[Android Studio]Android 数据存储-文件存储学习笔记-结合保存QQ账户与密码存储到指定文件中的演练
🟧🟨🟩🟦🟪 Android Debug🟧🟨🟩🟦🟪
Topic
发布安卓学习过程中遇到问题解决过程,希望我的解决方案可以对小伙伴们有帮助。

📋笔记目录
🪁文件存储
💾内部存储
📀存储数据到文件
💿从文件中读取数据
💯实战演练--保存QQ账号与密码
📖acticity_main.xml布局文件
📖 FileSaveQQ.java文件
📖MainActivity.java文件
⭐验证文件存储
🚩结尾
🪁文件存储
文件存储是Android中最基本的一种数据存储方式,其与Java中的文件存储类似,都是通过I/O流的形式把数据直接存储到文件中。
如果想要将数据存入文件中,有两种存储方式,一种是内部存储,一种是外部存储。其中内部存储是将数据以文件的形式存储到应用中,外部存储是将数据文件的形式存储到一些外部设备上,如SD卡。
今天学习的是Android 文件存储中的内部存储形式。
💾内部存储
内部存储是指将应用程序中的数据与文件的形式存储到应用中,此时存储的文件会被其所在的应用存序私有化,如果其他应用程序想要操作文应用程序中的文件则需要设置权限,当创建的应用程序被卸载时,其内部存储文件也随之被删除。
Android开发中,内部存储使用的是 Context 提供的 openFileOutput() 方法和 openFileInput() 方法,这两种方法能够返回进行读写操作的 FileoutputStream 对象和 FileInputstream 对象。
FileOutputStream fos = openFileOutput(String name,int mode);
FileInputStream fis = openFileInput(String name);openFileOutput()方法,用打开应用程序中对应的输出流,将数据存储到指定的文件中。
openFileInput()方法用于打开应用程序对应的输入流,读取指定文件中的数据。
它们的参数"name"表示文件名,"mode"表示文件的操作模式,也就是读写文件的形式.
"mode"的取值有四种,具体如下:
MODE_PRIVATE: 该文件只能被当前程序读写;
MODE_APPEND: 该文件的内容可以追加;
MODE_WORLD_READABLE: 该文件的内容以被其他程序读;
MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE: 该文件的内容可以被其他程序写。
值得注意的是,安卓系统有一套自己的安全模型,默认情况下,任何应用创建的文件都是私有的,其他程序无法访问,除非在文件创建时指定的操作模式为MODE_WORLD_READABLE或MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE,如果希望文件能够被其他程序进行读写操作,则需要同时指定该文件MODE_WORLD_READABLE 和 MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE的权限。
📀存储数据到文件
存储数据时,使用FileOutputStream对象将数据存储到文件中,实例代码如下:
String fileName = "data.txt"; //文件名称String content = "helloworld"; //保存数据FileOutputStream fos = null;try {fos = context.openFileOutput(FileName,MODE_PRIVATE);fos.write((content.getBytes()); //将数据写入文件中return true;} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}finally {try {if (fos != null){fos.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}上述代码中首先定义了两个String类型的变量fileName和content,这两个变量的值”data.txt“ 与 ”helloworld“分别表示文件名与要写入文件的数据,接着创建了FileOutputStream对象,fos通过该对象的write()方法将数据"helloworld"写入"data.txt"文件。
💿从文件中读取数据
存储好数据之后,如果需要获取这些数据,则需要从文件中读取存储的数据,关于读取内部存储文件中的数据,具体方式如下所示:
String content = "";FileInputStream fis = null;try { fis = context.openFileInput("data.txt"); //获取文件输入流对象byte[] buffer = new byte[fis.available()]; //创建缓冲区,并获取文件长度fis.read(buffer); //将文件内容读取到buffer缓冲区content = new String(buffer); //转换成字符串} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}finally {try {if (fis != null){fis.close(); //关闭输入流}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}上述代码中首先通过openFileinput()方法获取到文件输入流对象,然后通过available()方法获取文件的长度,并创建相应大小的byte数组作为缓冲区,再通过read()方法将文件内容读取到buffer缓冲区中,最后将读取到的内容转换成指定字符串。
💯实战演练--保存QQ账号与密码
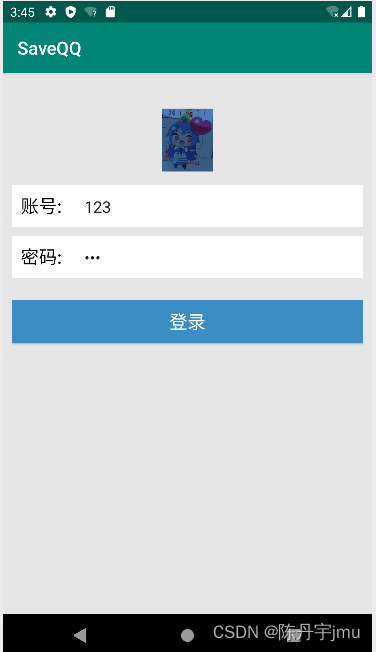
效果演示
1,创建程序
创建一个名为SaveQQ的应用程序,指定报名为cn.example.saveqq。
2,导入界面图片
将保存QQ密码界面所需要的图片head.png导入到项目中的drawable文件夹中,
