常用的辅助类2(StringBuilder、StringBuffer、处理时间相关的类、对象比较器)
Java知识点总结:想看的可以从这里进入
目录
- 7.7、字符串相关类
- 7.8、时间处理
- 7.8.1、JDK8前
- 7.8.2、JDK8后
- 1、时间日期类
- 2、格式化日期
- 3、其他
- 7.9、对象比较器
7.7、字符串相关类
-
String:JDK1.0出现,字符串类,被final修饰其值不可改。实现了Serializable和Comparable接口,可支持序列化和可以比较大小;创建后栈中保存一个地址的引用,每次改变的值都是重新分配一个新的内存地址赋值,而不是在原有的地址内修改。
-
StringBuilder:JDK 5.0出现,字符串类,其值可修改,线程不安全,但是速度最快。
-
StringBuffer:JDK1.0:JDK1.0出现,字符串类,其值可修改,线程安全,速度相对StringBuilder慢。
//三种构造方法 StringBuffer():初始容量为16的字符串缓冲区 StringBuffer(int size):构造指定容量的字符串缓冲区 StringBuffer(String str):将内容初始化为指定字符串内容
当三者作为方法参数传递的话,方法内部String不会改变其值,StringBuffer和StringBuilder会改变其值。
StringBuilder和StringBuffder的底层是一个字符数组,根据无参构造创建后的可扩容长度为16个字符(接受字符串的构造长度为字符串长度+16、也可指定初始长度),
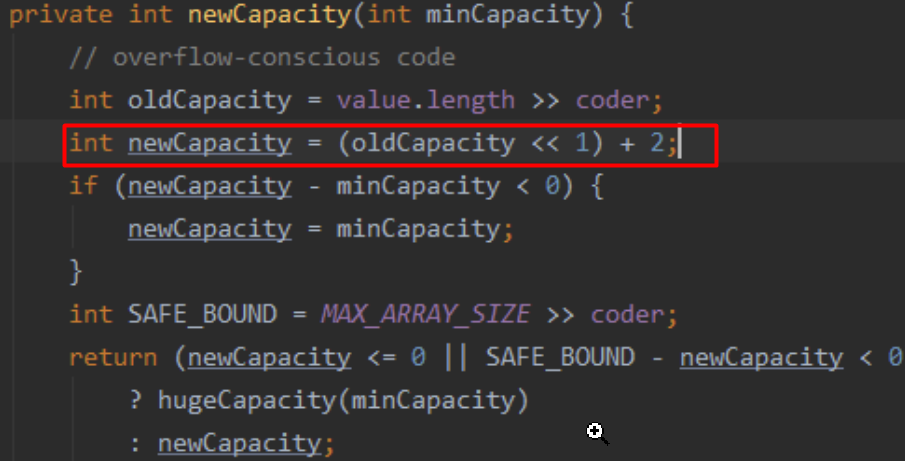
如果添加字符串过程中超出数组范围,就会对底层数组进行扩容,首先创建一个新的数组大小为原来的2倍加2,将原数组中的内容复制到新数组中,再将指针指向新创建的数组地址。
-
jdk16以前的扩容方法:
-
jdk16以后的扩容方法

StringBuilder和StringBuffder提供的方法基本类似:
StringBuilder和StringBuffder常用方法:
1、增:拼接字符串 .append("").append("").....;
2、删:删除指定范围的内容[start,end) .delete(int start,int end)
