二、Istio流量治理(一)
因语雀和CSDN MarkDown格式有区别,导入到CSDN时可能会有格式显示问题,请查看原文链接:
https://www.yuque.com/dycloud/pss8ys
一、Istio 流量治理概念
1.1 流量治理介绍
流量治理概念:
- 可以动态修改服务间访问的负载均衡策略,或者根据某个请求特征进行会话保持。
- 多版本并存时,动态切换流量策略,实现流量分割、流量迁移、灰度发布、蓝绿发布等流量管理功能。
- 自动处理局部故障,提高服务韧性,包括限制并发连接数或请求数、隔离故障服务实例等,保证服务在过载、故障或遭受攻击时还能保证基本的业务能力。
- 动态修改服务中的内容,或者模拟服务故障等。
Istio流量治理的目标
- 以基础设施的方式向用户提供各种非侵入的流量治理能力
- 用户无须关注通用的服务治理机制,只需要关注业务逻辑的实现即可
使用Istio进行流量管理从本质上是将流量与底层基础架构的伸缩机制相解耦,从而让运维工程师能够通过<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Pilot</font>指定他们希望流量自身需要遵循哪些规则,而非仅仅只能定义由哪些特定的pod/VM接收流量,并在这些pod/VM之间以受限于数量比例的方式分配流量
1.2 东西向流量治理
K8S 平台上部署的服务间的东西向流量治理:
没有托管至 Istio,仍然由 k8s 直接转发的流量:
- 由
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">kube-proxy</font>负责将<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">service</font>转换为节点内核<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">netfilter</font>上的<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">iptables/nftables/ipvs</font>规则,从而将Service落地为可用的负载均衡集群- 客户端负载均衡:客户端Pod自身所在节点内核基于
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">netfilter</font>上的规则扮演负载均衡器
- 客户端负载均衡:客户端Pod自身所在节点内核基于
托管至Istio,由Sidecar容器负责治理的服务请求流量 :
- Istio基于
