This does not apply to other, non-regexp,# filtering settings: component filters such as multipath and MD# are checked during pvscan --cache. To filter a device and prevent# scanning from the LVM system entirely, including lvmetad, use# devices/global_filter.use_lvmetad = 1# Configuration option global/lvmetad_update_wait_time.# Number of seconds a command will wait for lvmetad update to finish.# After waiting for this period, a command will not use lvmetad, and# will revert to disk scanning.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# lvmetad_update_wait_time = 10# Configuration option global/use_lvmlockd.# Use lvmlockd for locking among hosts using LVM on shared storage.# Applicable only if LVM is compiled with lockd support in which# case there is also lvmlockd(8) man page available for more# information.use_lvmlockd = 0# Configuration option global/lvmlockd_lock_retries.# Retry lvmlockd lock requests this many times.# Applicable only if LVM is compiled with lockd support# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# lvmlockd_lock_retries = 3# Configuration option global/sanlock_lv_extend.# Size in MiB to extend the internal LV holding sanlock locks.# The internal LV holds locks for each LV in the VG, and after enough# LVs have been created, the internal LV needs to be extended. lvcreate# will automatically extend the internal LV when needed by the amount# specified here. Setting this to 0 disables the automatic extension# and can cause lvcreate to fail. Applicable only if LVM is compiled# with lockd support# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# sanlock_lv_extend = 256# Configuration option global/thin_check_executable.# The full path to the thin_check command.# LVM uses this command to check that a thin metadata device is in a# usable state. When a thin pool is activated and after it is# deactivated, this command is run. Activation will only proceed if# the command has an exit status of 0. Set to "" to skip this check.# (Not recommended.) Also see thin_check_options.# (See package device-mapper-persistent-data or thin-provisioning-tools)# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# thin_check_executable = "/usr/sbin/thin_check"# Configuration option global/thin_dump_executable.# The full path to the thin_dump command.# LVM uses this command to dump thin pool metadata.# (See package device-mapper-persistent-data or thin-provisioning-tools)# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# thin_dump_executable = "/usr/sbin/thin_dump"# Configuration option global/thin_repair_executable.# The full path to the thin_repair command.# LVM uses this command to repair a thin metadata device if it is in# an unusable state. Also see thin_repair_options.# (See package device-mapper-persistent-data or thin-provisioning-tools)# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# thin_repair_executable = "/usr/sbin/thin_repair"# Configuration option global/thin_check_options.# List of options passed to the thin_check command.# With thin_check version 2.1 or newer you can add the option# --ignore-non-fatal-errors to let it pass through ignorable errors# and fix them later. With thin_check version 3.2 or newer you should# include the option --clear-needs-check-flag.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# thin_check_options = [ "-q", "--clear-needs-check-flag" ]# Configuration option global/thin_repair_options.# List of options passed to the thin_repair command.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# thin_repair_options = [ "" ]# Configuration option global/thin_disabled_features.# Features to not use in the thin driver.# This can be helpful for testing, or to avoid using a feature that is# causing problems. Features include: block_size, discards,# discards_non_power_2, external_origin, metadata_resize,# external_origin_extend, error_if_no_space.## Example# thin_disabled_features = [ "discards", "block_size" ]## This configuration option does not have a default value defined.# Configuration option global/cache_disabled_features.# Features to not use in the cache driver.# This can be helpful for testing, or to avoid using a feature that is# causing problems. Features include: policy_mq, policy_smq, metadata2.## Example# cache_disabled_features = [ "policy_smq" ]## This configuration option does not have a default value defined.# Configuration option global/cache_check_executable.# The full path to the cache_check command.# LVM uses this command to check that a cache metadata device is in a# usable state. When a cached LV is activated and after it is# deactivated, this command is run. Activation will only proceed if the# command has an exit status of 0. Set to "" to skip this check.# (Not recommended.) Also see cache_check_options.# (See package device-mapper-persistent-data or thin-provisioning-tools)# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# cache_check_executable = "/usr/sbin/cache_check"# Configuration option global/cache_dump_executable.# The full path to the cache_dump command.# LVM uses this command to dump cache pool metadata.# (See package device-mapper-persistent-data or thin-provisioning-tools)# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# cache_dump_executable = "/usr/sbin/cache_dump"# Configuration option global/cache_repair_executable.# The full path to the cache_repair command.# LVM uses this command to repair a cache metadata device if it is in# an unusable state. Also see cache_repair_options.# (See package device-mapper-persistent-data or thin-provisioning-tools)# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# cache_repair_executable = "/usr/sbin/cache_repair"# Configuration option global/cache_check_options.# List of options passed to the cache_check command.# With cache_check version 5.0 or newer you should include the option# --clear-needs-check-flag.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# cache_check_options = [ "-q", "--clear-needs-check-flag" ]# Configuration option global/cache_repair_options.# List of options passed to the cache_repair command.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# cache_repair_options = [ "" ]# Configuration option global/fsadm_executable.# The full path to the fsadm command.# LVM uses this command to help with lvresize -r operations.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# fsadm_executable = "/usr/sbin/fsadm"# Configuration option global/system_id_source.# The method LVM uses to set the local system ID.# Volume Groups can also be given a system ID (by vgcreate, vgchange,# or vgimport.) A VG on shared storage devices is accessible only to# the host with a matching system ID. See 'man lvmsystemid' for# information on limitations and correct usage.## Accepted values:# none# The host has no system ID.# lvmlocal# Obtain the system ID from the system_id setting in the 'local'# section of an lvm configuration file, e.g. lvmlocal.conf.# uname# Set the system ID from the hostname (uname) of the system.# System IDs beginning localhost are not permitted.# machineid# Use the contents of the machine-id file to set the system ID.# Some systems create this file at installation time.# See 'man machine-id' and global/etc.# file# Use the contents of another file (system_id_file) to set the# system ID.#system_id_source = "none"# Configuration option global/system_id_file.# The full path to the file containing a system ID.# This is used when system_id_source is set to 'file'.# Comments starting with the character # are ignored.# This configuration option does not have a default value defined.# Configuration option global/use_lvmpolld.# Use lvmpolld to supervise long running LVM commands.# When enabled, control of long running LVM commands is transferred# from the original LVM command to the lvmpolld daemon. This allows# the operation to continue independent of the original LVM command.# After lvmpolld takes over, the LVM command displays the progress# of the ongoing operation. lvmpolld itself runs LVM commands to# manage the progress of ongoing operations. lvmpolld can be used as# a native systemd service, which allows it to be started on demand,# and to use its own control group. When this option is disabled, LVM# commands will supervise long running operations by forking themselves.# Applicable only if LVM is compiled with lvmpolld support.use_lvmpolld = 1# Configuration option global/notify_dbus.# Enable D-Bus notification from LVM commands.# When enabled, an LVM command that changes PVs, changes VG metadata,# or changes the activation state of an LV will send a notification.notify_dbus = 1# Configuration option global/io_memory_size.# The amount of memory in KiB that LVM allocates to perform disk io.# LVM performance may benefit from more io memory when there are many# disks or VG metadata is large. Increasing this size may be necessary# when a single copy of VG metadata is larger than the current setting.# This value should usually not be decreased from the default; setting# it too low can result in lvm failing to read VGs.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# io_memory_size = 8192
}# Configuration section activation.