3、改:替换指定范围的内容[start,end) .replace(int start, int end, String str)修改指定索引处的字符:public void setCharAt(int n ,char ch)
4、插:在指定位置插入指定的内容 .insert(int offset, "")
5、查:获取指定索引处的字符 public char charAt(int n )
6、返回指定子字符串在当前字符串中第一次出现处的索引:public int indexOf(String str)
7、截取字符串[start,end):public String substring(int start,int end)
8、返回字符串的长度:public int length()
9、把当前字符序列逆转:.reverse()
对比一下使用String和StringBuilder在速度上的区别
计算一下追加 100,000,0次字符所用的时间
-
使用String
public static void main(String[] args) {long start = System.currentTimeMillis();String str = "";for(int i=0; i<1000000; i++){str += 1;}long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.printf("使用String用时:%d",end-start); }
-
换成StringBuilder
public static void main(String[] args) {long start = System.currentTimeMillis();StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();for(int i=0; i<1000000; i++){builder.append(1);}long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.printf("使用StringBuilder用时:%d",end-start); }
-
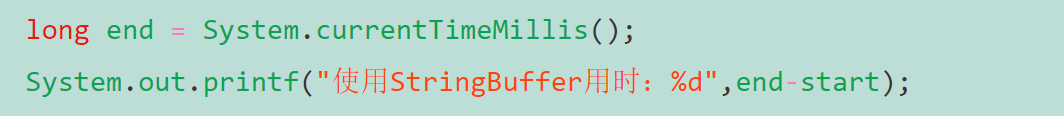
