[C++进阶]二叉树进阶的一些面试题(一)
首先我们先回忆我们过去学的二叉树和最近学的二叉搜索树,来完成下面的题目:
606. 根据二叉树创建字符串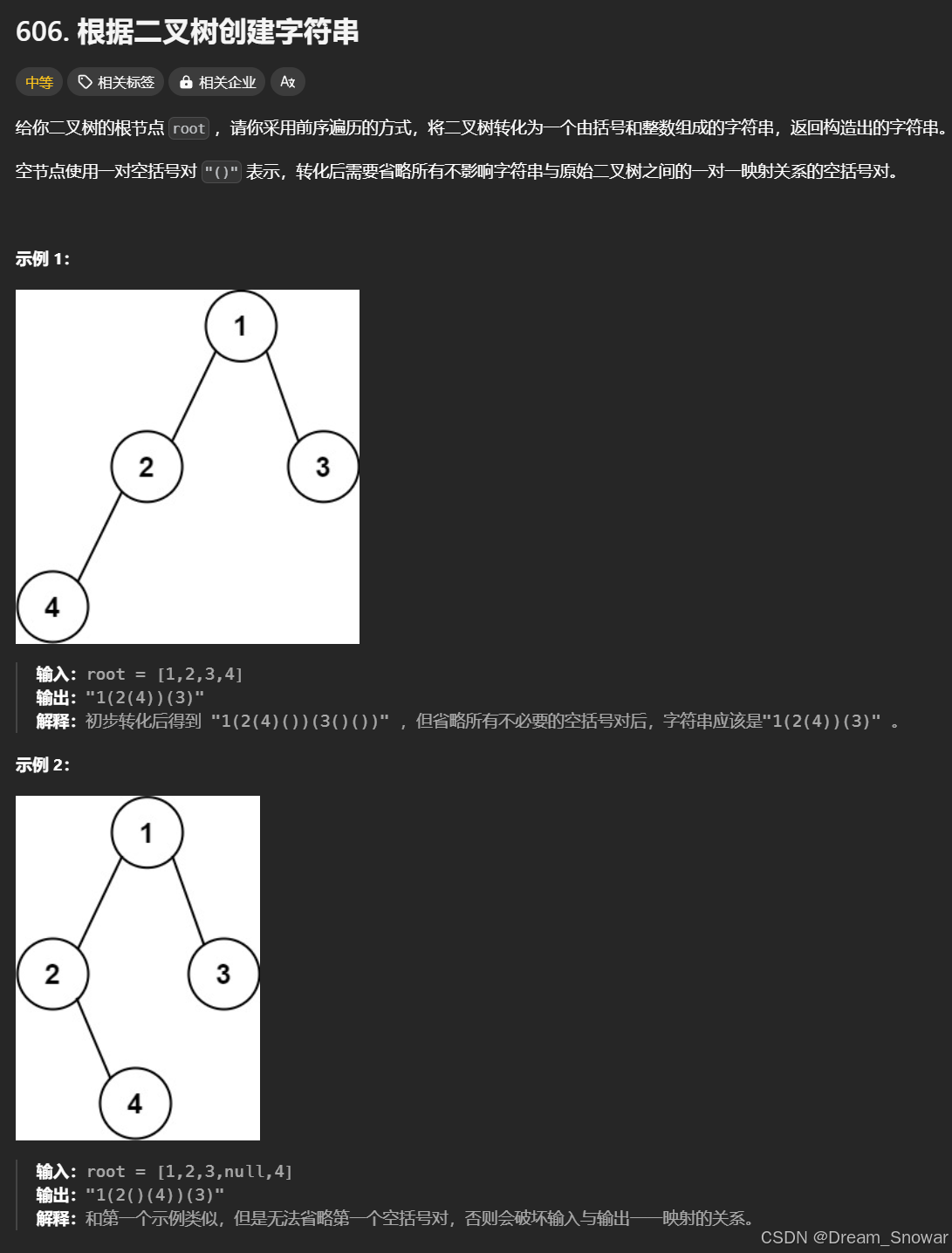
这道题属于与基础题,首先我们观察输入输出样例可以得到如果root->left为空,root->right不为空时,我们的空格仍然需要保留,如果当前节点有两个孩子,那我们在递归时,需要在两个孩子的结果外都加上一层括号;如果当前节点没有孩子,那我们不需要在节点后面加上任何括号;如果当前节点只有左孩子,那我们在递归时,只需要在左孩子的结果外加上一层括号,而不需要给右孩子加上任何括号;
代码示例:
class Solution {
public:string tree2str(TreeNode* root) {string str;if(root==nullptr){return str;}str+=to_string(root->val);if(root->left||root->right){ str+='(';str+=tree2str(root->left);str+=')';}if(root->right){str+='(';str+=tree2str(root->right);str+=')';}return str;}
};102. 二叉树的层序遍历

