【JUC基础】JUC入门基础
目录
- 什么是JUC
- 线程和进程
- 锁
- 传统的 synchronized
- Lock 锁
- Synchronized 与 Lock 的区别
- 生产者和消费者问题
- Synchronized 版
- Lock版
- Condition 的优势:精准通知和唤醒线程
- 8 锁现象
- 问题1:两个同步方法,先执行发短信还是打电话?
- 问题2:问题1基础上让发短信延迟 4s
- 问题三:换成一个普通方法结果?
- 问题四:如果使用的是两个对象,一个调用发短信,一个调用打电话,那么整个顺序是怎么样的呢?
- 问题五、六:如果我们把 synchronized 的方法加上 static 变成静态方法,那么顺序又是怎么样的呢?
- 问题七:如果使用一个静态同步方法、一个同步方法、一个对象调用顺序是什么?
- 问题八:如果我们使用一个静态同步方法、一个同步方法、两个对象调用顺序是什么?
什么是JUC
JUC 就是 java.util.concurrent 下面的类包,专门用于多线程的开发。

Lock:可重入锁、可重入读锁、可重入写锁

线程和进程
Java默认有几个线程?
答:2个线程。 main线程、GC线程
Java 真的可以开启线程吗?
答:开不了。Java 是没有权限去开启线程、操作硬件的,这是一个 native 的一个本地方法,它调用的底层的 C++ 代码。
// Thread类源码
public synchronized void start() {/*** This method is not invoked for the main method thread or "system"* group threads created/set up by the VM. Any new functionality added* to this method in the future may have to also be added to the VM.** A zero status value corresponds to state "NEW".*/if (threadStatus != 0)throw new IllegalThreadStateException();/* Notify the group that this thread is about to be started* so that it can be added to the group's list of threads* and the group's unstarted count can be decremented. */group.add(this);boolean started = false;try {start0();started = true;} finally {try {if (!started) {group.threadStartFailed(this);}} catch (Throwable ignore) {/* do nothing. If start0 threw a Throwable thenit will be passed up the call stack */}}}//这是一个C++底层,Java是没有权限操作底层硬件的private native void start0();
线程的状态有哪几种?
// Thread类源码
public enum State { //新生NEW,//运行RUNNABLE,//阻塞BLOCKED,//等待WAITING,//超时等待TIMED_WAITING,//终止TERMINATED;
}
并发:多线程操作同一个资源。CPU 只有一核,模拟出来多条线程。可以使用CPU快速交替,来模拟多线程。
并行:CPU多核,多个线程可以同时执行。 可以使用线程池。
获取CPU的核数:
// 获取CPU的核数
System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
wait / sleep:
- 1、来自不同的类 wait =>
Object,sleep =>Thread
// 一般情况企业中使用休眠
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;TimeUnit.DAYS.sleep(1); //休眠1天
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); //休眠1s
- 2、关于锁的释放 wait 会释放锁,sleep不会释放锁
- 3、使用的范围是不同的 wait 必须在同步代码块中,sleep 可以在任何地方睡
- 4、是否需要捕获异常 sleep 必须要捕获异常,wait 也是需要捕获异常,notify 和 notifyAll 不需要捕获异常
锁
传统的 synchronized
public class test {public static void main(String[] args) {//并发:多线程操作同一个资源类,将资源类丢入线程中Ticket ticket = new Ticket();new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++) {ticket.sale();}},"A").start();new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++) {ticket.sale();}},"B").start();new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++) {ticket.sale();}},"C").start();}
}// 资源类 OOP 属性、方法
class Ticket {private int number = 30;//卖票的方式public synchronized void sale() {if (number > 0) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "卖出了第" + (number--) + "张票剩余" + number + "张票");}}
}
Lock 锁
// ReentrantLock源码/*** Creates an instance of {@code ReentrantLock}.* This is equivalent to using {@code ReentrantLock(false)}.*/public ReentrantLock() {sync = new NonfairSync(); //非公平锁:十分不公平,可以插队;(默认为非公平锁)}/*** Creates an instance of {@code ReentrantLock} with the* given fairness policy.** @param fair {@code true} if this lock should use a fair ordering policy*/public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync(); //公平锁:十分公平,必须先来后到}