使用StringBuffder
public static void main(String[] args) {long start = System.currentTimeMillis();StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();for(int i=0; i<1000000; i++){buffer.append(1);}long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.printf("使用StringBuffer用时:%d",end-start); }
从上面可以明显的看出来使用String的时候相比较后两种速度慢的不是一点半点的,而是很多倍的差距了,而StringBuilder相比较StringBuffder也快了一些。
7.8、时间处理
7.8.1、JDK8前
-
计算时间差:
System类提供的public static long currentTimeMillis()用来返回当前时间与1970年1月1日0时0分0秒之间以毫秒为单位的时间差。通常用来计算某个程序的运行时间,进行快慢的对比
-
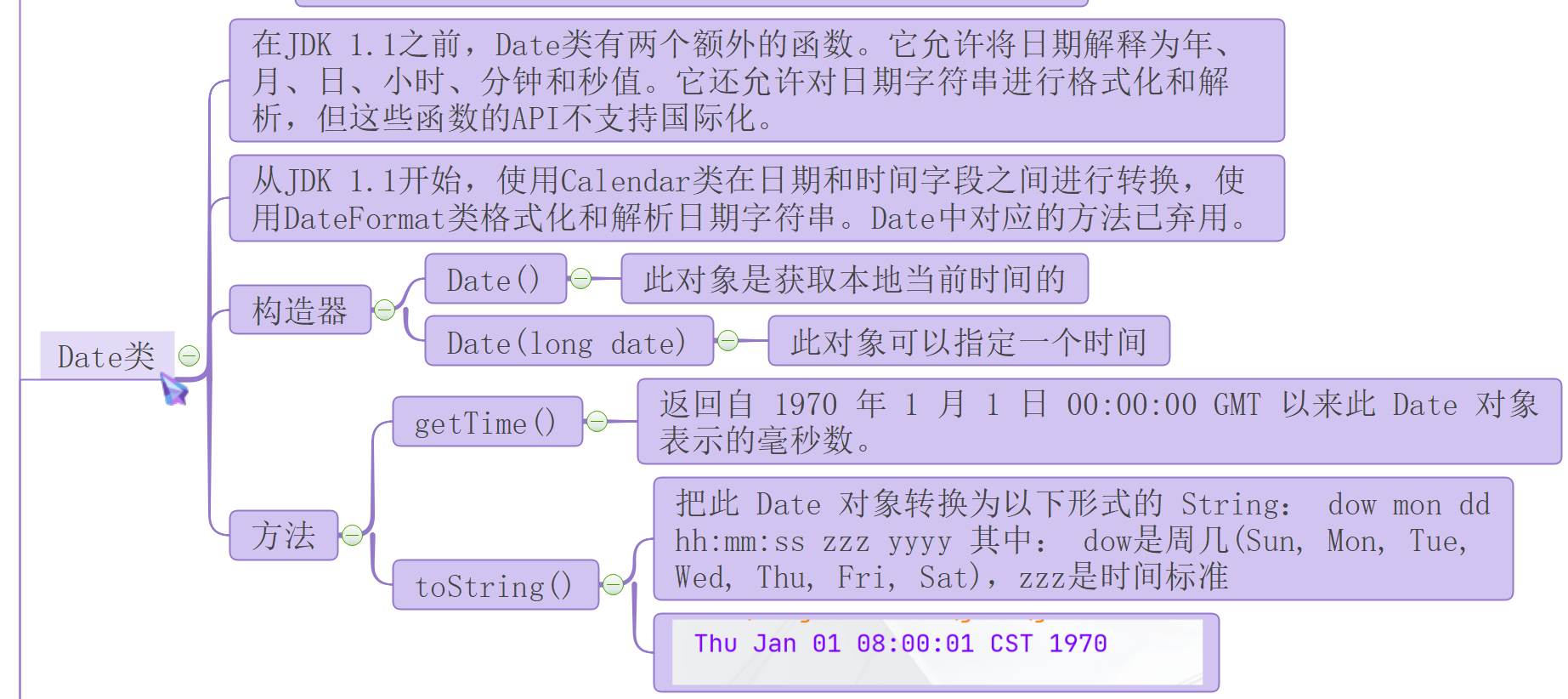
java.util.Date类
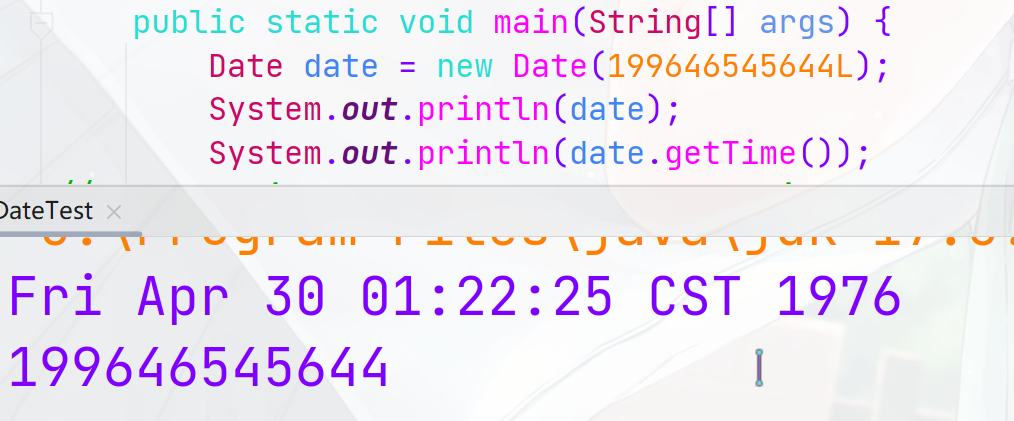
-
SimpleDateFormat类
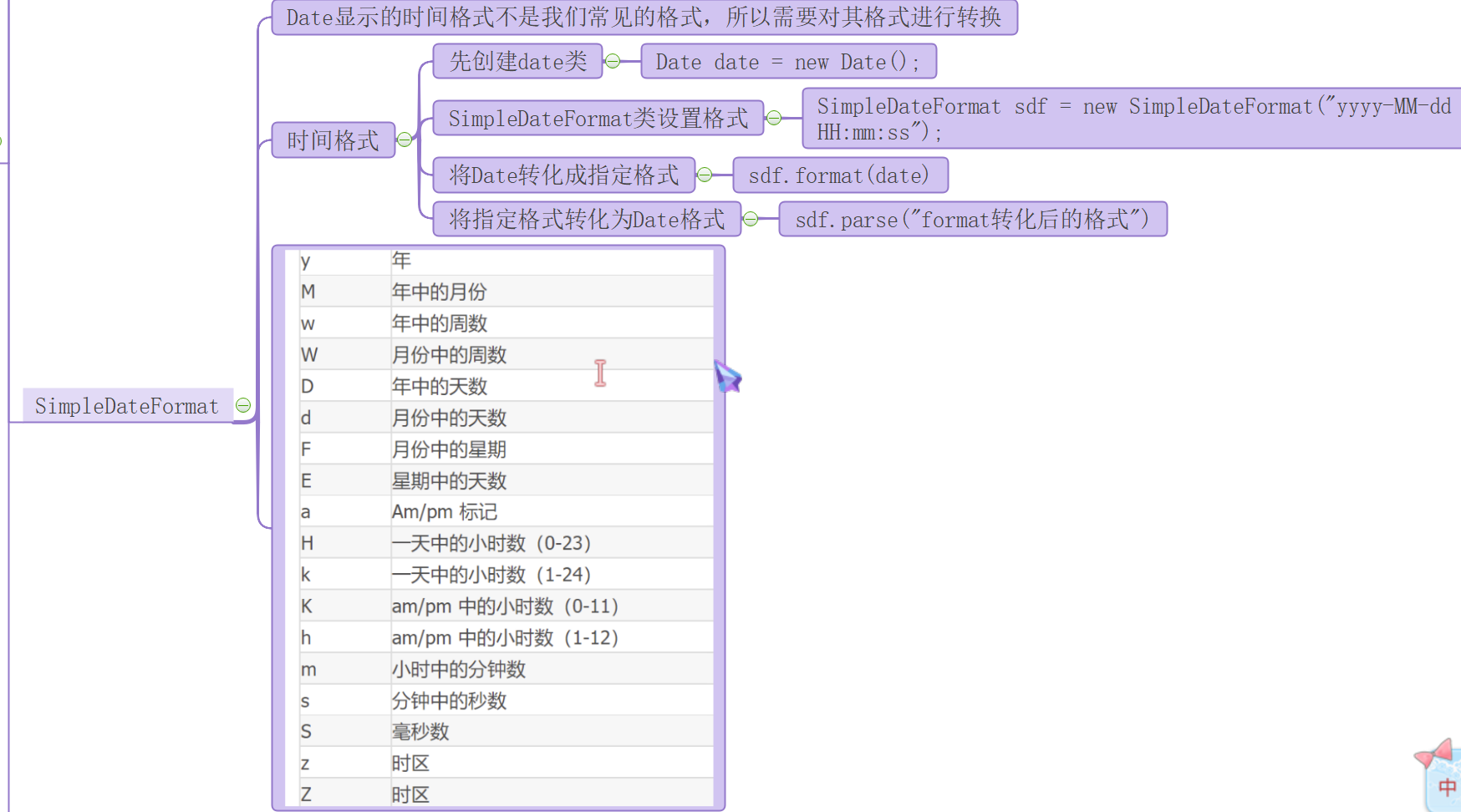
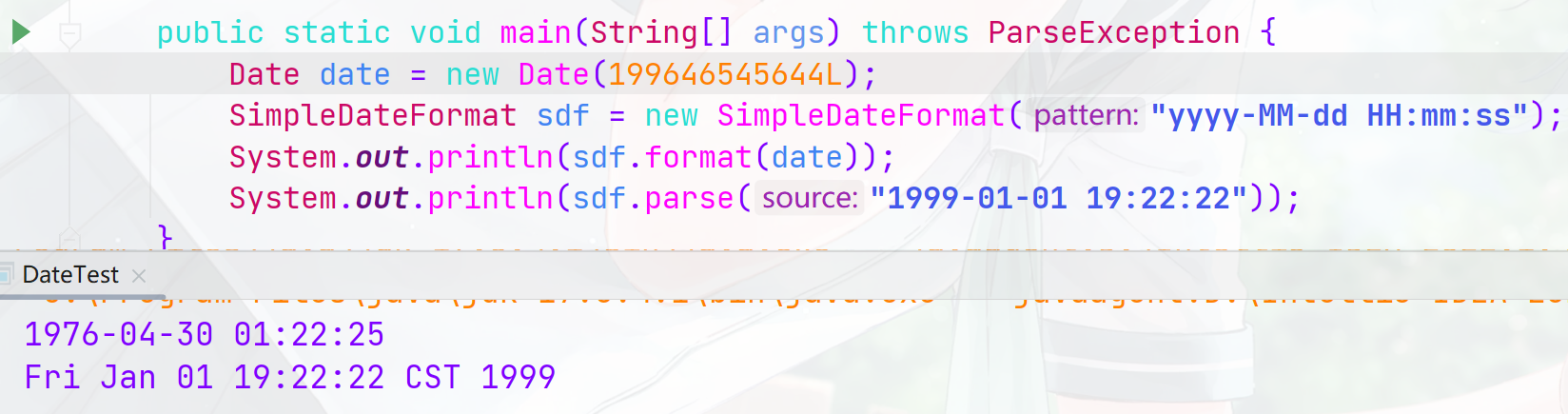
-
Calendar类

Calendar类中常用的常量字段如下:
常量字段 说明 Calendar.ERA get和set的字段号,表示纪元,只能为0或1。0表示BC(“before Christ”,即公元前);1表示AD(拉丁语“Anno Domini”,即公元)。 