3,放置界面图片
在activity_main.xml布局文件中放置一个ImageView控件,用于显示用户头像,两个TextView控件,用于分别用于显示"账号: "与"密码: "文本信息,两个EditText控件分别用于输入账号和密码信息,一个Button控件用于显示登录按钮。
4,创建工具类
由于QQ账号和密码需要存放在文件中,因此,需要在程序中的cn.example.saveqq包中创建一个工具类FileSaveQQ,在该类中实现QQ账号和密码的存储与读取功能。
📖acticity_main.xml布局文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"android:orientation="vertical"android:padding="10dp"android:background="#E6E6E6"><ImageViewandroid:layout_width="70dp"android:layout_height="70dp"android:layout_marginTop="30dp"android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"android:src="@drawable/head"/><LinearLayoutandroid:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:layout_marginTop="15dp"android:background="@android:color/white"android:orientation="horizontal"><TextViewandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:padding="10dp"android:text="账号:"android:textColor="#000"android:textSize="20sp" /><EditTextandroid:hint="输入的是数字"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:id="@+id/et_account"android:layout_marginLeft="5dp"android:background="@null"android:padding="10dp"/></LinearLayout><LinearLayoutandroid:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:layout_marginTop="10dp"android:background="@android:color/white"android:orientation="horizontal"><TextViewandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:id="@+id/tv_password"android:padding="10dp"android:text="密码:"android:textSize="20sp"android:textColor="#000"/><EditTextandroid:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:id="@+id/et_password"android:layout_marginLeft="5dp"android:background="@null"android:inputType="textPassword"android:padding="10dp"/></LinearLayout><Buttonandroid:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:id="@+id/btn_login"android:text="登录"android:layout_marginTop="25dp"android:background="#3c8dc4"android:textColor="@android:color/white"android:textSize="20sp"/></LinearLayout>📖 FileSaveQQ.java文件
package com.example.saveqq;import android.content.Context;import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;public class FileSaveQQ {public static boolean saveUserinfo(Context context,String account,String password){FileOutputStream fos = null;try {fos = context.openFileOutput("data.txt",Context.MODE_PRIVATE);fos.write((account + ":" +password).getBytes());return true;} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();return false;}finally {try {if (fos != null){fos.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}public static Map<String,String> getUserInfo(Context context){String content = "";FileInputStream fis = null;try {fis = context.openFileInput("data.txt");byte[] buffer = new byte[fis.available()];fis.read(buffer);content = new String(buffer);Map<String,String> userMap = new HashMap<String, String>();String[] infos = content.split(":");userMap.put("account",infos[0]);userMap.put("password",infos[1]);return userMap;} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();return null;}finally {try {if (fis != null){fis.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
