《红黑树驱动的Map/Set实现:C++高效关联容器全解析》
前引:在C++标准库中,
map和set作为关联容器的核心,凭借其对数级复杂度的查找效率成为开发利器。然而,理解其底层机制——红黑树的自平衡特性与迭代器设计——才是掌握高阶C++的关键。本文将以零依赖方式实现两套完整容器:基于红黑树的Map<K,V>与Set<T>,涵盖节点结构、插入删除的平衡修复、迭代器失效策略等核心环节,并通过性能对比验证其与STL的等效性。无论您是数据结构学习者还是性能优化实践者,本指南将带您穿透抽象接口,直抵关联容器的设计精髓!
目录
【一】map与set结构分析
【二】封装底层红黑树思路讲解
【三】map与set的比较难点
【四】红黑树插入实现
【五】红黑树Find查找
【六】迭代器模板(初始)
(1)Set的普通迭代器
(2)Set的const迭代器
(3)map的普通迭代器
(4)map的const迭代器
【七】迭代器的注意事项(精髓)
【八】map的operator【】
【九】迭代器完整代码
(1)红黑树底层涉及的迭代器
(2)map底层涉及的迭代器
(3)Set底层涉及的迭代器
【一】map与set结构分析
map的数据为pair<key,value>,一个类
set的数据为key,普通的数据类型
两种容器的底层都是红黑树,那么我们需要实现两棵红黑树?根据源码,认为最佳实践方案为:
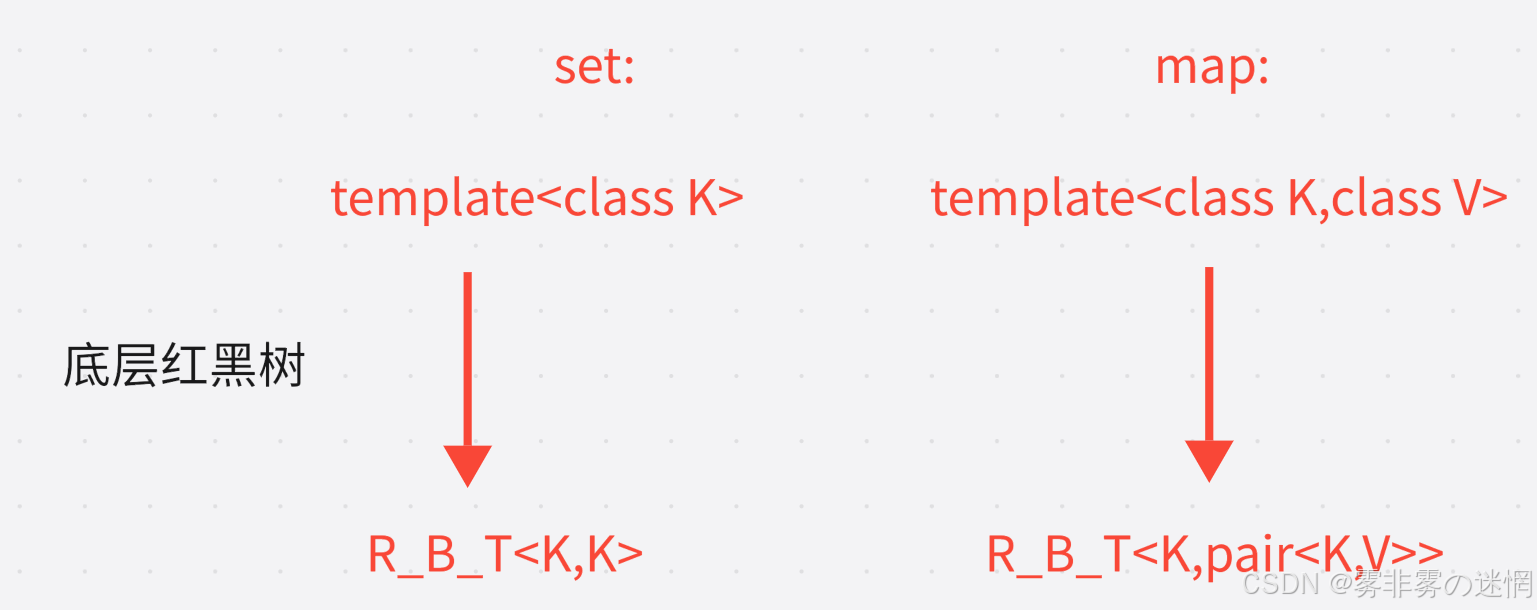
例如:
map的模板参数:class int,class string
底层红黑树接收的模板参数:<class int,class pair<int,string>>
set的模板参数:class int
底层红黑树接收的模板参数:<class int,class int>
【二】封装底层红黑树思路讲解
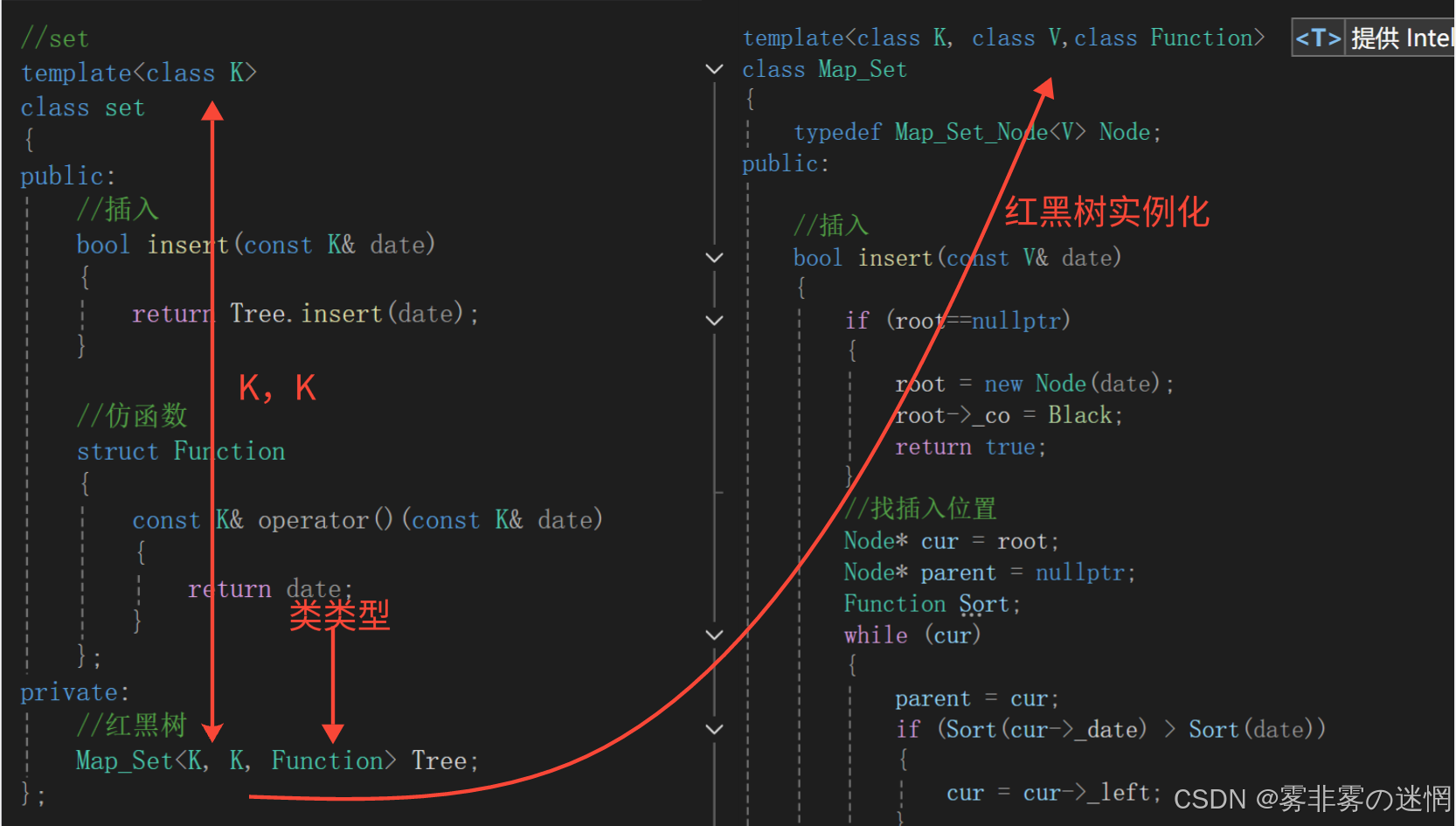
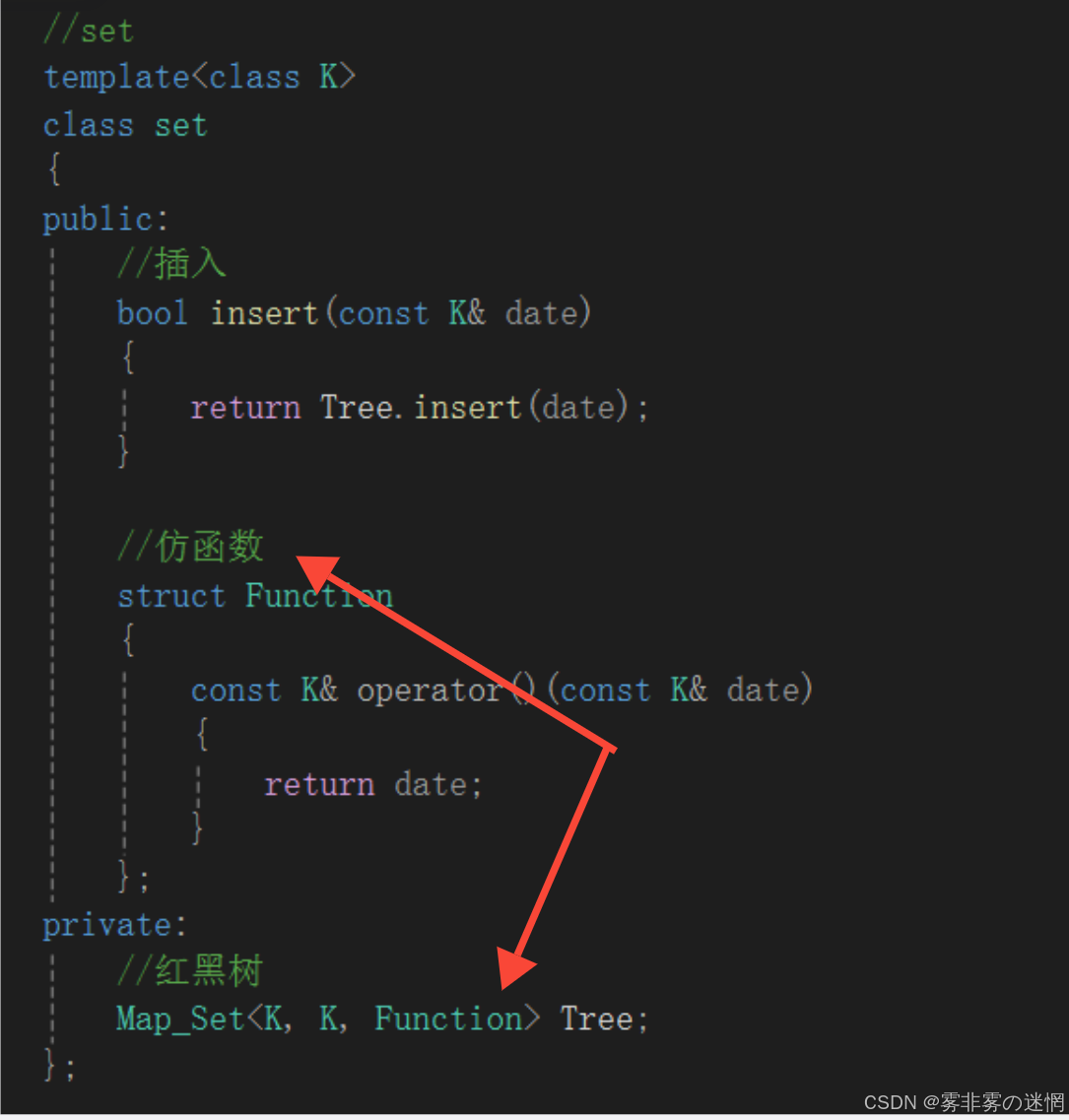
首先是set:
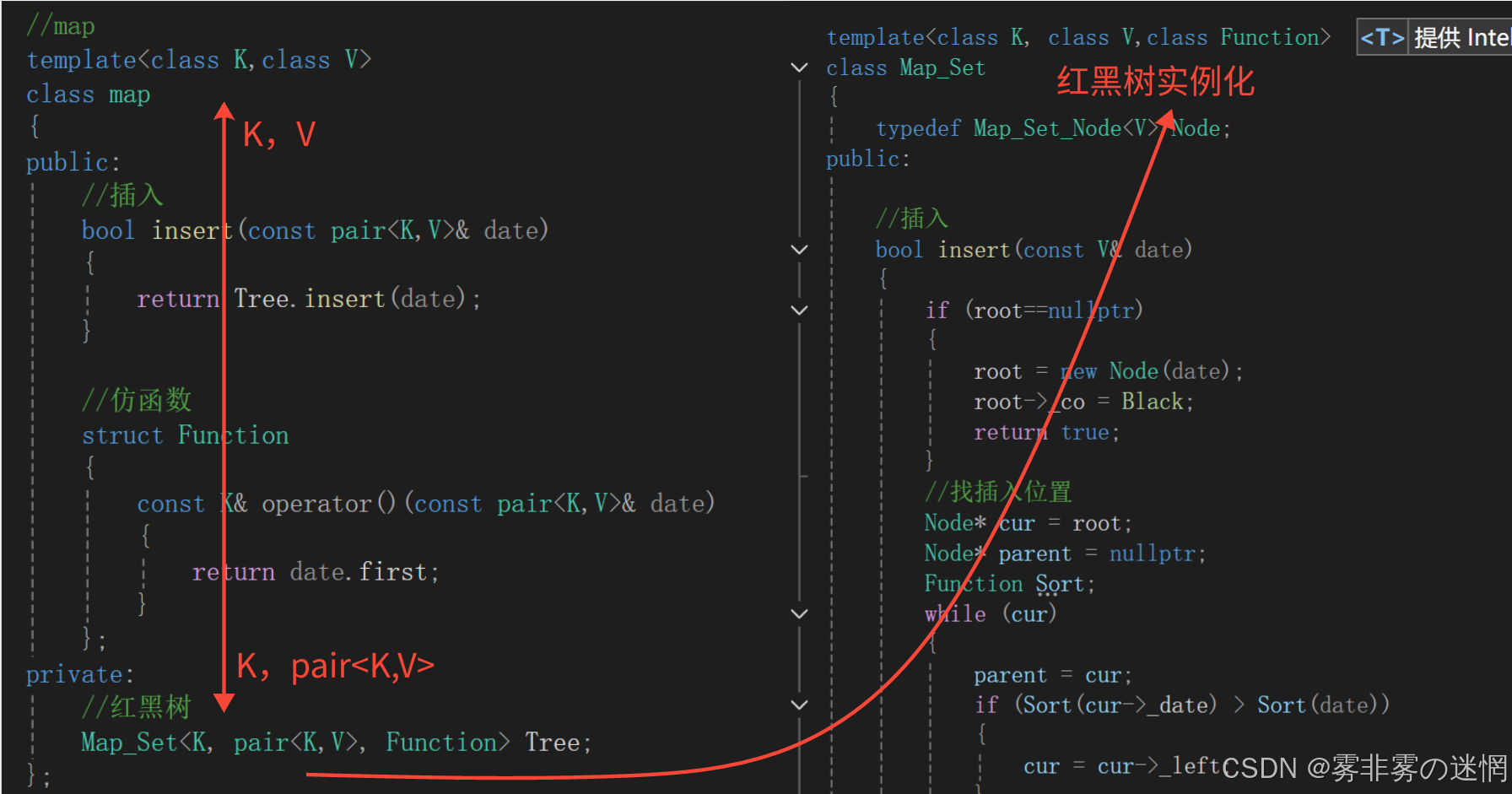
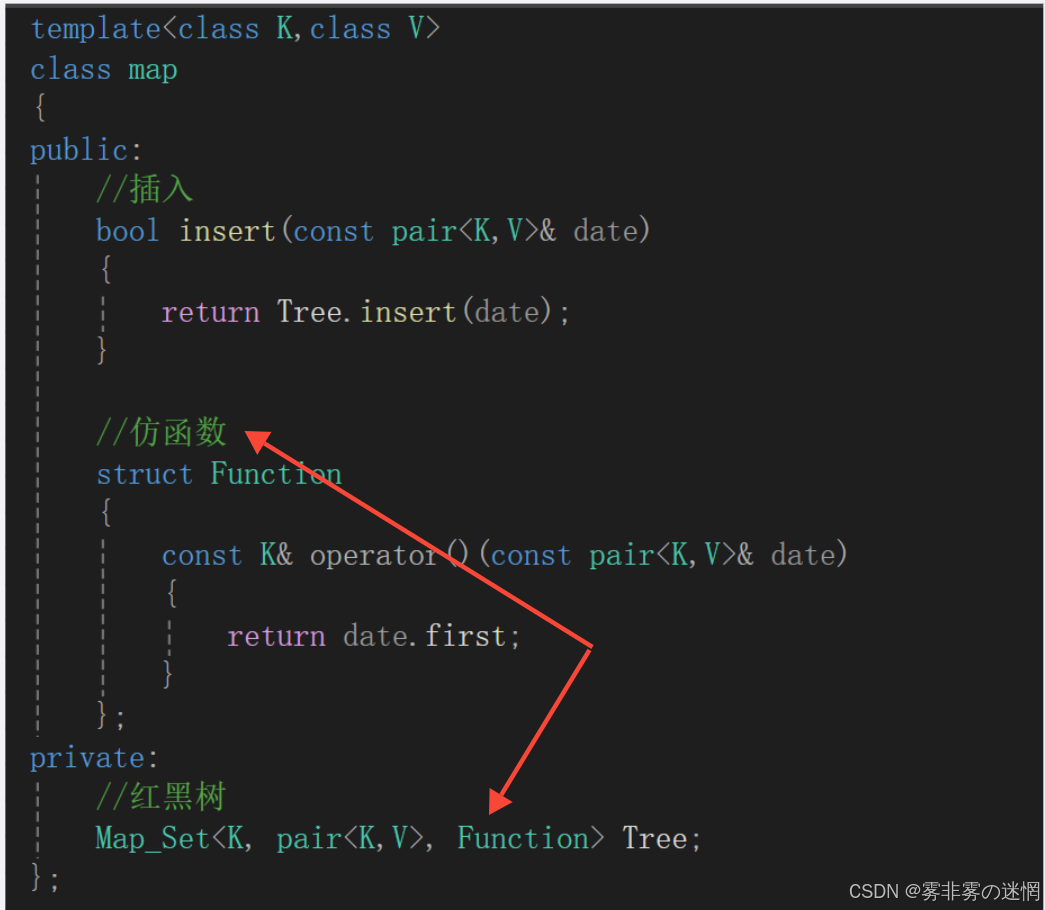
其次是map:
enum color
{Red,Black
};
//节点结构
template<class V>
struct RBTree
{Map_Set_Node(const V& date):_date(date),_parent(nullptr),_left(nullptr),_right(nullptr),_co(Red){ }//数据V _date;//指针Map_Set_Node*<V> _parent;Map_Set_Node*<V> _left;Map_Set_Node*<V> _right;//颜色enum color _co;