**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">kube-apiserver</font>**发现各个Service,并自动将这些Service转换为各Pod的**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Sidecar</font>**上的配置 - 客户端负载均衡:客户端Pod自身的
<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);">Sidecar</font>成为访问各目标<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);">Service</font>的负载均衡器,而不再由kube-proxy担任 - Sidecar是基于Envoy增强的Istio Proxy,可以支持高级流量治理策略
- (可选)流量治理策略,由管理员通过Istio API定义,并下发至各个以Sidecar形式存在的Istio Proxy
Sidecar 上的入向流量和出向流量
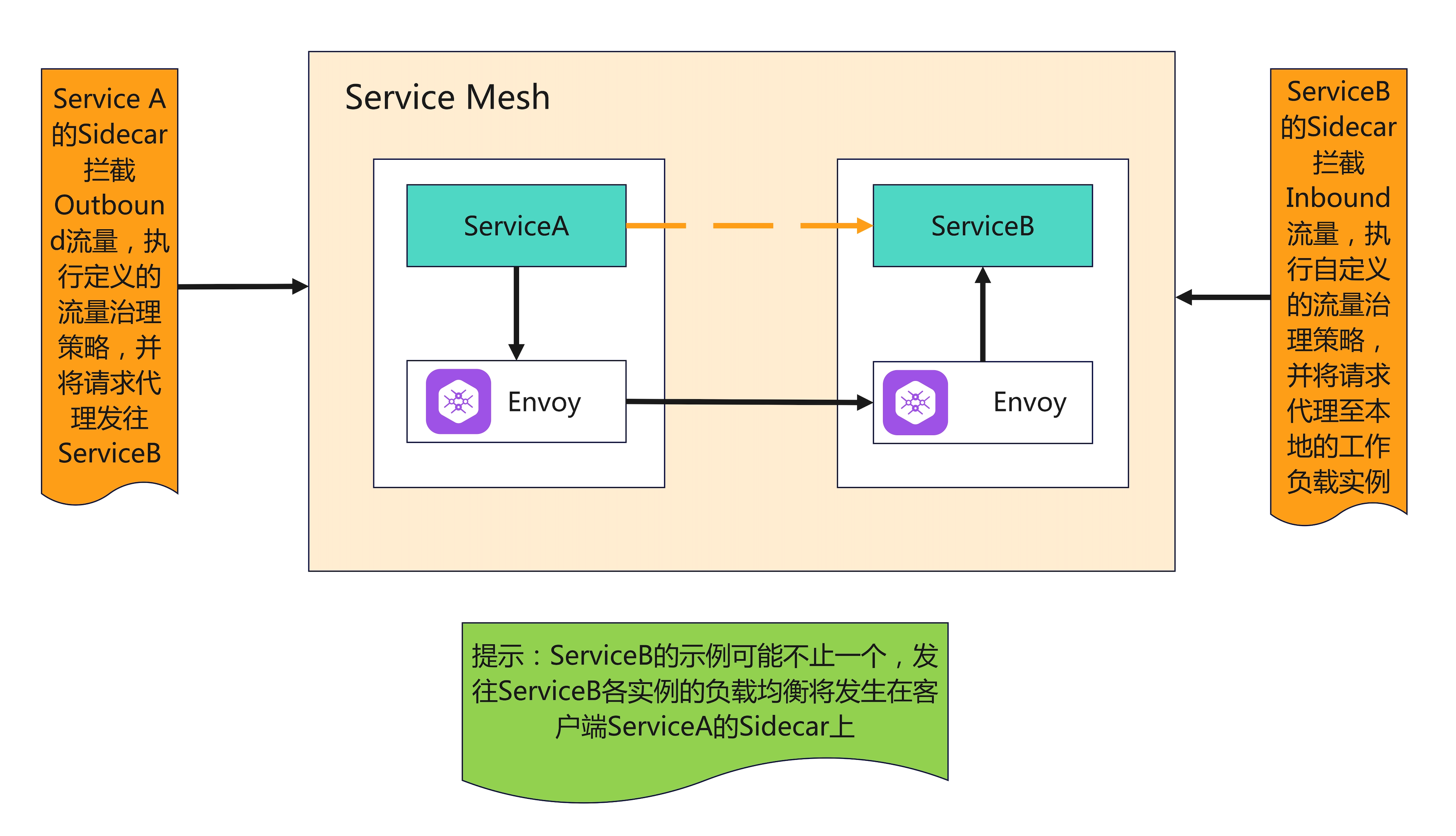
服务网格常用功能及执行位置
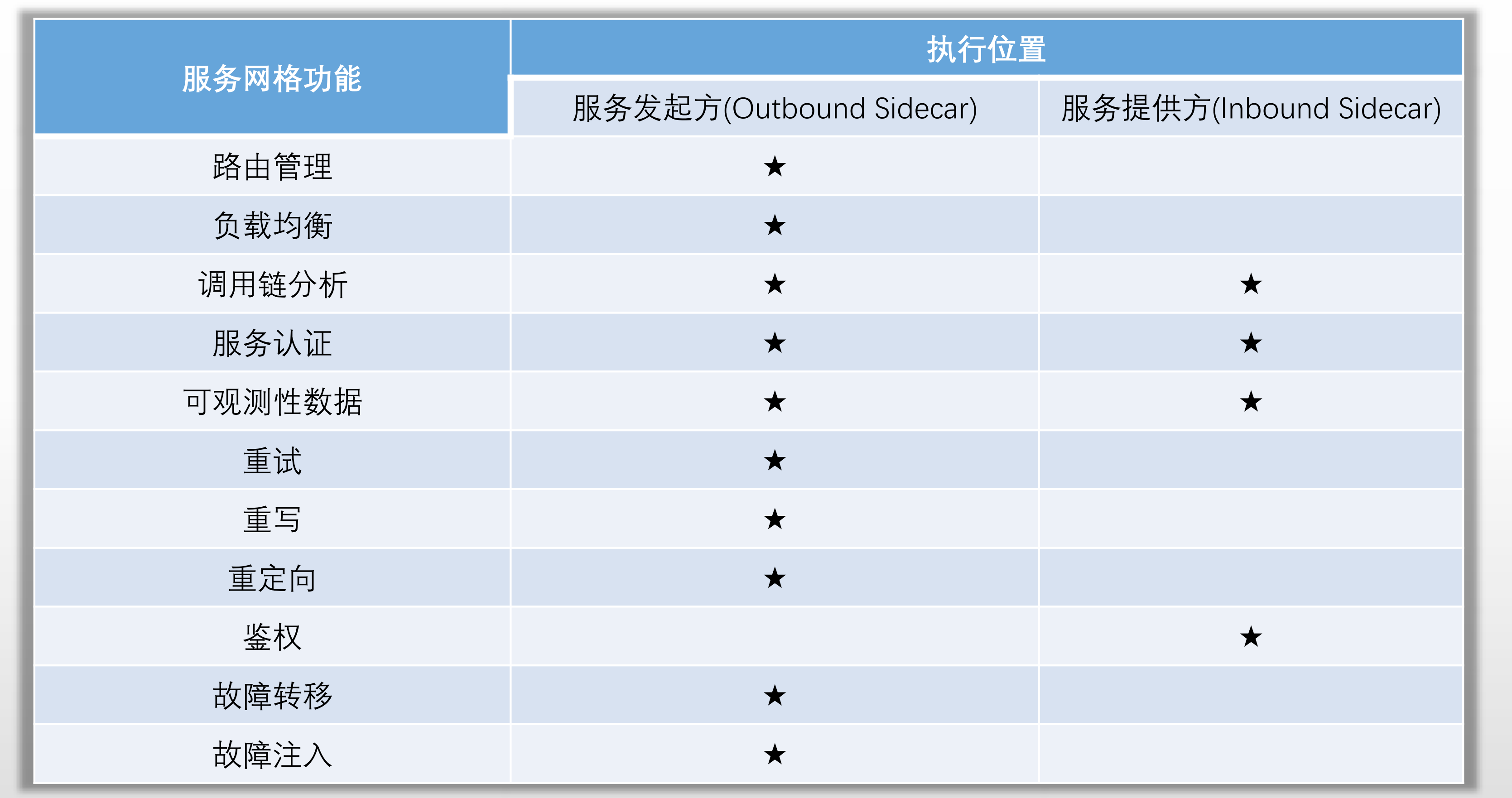
1.3 南北向流量治理
1.3.1 Istio 的入口流量(Ingress)治理:
- 传统微服务解决方案通常会包含一个入口网关
- 结合微服务的注册中心和配置中心,实现服务发现、负载均衡、限流、熔断、请求认证和鉴权等高级流量治理功能。
- 例如:Zuul、Spring Cloud Gateway 以及独立的第三方组件 APISIX 等。
- Istio 的数据平面同样需要一个类似的组件(
**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Ingress Gateway</font>**)来参与南北向流量的治理- 除了 Ingress 的 7 层流量接入和 TLS 终止能力外,
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">IngressGateway</font>还提供了高级流量治理的功能 - IngressGateway 同样基于 Envoy 实现,可以从 Istio 控制平面接受和应用配置。
- 除了 Ingress 的 7 层流量接入和 TLS 终止能力外,
1.3.2 Istio 的出站流量(Egress)治理
- 将外部服务注册到服务网格中,即可基于
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Sidecar</font>对访问该服务的流量进行治理,且几乎支持大部分的流量治理能力- 对于访问无须进行流量治理的外部服务的场景,可不用将其注册到网格中
- 出口网关(
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Egress Gateway</font>)可实现对访问外部服务的治理进行统一管理,尤其是管控允许访问的外部服务时更为简便
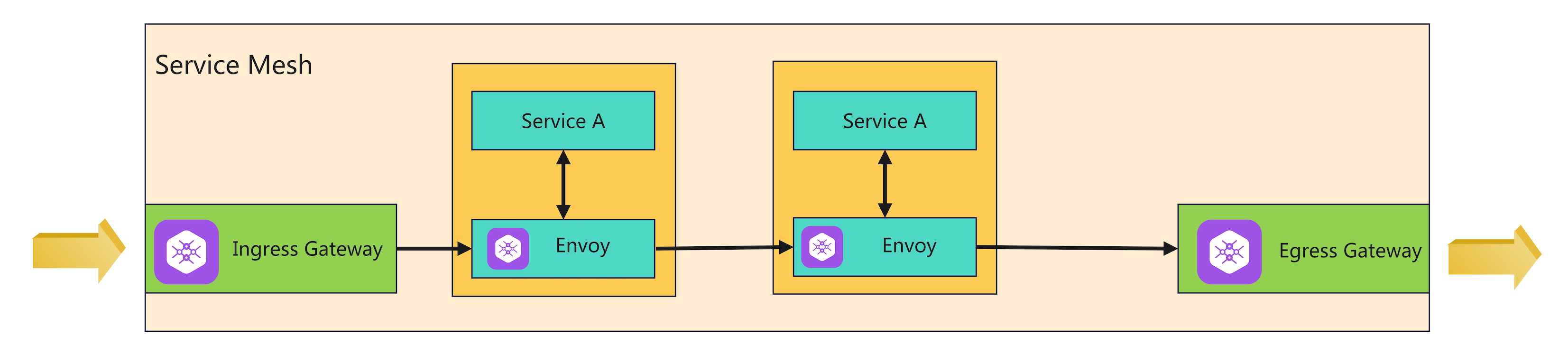
1.4 Istio 的流量治理规则及生效流程
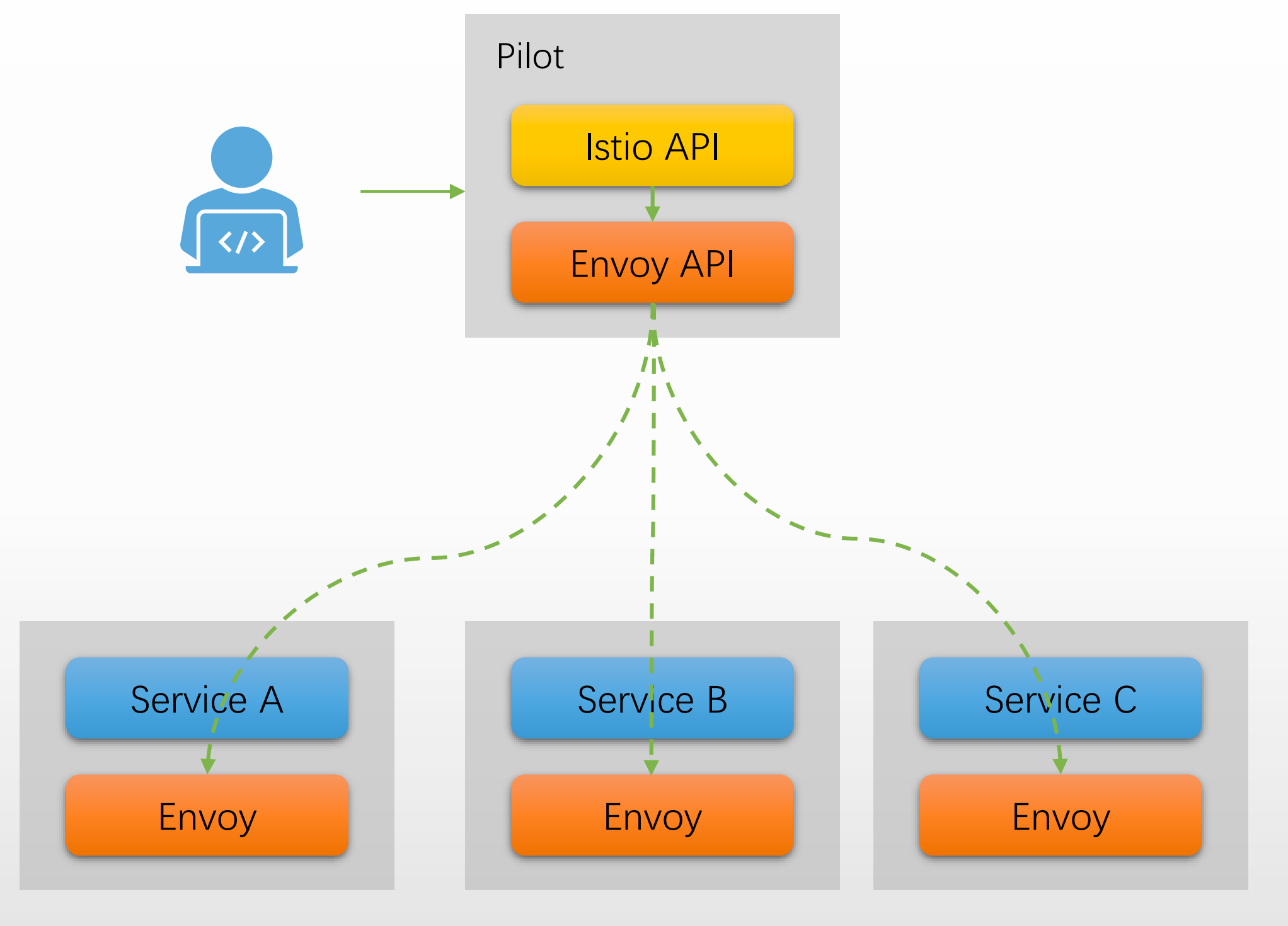
1.4.1 控制平面流程
1.4.1.1 管理员基于 Istio API 创建流量规则