activation {# Configuration option activation/checks.# Perform internal checks of libdevmapper operations.# Useful for debugging problems with activation. Some of the checks may# be expensive, so it's best to use this only when there seems to be a# problem.checks = 0# Configuration option activation/udev_sync.# Use udev notifications to synchronize udev and LVM.# The --nodevsync option overrides this setting.# When disabled, LVM commands will not wait for notifications from# udev, but continue irrespective of any possible udev processing in# the background. Only use this if udev is not running or has rules# that ignore the devices LVM creates. If enabled when udev is not# running, and LVM processes are waiting for udev, run the command# 'dmsetup udevcomplete_all' to wake them up.udev_sync = 1# Configuration option activation/udev_rules.# Use udev rules to manage LV device nodes and symlinks.# When disabled, LVM will manage the device nodes and symlinks for# active LVs itself. Manual intervention may be required if this# setting is changed while LVs are active.udev_rules = 1# Configuration option activation/verify_udev_operations.# Use extra checks in LVM to verify udev operations.# This enables additional checks (and if necessary, repairs) on entries# in the device directory after udev has completed processing its# events. Useful for diagnosing problems with LVM/udev interactions.verify_udev_operations = 0# Configuration option activation/retry_deactivation.# Retry failed LV deactivation.# If LV deactivation fails, LVM will retry for a few seconds before# failing. This may happen because a process run from a quick udev rule# temporarily opened the device.retry_deactivation = 1# Configuration option activation/missing_stripe_filler.# Method to fill missing stripes when activating an incomplete LV.# Using 'error' will make inaccessible parts of the device return I/O# errors on access. Using 'zero' will return success (and zero) on I/O# You can instead use a device path, in which case,# that device will be used in place of missing stripes. Using anything# other than 'error' with mirrored or snapshotted volumes is likely to# result in data corruption.# This configuration option is advanced.missing_stripe_filler = "error"# Configuration option activation/use_linear_target.# Use the linear target to optimize single stripe LVs.# When disabled, the striped target is used. The linear target is an# optimised version of the striped target that only handles a single# stripe.use_linear_target = 1# Configuration option activation/reserved_stack.# Stack size in KiB to reserve for use while devices are suspended.# Insufficent reserve risks I/O deadlock during device suspension.reserved_stack = 64# Configuration option activation/reserved_memory.# Memory size in KiB to reserve for use while devices are suspended.# Insufficent reserve risks I/O deadlock during device suspension.reserved_memory = 8192# Configuration option activation/process_priority.# Nice value used while devices are suspended.# Use a high priority so that LVs are suspended# for the shortest possible time.process_priority = -18# Configuration option activation/volume_list.# Only LVs selected by this list are activated.# If this list is defined, an LV is only activated if it matches an# entry in this list. If this list is undefined, it imposes no limits# on LV activation (all are allowed).## Accepted values:# vgname# The VG name is matched exactly and selects all LVs in the VG.# vgname/lvname# The VG name and LV name are matched exactly and selects the LV.# @tag# Selects an LV if the specified tag matches a tag set on the LV# or VG.# @*# Selects an LV if a tag defined on the host is also set on the LV# or VG. See tags/hosttags. If any host tags exist but volume_list# is not defined, a default single-entry list containing '@*'# is assumed.## Example# volume_list = [ "vg1", "vg2/lvol1", "@tag1", "@*" ]## This configuration option does not have a default value defined.# Configuration option activation/auto_activation_volume_list.# Only LVs selected by this list are auto-activated.# This list works like volume_list, but it is used only by# auto-activation commands. It does not apply to direct activation# commands. If this list is defined, an LV is only auto-activated# if it matches an entry in this list. If this list is undefined, it# imposes no limits on LV auto-activation (all are allowed.) If this# list is defined and empty, i.e. "[]", then no LVs are selected for# auto-activation. An LV that is selected by this list for# auto-activation, must also be selected by volume_list (if defined)# before it is activated. Auto-activation is an activation command that# includes the 'a' argument: --activate ay or -a ay. The 'a' (auto)# argument for auto-activation is meant to be used by activation# commands that are run automatically by the system, as opposed to LVM# commands run directly by a user. A user may also use the 'a' flag# directly to perform auto-activation. Also see pvscan(8) for more# information about auto-activation.## Accepted values:# vgname# The VG name is matched exactly and selects all LVs in the VG.# vgname/lvname# The VG name and LV name are matched exactly and selects the LV.# @tag# Selects an LV if the specified tag matches a tag set on the LV# or VG.# @*# Selects an LV if a tag defined on the host is also set on the LV# or VG. See tags/hosttags. If any host tags exist but volume_list# is not defined, a default single-entry list containing '@*'# is assumed.## Example# auto_activation_volume_list = [ "vg1", "vg2/lvol1", "@tag1", "@*" ]## This configuration option does not have a default value defined.# Configuration option activation/read_only_volume_list.# LVs in this list are activated in read-only mode.# If this list is defined, each LV that is to be activated is checked# against this list, and if it matches, it is activated in read-only# mode. This overrides the permission setting stored in the metadata,# e.g. from --permission rw.## Accepted values:# vgname# The VG name is matched exactly and selects all LVs in the VG.# vgname/lvname# The VG name and LV name are matched exactly and selects the LV.# @tag# Selects an LV if the specified tag matches a tag set on the LV# or VG.# @*# Selects an LV if a tag defined on the host is also set on the LV# or VG. See tags/hosttags. If any host tags exist but volume_list# is not defined, a default single-entry list containing '@*'# is assumed.## Example# read_only_volume_list = [ "vg1", "vg2/lvol1", "@tag1", "@*" ]## This configuration option does not have a default value defined.# Configuration option activation/raid_region_size.# Size in KiB of each raid or mirror synchronization region.# The clean/dirty state of data is tracked for each region.# The value is rounded down to a power of two if necessary, and# is ignored if it is not a multiple of the machine memory page size.raid_region_size = 2048# Configuration option activation/error_when_full.# Return errors if a thin pool runs out of space.# The --errorwhenfull option overrides this setting.# When enabled, writes to thin LVs immediately return an error if the# thin pool is out of data space. When disabled, writes to thin LVs# are queued if the thin pool is out of space, and processed when the# thin pool data space is extended. New thin pools are assigned the# behavior defined here.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# error_when_full = 0# Configuration option activation/readahead.# Setting to use when there is no readahead setting in metadata.## Accepted values:# none# Disable readahead.# auto# Use default value chosen by kernel.#readahead = "auto"# Configuration option activation/raid_fault_policy.# Defines how a device failure in a RAID LV is handled.# This includes LVs that have the following segment types:# raid1, raid4, raid5*, and raid6*.# If a device in the LV fails, the policy determines the steps# performed by dmeventd automatically, and the steps perfomed by the# manual command lvconvert --repair --use-policies.# Automatic handling requires dmeventd to be monitoring the LV.## Accepted values:# warn# Use the system log to warn the user that a device in the RAID LV# has failed. It is left to the user to run lvconvert --repair# manually to remove or replace the failed device. As long as the# number of failed devices does not exceed the redundancy of the LV# (1 device for raid4/5, 2 for raid6), the LV will remain usable.# allocate# Attempt to use any extra physical volumes in the VG as spares and# replace faulty devices.#raid_fault_policy = "warn"# Configuration option activation/mirror_image_fault_policy.# Defines how a device failure in a 'mirror' LV is handled.# An LV with the 'mirror' segment type is composed of mirror images# (copies) and a mirror log. A disk log ensures that a mirror LV does# not need to be re-synced (all copies made the same) every time a# machine reboots or crashes. If a device in the LV fails, this policy# determines the steps perfomed by dmeventd automatically, and the steps# performed by the manual command lvconvert --repair --use-policies.# Automatic handling requires dmeventd to be monitoring the LV.## Accepted values:# remove# Simply remove the faulty device and run without it. If the log# device fails, the mirror would convert to using an in-memory log.# This means the mirror will not remember its sync status across# crashes/reboots and the entire mirror will be re-synced. If a# mirror image fails, the mirror will convert to a non-mirrored# device if there is only one remaining good copy.# allocate# Remove the faulty device and try to allocate space on a new# device to be a replacement for the failed device. Using this# policy for the log is fast and maintains the ability to remember# sync state through crashes/reboots. Using this policy for a# mirror device is slow, as it requires the mirror to resynchronize# the devices, but it will preserve the mirror characteristic of# the device. This policy acts like 'remove' if no suitable device# and space can be allocated for the replacement.# allocate_anywhere# Not yet implemented. Useful to place the log device temporarily# on the same physical volume as one of the mirror images. This# policy is not recommended for mirror devices since it would break# the redundant nature of the mirror. This policy acts like# 'remove' if no suitable device and space can be allocated for the# replacement.#mirror_image_fault_policy = "remove"# Configuration option activation/mirror_log_fault_policy.# Defines how a device failure in a 'mirror' log LV is handled.# The mirror_image_fault_policy description for mirrored LVs also# applies to mirrored log LVs.mirror_log_fault_policy = "allocate"# Configuration option activation/snapshot_autoextend_threshold.# Auto-extend a snapshot when its usage exceeds this percent.# Setting this to 100 disables automatic extension.# The minimum value is 50 (a smaller value is treated as 50.)# Also see snapshot_autoextend_percent.# Automatic extension requires dmeventd to be monitoring the LV.## Example# Using 70% autoextend threshold and 20% autoextend size, when a 1G# snapshot exceeds 700M, it is extended to 1.2G, and when it exceeds# 840M, it is extended to 1.44G:# snapshot_autoextend_threshold = 70#snapshot_autoextend_threshold = 100# Configuration option activation/snapshot_autoextend_percent.# Auto-extending a snapshot adds this percent extra space.# The amount of additional space added to a snapshot is this# percent of its current size.## Example# Using 70% autoextend threshold and 20% autoextend size, when a 1G# snapshot exceeds 700M, it is extended to 1.2G, and when it exceeds# 840M, it is extended to 1.44G:# snapshot_autoextend_percent = 20#snapshot_autoextend_percent = 20# Configuration option activation/thin_pool_autoextend_threshold.# Auto-extend a thin pool when its usage exceeds this percent.# Setting this to 100 disables automatic extension.# The minimum value is 50 (a smaller value is treated as 50.)# Also see thin_pool_autoextend_percent.# Automatic extension requires dmeventd to be monitoring the LV.## Example# Using 70% autoextend threshold and 20% autoextend size, when a 1G# thin pool exceeds 700M, it is extended to 1.2G, and when it exceeds# 840M, it is extended to 1.44G:# thin_pool_autoextend_threshold = 70#thin_pool_autoextend_threshold = 100# Configuration option activation/thin_pool_autoextend_percent.# Auto-extending a thin pool adds this percent extra space.# The amount of additional space added to a thin pool is this# percent of its current size.## Example# Using 70% autoextend threshold and 20% autoextend size, when a 1G# thin pool exceeds 700M, it is extended to 1.2G, and when it exceeds# 840M, it is extended to 1.44G:# thin_pool_autoextend_percent = 20#thin_pool_autoextend_percent = 20# Configuration option activation/mlock_filter.# Do not mlock these memory areas.# While activating devices, I/O to devices being (re)configured is# suspended. As a precaution against deadlocks, LVM pins memory it is# using so it is not paged out, and will not require I/O to reread.# Groups of pages that are known not to be accessed during activation# do not need to be pinned into memory. Each string listed in this# setting is compared against each line in /proc/self/maps, and the# pages corresponding to lines that match are not pinned. On some# systems, locale-archive was found to make up over 80% of the memory# used by the process.## Example# mlock_filter = [ "locale/locale-archive", "gconv/gconv-modules.cache" ]## This configuration option is advanced.# This configuration option does not have a default value defined.# Configuration option activation/use_mlockall.# Use the old behavior of mlockall to pin all memory.# Prior to version 2.02.62, LVM used mlockall() to pin the whole# process's memory while activating devices.use_mlockall = 0# Configuration option activation/monitoring.# Monitor LVs that are activated.# The --ignoremonitoring option overrides this setting.# When enabled, LVM will ask dmeventd to monitor activated LVs.monitoring = 1# Configuration option activation/polling_interval.# Check pvmove or lvconvert progress at this interval (seconds).# When pvmove or lvconvert must wait for the kernel to finish# synchronising or merging data, they check and report progress at# intervals of this number of seconds. If this is set to 0 and there# is only one thing to wait for, there are no progress reports, but# the process is awoken immediately once the operation is complete.polling_interval = 15# Configuration option activation/auto_set_activation_skip.# Set the activation skip flag on new thin snapshot LVs.# The --setactivationskip option overrides this setting.# An LV can have a persistent 'activation skip' flag. The flag causes# the LV to be skipped during normal activation. The lvchange/vgchange# -K option is required to activate LVs that have the activation skip# flag set. When this setting is enabled, the activation skip flag is# set on new thin snapshot LVs.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# auto_set_activation_skip = 1# Configuration option activation/activation_mode.# How LVs with missing devices are activated.# The --activationmode option overrides this setting.## Accepted values:# complete# Only allow activation of an LV if all of the Physical Volumes it# uses are present. Other PVs in the Volume Group may be missing.# degraded# Like complete, but additionally RAID LVs of segment type raid1,# raid4, raid5, radid6 and raid10 will be activated if there is no# data loss, i.e. they have sufficient redundancy to present the# entire addressable range of the Logical Volume.# partial# Allows the activation of any LV even if a missing or failed PV# could cause data loss with a portion of the LV inaccessible.# This setting should not normally be used, but may sometimes# assist with data recovery.#activation_mode = "degraded"# Configuration option activation/lock_start_list.# Locking is started only for VGs selected by this list.# The rules are the same as those for volume_list.# This configuration option does not have a default value defined.# Configuration option activation/auto_lock_start_list.# Locking is auto-started only for VGs selected by this list.# The rules are the same as those for auto_activation_volume_list.# This configuration option does not have a default value defined.