}
📖MainActivity.java文件
package com.example.saveqq;import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;import android.os.Bundle;
import android.text.TextUtils;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;import java.util.Map;public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {private EditText et_account;private EditText et_password;private Button btn_login;@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);initView();Map<String,String> userInfo = FileSaveQQ.getUserInfo(this);if (userInfo != null){et_account.setText(userInfo.get("account"));et_password.setText(userInfo.get("password"));}}private void initView() {et_account = findViewById(R.id.et_account);et_password = findViewById(R.id.et_password);btn_login = findViewById(R.id.btn_login);btn_login.setOnClickListener(this);}@Overridepublic void onClick(View v) {switch (v.getId()){case R.id.btn_login:String account = et_account.getText().toString().trim();String password = et_password.getText().toString();if (TextUtils.isEmpty(account)){Toast.makeText(this,"请输入QQ号",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();return;}if (TextUtils.isEmpty(password)){Toast.makeText(this,"请输入密码",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();return;}Toast.makeText(this,"登录成功",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();boolean isSaveSucess = FileSaveQQ.saveUserinfo(this,account,password);if (isSaveSucess){Toast.makeText(this,"保存成功",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();}else {Toast.makeText(this,"保存失败",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();}break;}}
}
⭐验证文件存储
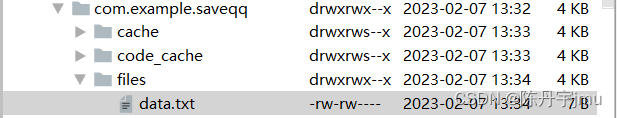
为了验证程序是否操作成功,可以通Device File Explorer视图中找到data/data目录,并在该目录中找到本程序对应报名中的data.txt文件,该文件所在的目录下图所示,双击Device File Explorer视图中的data.txt,即可Android Studio编辑框中查看data,txt文件中存储的QQ账号和密码数据,此时说明存储成功。
如需使用设备的文件系统,请按以下步骤操作:
- 如需打开设备浏览器,请依次选择 View > Tool Windows > Device File Explorer,或点击工具窗口栏中的 Device File Explorer 按钮。
- 从列表中选择设备。
- 在文件浏览器窗口中与设备内容交互:
- 右键点击某个文件或目录即可创建新的文件或目录。
- 保存、上传、删除所选文件或目录,或将其同步到您的计算机。
- 双击某个文件可在 Android Studio 中将其打开。
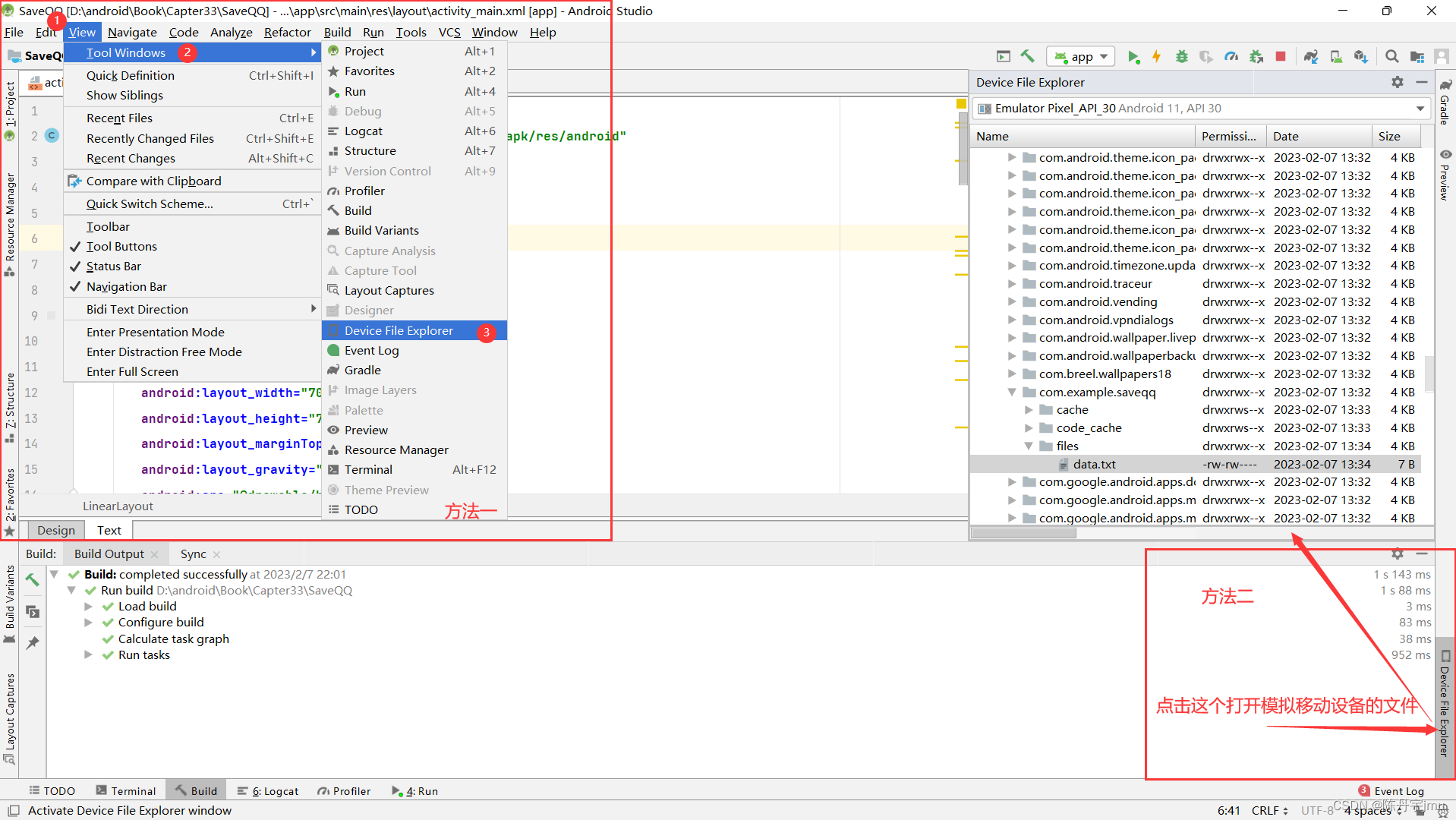
可以找到Android Studio 模拟机上的所装载的应用程序的文件存储内容。
🚩结尾
至此,文件存储的相关知识已讲解完成,该知识所用到的核心技术是利用I/O流来进行文件读写操作,其中,Context类中提供的openFileInput()和OpenFileOutput()方法的用法,一定要掌握。

🎁欢迎各位→点赞👍 + 收藏⭐️ + 留言📝
🌈写给读者:很高兴你能看到我的文章,希望我的文章可以帮助到你,祝万事顺意🏳️🌈