};//红黑树底层
template<class K, class V>
class Map_Set
{typedef Map_Set_Node<V> Node;
public://实现private:Node* root = nullptr;
};【三】map与set的比较难点
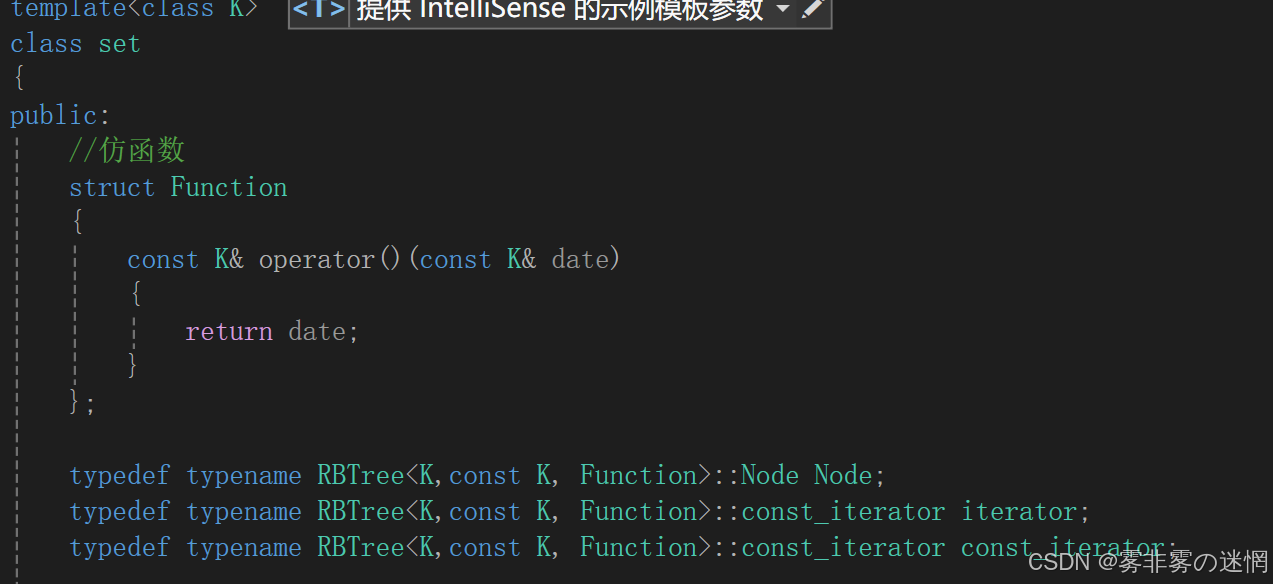
根据map和set模板参数不能直接比较,我们要借助仿函数作为红黑树的另一个模板参数:
随后可以在红黑树中直接根据类类型:Function实例化对象,调用“()”完成比较
【四】红黑树插入实现
注意:比较数据的大小我们是借助仿函数来实现的
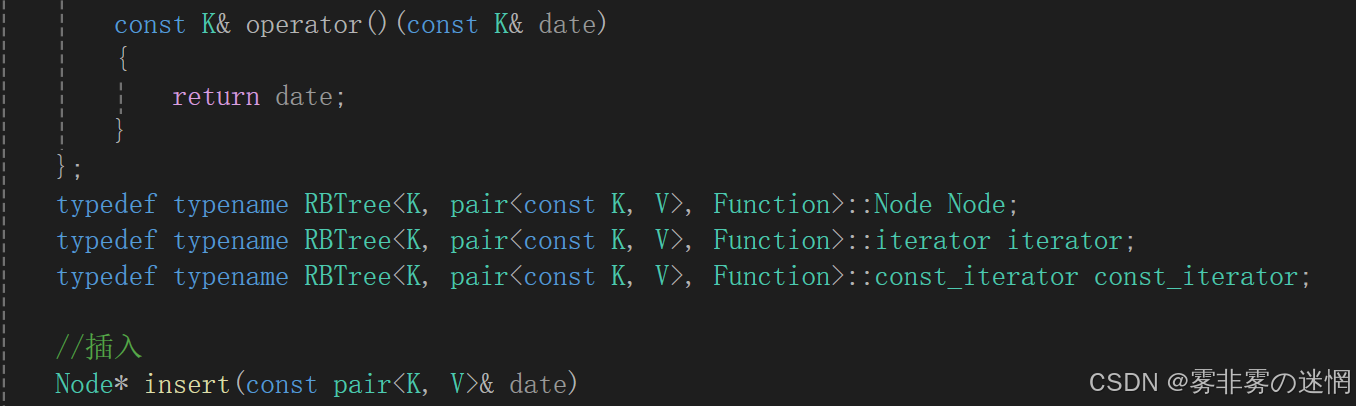
//插入
bool insert(const V& date)
{if (root==nullptr){root = new Node(date);root->_co = Black;return true;}//找插入位置Node* cur = root;Node* parent = nullptr;Function Sort;while (cur){parent = cur;if (Sort(cur->_date) > Sort(date)){cur = cur->_left;}else if (Sort(cur->_date) < Sort(date)){cur = cur->_right;}else//如果相等就退出{cout << "值相等无法插入" << endl;return false;}}//连接+插入cur = new Node(date);if (Sort(parent->_date) < Sort(date)){parent->_right = cur;}else{parent->_left = cur;}cur->_parent = parent;//调整Node* grandfather = nullptr;Node* uncle = nullptr;while (parent && parent->_co == Red){grandfather = parent->_parent;//左边调整if (parent == grandfather->_left){uncle = grandfather->_right;//如果uncle存在且为红if (uncle && uncle->_co == Red){parent->_co = Black;uncle->_co = Black;grandfather->_co = Red;//向上更新cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{//根据cur的位置旋转if (cur == parent->_left){//右旋Whirl_R(grandfather);}else{//左右双旋Whirl_L_R(grandfather);}break;}}else//右边调整{uncle = grandfather->_left;//如果uncle存在且为红if (uncle && uncle->_co == Red){parent->_co = Black;uncle->_co = Black;grandfather->_co = Red;//向上调整cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else//如果uncle不存在或者存在为黑{//根据cur选择旋转if (cur == parent->_right){//左旋Whirl_L(grandfather);}else{//右左双旋Whirl_R_L(grandfather);}break;}}}root->_co = Black;return true;
}
//左旋
void Whirl_L(Node* parent)
{Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;Node* cur = parent->_right;Node* curleft = cur->_left;//连接cur和parentcur->_left = parent;parent->_parent = cur;//连接curleft和parentparent->_right = curleft;if (curleft){curleft->_parent = parent;}//连接ppnode和curif (ppnode){cur->_parent = ppnode;if (ppnode->_left == parent){ppnode->_left = cur;}else{ppnode->_right = cur;}}else{root = cur;cur->_parent = nullptr;}//更新颜色cur->_co = Black;parent->_co = Red;
}
//右旋
void Whirl_R(Node* parent)
{Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;Node* cur = parent->_left;Node* curright = cur->_right;//连接cur和parentcur->_right = parent;parent->_parent = cur;//连接curleft和parentparent->_left = curright;if (curright){curright->_parent = parent;}//连接ppnode和curif (ppnode){cur->_parent = ppnode;if (ppnode->_left == parent){ppnode->_left = cur;}else{ppnode->_right = cur;}}else{root = cur;cur->_parent = nullptr;}//更新颜色cur->_co = Black;parent->_co = Red;
}
//左右双旋
void Whirl_L_R(Node* parent)
{Node* cur = parent->_left;Node* curright = cur->_right;//左旋Whirl_L(cur);//右旋Whirl_R(parent);//更新颜色curright->_co = Black;cur->_co = Red;parent->_co = Red;
}
//右左双旋
void Whirl_R_L(Node* parent)
{Node* cur = parent->_right;Node* curleft = cur->_left;//右旋Whirl_R(cur);//左旋Whirl_L(parent);//更新颜色curleft->_co = Black;cur->_co = Red;parent->_co = Red;
}【五】红黑树Find查找
注意:不论是map还是set都是根据Key查找的,因此map里面的仿函数需要重载
//Find查找
Node find(const V& date)
{Function Find;if (root == nullptr){cout << "查找失败,根为空" << endl;return nullptr;}Node* cur = root;while (cur){if (Find(cur->_date) > Find(date)){cur = cur->_left;}else if(Find(cur->_date) < Find(date)){cur = cur->_right;}else{return cur;}}return nullptr;
}【六】迭代器模板(初始)
迭代器所需要实现的工具如下所示:

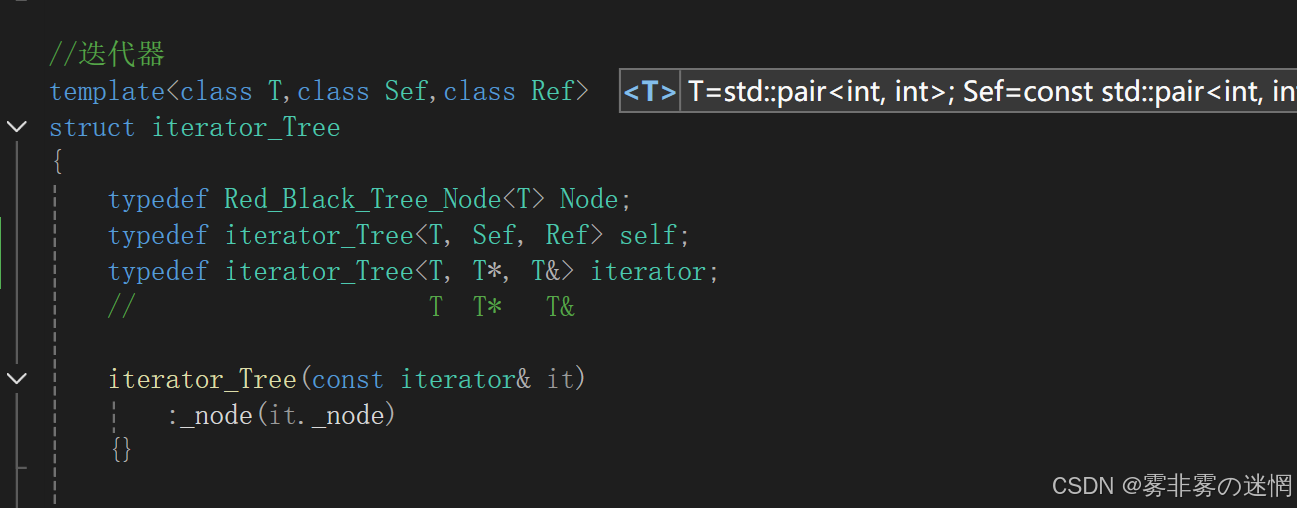
迭代器里面的模板参数T可以自由变换为 K 或者 pair<K,V>
//迭代器
template<class T>
struct iterator_Tree