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;public class test {public static void main(String[] args) {Ticket2 ticket = new Ticket2();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++) {ticket.sale();}}, "A").start();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++) {ticket.sale();}}, "B").start();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++) {ticket.sale();}}, "C").start();}
}//lock三部曲
//1、 Lock lock=new ReentrantLock();
//2、 lock.lock() 加锁
//3、 finally=> 解锁:lock.unlock();
class Ticket2 {private int number = 30;// 创建锁Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();//卖票的方式public void sale() {lock.lock(); // 开启锁try {if (number > 0) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "卖出了第" + (number--) + "张票剩余" + number + "张票");}} finally {lock.unlock(); // 关闭锁}}
}
Synchronized 与 Lock 的区别
- Synchronized 内置的 Java关键字,Lock是一个 Java 类。
- Synchronized 无法判断获取锁的状态,Lock可以判断。
- Synchronized 会自动释放锁,Lock 必须要手动加锁和手动释放锁,可能会遇到死锁。
- Synchronized 线程1(获得锁->阻塞)、线程2(等待);Lock 就不一定会一直等待下去,Lock 会有一个trylock 去尝试获取锁,不会造成长久的等待。
- Synchronized 是可重入锁,不可以中断的,非公平的;Lock是可重入的,可以判断锁,可以自己设置公平锁和非公平锁。
- Synchronized 适合锁少量的代码同步问题,Lock适合锁大量的同步代码。
生产者和消费者问题
Synchronized 版
- Synchronized、wait、notify
/*** 线程之间的通信问题:生产者和消费者问题! 等待唤醒,通知唤醒* 线程交替执行 A B 操作同一个变量 num = 0* A num+1* B num-1*/
//顺序:判断待->业务->通知
public class test {public static void main(String[] args) {Data data = new Data();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {try {data.increment();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, "A").start();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {try {data.decrement();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, "B").start();}
}class Data {private int number = 0;//+1public synchronized void increment() throws InterruptedException {if (number != 0) {//等待this.wait();}number++;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + number);// 通知其他线程,我-1完毕了this.notifyAll();}//-1public synchronized void decrement() throws InterruptedException {if (number == 0) {//等待this.wait();}number--;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + number);// 通知其他线程,我-1完毕了this.notifyAll();}
}/*A=>1B=>0A=>1B=>0...
*/
俩个加俩个减 存在问题(虚假唤醒):
如果有四个线程,会出现虚假唤醒。
if 改为 while 即可,防止虚假唤醒。
结论:
就是用 if 判断的话,唤醒后线程会从 wait 之后的代码开始运行,但是不会重新判断if条件,直接继续运行 if 代码块之后的代码,而如果使用 while 的话,也会从 wait 之后的代码运行,但是唤醒后会重新判断循环条件,如果不成立再执行 while 代码块之后的代码块,成立的话继续 wait。这也就是为什么用 while 而不用if的原因了,因为线程被唤醒后,执行开始的地方是 wait 之后。
public class test {public static void main(String[] args) {Data data = new Data();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {try {data.increment();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, "A").start();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {try {data.decrement();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, "B").start();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {try {data.increment();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, "C").start();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {try {data.decrement();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, "D").start();}
}class Data {private int number = 0;//+1public synchronized void increment() throws InterruptedException {while (number != 0) {//等待this.wait();}number++;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + number);// 通知其他线程,我-1完毕了this.notifyAll();}//-1public synchronized void decrement() throws InterruptedException {while (number == 0) {//等待this.wait();}number--;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + number);// 通知其他线程,我-1完毕了this.notifyAll();}