- 操作主体:Kubernetes/Istio管理员(通常用
<font style="color:rgb(51, 54, 57);">kubectl</font>、<font style="color:rgb(51, 54, 57);">Kiali</font>、<font style="color:rgb(51, 54, 57);">Helm</font>等方式) - 内容形式:创建、应用对应的Kubernetes CRD(CustomResourceDefinition)
- 涉及资源/对象:
**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">VirtualService</font>**:定义流量在服务间如何路由和转发**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">DestinationRule</font>**:指定到目标服务的负载均衡、子集(版本)、连接池和安全策略**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Gateway</font>**:定义入口网关的端口、协议及主机名**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">ServiceEntry</font>**:将外部服务纳入Mesh治理**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">EnvoyFilter</font>**:用于自定义扩展Envoy的行为**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">WorkloadEntry</font>**/**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Group</font>**:管理非K8s环境下的工作负载纳管到Mesh
- 作用:表达业务层面的流量需求、安全要求和流控规则。
1.4.1.2 <font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Pilot</font> 将流量规则转换为 Envoy 配置
- Pilot组件简介:Istio的流量管控核心,现集成在
<font style="color:rgb(251, 71, 135);">istiod</font>中。 - 工作细节:
- Pilot通过
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">watch</font>机制实时监听K8s上CRD资源变更。 - 将用户的高层流量治理规则(如灰度、蓝绿、熔断等业务意图)解析/编译为