Calendar.YEAR 用于get和set的字段号,表示年份 Calendar.MONTH 用于get和set的字段号,表示月份,0表示1月,1表示2月……… Calendar.WEEK_OF_YEAR` 用于get和set的字段号,一年中的星期数,即本年中第几个星期 Calendar.WEEK_OF_MONTH 用于get和set的字段号,当前月中的星期数,即本月中第几个星期 Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR 用于get和set的字段号,一年中第几天 Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK 用于get和set的字段号,一周中第几天,注意,周日是1,周一是2,… Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK_IN_MONTH get和set的字段号,表示当前月份中的星期几 Calendar.DATE 用于get和set的字段号,一月中第几天,同DAY_OF_MONTH的值是一样的 Calendar.HOUR 小时(12小时制) Calendar.AM_PM 用于get和set的字段号,用于指示HOUR是在中午之前还是在中午之后。在中午12点之前返回0,在中午12点(包括12点)之后返回1 Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY 一天中第几个小时(24小时制) Calendar.MINUTE 分钟 Calendar.SECOND 秒 Calendar.MILLISECOND 毫秒 AY_OF_MONTH 一月中第几天 Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK_IN_MONTH 当前月中的第几个星期 Calendar.JANUARY 1月 Calendar.FEBRUARY 2月 Calendar.MARCH 3月 Calendar.APRIL 4月 Calendar.MAY 5月 Calendar.JUNE 6月 Calendar.JULY 7月 Calendar.AUGUST 8月 Calendar.SEPTEMBER 9月 Calendar.OCTOBER 10月 Calendar.NOVEMBER 11月 Calendar.DECEMBER 12月 