}# Configuration section metadata.
# This configuration section has an automatic default value.
# metadata {# Configuration option metadata/check_pv_device_sizes.# Check device sizes are not smaller than corresponding PV sizes.# If device size is less than corresponding PV size found in metadata,# there is always a risk of data loss. If this option is set, then LVM# issues a warning message each time it finds that the device size is# less than corresponding PV size. You should not disable this unless# you are absolutely sure about what you are doing!# This configuration option is advanced.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# check_pv_device_sizes = 1# Configuration option metadata/record_lvs_history.# When enabled, LVM keeps history records about removed LVs in# metadata. The information that is recorded in metadata for# historical LVs is reduced when compared to original# information kept in metadata for live LVs. Currently, this# feature is supported for thin and thin snapshot LVs only.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# record_lvs_history = 0# Configuration option metadata/lvs_history_retention_time.# Retention time in seconds after which a record about individual# historical logical volume is automatically destroyed.# A value of 0 disables this feature.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# lvs_history_retention_time = 0# Configuration option metadata/pvmetadatacopies.# Number of copies of metadata to store on each PV.# The --pvmetadatacopies option overrides this setting.## Accepted values:# 2# Two copies of the VG metadata are stored on the PV, one at the# front of the PV, and one at the end.# 1# One copy of VG metadata is stored at the front of the PV.# 0# No copies of VG metadata are stored on the PV. This may be# useful for VGs containing large numbers of PVs.## This configuration option is advanced.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# pvmetadatacopies = 1# Configuration option metadata/vgmetadatacopies.# Number of copies of metadata to maintain for each VG.# The --vgmetadatacopies option overrides this setting.# If set to a non-zero value, LVM automatically chooses which of the# available metadata areas to use to achieve the requested number of# copies of the VG metadata. If you set a value larger than the the# total number of metadata areas available, then metadata is stored in# them all. The value 0 (unmanaged) disables this automatic management# and allows you to control which metadata areas are used at the# individual PV level using pvchange --metadataignore y|n.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# vgmetadatacopies = 0# Configuration option metadata/pvmetadatasize.# Approximate number of sectors to use for each metadata copy.# VGs with large numbers of PVs or LVs, or VGs containing complex LV# structures, may need additional space for VG metadata. The metadata# areas are treated as circular buffers, so unused space becomes filled# with an archive of the most recent previous versions of the metadata.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# pvmetadatasize = 255# Configuration option metadata/pvmetadataignore.# Ignore metadata areas on a new PV.# The --metadataignore option overrides this setting.# If metadata areas on a PV are ignored, LVM will not store metadata# in them.# This configuration option is advanced.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# pvmetadataignore = 0# Configuration option metadata/stripesize.# This configuration option is advanced.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# stripesize = 64# Configuration option metadata/dirs.# Directories holding live copies of text format metadata.# These directories must not be on logical volumes!# It's possible to use LVM with a couple of directories here,# preferably on different (non-LV) filesystems, and with no other# on-disk metadata (pvmetadatacopies = 0). Or this can be in addition# to on-disk metadata areas. The feature was originally added to# simplify testing and is not supported under low memory situations -# the machine could lock up. Never edit any files in these directories# by hand unless you are absolutely sure you know what you are doing!# Use the supplied toolset to make changes (e.g. vgcfgrestore).## Example# dirs = [ "/etc/lvm/metadata", "/mnt/disk2/lvm/metadata2" ]## This configuration option is advanced.# This configuration option does not have a default value defined.
# }# Configuration section report.
# LVM report command output formatting.
# This configuration section has an automatic default value.
# report {# Configuration option report/output_format.# Format of LVM command's report output.# If there is more than one report per command, then the format# is applied for all reports. You can also change output format# directly on command line using --reportformat option which# has precedence over log/output_format setting.# Accepted values:# basic# Original format with columns and rows. If there is more than# one report per command, each report is prefixed with report's# name for identification.# json# JSON format.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# output_format = "basic"# Configuration option report/compact_output.# Do not print empty values for all report fields.# If enabled, all fields that don't have a value set for any of the# rows reported are skipped and not printed. Compact output is# applicable only if report/buffered is enabled. If you need to# compact only specified fields, use compact_output=0 and define# report/compact_output_cols configuration setting instead.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# compact_output = 0# Configuration option report/compact_output_cols.# Do not print empty values for specified report fields.# If defined, specified fields that don't have a value set for any# of the rows reported are skipped and not printed. Compact output# is applicable only if report/buffered is enabled. If you need to# compact all fields, use compact_output=1 instead in which case# the compact_output_cols setting is then ignored.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# compact_output_cols = ""# Configuration option report/aligned.# Align columns in report output.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# aligned = 1# Configuration option report/buffered.# Buffer report output.# When buffered reporting is used, the report's content is appended# incrementally to include each object being reported until the report# is flushed to output which normally happens at the end of command# execution. Otherwise, if buffering is not used, each object is# reported as soon as its processing is finished.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# buffered = 1# Configuration option report/headings.# Show headings for columns on report.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# headings = 1# Configuration option report/separator.# A separator to use on report after each field.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# separator = " "# Configuration option report/list_item_separator.# A separator to use for list items when reported.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# list_item_separator = ","# Configuration option report/prefixes.# Use a field name prefix for each field reported.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# prefixes = 0# Configuration option report/quoted.# Quote field values when using field name prefixes.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# quoted = 1# Configuration option report/columns_as_rows.# Output each column as a row.# If set, this also implies report/prefixes=1.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# columns_as_rows = 0# Configuration option report/binary_values_as_numeric.# Use binary values 0 or 1 instead of descriptive literal values.# For columns that have exactly two valid values to report# (not counting the 'unknown' value which denotes that the# value could not be determined).# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# binary_values_as_numeric = 0# Configuration option report/time_format.# Set time format for fields reporting time values.# Format specification is a string which may contain special character# sequences and ordinary character sequences. Ordinary character# sequences are copied verbatim. Each special character sequence is# introduced by the '%' character and such sequence is then# substituted with a value as described below.## Accepted values:# %a# The abbreviated name of the day of the week according to the# current locale.# %A# The full name of the day of the week according to the current# locale.# %b# The abbreviated month name according to the current locale.# %B# The full month name according to the current locale.# %c# The preferred date and time representation for the current# locale (alt E)# %C# The century number (year/100) as a 2-digit integer. (alt E)# %d# The day of the month as a decimal number (range 01 to 31).# (alt O)# %D# Equivalent to %m/%d/%y. (For Americans only. Americans should# note that in other countries%d/%m/%y is rather common. This# means that in international context this format is ambiguous and# should not be used.# %e# Like %d, the day of the month as a decimal number, but a leading# zero is replaced by a space. (alt O)# %E# Modifier: use alternative local-dependent representation if# available.# %F# Equivalent to %Y-%m-%d (the ISO 8601 date format).# %G# The ISO 8601 week-based year with century as adecimal number.# The 4-digit year corresponding to the ISO week number (see %V).# This has the same format and value as %Y, except that if the# ISO week number belongs to the previous or next year, that year# is used instead.# %g# Like %G, but without century, that is, with a 2-digit year# (00-99).# %h# Equivalent to %b.