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Envoy</font>可识别、可执行业务的底层XDS配置(例如<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Listener</font>、<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Cluster</font>、<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Route</font>等)。 - 执行配置“合并”“去重”“冲突解决”等逻辑,确保每个Sidecar/Gateway配置最小且精准。
- Pilot通过
1.4.1.3 <font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Pilot</font> 基于 xDS 下发配置到数据面的 <font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Envoy</font>
- xDS 协议:Envoy 与控制面交互的标准API集,包括
<font style="color:rgb(51, 54, 57);"> Listener Discovery Service</font>、<font style="color:rgb(51, 54, 57);">Route Discovery Service</font>、<font style="color:rgb(51, 54, 57);">Cluster Discovery Service</font>、<font style="color:rgb(51, 54, 57);">Endpoint Discovery Service</font>等。 - 工作细节:
- Pilot主动或被动向所有envoy代理推送他们所需的、专属的XDS配置(按
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">namespace</font>、<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">service</font>、<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">labels</font>等裁剪)。 - 一旦治理CRD发生变更,或集群工作负载有修改,Pilot会及时更新相关envoy的配置,让新的流量治理规则生效。
- 整个流程无需重启服务/代理,配置热更新。
- Pilot主动或被动向所有envoy代理推送他们所需的、专属的XDS配置(按
1.4.2 数据平面流程
1.4.2.1 <font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Sidecar Envoy</font>拦截本地业务进程的<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Inbound</font>和<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Outbound</font>流量,并解析流量