public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();//查看是公元前(0)还是公元后(1)System.out.println("判断公元:"+calendar.get(Calendar.ERA));//获取月份:返回值+1System.out.println("获取月份:"+calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH));//将年份设置为1999calendar.set(Calendar.YEAR,1999);System.out.println("修改年份为1999:"+calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR));//将年份+1calendar.add(Calendar.YEAR,1);System.out.println("将年份+1:"+calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR));//返回Date格式日期System.out.println("获取date格式日期:"+calendar.getTime());//设置时间calendar.setTime(new Date("Tue Feb 08 18:29:23 CST 2222"));System.out.println("设置时间:"+calendar.getTime());; }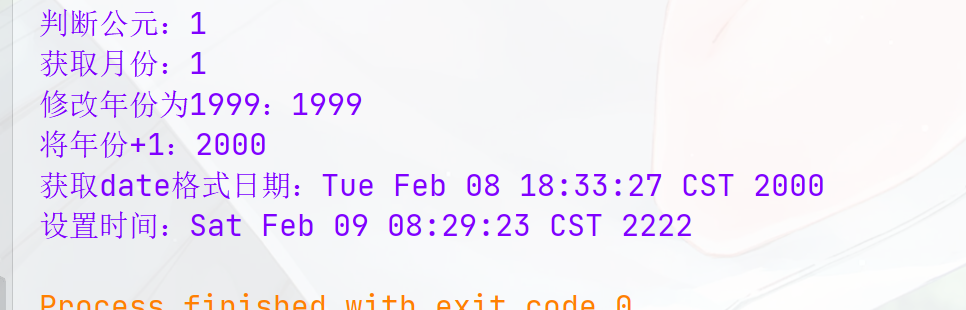
7.8.2、JDK8后
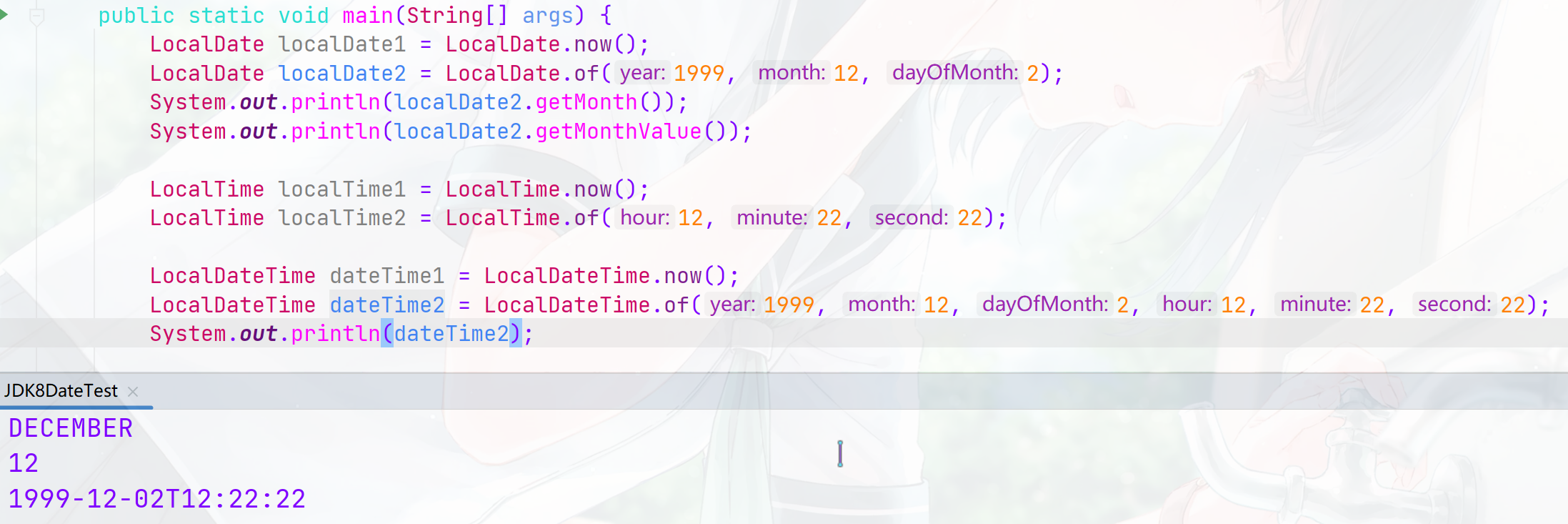
1、时间日期类
在JDK8以前,不论是Date类、还是Calendar类,都不是特别好用,所以时期时间问题一直都是一个让人头疼的问题。所以在JDK8中第三次引入了关于日期时间的API,新的 java.time 中包含了关于本地日期(LocalDate)、本地时间(LocalTime)、本地日期时间()、时区(ZonedDateTime)和持续时间(Duration)的类。而在 Date 类中新增了 toInstant() 方法,用于把 Date 转换成新的表示形式。

2、格式化日期
java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter 类:该类提供了三种格式化方法:
-