# %H# The hour as a decimal number using a 24-hour clock# (range 00 to 23). (alt O)# %I# The hour as a decimal number using a 12-hour clock# (range 01 to 12). (alt O)# %j# The day of the year as a decimal number (range 001 to 366).# %k# The hour (24-hour clock) as a decimal number (range 0 to 23);# single digits are preceded by a blank. (See also %H.)# %l# The hour (12-hour clock) as a decimal number (range 1 to 12);# single digits are preceded by a blank. (See also %I.)# %m# The month as a decimal number (range 01 to 12). (alt O)# %M# The minute as a decimal number (range 00 to 59). (alt O)# %O# Modifier: use alternative numeric symbols.# %p# Either "AM" or "PM" according to the given time value,# or the corresponding strings for the current locale. Noon is# treated as "PM" and midnight as "AM".# %P# Like %p but in lowercase: "am" or "pm" or a corresponding# string for the current locale.# %r# The time in a.m. or p.m. notation. In the POSIX locale this is# equivalent to %I:%M:%S %p.# %R# The time in 24-hour notation (%H:%M). For a version including# the seconds, see %T below.# %s# The number of seconds since the Epoch,# 1970-01-01 00:00:00 +0000 (UTC)# %S# The second as a decimal number (range 00 to 60). (The range is# up to 60 to allow for occasional leap seconds.) (alt O)# %t# A tab character.# %T# The time in 24-hour notation (%H:%M:%S).# %u# The day of the week as a decimal, range 1 to 7, Monday being 1.# See also %w. (alt O)# %U# The week number of the current year as a decimal number,# range 00 to 53, starting with the first Sunday as the first# day of week 01. See also %V and %W. (alt O)# %V# The ISO 8601 week number of the current year as a decimal number,# range 01 to 53, where week 1 is the first week that has at least# 4 days in the new year. See also %U and %W. (alt O)# %w# The day of the week as a decimal, range 0 to 6, Sunday being 0.# See also %u. (alt O)# %W# The week number of the current year as a decimal number,# range 00 to 53, starting with the first Monday as the first day# of week 01. (alt O)# %x# The preferred date representation for the current locale without# the time. (alt E)# %X# The preferred time representation for the current locale without# the date. (alt E)# %y# The year as a decimal number without a century (range 00 to 99).# (alt E, alt O)# %Y# The year as a decimal number including the century. (alt E)# %z# The +hhmm or -hhmm numeric timezone (that is, the hour and minute# offset from UTC).# %Z# The timezone name or abbreviation.# %%# A literal '%' character.## This configuration option has an automatic default value.# time_format = "%Y-%m-%d %T %z"# Configuration option report/devtypes_sort.# List of columns to sort by when reporting 'lvm devtypes' command.# See 'lvm devtypes -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# devtypes_sort = "devtype_name"# Configuration option report/devtypes_cols.# List of columns to report for 'lvm devtypes' command.# See 'lvm devtypes -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# devtypes_cols = "devtype_name,devtype_max_partitions,devtype_description"# Configuration option report/devtypes_cols_verbose.# List of columns to report for 'lvm devtypes' command in verbose mode.# See 'lvm devtypes -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# devtypes_cols_verbose = "devtype_name,devtype_max_partitions,devtype_description"# Configuration option report/lvs_sort.# List of columns to sort by when reporting 'lvs' command.# See 'lvs -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# lvs_sort = "vg_name,lv_name"# Configuration option report/lvs_cols.# List of columns to report for 'lvs' command.# See 'lvs -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# lvs_cols = "lv_name,vg_name,lv_attr,lv_size,pool_lv,origin,data_percent,metadata_percent,move_pv,mirror_log,copy_percent,convert_lv"# Configuration option report/lvs_cols_verbose.# List of columns to report for 'lvs' command in verbose mode.# See 'lvs -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# lvs_cols_verbose = "lv_name,vg_name,seg_count,lv_attr,lv_size,lv_major,lv_minor,lv_kernel_major,lv_kernel_minor,pool_lv,origin,data_percent,metadata_percent,move_pv,copy_percent,mirror_log,convert_lv,lv_uuid,lv_profile"# Configuration option report/vgs_sort.# List of columns to sort by when reporting 'vgs' command.# See 'vgs -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# vgs_sort = "vg_name"# Configuration option report/vgs_cols.# List of columns to report for 'vgs' command.# See 'vgs -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# vgs_cols = "vg_name,pv_count,lv_count,snap_count,vg_attr,vg_size,vg_free"# Configuration option report/vgs_cols_verbose.# List of columns to report for 'vgs' command in verbose mode.# See 'vgs -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# vgs_cols_verbose = "vg_name,vg_attr,vg_extent_size,pv_count,lv_count,snap_count,vg_size,vg_free,vg_uuid,vg_profile"# Configuration option report/pvs_sort.# List of columns to sort by when reporting 'pvs' command.# See 'pvs -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# pvs_sort = "pv_name"# Configuration option report/pvs_cols.# List of columns to report for 'pvs' command.# See 'pvs -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# pvs_cols = "pv_name,vg_name,pv_fmt,pv_attr,pv_size,pv_free"# Configuration option report/pvs_cols_verbose.# List of columns to report for 'pvs' command in verbose mode.# See 'pvs -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# pvs_cols_verbose = "pv_name,vg_name,pv_fmt,pv_attr,pv_size,pv_free,dev_size,pv_uuid"# Configuration option report/segs_sort.# List of columns to sort by when reporting 'lvs --segments' command.# See 'lvs --segments -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# segs_sort = "vg_name,lv_name,seg_start"# Configuration option report/segs_cols.# List of columns to report for 'lvs --segments' command.# See 'lvs --segments -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# segs_cols = "lv_name,vg_name,lv_attr,stripes,segtype,seg_size"# Configuration option report/segs_cols_verbose.# List of columns to report for 'lvs --segments' command in verbose mode.# See 'lvs --segments -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# segs_cols_verbose = "lv_name,vg_name,lv_attr,seg_start,seg_size,stripes,segtype,stripesize,chunksize"# Configuration option report/pvsegs_sort.# List of columns to sort by when reporting 'pvs --segments' command.# See 'pvs --segments -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# pvsegs_sort = "pv_name,pvseg_start"# Configuration option report/pvsegs_cols.# List of columns to sort by when reporting 'pvs --segments' command.# See 'pvs --segments -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# pvsegs_cols = "pv_name,vg_name,pv_fmt,pv_attr,pv_size,pv_free,pvseg_start,pvseg_size"# Configuration option report/pvsegs_cols_verbose.# List of columns to sort by when reporting 'pvs --segments' command in verbose mode.# See 'pvs --segments -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# pvsegs_cols_verbose = "pv_name,vg_name,pv_fmt,pv_attr,pv_size,pv_free,pvseg_start,pvseg_size,lv_name,seg_start_pe,segtype,seg_pe_ranges"# Configuration option report/vgs_cols_full.# List of columns to report for lvm fullreport's 'vgs' subreport.# See 'vgs -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# vgs_cols_full = "vg_all"# Configuration option report/pvs_cols_full.# List of columns to report for lvm fullreport's 'vgs' subreport.# See 'pvs -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# pvs_cols_full = "pv_all"# Configuration option report/lvs_cols_full.# List of columns to report for lvm fullreport's 'lvs' subreport.# See 'lvs -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# lvs_cols_full = "lv_all"# Configuration option report/pvsegs_cols_full.# List of columns to report for lvm fullreport's 'pvseg' subreport.# See 'pvs --segments -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# pvsegs_cols_full = "pvseg_all,pv_uuid,lv_uuid"# Configuration option report/segs_cols_full.# List of columns to report for lvm fullreport's 'seg' subreport.# See 'lvs --segments -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# segs_cols_full = "seg_all,lv_uuid"# Configuration option report/vgs_sort_full.# List of columns to sort by when reporting lvm fullreport's 'vgs' subreport.# See 'vgs -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# vgs_sort_full = "vg_name"# Configuration option report/pvs_sort_full.# List of columns to sort by when reporting lvm fullreport's 'vgs' subreport.# See 'pvs -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# pvs_sort_full = "pv_name"# Configuration option report/lvs_sort_full.# List of columns to sort by when reporting lvm fullreport's 'lvs' subreport.# See 'lvs -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# lvs_sort_full = "vg_name,lv_name"# Configuration option report/pvsegs_sort_full.# List of columns to sort by when reporting for lvm fullreport's 'pvseg' subreport.# See 'pvs --segments -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# pvsegs_sort_full = "pv_uuid,pvseg_start"# Configuration option report/segs_sort_full.# List of columns to sort by when reporting lvm fullreport's 'seg' subreport.# See 'lvs --segments -o help' for the list of possible fields.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# segs_sort_full = "lv_uuid,seg_start"# Configuration option report/mark_hidden_devices.# Use brackets [] to mark hidden devices.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# mark_hidden_devices = 1# Configuration option report/two_word_unknown_device.# Use the two words 'unknown device' in place of '[unknown]'.# This is displayed when the device for a PV is not known.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# two_word_unknown_device = 0