**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">sidecar代理</font>**:- 每个Workload Pod里自动注入一个
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Envoy</font>容器(<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Sidecar</font>模型)。
- 每个Workload Pod里自动注入一个
- 流量拦截机制:
- 通过
**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">iptables</font>**,将服务实例的所有入口流量(Inbound)和出口流量(Outbound)都劫持到Envoy代理,由它转发/管理。
- 通过
- 转发解析点(后面会有一篇文章专门讲解流量劫持过程):
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Inbound</font>:外部流量(可能经过ingress gateway)进入本Pod时,先进入本Pod里的Envoy,执行入站流控规则之后,再进入业务进程。<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Outbound</font>:业务进程去访问Mesh内其他服务(或外部服务)时,其出口流量也先由sidecar Envoy拦截,并可执行各种流控策略。
1.4.2.2 流量经过<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Envoy</font>时执行管理员定义的流量规则,完成流量治理功能
- 流量治理执行点:
- 所有你通过CRD表达的流量路由(
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">VirtualService</font>)、目标子集和负载均衡(<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">DestinationRule</font>)、限流熔断/安全(<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">DestinationRule</font>/<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">EnvoyFilter</font>)、访问外部服务(<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">ServiceEntry</font>)等,都在**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Envoy</font>**滤器链中得到真实执行。
