【网络运维】Linux 文本处理利器:sed 命令
Linux 文本处理利器:sed 命令
sed 简介
sed(Stream Editor)是一款非交互式的流编辑器,诞生于 1973–1974 年间的贝尔实验室,由 McMahon 开发。它专为文本处理而生,功能强大,是 Linux 文本处理常客之一。
(另外两名常客通常视为 grep命令和 awk命令)
其中,sed 与 awk 并称 Linux/Unix 两大文字处理王牌工具,sed 侧重于替换,awk 侧重于分割与重组。
本文将深入探讨 sed 命令的使用方法与实用技巧。
sed 工作流程
sed 的工作流程可简单概括为:
读取行 → 执行 → 显示 → 读取行 → 执行 → 显示 → ……(重复流程)
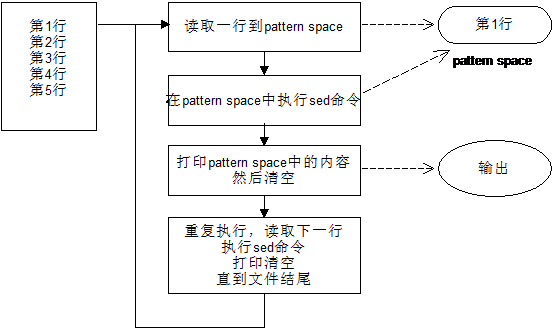
详细步骤:
- 读取行:从输入流(文件、管道、标准输入)读取一行存入
pattern space。 - 执行:按顺序对当前行应用 sed 命令。
- 显示:将处理后的数据发送到输出流,并清空
pattern space。 - 循环:重复上述过程直到所有输入处理完毕。
注意事项:
pattern space是内存中的临时区域,关机或关闭终端后数据丢失。- 默认不修改源文件,除非使用
-i选项。 hold space是另一个内存区域,用于持久化存储数据,供后续检索使用。- 未指定输入文件时,sed 从标准输入读取数据。
环境准备
[furongwang@shell ~]$ vim test
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/bin/false
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/bin/false
mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/bin/false
ftp:x:14:11:ftp:/home/ftp:/bin/false
&nobody:$:99:99:nobody:/:/bin/false
zhangy:x:1000:100:,,,:/home/zhangy:/bin/bash
http:x:33:33::/srv/http:/bin/false
dbus:x:81:81:System message bus:/:/bin/false
hal:x:82:82:HAL daemon:/:/bin/false
mysql:x:89:89::/var/lib/mysql:/bin/false
aaa:x:1001:1001::/home/aaa:/bin/bash
ba:x:1002:1002::/home/zhangy:/bin/bash
test:x:1003:1003::/home/test:/bin/bash
@zhangying:*:1004:1004::/home/test:/bin/bash
policykit:x:102:1005:Po
sed 命令语法
基本格式:
sed [option] [sed-command] [input-file]
常用选项:
| 选项 | 说明 |
|---|---|
-n | 禁止自动打印模式空间 |
-e | 添加要执行的脚本 |
-f | 从文件中读取脚本,脚本中的每一个 sed 命令独自成一行 |
-i | 直接修改源文件(可指定备份后缀) |
-r | 使用扩展正则表达式 |
示例:
打印文件内容(模拟 cat):
sed '' data.txt(任意文件名)
[furongwang@shell ~]$ cat data.txt
I am studing sed
I am www.twle.cn
I am a no-work-men
I am so handsome[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed '' data.txt
I am studing sed
I am www.twle.cn
I am a no-work-men
I am so handsome
从标准输入读取:
sed ''# 输入内容后按 Ctrl+D 结束
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed ''
# 输入hello world,并回车
hello world
# 输出hello world
hello world
# 按ctrl+d推出
行寻址与模式寻址
行寻址语法:
[address1[,address2]]命令
示例:
# 打印第1行
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed -n '1p' test# 打印第1到3行
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed -n '1,3p' test# 打印第3行到最后
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed -n '3,$p' test# 打印第2行及后面2行
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed -n '2,+2p' test# 每隔2行打印一次
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed -n '1~2p' test
模式寻址:
# 打印含 "zhang" 的行
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed -n '/zhang/p' test# 打印从 root 开头到 mail 开头的行
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed -n '/^root/,/^mail/p' test
常用子命令详解
1. 打印(p / P)
p:打印整个模式空间P:打印模式空间的第一行
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed -n '1p' test # 打印第1行
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed -n '1,3p' test # 打印1~3行
2. 读取下一行(n / N)
n:读取下一行覆盖当前行N:追加下一行到当前行(用\n连接)
# 打印偶数行
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed -n 'n;p' test# 合并相邻两行
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed 'N;s/\n/==/' test
3. 替换(s)
# 替换每行第一个 root
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed 's/root/tankzhang/' test# 替换所有 root
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed 's/root/tankzhang/g' test# 替换每行第3个 my
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed 's/my/your/3' test1.txt# 自定义分隔符
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed 's#root#hello#' test
4. 插入与追加(i / a)
# 在匹配行上方插入
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed '/root/i====aaaa====' test# 在匹配行下方追加
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed '/root/a====iiii====' test
5. 删除(d / D)
d:删除整个模式空间D:删除模式空间的第一行
# 删除1~14行
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed '1,14d' test# 删除含 false 或 bash 的行
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed '/\(false\|bash\)/d' test
6. 写文件(w / W)
# 将 root 开头的行写入文件
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed -n '/^root/w output.txt' test
[furongwang@shell ~]$ cat output.txt
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash# 小写w写入
[furongwang@shell ~]$ vim scripts
1{
N
w write.log
}
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed -n -f scripts test# 小写w写入包含模式中所有行
[furongwang@shell ~]$ cat write.log
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/bin/false# 大写W写入只包含模式中第一行
[furongwang@shell ~]$ vim scripts
1{
N
W write.log
}
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed -n -f scripts test
[furongwang@shell ~]$ cat write.log
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
7. 退出(q)
# 处理到第3行退出
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed '3q' test
8. 取反(!)