}
Lock版
- Lock、await(Condition)、signal(Condition)
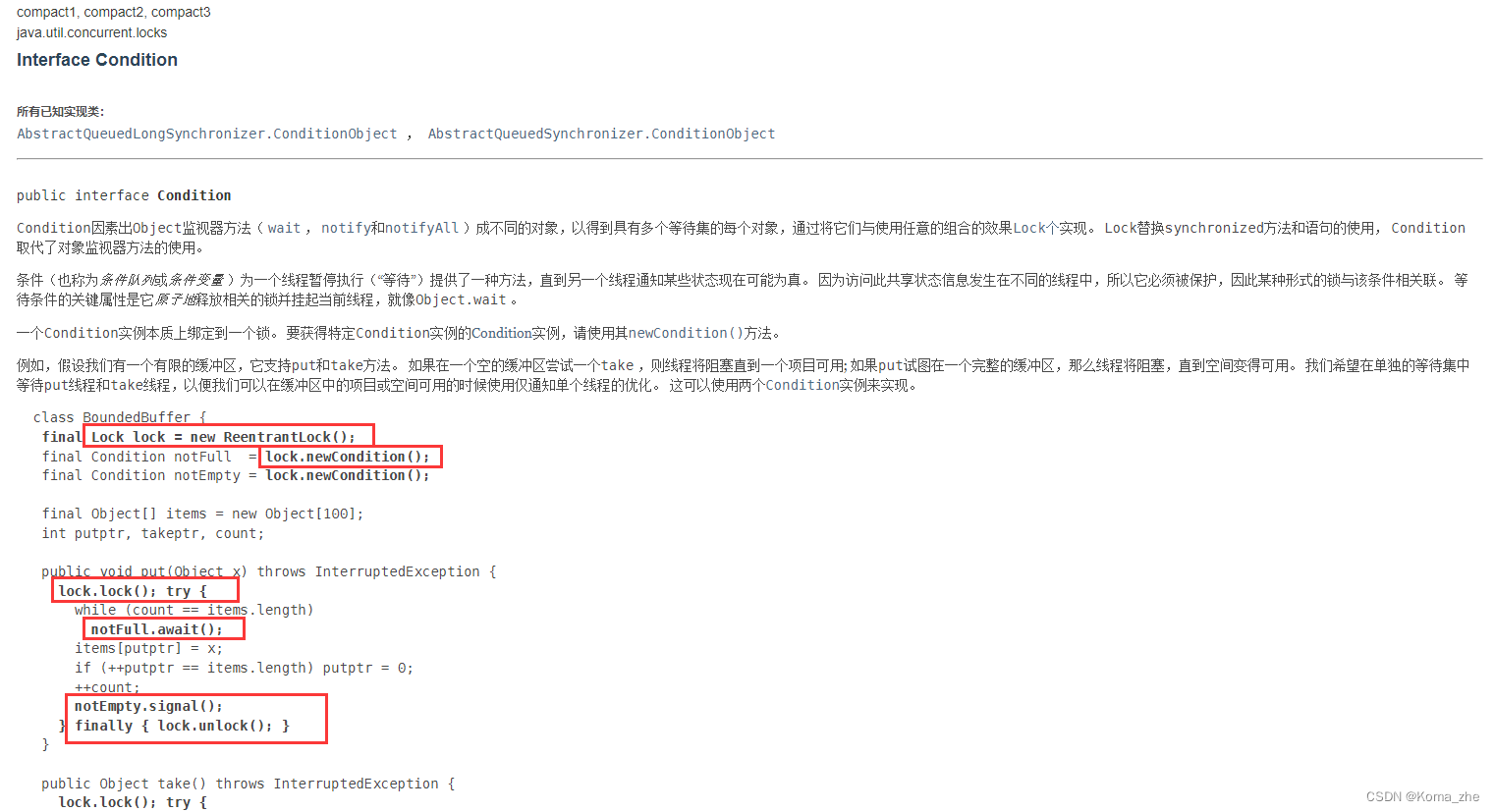
public class test {public static void main(String[] args) {Data2 data = new Data2();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {try {data.increment();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, "A").start();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {try {data.decrement();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, "B").start();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {try {data.increment();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, "C").start();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {try {data.decrement();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, "D").start();}
}class Data2 {private int num = 0;Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();Condition condition = lock.newCondition();// +1public void increment() throws InterruptedException {lock.lock();try {// 判断等待while (num != 0) {condition.await();}num++;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + num);// 通知其他线程 +1 执行完毕condition.signalAll();}finally {lock.unlock();}}// -1public void decrement() throws InterruptedException {lock.lock();try {// 判断等待while (num == 0) {condition.await();}num--;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + num);// 通知其他线程 +1 执行完毕condition.signalAll();}finally {lock.unlock();}}
}
Condition 的优势:精准通知和唤醒线程
要指定通知的下一个进行顺序,可以使用 Condition 来指定通知进程。
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;/*** Description:* A 执行完 调用B* B 执行完 调用C* C 执行完 调用A**/
public class test {public static void main(String[] args) {Data3 data3 = new Data3();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {data3.printA();}},"A").start();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {data3.printB();}},"B").start();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {data3.printC();}},"C").start();}
}class Data3 {private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();private Condition condition1 = lock.newCondition();private Condition condition2 = lock.newCondition();private Condition condition3 = lock.newCondition();private int num = 1; // 实现1A 2B 3Cpublic void printA() {lock.lock();try {// 业务代码 判断 -> 执行 -> 通知while (num != 1) {condition1.await();}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "==> AAAA" );// 唤醒,唤醒指定的人Bnum = 2;condition2.signal();}catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}finally {lock.unlock();}}public void printB() {lock.lock();try {// 业务代码 判断 -> 执行 -> 通知while (num != 2) {condition2.await();}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "==> BBBB" );num = 3;condition3.signal();}catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}finally {lock.unlock();}}public void printC() {lock.lock();try {// 业务代码 判断 -> 执行 -> 通知while (num != 3) {condition3.await();}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "==> CCCC" );num = 1;condition1.signal();}catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}finally {lock.unlock();}}
}
/*
A==> AAAA
B==> BBBB
C==> CCCC
A==> AAAA
B==> BBBB
C==> CCCC
...