- 所有你通过CRD表达的流量路由(
- 主要治理功能举例:
- 按header/权重/URI实现灰度和A/B
- 按目标subset实现蓝绿/金丝雀
- 当前工作负载自动负载均衡
- 线路上自动加密(mTLS)
- 限制QPS/连接数/熔断保护
- 强制访问认证/授权
- 插拔自定义流控插件
- 可视化/观测:
- Envoy实时采集流量遥测数据,供Kiali、Prometheus等监控展示调用链、延迟、成功率等mesh健康状况。
1.5 Istio 流量治理的关键配置
1.5.1 入口网关和出口网关
- Istio通过
**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Ingress</font>**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;"> </font>**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Gateway</font>**为网格引入外部流量;- Gateway中运行的主程序亦为
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Envoy</font>,它同样从控制平面接收配置,并负责完成相关的流量传输; - 换言之,Gateway资源对象用于将外部访问映射到内部服务,它自身只负责通信子网的相关功能,例如套接 字,而七层路由功能则由
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">VirutalService</font>实现;
- Gateway中运行的主程序亦为
- Istio基于
**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">ServiceEntry</font>**资源对象将外部服务注册到网格内,从而像将外部服务以类同内部服务一样的方式进行访问治理;- 对于外部服务,网格内
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Sidecar</font>方式运行的Envoy即能执行治理; - 若需要将外出流量收束于特定几个节点时则需要使用专用的
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Egress Gateway</font>完成,并基于此<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Egress Gateway</font>执行相应的流量治理;
- 对于外部服务,网格内
1.5.2 流量路由及分发机制