{// K K function// K pair<K,T> functiontypedef Red_Black_Tree_Node<T> Node;typedef iterator_Tree<T> iterator;iterator_Tree(Node* cur):_node(cur){}Node* _node;T operator*(){return _node->_date;}bool operator!=(const iterator& s){return _node != s._node;}T* operator->(){return &_node->_date;}iterator& operator++(){//如果右不为空,访问树的最左节点if (_node->_right){Node* curleft = _node->_right;while (curleft->_left){curleft = curleft->_left;}_node = curleft;}else//右为空,访问树的左节点的那个父亲{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent){if (cur == parent->_left){break;}else{cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}}_node = parent;}return *this;}
};
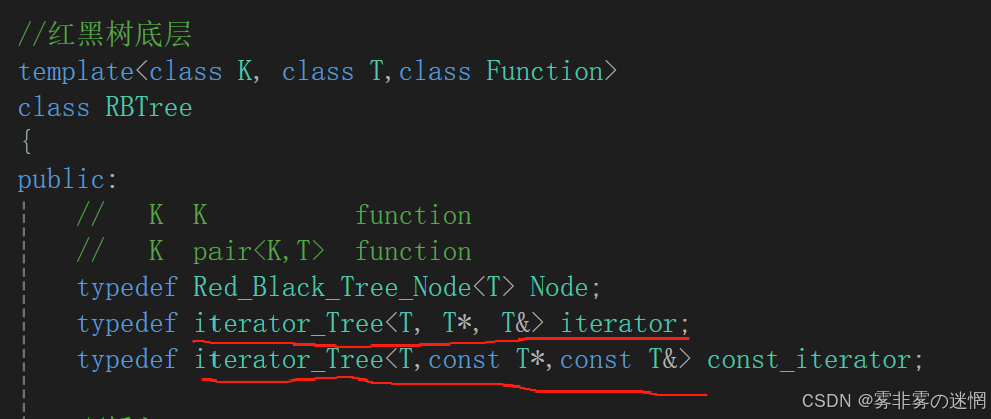
(1)Set的普通迭代器
注意:必须使用typename,是因为typename 是解决模板中依赖名称歧义的关键工具,确保编译器正确解析嵌套类型或模板成员。忽略它可能导致编译错误或意外行为
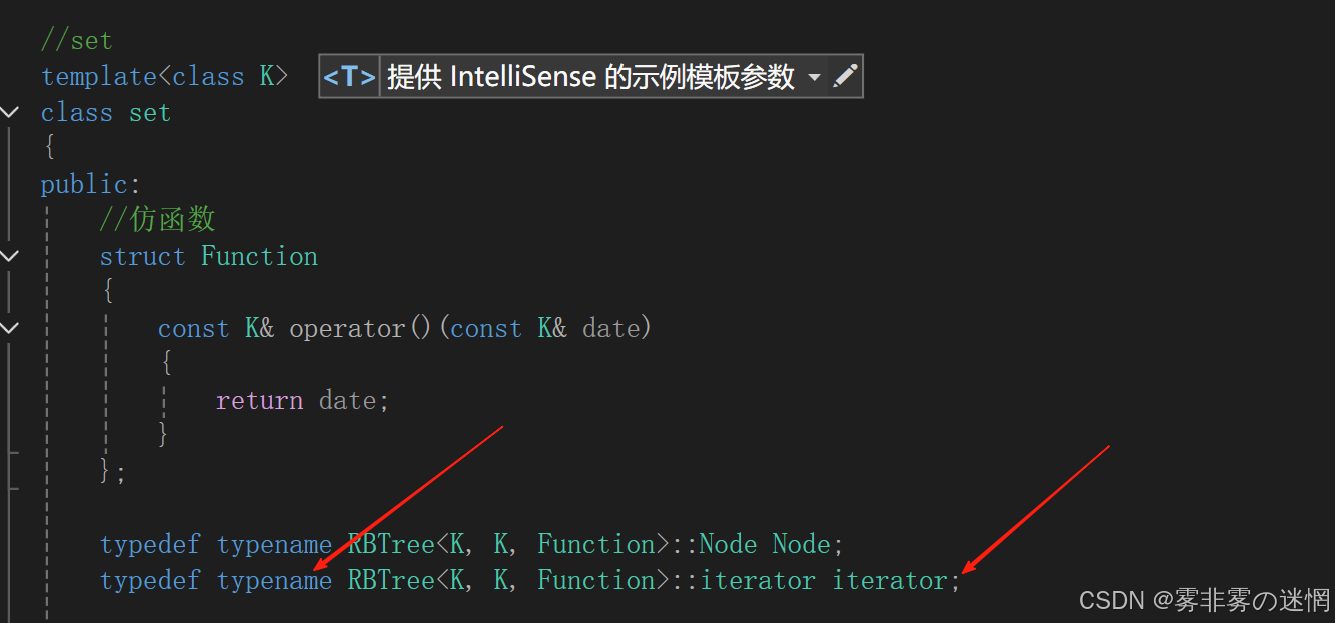
但是这样的Set的数据可以修改,不符合Set的结构,因此我们还需要再提供const的迭代器
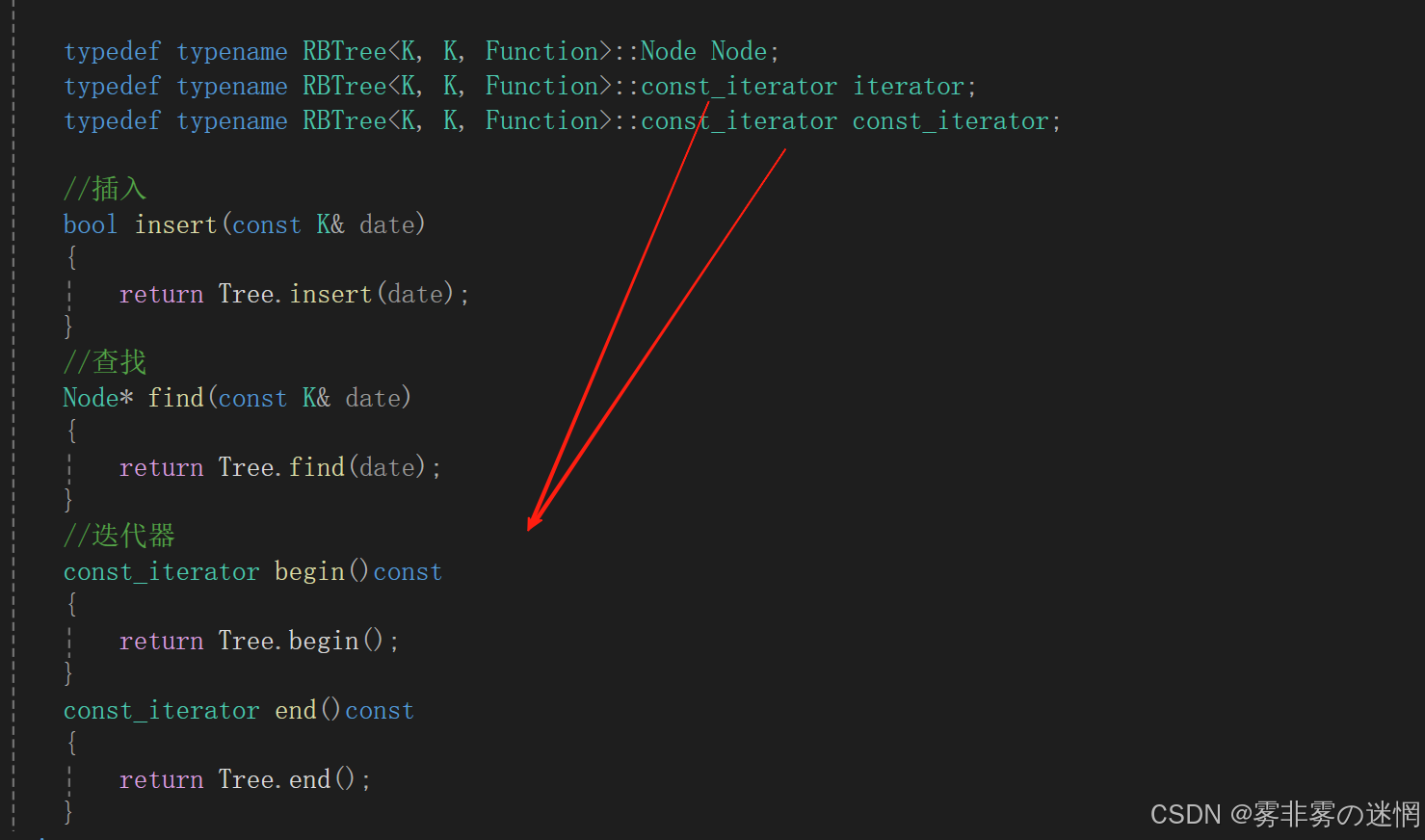
(2)Set的const迭代器
由于迭代器里面有节点的重定义,需要用到模板参数T,所以我们稍微增加一下迭代器的模板参数
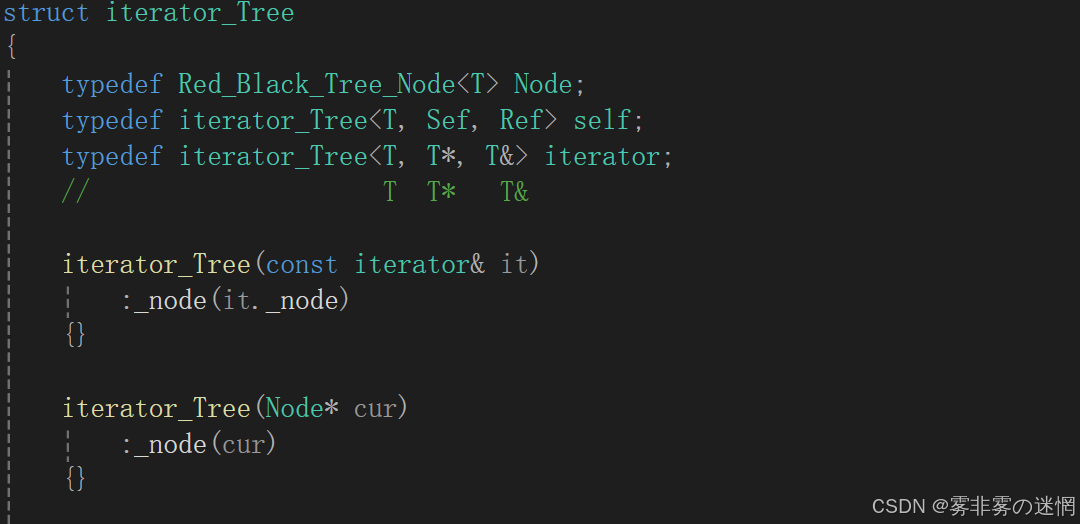
注意:第一个模板参数T是留给节点的,所以我们再多给两个模板参数;
同时Set的普通和const迭代器是同一个,因此需要更改一下下面的begin和end
(3)map的普通迭代器
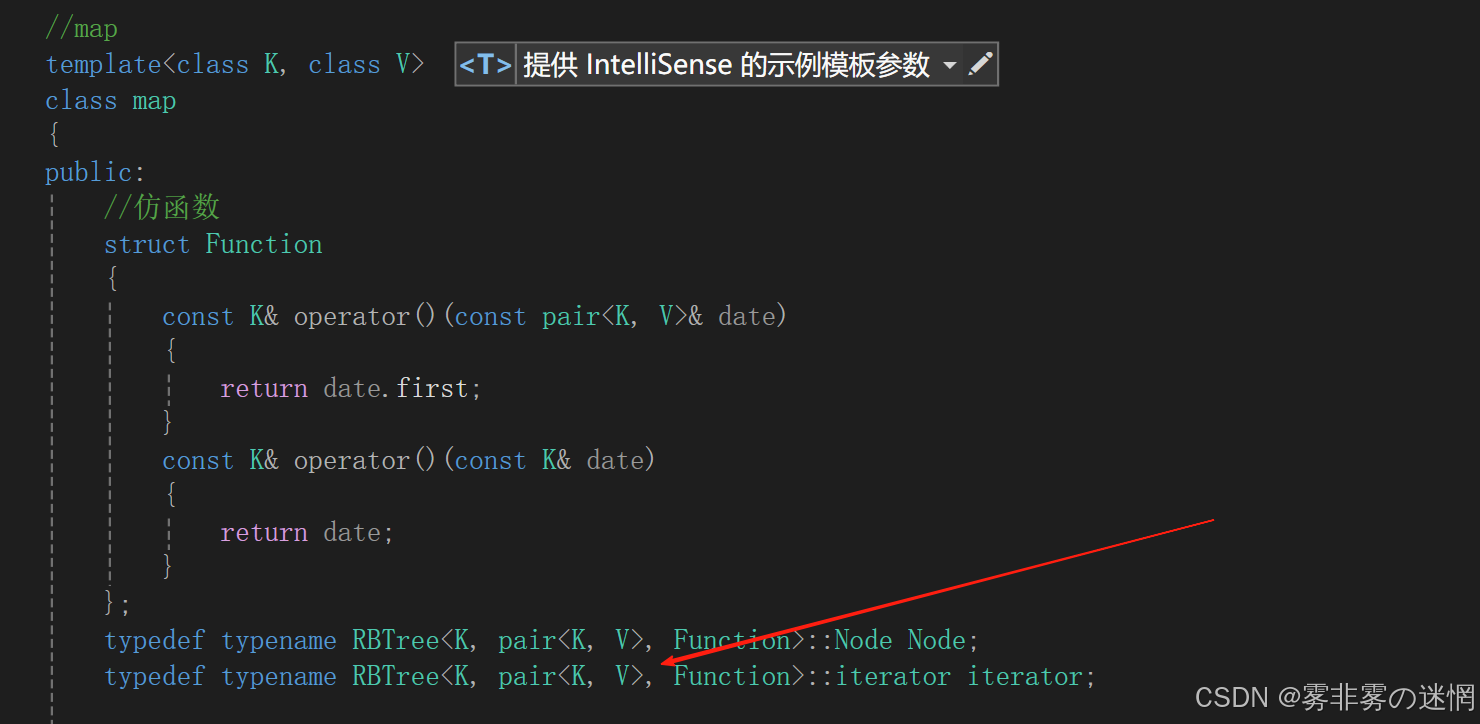
但是此时map的左右两个值都是可以修改的,所以我们还需要再模仿库里面将单个first修饰一下
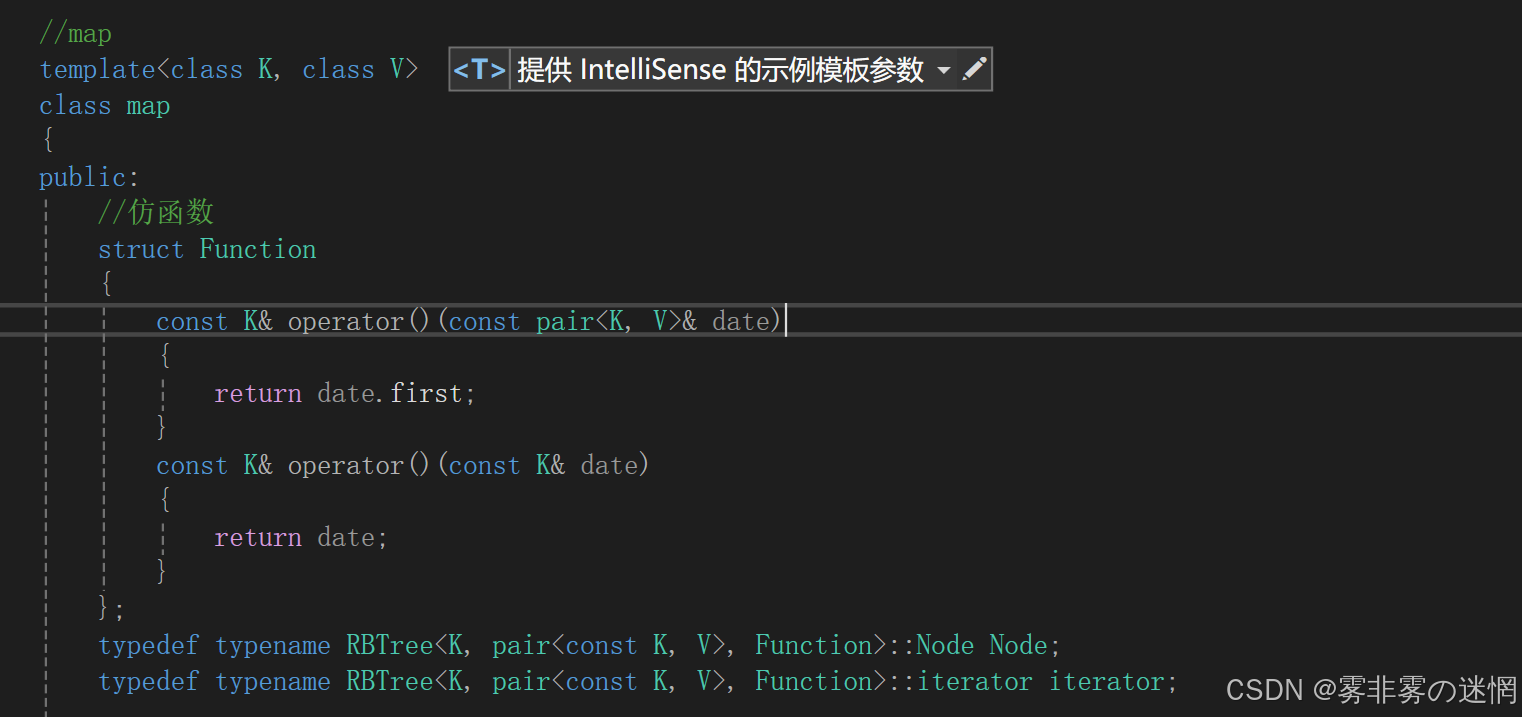
(4)map的const迭代器
const的迭代器的Key和value都不能修改,刚好直接用Set的const迭代器
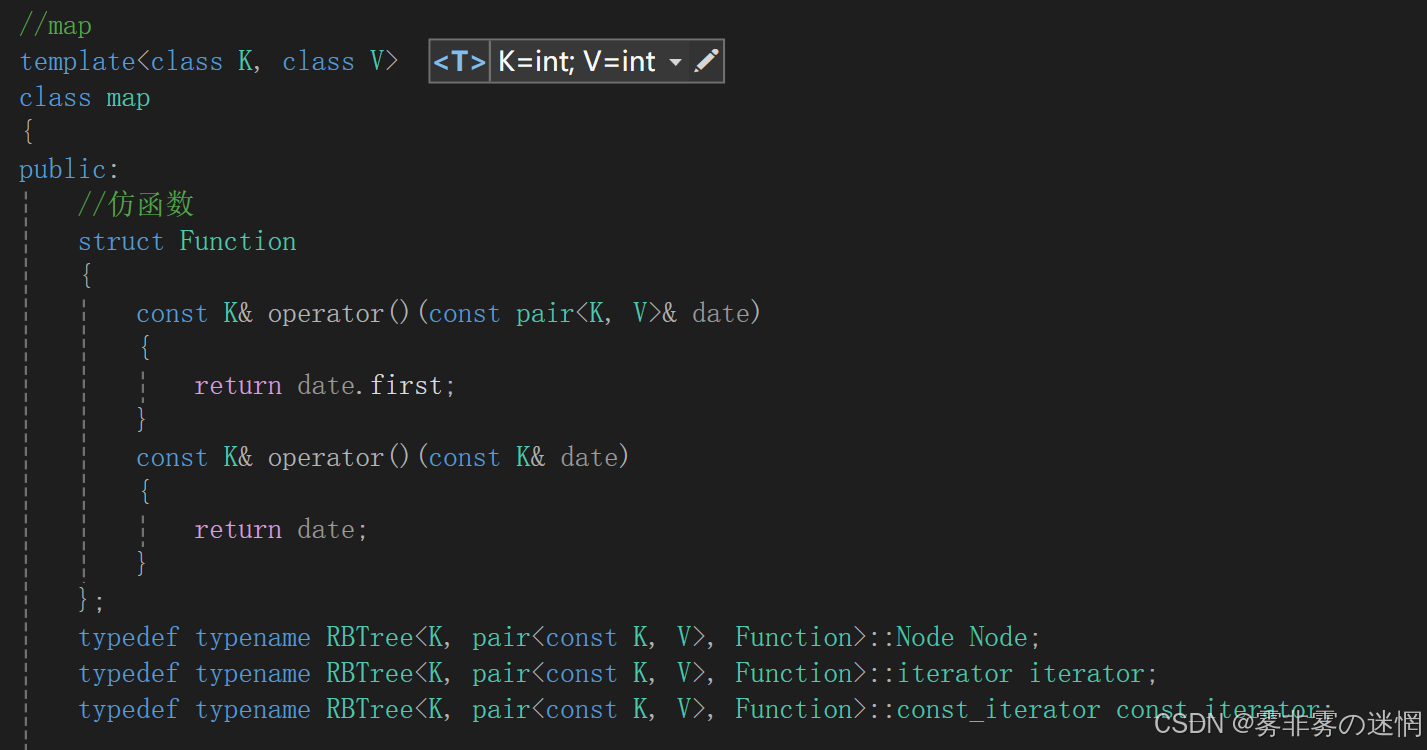
