【JavaSE】Java基础语法(四十二):NIO
文章目录
- 1. 概述
- 2. NIO与BIO的区别
- 3. NIO三大模块
- 4. NIO创建缓冲区对象【应用】
- 5. NIO缓冲区添加数据【应用】
- 6. NIO缓冲区获取数据【应用】
- 7. 小结

1. 概述
- BIO
Blocking IO,阻塞型IO - NIO
No Blocking IO,非阻塞型IO - 阻塞IO的弊端
在等待的过程中,什么事也做不了 - 非阻塞IO的好处
不需要一直等待,当一切就绪了再去做
2. NIO与BIO的区别
- 区别一
BIO是阻塞的,NIO是非阻塞的 - 区别二
BIO是面向流的,NIO是面向缓冲区的
BIO中数据传输是单向的,NIO中的缓冲区是双向的
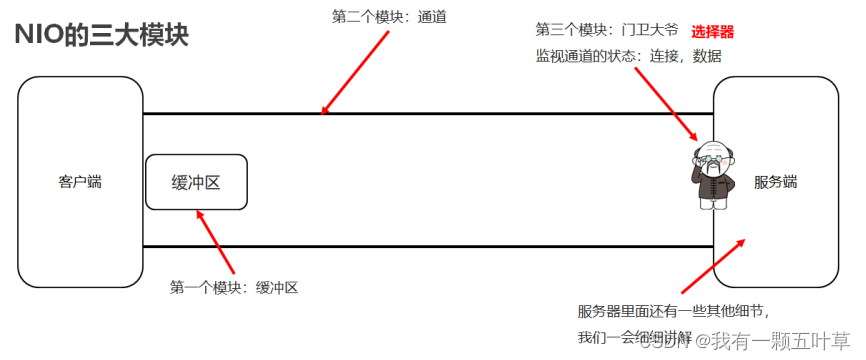
3. NIO三大模块
- 缓冲区
用来存储数据 - 通道
用来建立连接和传输数据 - 选择器
监视通道状态
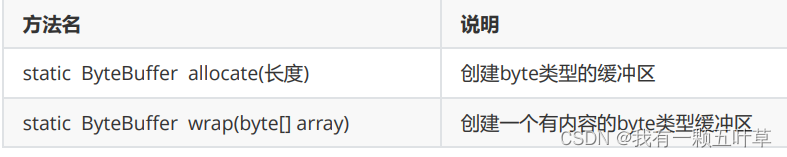
4. NIO创建缓冲区对象【应用】
-
方法介绍
-
代码示例
public class CreateByteBufferDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) {//method1();//method2();ByteBuffer wrap = ByteBuffer.wrap("aaa".getBytes());for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {System.out.println(wrap.get());}}private static void method2() {byte [] bytes = {97,98,99};ByteBuffer byteBuffer2 = ByteBuffer.wrap(bytes);//缓冲区的长度3//缓冲区里面的内容就是字节数组的内容.for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {System.out.println(byteBuffer2.get());}System.out.println(byteBuffer2.get());}private static void method1() {ByteBuffer byteBuffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);//getfor (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println(byteBuffer1.get());}System.out.println(byteBuffer1.get());} }
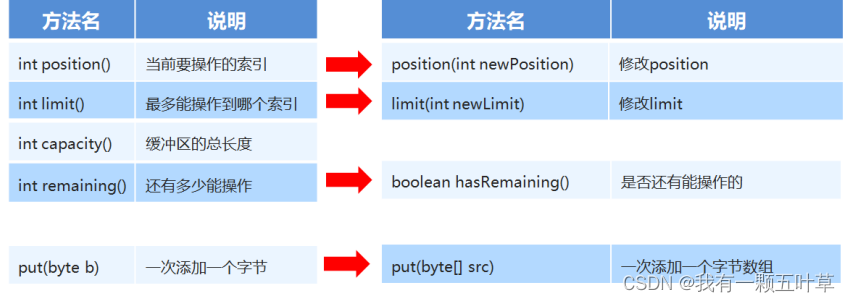
5. NIO缓冲区添加数据【应用】
-
方法介绍
-
代码示例
public class ByteBufferDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) {// int position() 当前要操作的索引// int limit() 最多能操作到哪个索引// int capacity() 缓冲区的总长度ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);System.out.println(byteBuffer.position());//0System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit());//10System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity());//10// put(byte b) 一次添加一个字节// byteBuffer.put((byte) 97);// System.out.println(byteBuffer.position());// System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit());// System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity());// put(byte[] src) 