*/
8 锁现象
如何判断锁的是谁?锁会锁住:对象、Class
问题1:两个同步方法,先执行发短信还是打电话?
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class test {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Phone phone = new Phone();new Thread(() -> {phone.sendMs();}).start();TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);new Thread(() -> {phone.call();}).start();}
}class Phone {public synchronized void sendMs() {System.out.println("发短信");}public synchronized void call() {System.out.println("打电话");}
}//发短信
//打电话
问题2:问题1基础上让发短信延迟 4s
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class test {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Phone phone = new Phone();new Thread(() -> {try {phone.sendMs();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}).start();TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);new Thread(() -> {phone.call();}).start();}
}class Phone {public synchronized void sendMs() throws InterruptedException {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);System.out.println("发短信");}public synchronized void call() {System.out.println("打电话");}
}//发短信
//打电话
问题一问题二说明并不是顺序执行,而是 synchronized 锁住的对象是方法的调用,对于两个方法用的是同一个锁,谁先拿到谁先执行,另外一个等待。
问题三:换成一个普通方法结果?
hello 是一个普通方法,不受 synchronized 锁的影响,不用等待锁的释放。
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class test {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Phone phone = new Phone();new Thread(() -> {try {phone.sendMs();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}).start();TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);new Thread(() -> {phone.hello();}).start();}
}class Phone {public synchronized void sendMs() throws InterruptedException {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);System.out.println("发短信");}public synchronized void call() {System.out.println("打电话");}public void hello() {System.out.println("hello");}
}
//hello
//发短信
问题四:如果使用的是两个对象,一个调用发短信,一个调用打电话,那么整个顺序是怎么样的呢?
两个对象两把锁,不会出现等待的情况,发短信睡了4s,所以先执行打电话
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class test {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Phone phone1 = new Phone();Phone phone2 = new Phone();new Thread(() -> {try {phone1.sendMs();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}).start();TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);new Thread(() -> {phone2.call();}).start();}
}class Phone {public synchronized void sendMs() throws InterruptedException {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);System.out.println("发短信");}public synchronized void call() {System.out.println("打电话");}public void hello() {System.out.println("hello");}
}
//打电话
//发短信
问题五、六:如果我们把 synchronized 的方法加上 static 变成静态方法,那么顺序又是怎么样的呢?
static 静态方法来说,对于整个类 Class 来说只有一份,对于不同的对象使用的是同一份方法,相当于这个方法是属于类的,如果静态 static 方法使用 synchronized 锁定,那么这个 synchronized 锁会锁住整个对象,不管多少个对象,对于静态的锁都只有一把锁,谁先拿到这个锁就先执行,其他的进程都需要等待。
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class test {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {new Thread(() -> {try {Phone.sendMs();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}).start();TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);new Thread(() -> {Phone.call();}).start();}
}class Phone {public static synchronized void sendMs() throws InterruptedException {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);System.out.println("发短信");}public static synchronized void call() {System.out.println("打电话");}
}
//发短信
//打电话
问题七:如果使用一个静态同步方法、一个同步方法、一个对象调用顺序是什么?
因为一个锁的是Class类的模板,一个锁的是对象的调用者。所以不存在等待,直接运行
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class test {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Phone phone1 = new Phone();
// Phone phone2 = new Phone();new Thread(() -> {try {Phone.sendMs();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}).start();TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);new Thread(() -> {phone1.call();}).start();}
}class Phone {public static synchronized void sendMs() throws InterruptedException {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);System.out.println("发短信");}public synchronized void call() {System.out.println("打电话");}public void hello() {System.out.println("hello");}
}
//打电话
//发短信
问题八:如果我们使用一个静态同步方法、一个同步方法、两个对象调用顺序是什么?
两把锁锁的不是同一个东西
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class test {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Phone phone1 = new Phone();Phone phone2 = new Phone();new Thread(() -> {try {Phone.sendMs();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}).start();TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);new Thread(() -> {phone2.call();}).start();}
}class Phone {public static synchronized void sendMs() throws InterruptedException {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);System.out.println("发短信");}public synchronized void call() {System.out.println("打电话");}public void hello() {System.out.println("hello");}
}
//打电话
//发短信