我们可以通过队列来解决
核心思想:我们在层序遍历过程中,增加一-个levelSize,记录每层的数据个数,树不为空的情况下,第1层levelSize=1,循环控制,第1层出完了,第2层就都进队列了,队列中size就是第2层的数据个数。以此内推,假设levelSize为第n层的数据个数,因为层序遍历思想为当前层结点出队列,带入下一层结点(也就是子结点),循环控制第n层数据出完了,那么第n+1结点都进队列了,队列size,就是下一层的levelSize。
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {vector<vector<int>> vv;queue<TreeNode*> q;int levelsize=0;if(root){q.push(root);levelsize=1;}while(levelsize){vector<int> v;while(levelsize--){TreeNode*front=q.front();q.pop();v.push_back(front->val);if(front->left)q.push(front->left);if(front->right)q.push(front->right);}levelsize=q.size();vv.push_back(v);}return vv;}
};107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II

上题我们搞完了,这题我们其实有个很简单的办法,我们把上题的代码赋值过来直接逆置即可
代码示例:
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode* root) {vector<vector<int>> vv;queue<TreeNode*> q;int levelsize=0;if(root){q.push(root);levelsize=1;}while(levelsize){vector<int> v;while(levelsize--){TreeNode*front=q.front();q.pop();v.push_back(front->val);if(front->left)q.push(front->left);if(front->right)q.push(front->right);}vv.push_back(v);levelsize=q.size();}reverse(vv.begin(),vv.end());return vv;}
};236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先

本题思路有二,我们一个一个来讲
方法一:递归
首先我们对于题意进行分析,我们可以知道公共祖先分为以下几种情况:
1.p或q在root节点处,此时最近的公共祖先就是root
2.p和q分别分布在root的左右子树,此时公共祖先就是root
3.p和q分布在root的同一子树,此时我们可以把该子节点看作root,继续判断。
代码实现:
class Solution {
public:bool Intree(TreeNode* t,TreeNode* x){if(!t){return false;}return x==t||Intree(t->left,x)||Intree(t->right,x);}TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {if(root==p||root==q){return root;}bool pinleft=Intree(root->left,p);bool pinright=!pinleft;bool qinleft=Intree(root->left,q);bool qinright=!qinleft;if((pinleft&&qinright)||(pinright&&qinleft)){return root;}else if(pinleft&&qinleft){return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left,p,q);}else{return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right,p,q);}}
};下面我们来讲讲第二种方法
思路2:如果能求出两个结点到根的路径,那么就可以转换为链表相交问题。如: 6到根3的路径为6->5->3, 4到根3的路径为4->2->5->3,那么看做两个链表找交点,交点5就是最近公共祖先。

代码示例:
class Solution {
public:bool GetPath(TreeNode* root,TreeNode* x,stack<TreeNode*>& path){if(root==nullptr)return false;path.push(root);if(root==x)return true;if(GetPath(root->left,x,path))return true;if(GetPath(root->right,x,path))return true;path.pop();return false;}TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {stack<TreeNode*> ppath,qpath;GetPath(root,p,ppath);GetPath(root,q,qpath);//确定长度while(ppath.size()!=qpath.size()){//长的先if(ppath.size()>qpath.size()){ppath.pop();}else{qpath.pop();}}//找交点while(ppath.top()!=qpath.top()){ppath.pop();qpath.pop();}//输出交点return ppath.top();}
};JZ36 二叉搜索树与双向链表

这题在我们学完二叉搜索树之后大家应该觉得不难吧,核心思想:中序遍历
代码示例:
#include <cstddef>
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* head=nullptr;TreeNode* cur=nullptr;TreeNode* Convert(TreeNode* pRootOfTree) {if(pRootOfTree==nullptr)return nullptr;Convert(pRootOfTree->left);if(cur==nullptr){head=pRootOfTree;cur=pRootOfTree;}else {cur->right=pRootOfTree;pRootOfTree->left=cur;cur=pRootOfTree;}Convert(pRootOfTree->right);return head;}
};105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树

本题咋一看很简单,仔细一看好像有点难,但是一看提示,瞬间就来了思路,其实很简单是不是.
我的思路:根据前序确定根,然后再中序中确定根所处的位置,分割两个区间,然后递归即可。,递归截止的条件为当左右不构成区间。
代码示例:
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* build(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder, int& prei, int inbegin, int inend) {if(inbegin>inend)return nullptr;//前序确定根TreeNode* root=new TreeNode(preorder[prei]);//中序分割左右子树int rooti=inbegin;while(rooti<=inend){if(preorder[prei] ==inorder[rooti])break;elserooti++;}prei++;root->left=build(preorder,inorder,prei,inbegin,rooti-1);root->right=build(preorder,inorder,prei,rooti+1,inend);return root;}TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {int i=0;return build(preorder,inorder,i,0,inorder.size()-1);}
};106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树

这题是上一题的兄弟题,我们直接上代码了,不懂的再想想,画画递归展开图
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* build(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder,int& posti,int inbegin,int inend){if(inbegin>inend)return nullptr;TreeNode* newnode=new TreeNode(postorder[posti]);int inpos=inbegin;while(inpos<=inend){if(postorder[posti]==inorder[inpos]){break;}inpos++;}posti--;newnode->right = build(inorder,postorder,posti,inpos+1,inend);newnode->left = build(inorder,postorder,posti,inbegin,inpos-1);return newnode;}TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {int i=postorder.size()-1;return build(inorder,postorder,i,0,inorder.size()-1);}
};