【七】迭代器的注意事项(精髓)
(1)这里需要将第一个模板参数T给节点,故需要在后面增加模板参数
(2)map迭代器的精髓在于给pair的first增加了const的修饰,同时注意下面的底层也要一样
(3)Set同理
(4)self表示当前的迭代器,不局限于<T,T*,T&>,iterator是普通迭代器
(5)iterator有两个构造函数,第一个是从普通到const的转化构造,第二个是普通的迭代器构造
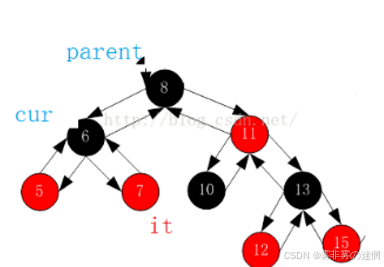
(6)对于红黑树的++,需要根据cur,parent的位置来不断找父节点
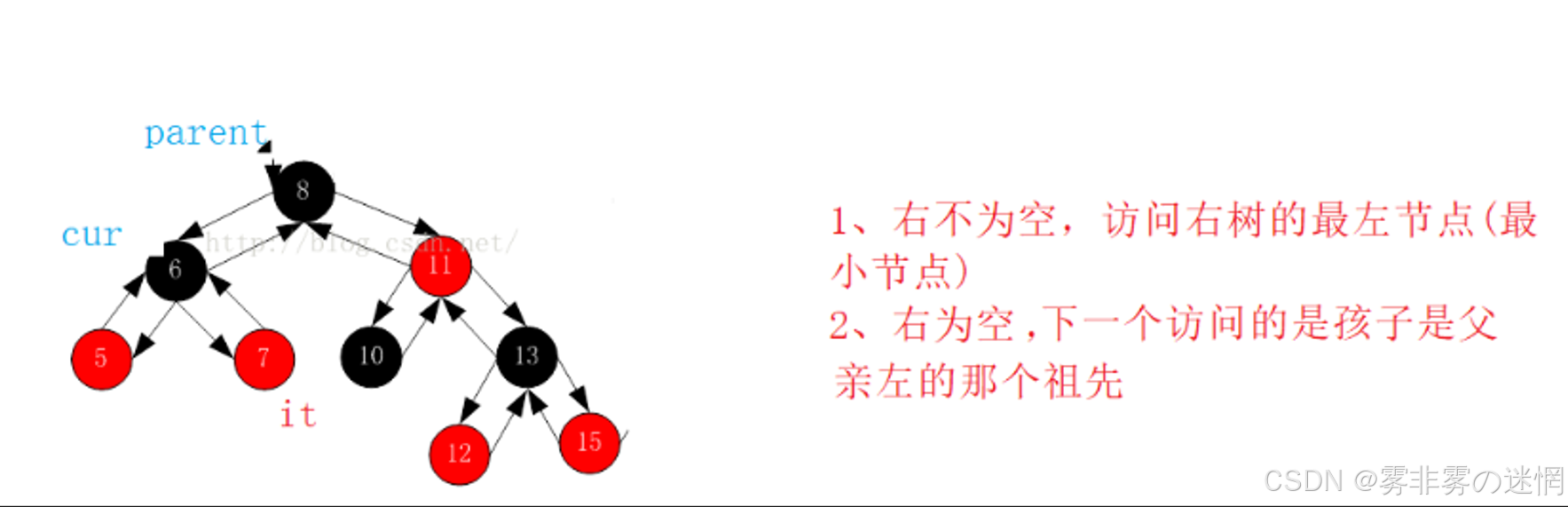
self& operator++() {//如果右不为空,访问树的最左节点if (_node->_right){Node* curleft = _node->_right;while (curleft->_left){curleft = curleft->_left;}_node = curleft;}else//右为空,访问树的左节点的那个父亲{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent){if (cur == parent->_left){break;}else{cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}}_node = parent;}return *this; }(7)对于红黑树的--,即反过来调整:
如果左不为空:访问下一个左孩子的最右节点
如果左为空:下一个访问的是孩子是父亲右的那个祖先
self& operator--() {//如果左不为空,访问下一个左孩子的最右节点if (_node->_left){Node* cur = _node->_left;while (cur->_right){cur = cur->_right;}_node = cur;}else//如果左为空,访问下一个孩子是父亲右的那个父亲节点{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent){if (cur == parent->_right){break;}else{cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}}_node = parent;}return *this; }
【八】map的operator【】
(1)需要修改红黑树的插入返回值为:pair<iterator,bool>
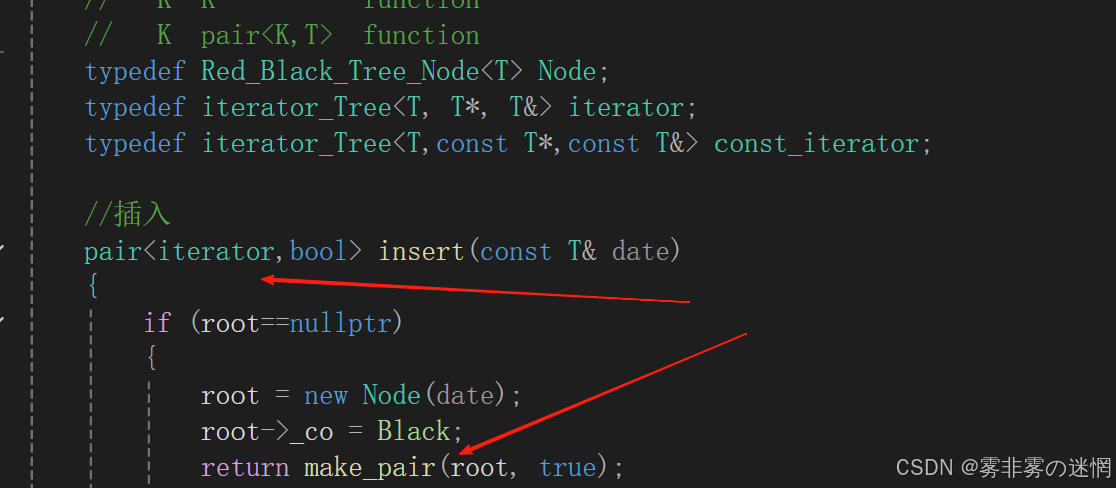