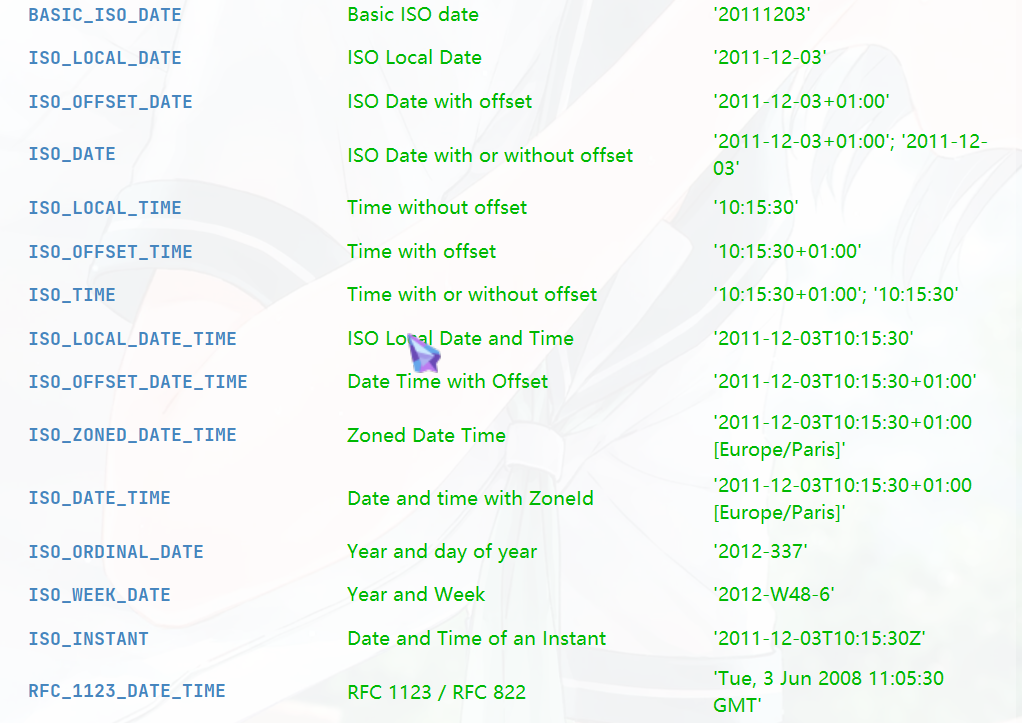
预定义的标准格式。如:ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME;ISO_LOCAL_DATE;ISO_LOCAL_TIME
-
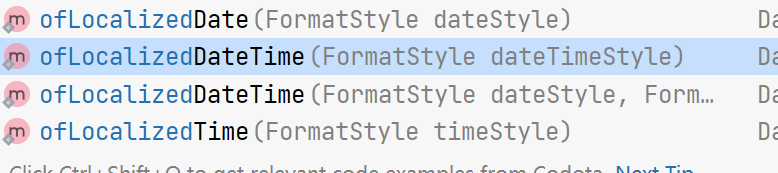
本地化相关的格式。

-
自定义的格式。如:ofPattern(“yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss“)
//时间
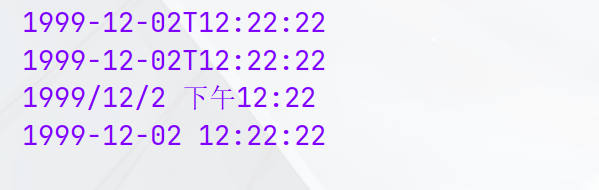
LocalDateTime dateTime2 = LocalDateTime.of(1999, 12, 2, 12, 22, 22);
System.out.println(dateTime2);
//第一种格式化
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter1 = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME;
String format1 = dateTimeFormatter1.format(dateTime2);
System.out.println(format1);
//第二种格式化
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter2 = DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDateTime(FormatStyle.SHORT);
String format2 = dateTimeFormatter2.format(dateTime2);
System.out.println(format2);
//第三种格式化
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter3 = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
String format3 = dateTimeFormatter3.format(dateTime2);