# }# Configuration section dmeventd.
# Settings for the LVM event daemon.
dmeventd {# Configuration option dmeventd/mirror_library.# The library dmeventd uses when monitoring a mirror device.# libdevmapper-event-lvm2mirror.so attempts to recover from# failures. It removes failed devices from a volume group and# reconfigures a mirror as necessary. If no mirror library is# provided, mirrors are not monitored through dmeventd.mirror_library = "libdevmapper-event-lvm2mirror.so"# Configuration option dmeventd/raid_library.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# raid_library = "libdevmapper-event-lvm2raid.so"# Configuration option dmeventd/snapshot_library.# The library dmeventd uses when monitoring a snapshot device.# libdevmapper-event-lvm2snapshot.so monitors the filling of snapshots# and emits a warning through syslog when the usage exceeds 80%. The# warning is repeated when 85%, 90% and 95% of the snapshot is filled.snapshot_library = "libdevmapper-event-lvm2snapshot.so"# Configuration option dmeventd/thin_library.# The library dmeventd uses when monitoring a thin device.# libdevmapper-event-lvm2thin.so monitors the filling of a pool# and emits a warning through syslog when the usage exceeds 80%. The# warning is repeated when 85%, 90% and 95% of the pool is filled.thin_library = "libdevmapper-event-lvm2thin.so"# Configuration option dmeventd/thin_command.# The plugin runs command with each 5% increment when thin-pool data volume# or metadata volume gets above 50%.# Command which starts with 'lvm ' prefix is internal lvm command.# You can write your own handler to customise behaviour in more details.# User handler is specified with the full path starting with '/'.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# thin_command = "lvm lvextend --use-policies"# Configuration option dmeventd/executable.# The full path to the dmeventd binary.# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# executable = "/usr/sbin/dmeventd"
}# Configuration section tags.
# Host tag settings.
# This configuration section has an automatic default value.
# tags {# Configuration option tags/hosttags.# Create a host tag using the machine name.# The machine name is nodename returned by uname(2).# This configuration option has an automatic default value.# hosttags = 0# Configuration section tags/<tag>.# Replace this subsection name with a custom tag name.# Multiple subsections like this can be created. The '@' prefix for# tags is optional. This subsection can contain host_list, which is a# list of machine names. If the name of the local machine is found in# host_list, then the name of this subsection is used as a tag and is# applied to the local machine as a 'host tag'. If this subsection is# empty (has no host_list), then the subsection name is always applied# as a 'host tag'.## Example# The host tag foo is given to all hosts, and the host tag# bar is given to the hosts named machine1 and machine2.# tags { foo { } bar { host_list = [ "machine1", "machine2" ] } }## This configuration section has variable name.# This configuration section has an automatic default value.# tag {# Configuration option tags/<tag>/host_list.# A list of machine names.# These machine names are compared to the nodename returned# by uname(2). If the local machine name matches an entry in# this list, the name of the subsection is applied to the# machine as a 'host tag'.# This configuration option does not have a default value defined.# }
# }
您在 /var/spool/mail/root 中有新邮件
[root@web ~]# vim /etc/lvm/lvm.conf
您在 /var/spool/mail/root 中有邮件
[root@web ~]# vim /etc/lvm/lvm.conf
您在 /var/spool/mail/root 中有邮件
[root@web ~]# lvs
WARNING: Ignoring duplicate config value: snapshot_autoextend_percentWARNING: Device for PV r1noGN-Dn5A-udh3-qROp-C2Tj-HSil-AMqIZX not found or rejected by a filter.Couldn't find device with uuid r1noGN-Dn5A-udh3-qROp-C2Tj-HSil-AMqIZX.LV VG Attr LSize Pool Origin Data% Meta% Move Log Cpy%Sync Convertroot centos -wi-ao---- <17.00gswap centos -wi-ao---- 2.00glv01 vg01 -wi-a----- <3.09glv02 vg01 -wi-a----- 120.00mlv03 vg01 -wi-a----- 36.00mlv1 vg1 owi-aor-r- 1.50g 100.00lv1-snap vg1 swi-aos--- 128.00m lv1 23.59lv7 vg7 -wi-ao---- <2.10glv8 vg7 -wi-a----- 1.20glv_mysql vg_mysql -wi-ao---- 8.00g
[root@web ~]# df -h
文件系统 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点
devtmpfs 470M 0 470M 0% /dev
tmpfs 487M 0 487M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 487M 39M 448M 8% /run
tmpfs 487M 0 487M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/centos-root 17G 17G 631M 97% /
/dev/sda1 1014M 172M 843M 17% /boot
/dev/sdb2 976M 2.6M 907M 1% /u2
/dev/sr0 4.4G 4.4G 0 100% /mnt
tmpfs 98M 12K 98M 1% /run/user/42
tmpfs 98M 0 98M 0% /run/user/0
/dev/mapper/vg7-lv7 2.1G 6.0M 2.0G 1% /u7
/dev/mapper/vg_mysql-lv_mysql 7.8G 1.2G 6.2G 17% /usr/local/mysql
/dev/mapper/vg1-lv1 1.5G 35M 1.4G 3% /uc1
/dev/mapper/vg1-lv1--snap 1.5G 4.6M 1.4G 1% /mmt/lv1-snap
您在 /var/spool/mail/root 中有邮件
[root@web ~]# vim /etc/fstab
您在 /var/spool/mail/root 中有邮件
[root@web ~]# cat /etc/fstab#
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Sat Apr 19 17:11:28 2025
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
# See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info
#
/dev/mapper/centos-root / xfs defaults 0 0
UUID=0671af2f-69a1-4a84-bb51-ceb937bc1a92 /boot xfs defaults 0 0
/dev/mapper/centos-swap swap swap defaults 0 0
/dev/sdb2 /u2 ext4 defaults,usrquota,grpquota 0 0
/dev/sdd6 swap swap defaults 0 0
/tmp/swapfile swap swap defaults,pir=1 0 0
[root@web ~]# umount /u2
您在 /var/spool/mail/root 中有邮件
[root@web ~]# mount -a
[root@web ~]# mount |grep u1
[root@web ~]# yum -y install quota
已加载插件:fastestmirror, langpacks
Determining fastest mirrors
local | 3.6 kB 00:00:00
软件包 1:quota-4.01-19.el7.x86_64 已安装并且是最新版本
无须任何处理
您在 /var/spool/mail/root 中有邮件
[root@web ~]# quotacheck -acug
您在 /var/spool/mail/root 中有邮件
[root@web ~]# ll /u2
总用量 32
-rw------- 1 root root 6144 7月 23 22:00 aquota.group
-rw------- 1 root root 6144 7月 23 22:00 aquota.user
drwx------ 2 root root 16384 7月 13 21:58 lost+found
[root@web ~]# mount |grep u2
/dev/sdb2 on /u2 type ext4 (rw,relatime,quota,usrquota,grpquota,data=ordered)
您在 /var/spool/mail/root 中有邮件
[root@web ~]# quotaon -a
[root@web ~]# edquata -u stu1
bash: edquata: 未找到命令...
您在 /var/spool/mail/root 中有邮件
[root@web ~]# edquota -u stu1
edquota: user stu1 does not exist.
[root@web ~]# tail -5 /etc/passwd
OOO:x:1020:1020::/home/OOO:/bin/bash
jerry:x:1021:1229::/home/jerry:/bin/bash
kefu:x:1022:1022::/home/kefu:/bin/bash
kefu2:x:1023:1023::/home/kefu2:/bin/bash
user01:x:1024:1024::/home/user01:/bin/bash
[root@web ~]# edquota -u kefu
您在 /var/spool/mail/root 中有邮件
[root@web ~]# su - kefu
[kefu@web ~]$ 123
bash: 123: 未找到命令...
[kefu@web ~]$ dd if=/dev/zero of=test99 bs=1M count=11
记录了11+0 的读入
记录了11+0 的写出
11534336字节(12 MB)已复制,0.00854355 秒,1.4 GB/秒
[kefu@web ~]$ dd if=/dev/zero of=test99 bs=1M count=13
记录了13+0 的读入
记录了13+0 的写出
13631488字节(14 MB)已复制,0.00946287 秒,1.4 GB/秒
[kefu@web ~]$ edquota-u kefu
bash: edquota-u: 未找到命令...
[kefu@web ~]$ equota -u kefu
bash: equota: 未找到命令...
