[论文精读]Semi-Supervised Classification with Graph Convolutional Networks
论文原文:[1609.02907] Semi-Supervised Classification with Graph Convolutional Networks (arxiv.org)
论文代码:GitHub - tkipf/gcn: Implementation of Graph Convolutional Networks in TensorFlow
英文是纯手打的!论文原文的summarizing and paraphrasing。可能会出现难以避免的拼写错误和语法错误,若有发现欢迎评论指正!文章偏向于笔记,谨慎食用!
1. 省流版
1.1. 心得
(1)怎么开头我就不知道在说什么啊这个论文感觉表述不是很清晰?
(2)数学部分推理很清晰
1.2. 论文框架图
2. 论文逐段阅读
2.1. Abstract
①Their convolution is based on localized first-order approximation
②They encode node features and local graph structure in hidden layers
2.2. Introduction
①The authors think adopting Laplacian regularization in the loss function helps to label:
where represents supervised loss with labeled data,
is a differentiable function,
denotes weight,
denotes matrix with combination of node feature vectors,
represents the unnormalized graph Laplacian,
is adjacency matrix,
is degree matrix.
②The model trains labeled nodes and is able to learn labeled and unlabeled nodes
③GCN achieves higher accuracy and efficiency than others
2.3. Fast approximate convolutions on graphs
①GCN (undirected graph):
where denotes autoregressive adjacency matrix, which means
,
denotes identity matrix,
denotes autoregressive degree matrix,
represents the trainable weight matrix in
-th layer,
denotes the activation matrix in
-th layer,
represents activation function
2.3.1. Spectral graph convolutions
①Spectral convolutions on graphs:
where the filter ,
comes from normalized graph Laplacian
and is the matrix of
's eigenvectors,
denotes a diagonal matrix with eigenvalues.
②However, it is too time-consuming to compute matrix especially for large graph. Ergo, approximating it in -th order by Chebyshev polynomials:
where ,
denotes Chebyshev coefficients vector,
recursive Chebyshev polynomials are with baseline
and
③Then get new function:
where ,
.
④Through this approximation method, time complexity reduced from to
2.3.2. Layer-wise linear model
①Then, the authors stack the function above to build multiple conv layers and set ,
②They simplified 2.3.1. ③ to:
where and
are free parameters
③Nevertheless, more parameters bring more overfitting problem. It leads the authors change the expression to:
where they define ,
eigenvalues are in .
But keep using it may cause exploding/vanishing gradients or numerical instabilities.
④Then they adjust
⑤The convolved signal matrix :
where denotes input channels, namely feature dimensionality of each node,
denotes the number of filters or feature maps,
represents matrix of filter parameters
2.4. Semi-supervised node classification
2.4.1. Example
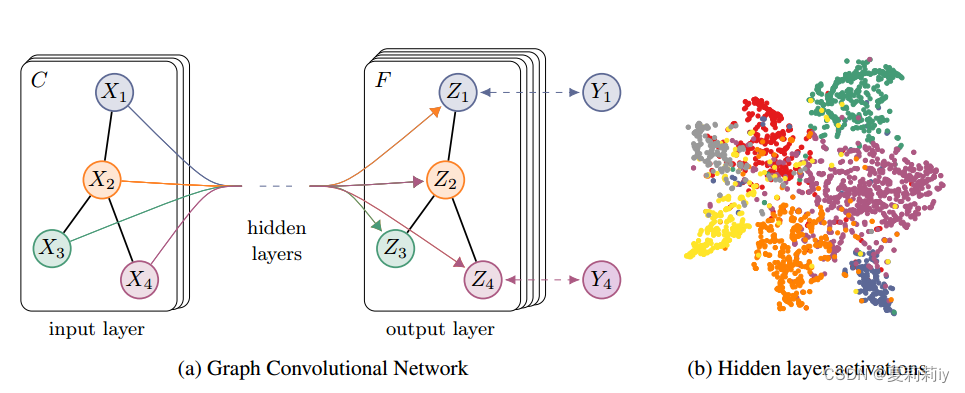
2.4.2. Implementation
2.5. Related work
2.5.1. Graph-based semi-supervised learning
2.5.2. Neural networks on graphs
2.6. Experiments
2.6.1. Datasets
2.6.2. Experimental set-up
2.6.3. Baselines
2.7. Results
2.7.1. Semi-supervised node classifiication
2.7.2. Evaluation of propagation model
2.7.3. Training time per epoch
2.8. Discussion
2.8.1. Semi-supervised model
2.8.2. Limitations and future work
2.9. Conclusion
3. 知识补充
4. Reference List
Kipf, T. & Welling, M. (2017) 'Semi-Supervised Classification with Graph Convolutional Networks', ICLR 2017, doi: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1609.02907