(2)完成operator【】:先接收insert的返回值,再返回接收的数据的second值
V& operator[](const K& key)
{pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));return ret.first->second;
}【九】迭代器完整代码
//迭代器
template<class T,class Sef,class Ref>
struct iterator_Tree
{typedef Red_Black_Tree_Node<T> Node;typedef iterator_Tree<T, Sef, Ref> self;//self是当前类型typedef iterator_Tree<T, T*, T&> iterator;// T T* T&iterator_Tree(const iterator& it):_node(it._node){}iterator_Tree(Node* cur):_node(cur){}Node* _node;T operator*(){return _node->_date;}bool operator!=(const iterator& s){return _node != s._node;}Sef operator->(){return &_node->_date;}self& operator++(){//如果右不为空,访问树的最左节点if (_node->_right){Node* curleft = _node->_right;while (curleft->_left){curleft = curleft->_left;}_node = curleft;}else//右为空,访问树的左节点的那个父亲{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent){if (cur == parent->_left){break;}else{cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}}_node = parent;}return *this;}(1)红黑树底层涉及的迭代器
typedef Red_Black_Tree_Node<T> Node;
typedef iterator_Tree<T, T*, T&> iterator;
typedef iterator_Tree<T,const T*,const T&> const_iterator;//Begin、end
iterator begin()
{Node* leftMin = root;while (leftMin && leftMin->_left){leftMin = leftMin->_left;}return leftMin;