相似命令是: 'quota'
[kefu@web ~]$ edquota -u kefu
edquota: Cannot set quota for user 1022 from kernel on /dev/sdb2: 不允许的操作
edquota: Cannot write quota for 1022 on /dev/sdb2: 不允许的操作
[kefu@web ~]$ quota
Disk quotas for user kefu (uid 1022): no limited resources used
[kefu@web ~]$ su - caozx26
密码:
上一次登录:日 7月 13 21:44:42 CST 2025:0 上
[caozx26@web ~]$ sudo su
[sudo] caozx26 的密码:
[root@web caozx26]# edquota -u kefu
[root@web caozx26]# edquota -t
[root@web caozx26]# su - kefu
上一次登录:三 7月 23 22:06:56 CST 2025pts/0 上
[kefu@web ~]$ ls /dev/sdb2
/dev/sdb2
[kefu@web ~]$ ll /dev/sdb3
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 19 7月 20 19:43 /dev/sdb3
[kefu@web ~]$ cd /dev/sdb2
-bash: cd: /dev/sdb2: 不是目录
[kefu@web ~]$ ls /dev/sdb2
/dev/sdb2
[kefu@web ~]$ cat /dev/sdb2
cat: /dev/sdb2: 权限不够
[kefu@web ~]$ su - caozx26
密码:
上一次登录:三 7月 23 22:15:21 CST 2025pts/0 上
[caozx26@web ~]$ sudo su
[root@web caozx26]# display /dev/sdb2
bash: display: 未找到命令...
[root@web caozx26]# df -h
文件系统 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点
devtmpfs 470M 0 470M 0% /dev
tmpfs 487M 0 487M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 487M 39M 448M 8% /run
tmpfs 487M 0 487M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/centos-root 17G 17G 618M 97% /
/dev/sda1 1014M 172M 843M 17% /boot
/dev/sr0 4.4G 4.4G 0 100% /mnt
tmpfs 98M 12K 98M 1% /run/user/42
tmpfs 98M 0 98M 0% /run/user/0
/dev/mapper/vg7-lv7 2.1G 6.0M 2.0G 1% /u7
/dev/mapper/vg_mysql-lv_mysql 7.8G 1.2G 6.2G 17% /usr/local/mysql
/dev/mapper/vg1-lv1 1.5G 35M 1.4G 3% /uc1
/dev/mapper/vg1-lv1--snap 1.5G 4.6M 1.4G 1% /mmt/lv1-snap
/dev/sdb2 976M 2.6M 907M 1% /u2
[root@web caozx26]# pvdisplay /dev/sdb2
WARNING: Ignoring duplicate config value: snapshot_autoextend_percentWARNING: Device for PV r1noGN-Dn5A-udh3-qROp-C2Tj-HSil-AMqIZX not found or rejected by a filter.Couldn't find device with uuid r1noGN-Dn5A-udh3-qROp-C2Tj-HSil-AMqIZX.Failed to find physical volume "/dev/sdb2".
[root@web caozx26]# lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda 8:0 0 20G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 1G 0 part /boot
└─sda2 8:2 0 19G 0 part├─centos-root 253:0 0 17G 0 lvm /└─centos-swap 253:1 0 2G 0 lvm [SWAP]
sdb 8:16 0 10G 0 disk
├─sdb1 8:17 0 1G 0 part
├─sdb2 8:18 0 1G 0 part /u2
├─sdb3 8:19 0 1G 0 part
├─sdb4 8:20 0 1K 0 part
├─sdb5 8:21 0 1G 0 part
│ └─vg01-lv01 253:3 0 3.1G 0 lvm
├─sdb6 8:22 0 1G 0 part
│ └─vg01-lv01 253:3 0 3.1G 0 lvm
├─sdb7 8:23 0 1G 0 part
│ ├─vg01-lv01 253:3 0 3.1G 0 lvm
│ ├─vg01-lv02 253:4 0 120M 0 lvm
│ └─vg01-lv03 253:5 0 36M 0 lvm
├─sdb8 8:24 0 1G 0 part
│ └─vg01-lv01 253:3 0 3.1G 0 lvm
└─sdb9 8:25 0 900M 0 part
sdc 8:32 0 10G 0 disk
├─sdc1 8:33 0 2G 0 part
│ └─vg_mysql-lv_mysql 253:2 0 8G 0 lvm /usr/local/mysql
├─sdc2 8:34 0 2G 0 part
│ └─vg_mysql-lv_mysql 253:2 0 8G 0 lvm /usr/local/mysql
├─sdc3 8:35 0 1K 0 part
├─sdc5 8:37 0 2G 0 part
│ └─vg_mysql-lv_mysql 253:2 0 8G 0 lvm /usr/local/mysql
├─sdc6 8:38 0 2G 0 part
│ └─vg_mysql-lv_mysql 253:2 0 8G 0 lvm /usr/local/mysql
└─sdc7 8:39 0 900M 0 part└─vg_mysql-lv_mysql 253:2 0 8G 0 lvm /usr/local/mysql
sdd 8:48 0 20G 0 disk
├─sdd1 8:49 0 2G 0 part
├─sdd2 8:50 0 2G 0 part
│ ├─vg1-lv1_rmeta_1 253:10 0 4M 0 lvm
│ │ └─vg1-lv1-real 253:13 0 1.5G 0 lvm
│ │ ├─vg1-lv1 253:12 0 1.5G 0 lvm /uc1
│ │ └─vg1-lv1--snap 253:15 0 1.5G 0 lvm /mmt/lv1-snap
│ ├─vg1-lv1_rimage_1 253:11 0 1.5G 0 lvm
│ │ └─vg1-lv1-real 253:13 0 1.5G 0 lvm
│ │ ├─vg1-lv1 253:12 0 1.5G 0 lvm /uc1
│ │ └─vg1-lv1--snap 253:15 0 1.5G 0 lvm /mmt/lv1-snap
│ └─vg1-lv1--snap-cow 253:14 0 128M 0 lvm
│ └─vg1-lv1--snap 253:15 0 1.5G 0 lvm /mmt/lv1-snap
├─sdd3 8:51 0 2G 0 part
├─sdd4 8:52 0 512B 0 part
├─sdd5 8:53 0 2G 0 part
├─sdd6 8:54 0 2G 0 part [SWAP]
├─sdd7 8:55 0 2G 0 part
│ └─vg7-lv7 253:7 0 2.1G 0 lvm /u7
└─sdd8 8:56 0 2G 0 part├─vg7-lv7 253:7 0 2.1G 0 lvm /u7└─vg7-lv8 253:8 0 1.2G 0 lvm
sr0 11:0 1 4.4G 0 rom /mnt
vg1-lv1_rmeta_0 253:6 0 4M 0 lvm
└─vg1-lv1-real 253:13 0 1.5G 0 lvm├─vg1-lv1 253:12 0 1.5G 0 lvm /uc1└─vg1-lv1--snap 253:15 0 1.5G 0 lvm /mmt/lv1-snap
vg1-lv1_rimage_0 253:9 0 1.5G 0 lvm
└─vg1-lv1-real 253:13 0 1.5G 0 lvm├─vg1-lv1 253:12 0 1.5G 0 lvm /uc1└─vg1-lv1--snap 253:15 0 1.5G 0 lvm /mmt/lv1-snap
[root@web caozx26]# pvs
WARNING: Ignoring duplicate config value: snapshot_autoextend_percentWARNING: Device for PV r1noGN-Dn5A-udh3-qROp-C2Tj-HSil-AMqIZX not found or rejected by a filter.Couldn't find device with uuid r1noGN-Dn5A-udh3-qROp-C2Tj-HSil-AMqIZX.PV VG Fmt Attr PSize PFree/dev/sda2 centos lvm2 a-- <19.00g 0/dev/sdb5 vg01 lvm2 a-- 1020.00m 724.00m/dev/sdb6 vg01 lvm2 a-- 1020.00m 0/dev/sdb7 vg01 lvm2 a-- 1020.00m 40.00m/dev/sdb8 vg01 lvm2 a-- 1020.00m 0/dev/sdc1 vg_mysql lvm2 a-- <2.00g 0/dev/sdc2 vg_mysql lvm2 a-- <2.00g 0/dev/sdc5 vg_mysql lvm2 a-- <2.00g 0/dev/sdc6 vg_mysql lvm2 a-- <2.00g 0/dev/sdc7 vg_mysql lvm2 a-- 896.00m 880.00m/dev/sdd1 vg1 lvm2 a-- <2.00g <2.00g/dev/sdd2 vg1 lvm2 a-- <2.00g 376.00m/dev/sdd5 vg2 lvm2 a-- <2.00g <2.00g/dev/sdd7 vg7 lvm2 a-- <2.00g 0/dev/sdd8 vg7 lvm2 a-- <2.00g 708.00m[unknown] vg2 lvm2 a-m <2.00g <2.00g
[root@web caozx26]# lvs
WARNING: Ignoring duplicate config value: snapshot_autoextend_percentWARNING: Device for PV r1noGN-Dn5A-udh3-qROp-C2Tj-HSil-AMqIZX not found or rejected by a filter.Couldn't find device with uuid r1noGN-Dn5A-udh3-qROp-C2Tj-HSil-AMqIZX.LV VG Attr LSize Pool Origin Data% Meta% Move Log Cpy%Sync Convertroot centos -wi-ao---- <17.00gswap centos -wi-ao---- 2.00glv01 vg01 -wi-a----- <3.09glv02 vg01 -wi-a----- 120.00mlv03 vg01 -wi-a----- 36.00mlv1 vg1 owi-aor-r- 1.50g 100.00lv1-snap vg1 swi-aos--- 128.00m lv1 23.59lv7 vg7 -wi-ao---- <2.10glv8 vg7 -wi-a----- 1.20glv_mysql vg_mysql -wi-ao---- 8.00g
[root@web caozx26]# blkid /dev/sdb2
/dev/sdb2: UUID="faacf3c9-5c84-4fae-a3d2-f323d9cbc0ef" TYPE="ext4"
[root@web caozx26]# cd /u2
[root@web u2]# ls
aquota.group aquota.user lost+found
[root@web u2]# ll -d
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 7月 23 22:00 .