一次添加一个字节数组// byteBuffer.put("aaa".getBytes());// System.out.println(byteBuffer.position());//3// System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit());//10// System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity());//10// position(int newPosition) 修改position// byteBuffer.position(1);// limit(int newLimit) 修改limit// byteBuffer.limit(5);// System.out.println(byteBuffer.position());// System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit());// System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity());// int remaining() 还有多少能操作// boolean hasRemaining() 是否还有能操作的byteBuffer.put("0123456789".getBytes());System.out.println(byteBuffer.remaining());System.out.println(byteBuffer.hasRemaining());} }
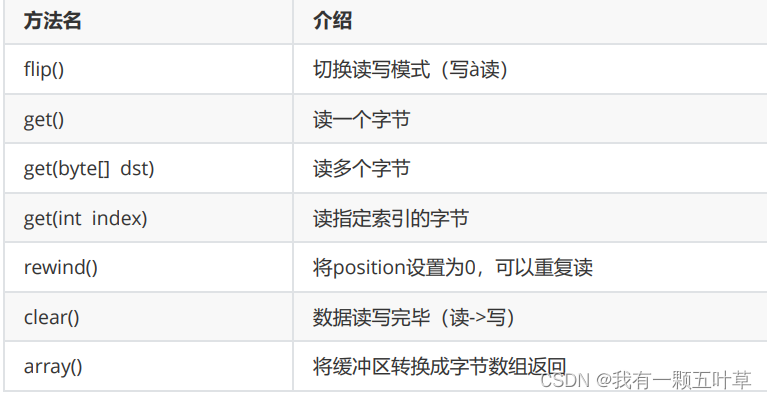
6. NIO缓冲区获取数据【应用】
-
方法介绍
-
代码示例
public class ByteBufferDemo3 {public static void main(String[] args) {ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);byteBuffer.put("abc".getBytes());// flip() 切换读写模式(写读)byteBuffer.flip();// get() 读一个字节// while(byteBuffer.limit() != byteBuffer.position()){// System.out.println((char) byteBuffer.get());// }for (int i = 0; i < byteBuffer.limit(); i++) {System.out.println((char) byteBuffer.get());}// get(byte[] dst) 读多个字节// byte [] bytes = new byte[byteBuffer.limit()];// byteBuffer.get(bytes);// System.out.println(new String(bytes));// get(int index) 读指定索引的字节// System.out.println((char) byteBuffer.get(0));// rewind() 将position设置为0,可以重复读// byteBuffer.rewind();// for (int i = 0; i < byteBuffer.limit(); i++) {// System.out.println((char) byteBuffer.get());// }// clear() 数据读写完毕(读->写)byteBuffer.clear();byteBuffer.put("qqq".getBytes());// array() 将缓冲区转换成字节数组返回byte[] bytes = byteBuffer.array();System.out.println(new String(bytes));}
}
7. 小结
1. 需求:我要把数据写到缓冲区中。
数据是从外面进入到缓冲区的,所以缓冲区在做读数据的操作。
2. 需求:我要把数据从缓冲区中读出来。
数据是从缓冲区里面到外面的。所以缓冲区在做写数据的操作。
3. capacity:容量(长度)
limit: 界限(最多能读/写到哪里)
posotion:位置(读/写哪个索引)
-
获取缓冲区里面数据之前,需要调用flip方法
-
再次写数据之前,需要调用clear方法,
但是数据还未消失,等再次写入数据,被覆盖了才会消失。