}
iterator end()
{return nullptr;
}
const_iterator begin()const
{Node* leftMin = root;while (leftMin && leftMin->_left){leftMin = leftMin->_left;}return leftMin;
}
const_iterator end()const
{return nullptr;
}(2)map底层涉及的迭代器
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, Function>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, Function>::const_iterator const_iterator;////查找
//Node* find(const K& date)
//{
// return Tree.find(date);
//}
//迭代器
iterator begin()
{return Tree.begin();
}
iterator end()
{return Tree.end();
}
//迭代器
const_iterator begin()const
{return Tree.begin();
}
const_iterator end()const
{return Tree.end();
}(3)Set底层涉及的迭代器
typedef typename RBTree<K,const K, Function>::const_iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K,const K, Function>::const_iterator const_iterator;//迭代器
const_iterator begin()const
{return Tree.begin();
}
const_iterator end()const
{return Tree.end();
}【十】unordered_map or _set
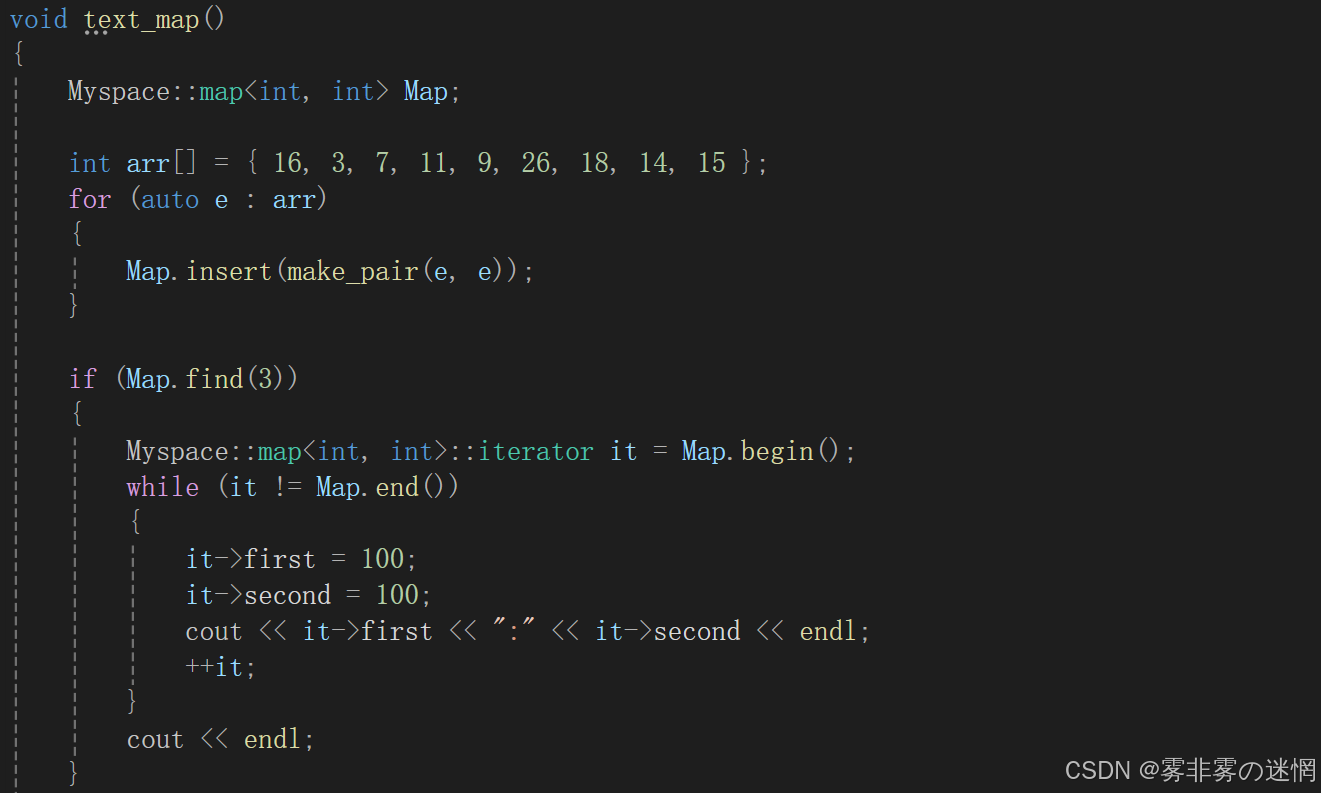
对于实用性:我们只需要知道这两种容器的使用相较于正常的map和Set在特性上有些区别:
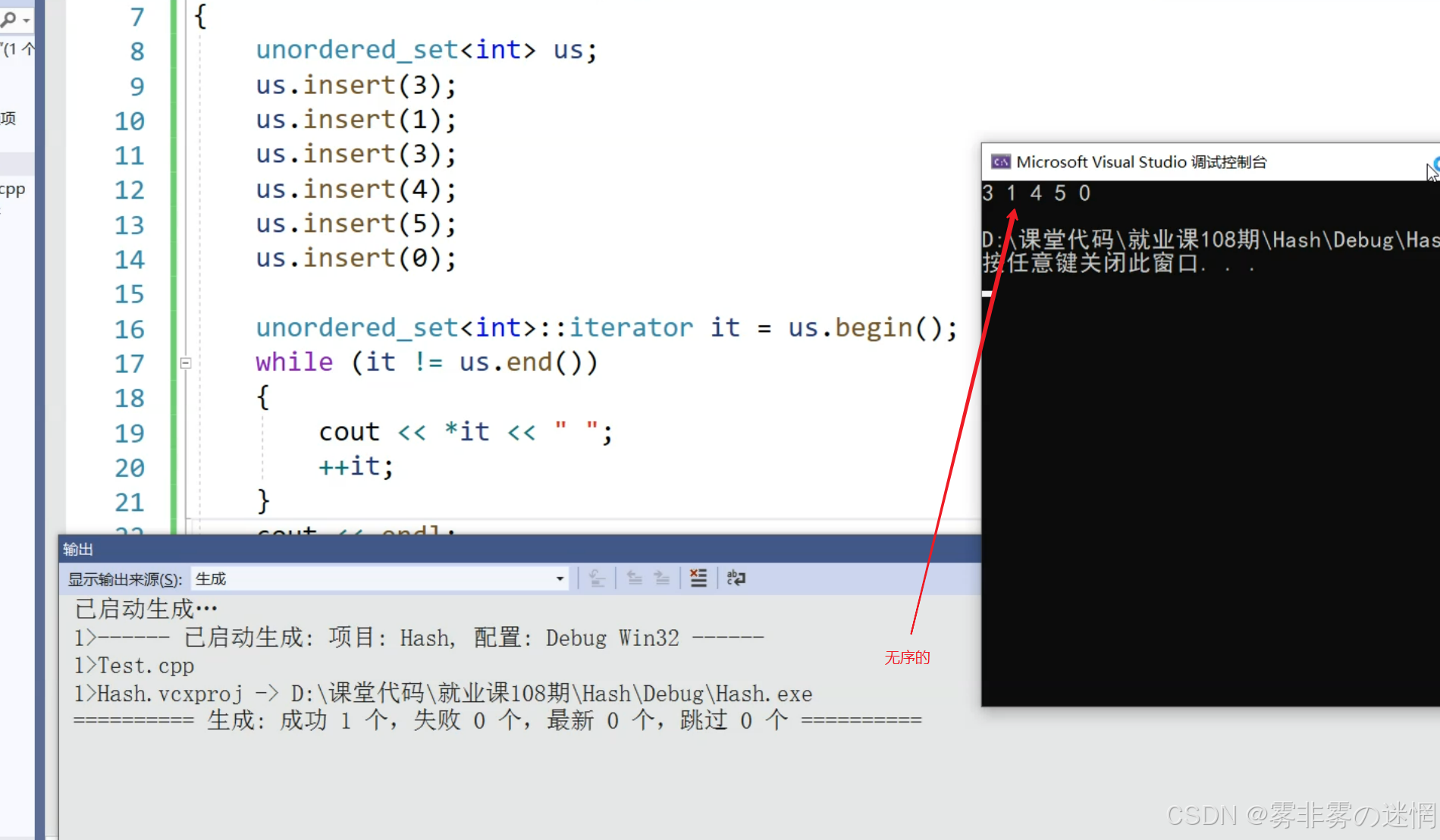
Set:
- 无序性:元素存储顺序与插入顺序无关,取决于哈希函数的结果和冲突解决策略。
- 自定义类型支持:若存储自定义类型,需提供哈希函数和相等比较函数。
map:
- 无序性:键值对的存储顺序与插入顺序无关,由哈希函数决定
- 自定义键类型:使用自定义类型作为键时,需提供哈希函数和相等比较函数