[root@web u2]# ls
aquota.group aquota.user lost+found
[root@web u2]# cd aquota.group
bash: cd: aquota.group: 不是目录
[root@web u2]# ls aquota.group
aquota.group
[root@web u2]# ll -d
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 7月 23 22:00 .
[root@web u2]# ls -d
.
[root@web u2]# ll
总用量 32
-rw------- 1 root root 6144 7月 23 22:00 aquota.group
-rw------- 1 root root 7168 7月 23 22:00 aquota.user
drwx------ 2 root root 16384 7月 13 21:58 lost+found
[root@web u2]# ls -l /u2
总用量 32
-rw------- 1 root root 6144 7月 23 22:00 aquota.group
-rw------- 1 root root 7168 7月 23 22:00 aquota.user
drwx------ 2 root root 16384 7月 13 21:58 lost+found
[root@web u2]# setenforce 0
setenforce: SELinux is disabled
[root@web u2]# sudo quota -u kefu /u2
Disk quotas for user kefu (uid 1022): no limited resources used
quota: user /u2 does not exist.
[root@web u2]# quota -u kefu /dev/sdb2
Disk quotas for user kefu (uid 1022): no limited resources used
quota: user /dev/sdb2 does not exist.
[root@web u2]# quota -u kefu
Disk quotas for user kefu (uid 1022): no limited resources used
[root@web u2]# mount |grep /u2
/dev/sdb2 on /u2 type ext4 (rw,relatime,quota,usrquota,grpquota,data=ordered)
[root@web u2]# edquota -u kefu
[root@web u2]# quota -uvs kefu
Disk quotas for user kefu (uid 1022):Filesystem space quota limit grace files quota limit grace/dev/sdb2 0K 10240K 12288K 0 10 15
[root@web u2]# su - kefu
上一次登录:三 7月 23 22:17:06 CST 2025pts/0 上
[kefu@web ~]$ ;s
-bash: 未预期的符号 `;' 附近有语法错误
[kefu@web ~]$ ls
test99
[kefu@web ~]$ ll -d test99
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kefu kefu 13631488 7月 23 22:08 test99
[kefu@web ~]$ cd /u1
[kefu@web u1]$ cd /u2
[kefu@web u2]$ lvs
WARNING: Ignoring duplicate config value: snapshot_autoextend_percentWARNING: Running as a non-root user. Functionality may be unavailable./run/lvm/lvmetad.socket: access failed: 权限不够WARNING: Failed to connect to lvmetad. Falling back to device scanning./dev/mapper/control: open failed: 权限不够Failure to communicate with kernel device-mapper driver.Incompatible libdevmapper 1.02.170-RHEL7 (2020-03-24) and kernel driver (unknown version).
[kefu@web u2]$ su - caozx26
密码:
上一次登录:三 7月 23 22:18:20 CST 2025pts/0 上
[caozx26@web ~]$ sudo su
[sudo] caozx26 的密码:
[root@web caozx26]# lvs
WARNING: Ignoring duplicate config value: snapshot_autoextend_percentWARNING: Device for PV r1noGN-Dn5A-udh3-qROp-C2Tj-HSil-AMqIZX not found or rejected by a filter.Couldn't find device with uuid r1noGN-Dn5A-udh3-qROp-C2Tj-HSil-AMqIZX.LV VG Attr LSize Pool Origin Data% Meta% Move Log Cpy%Sync Convertroot centos -wi-ao---- <17.00gswap centos -wi-ao---- 2.00glv01 vg01 -wi-a----- <3.09glv02 vg01 -wi-a----- 120.00mlv03 vg01 -wi-a----- 36.00mlv1 vg1 owi-aor-r- 1.50g 100.00lv1-snap vg1 swi-aos--- 128.00m lv1 23.59lv7 vg7 -wi-ao---- <2.10glv8 vg7 -wi-a----- 1.20glv_mysql vg_mysql -wi-ao---- 8.00g
[root@web caozx26]# df -h
文件系统 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点
devtmpfs 470M 0 470M 0% /dev
tmpfs 487M 0 487M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 487M 39M 448M 8% /run
tmpfs 487M 0 487M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/centos-root 17G 17G 617M 97% /
/dev/sda1 1014M 172M 843M 17% /boot
/dev/sr0 4.4G 4.4G 0 100% /mnt
tmpfs 98M 12K 98M 1% /run/user/42
tmpfs 98M 0 98M 0% /run/user/0
/dev/mapper/vg7-lv7 2.1G 6.0M 2.0G 1% /u7
/dev/mapper/vg_mysql-lv_mysql 7.8G 1.2G 6.2G 17% /usr/local/mysql
/dev/mapper/vg1-lv1 1.5G 35M 1.4G 3% /uc1
/dev/mapper/vg1-lv1--snap 1.5G 4.6M 1.4G 1% /mmt/lv1-snap
/dev/sdb2 976M 2.6M 907M 1% /u2
[root@web caozx26]# cat /etc/fstab#
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Sat Apr 19 17:11:28 2025
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
# See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info
#
/dev/mapper/centos-root / xfs defaults 0 0
UUID=0671af2f-69a1-4a84-bb51-ceb937bc1a92 /boot xfs defaults 0 0
/dev/mapper/centos-swap swap swap defaults 0 0
/dev/sdb2 /u2 ext4 defaults,usrquota,grpquota 0 0
/dev/sdd6 swap swap defaults 0 0
/tmp/swapfile swap swap defaults,pir=1 0 0
[root@web caozx26]# vim /etc/fstab
[root@web caozx26]# cat /etc/fstab#
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Sat Apr 19 17:11:28 2025
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
# See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info
#
/dev/mapper/centos-root / xfs defaults 0 0
UUID=0671af2f-69a1-4a84-bb51-ceb937bc1a92 /boot xfs defaults 0 0
/dev/mapper/centos-swap swap swap defaults 0 0
/dev/sdb2 /u2 ext4 defaults,usrquota,grpquota 0 0
/dev/sdd6 swap swap defaults 0 0
/tmp/swapfile swap swap defaults,pir=1 0 0
/dev/vg7/lv7 /u7 ext4 defaults,usrquota,grpquota 0 0
[root@web caozx26]# lvdisplay /dev/vg7/lv7
WARNING: Ignoring duplicate config value: snapshot_autoextend_percent--- Logical volume ---LV Path /dev/vg7/lv7LV Name lv7VG Name vg7LV UUID 3fRcmT-SVql-wET3-8my5-JWGw-pe32-4Yb8N4LV Write Access read/writeLV Creation host, time web.cn, 2025-07-20 20:08:33 +0800LV Status available# open 1LV Size <2.10 GiBCurrent LE 537Segments 2Allocation inheritRead ahead sectors auto- currently set to 8192Block device 253:7[root@web caozx26]# lvs
WARNING: Ignoring duplicate config value: snapshot_autoextend_percentWARNING: Device for PV r1noGN-Dn5A-udh3-qROp-C2Tj-HSil-AMqIZX not found or rejected by a filter.Couldn't find device with uuid r1noGN-Dn5A-udh3-qROp-C2Tj-HSil-AMqIZX.LV VG Attr LSize Pool Origin Data% Meta% Move Log Cpy%Sync Convertroot centos -wi-ao---- <17.00gswap centos -wi-ao---- 2.00glv01 vg01 -wi-a----- <3.09glv02 vg01 -wi-a----- 120.00mlv03 vg01 -wi-a----- 36.00mlv1 vg1 owi-aor-r- 1.50g 100.00lv1-snap vg1 swi-aos--- 128.00m lv1 23.59lv7 vg7 -wi-ao---- <2.10glv8 vg7 -wi-a----- 1.20glv_mysql vg_mysql -wi-ao---- 8.00g
[root@web caozx26]# lvs
WARNING: Ignoring duplicate config value: snapshot_autoextend_percentWARNING: Device for PV r1noGN-Dn5A-udh3-qROp-C2Tj-HSil-AMqIZX not found or rejected by a filter.Couldn't find device with uuid r1noGN-Dn5A-udh3-qROp-C2Tj-HSil-AMqIZX.LV VG Attr LSize Pool Origin Data% Meta% Move Log Cpy%Sync Convertroot centos -wi-ao---- <17.00gswap centos -wi-ao---- 2.00glv01 vg01 -wi-a----- <3.09glv02 vg01 -wi-a----- 120.00mlv03 vg01 -wi-a----- 36.00mlv1 vg1 owi-aor-r- 1.50g 100.00lv1-snap vg1 swi-aos--- 128.00m lv1 23.59lv7 vg7 -wi-ao---- <2.10glv8 vg7 -wi-a----- 1.20glv_mysql vg_mysql -wi-ao---- 8.00g
[root@web caozx26]# blkid /dev/vg7/lv7
/dev/vg7/lv7: UUID="c640c94d-33a2-499f-824c-55112dbbd647" TYPE="ext4"
[root@web caozx26]# cat /etc/fstab#
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Sat Apr 19 17:11:28 2025
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
# See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info
#
/dev/mapper/centos-root / xfs defaults 0 0
UUID=0671af2f-69a1-4a84-bb51-ceb937bc1a92 /boot xfs defaults 0 0
/dev/mapper/centos-swap swap swap defaults 0 0
/dev/sdb2 /u2 ext4 defaults,usrquota,grpquota 0 0
/dev/sdd6 swap swap defaults 0 0
/tmp/swapfile swap swap defaults,pir=1 0 0
/dev/vg7/lv7 /u7 ext4 defaults,usrquota,grpquota 0 0
[root@web caozx26]# df -h
文件系统 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点
devtmpfs 470M 0 470M 0% /dev
tmpfs 487M 0 487M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 487M 39M 448M 8% /run
tmpfs 487M 0 487M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/centos-root 17G 17G 618M 97% /
/dev/sda1 1014M 172M 843M 17% /boot
/dev/sr0 4.4G 4.4G 0 100% /mnt
tmpfs 98M 12K 98M 1% /run/user/42
tmpfs 98M 0 98M 0% /run/user/0
/dev/mapper/vg7-lv7 2.1G 6.0M 2.0G 1% /u7
/dev/mapper/vg_mysql-lv_mysql 7.8G 1.2G 6.2G 17% /usr/local/mysql
/dev/mapper/vg1-lv1 1.5G 35M 1.4G 3% /uc1
/dev/mapper/vg1-lv1--snap 1.5G 4.6M 1.4G 1% /mmt/lv1-snap
/dev/sdb2 976M 2.6M 907M 1% /u2
[root@web caozx26]# umount /u7
[root@web caozx26]# mount -a
[root@web caozx26]# mount |grep u7
/dev/mapper/vg7-lv7 on /u7 type ext4 (rw,relatime,quota,usrquota,grpquota,data=ordered)
[root@web caozx26]# ll /u7
总用量 16
drwx------ 2 root root 16384 7月 20 20:18 lost+found
[root@web caozx26]# quotacheck -acug
quotacheck: Quota for users is enabled on mountpoint /u2 so quotacheck might damage the file.