# 打印非 root 开头的行
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed -n '/^root/!p' test
高级用法
多命令执行:
# 使用分号分隔
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed '1d;2d;5d' test# 使用 -e 选项
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed -e '1d' -e '2d' test# 使用脚本文件
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed -f script.sed test
正则表达式与子串:
# 使用转义括号
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed 's/\(root\)/\1user/g' test# 使用 -r 避免转义
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed -r 's/(root)/\1user/g' test# 使用 & 代表匹配内容
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed 's/root/&user/g' test
模式空间与保持空间(g/G/h/H):
| 命令 | 说明 |
|---|---|
g | 用保持空间内容覆盖模式空间 |
G | 将保持空间内容追加到模式空间 |
h | 用模式空间内容覆盖保持空间 |
H | 将模式空间内容追加到保持空间 |
# 每行后加空行
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed 'G' test# 复制匹配行到文件末尾
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed -e '/root/h' -e '$G' test
附:sed 命令完整帮助信息
[furongwang@shell ~]$ sed --help
Usage: sed [OPTION]... {script-only-if-no-other-script} [input-file]...-n, --quiet, --silentsuppress automatic printing of pattern space-e script, --expression=scriptadd the script to the commands to be executed-f script-file, --file=script-fileadd the contents of script-file to the commands to be executed--follow-symlinksfollow symlinks when processing in place-i[SUFFIX], --in-place[=SUFFIX]edit files in place (makes backup if SUFFIX supplied)-c, --copyuse copy instead of rename when shuffling files in -i mode-b, --binarydoes nothing; for compatibility with WIN32/CYGWIN/MSDOS/EMX (open files in binary mode (CR+LFs are not treated specially))-l N, --line-length=Nspecify the desired line-wrap length for the `l' command--posixdisable all GNU extensions.-r, --regexp-extendeduse extended regular expressions in the script.-s, --separateconsider files as separate rather than as a single continuouslong stream.-u, --unspaceedload minimal amounts of data from the input files and flushthe output spaces more often-z, --null-dataseparate lines by NUL characters--helpdisplay this help and exit--versionoutput version information and exitIf no -e, --expression, -f, or --file option is given, then the first
non-option argument is taken as the sed script to interpret. All
remaining arguments are names of input files; if no input files are
specified, then the standard input is read.GNU sed home page: <http://www.gnu.org/software/sed/>.
General help using GNU software: <http://www.gnu.org/gethelp/>.
E-mail bug reports to: <bug-sed@gnu.org>.
Be sure to include the word ``sed'' somewhere in the ``Subject:'' field.
-n, --quiet, --silent 取消自动打印模式空间-e 脚本, --expression=脚本 添加“脚本”到程序的运行列表-f 脚本文件, --file=脚本文件 添加“脚本文件”到程序的运行列表--follow-symlinks 直接修改文件时跟随软链接-i[扩展名], --in-place[=扩展名] 直接修改文件(如果指定扩展名就备份文件)-l N, --line-length=N 指定“l”命令的换行期望长度--posix 关闭所有 GNU 扩展-r, --regexp-extended 在脚本中使用扩展正则表达式-s, --separate 将输入文件视为各个独立的文件而不是一个长的连续输入-u, --unspaceed 从输入文件读取最少的数据,更频繁的刷新输出--help 打印帮助并退出--version 输出版本信息并退出-a ∶新增, a 的后面可以接字串,而这些字串会在新的一行出现(目前的下一行)~-c ∶取代, c 的后面可以接字串,这些字串可以取代 n1,n2 之间的行!-d ∶删除,因为是删除啊,所以 d 后面通常不接任何咚咚;-i ∶插入, i 的后面可以接字串,而这些字串会在新的一行出现(目前的上一行);-p ∶列印,亦即将某个选择的资料印出。通常 p 会与参数 sed -n 一起运作~-s ∶取代,可以直接进行取代的工作哩!通常这个 s 的动作可以搭配正规表示法