System.out.println(format3);
3、其他
-
ZoneId:包含了所有的时区信息

-
ZonedDateTime:根据时区获取时间

-
Cloc:使用时区提供对当前即时、日期和时间的访问的时钟。
-
TemporalAdjuster :时间校正器。
-
Period:用于计算两个日期的间隔
-
Duration:计算两个时间的间隔
7.9、对象比较器
在Java中经常会涉及到对象排序问题(比如买东西时,可以选择根据价格排序),这就会涉及到对象之间的比较,Java实现对象排序的方式有两种:
-
自然排序:java.lang.Comparable接口,可以对实现它的每个类的对象进行整体排序。默认从小到大。
像String、包装类等等都实现Comparable接口,其中字符的比较是Unicode值,数值是直接比较数值。数组、对象列表可以通过Collections.sort 或Arrays.sort进行自动排序


我们自定义的类也可以实现Comparable接口,重写compareTo(Object obj)方法,写明比较的规则。
- 类实现Comparable接口
- 实现接口的compareTo(Object obj) 方法,通过此方法对比两个对象的大小(如果当前对象this大于形参对象,则返回正整数,如果当前对象this小于形参对象,则返回负整数,如果当前对象this等于形参对象,则返回零。)
-
定制排序:java.util.Comparator接口,当没有实现java.lang.Comparable接口而又不方便修改代码,或者实现了java.lang.Comparable接口的排序规则不适合当前的操作,那么可以考虑使用Comparator的对象来排序,强行对多个对象进行整体排序的比较。
重写compare(Object o1,Object o2)方法,比较o1和o2的大小:如果方法返回正整数,则表示o1大于o2;如果返回0,表示相等;返回负整数,表示o1小于o2。
-
首先使用匿名内部类的形式创建 Comparator 对象,然后重写compare方法

-
将 Comparator 传递给 sort 方法(如 Collections.sort 或 Arrays.sort),从而允许在排序顺序上实现精确控制。
-