Please turn quotas off or use -f to force checking.
[root@web caozx26]# ll /u7
总用量 16
drwx------ 2 root root 16384 7月 20 20:18 lost+found
[root@web caozx26]# vim /etc/fstab
[root@web caozx26]# cat /etc/fstab#
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Sat Apr 19 17:11:28 2025
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
# See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info
#
/dev/mapper/centos-root / xfs defaults 0 0
UUID=0671af2f-69a1-4a84-bb51-ceb937bc1a92 /boot xfs defaults 0 0
/dev/mapper/centos-swap swap swap defaults 0 0
/dev/sdb2 /u2 ext4 defaults 0 0
/dev/sdd6 swap swap defaults 0 0
/tmp/swapfile swap swap defaults,pir=1 0 0
/dev/vg7/lv7 /u7 ext4 defaults,usrquota,grpquota 0 0
[root@web caozx26]# mount -a
[root@web caozx26]# mount |grep u7
/dev/mapper/vg7-lv7 on /u7 type ext4 (rw,relatime,quota,usrquota,grpquota,data=ordered)
[root@web caozx26]# quotacheck -acug
quotacheck: Quota for users is enabled on mountpoint /u2 so quotacheck might damage the file.
Please turn quotas off or use -f to force checking.
[root@web caozx26]# quotaoff -avug
/dev/sdb2 [/u2]: group quotas turned off
/dev/sdb2 [/u2]: user quotas turned off
/dev/mapper/vg7-lv7 [/u7]: group quotas turned off
/dev/mapper/vg7-lv7 [/u7]: user quotas turned off
[root@web caozx26]# quotacheck -acug
[root@web caozx26]# ll /u7
总用量 32
-rw------- 1 root root 6144 7月 23 23:08 aquota.group
-rw------- 1 root root 6144 7月 23 23:08 aquota.user
drwx------ 2 root root 16384 7月 20 20:18 lost+found
[root@web caozx26]# quotaon -a
[root@web caozx26]# edquota -u kefu2
[root@web caozx26]# quota -uvs kefu2
Disk quotas for user kefu2 (uid 1023):Filesystem space quota limit grace files quota limit grace/dev/sdb2 0K 0K 0K 0 0 0
/dev/mapper/vg7-lv70K 10240K 12288K 0 10 15
[root@web caozx26]# su - kefu2
[kefu2@web ~]$ dd if=/dev/zero of=test99 bs=1M count=11
记录了11+0 的读入
记录了11+0 的写出
11534336字节(12 MB)已复制,0.00745521 秒,1.5 GB/秒
[kefu2@web ~]$ dd if=/dev/zero of=test99 bs=1M count=13
记录了13+0 的读入
记录了13+0 的写出
13631488字节(14 MB)已复制,0.0136268 秒,1.0 GB/秒
[kefu2@web ~]$ ls
test99
[kefu2@web ~]$ quota -uvs kefu2
Disk quotas for user kefu2 (uid 1023):Filesystem space quota limit grace files quota limit grace/dev/sdb2 0K 0K 0K 0 0 0
/dev/mapper/vg7-lv70K 10240K 12288K 0 10 15
[kefu2@web ~]$ ls -l /u7/auoata*
ls: 无法访问/u7/auoata*: 没有那个文件或目录
[kefu2@web ~]$ ls -l /uj7\
> ^C
[kefu2@web ~]$ ls -l /u7
总用量 32
-rw------- 1 root root 6144 7月 23 23:08 aquota.group
-rw------- 1 root root 7168 7月 23 23:08 aquota.user
drwx------ 2 root root 16384 7月 20 20:18 lost+found
[kefu2@web ~]$ ls -l /u7/aquota*
-rw------- 1 root root 6144 7月 23 23:08 /u7/aquota.group
-rw------- 1 root root 7168 7月 23 23:08 /u7/aquota.user
[kefu2@web ~]$ quotaon -p /u7
group quota on /u7 (/dev/mapper/vg7-lv7) is on
user quota on /u7 (/dev/mapper/vg7-lv7) is on
[kefu2@web ~]$ dd if=/dev/zero of=/u7/test12 bs=1M count=12
dd: 打开"/u7/test12" 失败: 权限不够
[kefu2@web ~]$ su - caozx26
密码:
上一次登录:三 7月 23 22:41:43 CST 2025pts/0 上
[caozx26@web ~]$ sudo su
[sudo] caozx26 的密码:
[root@web caozx26]# setfacl -m u:kefu2:rwx /u7
[root@web caozx26]# su - kefu2
上一次登录:三 7月 23 23:14:04 CST 2025pts/0 上
[kefu2@web ~]$ ll -d /u7
drwxrwxr-x+ 3 root root 4096 7月 23 23:08 /u7
[kefu2@web ~]$ cd /u7
[kefu2@web u7]$ ll
总用量 32
-rw------- 1 root root 6144 7月 23 23:08 aquota.group
-rw------- 1 root root 7168 7月 23 23:08 aquota.user
drwx------ 2 root root 16384 7月 20 20:18 lost+found
[kefu2@web u7]$ touch file{1..8}
[kefu2@web u7]$ ls
aquota.group aquota.user file1 file2 file3 file4 file5 file6 file7 file8 lost+found
[kefu2@web u7]$ touch file{9..11}
dm-7: warning, user file quota exceeded.
[kefu2@web u7]$ ll
总用量 32
-rw------- 1 root root 7168 7月 23 23:08 aquota.group
-rw------- 1 root root 7168 7月 23 23:08 aquota.user
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kefu2 kefu2 0 7月 23 23:52 file1
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kefu2 kefu2 0 7月 23 23:52 file10
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kefu2 kefu2 0 7月 23 23:52 file11
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kefu2 kefu2 0 7月 23 23:52 file2
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kefu2 kefu2 0 7月 23 23:52 file3
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kefu2 kefu2 0 7月 23 23:52 file4
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kefu2 kefu2 0 7月 23 23:52 file5
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kefu2 kefu2 0 7月 23 23:52 file6
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kefu2 kefu2 0 7月 23 23:52 file7
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kefu2 kefu2 0 7月 23 23:52 file8
-rw-rw-r-- 1 kefu2 kefu2 0 7月 23 23:52 file9
drwx------ 2 root root 16384 7月 20 20:18 lost+found
[kefu2@web u7]$ touch file{12..16}
dm-7: write failed, user file limit reached.
touch: 无法创建"file16": 超出磁盘限额
[kefu2@web u7]$ rm -f file *
rm: 无法删除"aquota.group": 不允许的操作
rm: 无法删除"aquota.user": 不允许的操作
rm: 无法删除"lost+found": 是一个目录
[kefu2@web u7]$ rm -f file*
[kefu2@web u7]$ ls
aquota.group aquota.user lost+found
[kefu2@web u7]$ dd if=/dev/zero of=/u7/file1 bs=1M count=11
dm-7: warning, user block quota exceeded.
记录了11+0 的读入
记录了11+0 的写出
11534336字节(12 MB)已复制,0.0178305 秒,647 MB/秒
[kefu2@web u7]$ ls
aquota.group aquota.user file1 lost+found
[kefu2@web u7]$ dd if=/dev/zero of=/u7/file2 bs=2M count=1
dm-7: write failed, user block limit reached.
dd: 写入"/u7/file2" 出错: 超出磁盘限额
记录了1+0 的读入
记录了0+0 的写出
1048576字节(1.0 MB)已复制,0.00197683 秒,530 MB/秒
[kefu2@web u7]$