**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Virtual Services</font>**和**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Destination Rules</font>**是Istio流量路由功能的核心组件。
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Virtual Services</font>用于将分类流量并将其路由到指定的目的地(Destination),而<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Destination Rules</font>则用于配置那个指定Destination如何处理流量**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Virtual Services </font>**- 用于在Istio及其底层平台(例如Kubernetes)的基础上配置如何将请求路由到网格中的各
**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Service</font>**之上 - 通常由一组路由规则(routing rules )组成,这些路由规则按顺序进行评估,从而使Istio能够将那些对
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Virtual Service</font>的每个给定请求匹配到网格内特定的目标之上 - 事实上,其定义的是分发给网格内各
**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Envoy</font>**的**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">VirtualHost</font>**和**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Route</font>**的相关配置
- 用于在Istio及其底层平台(例如Kubernetes)的基础上配置如何将请求路由到网格中的各
**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Destination Rules</font>**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;"> </font>- 定义流量在“目标”内部的各端点之间的分发机制,例如将各端点进行分组,分组内端点间的流量均衡机制,异常探测等
- 事实上,其定义的是分发给网格内各
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Envoy</font>的<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Cluster</font>的相关配置
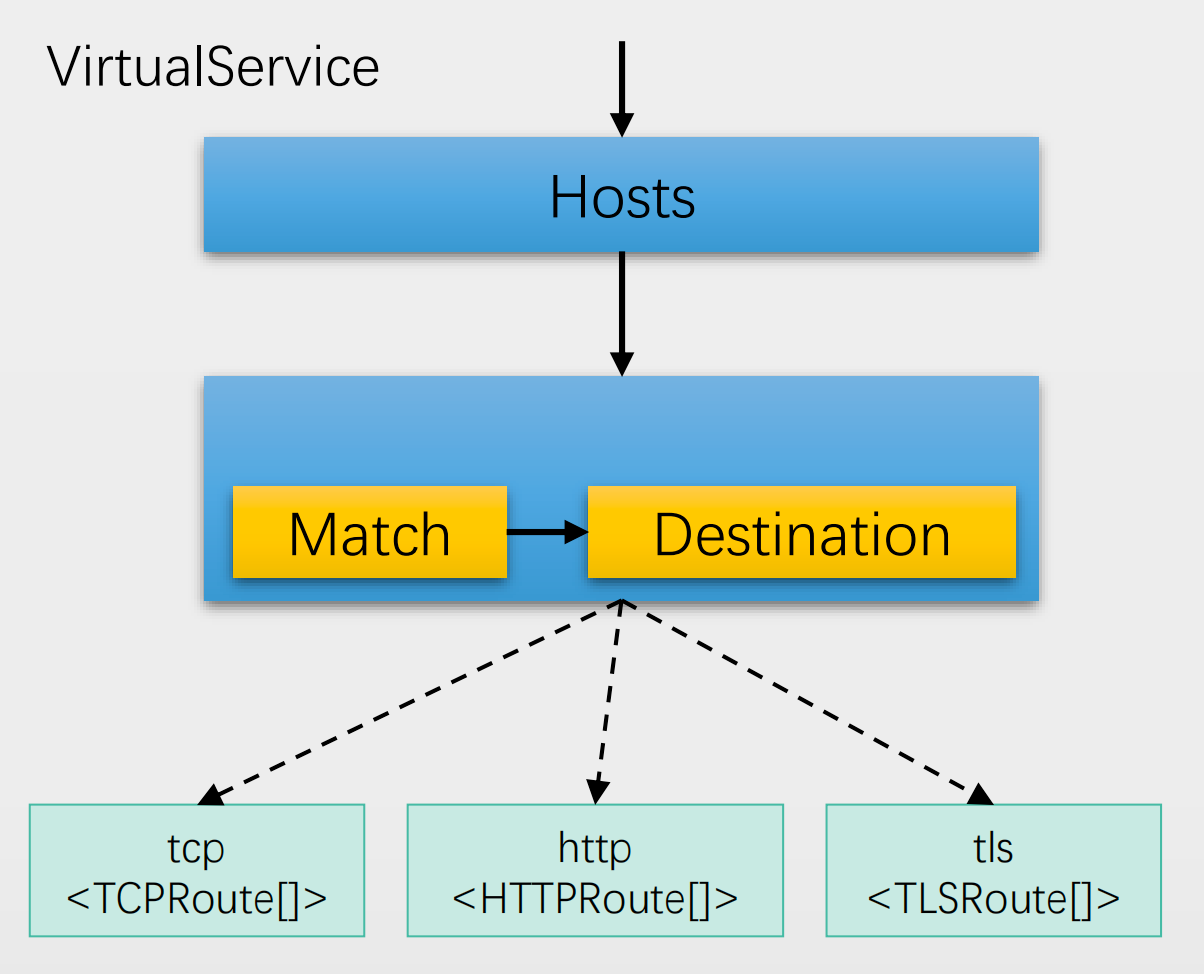
简单来说:
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">VirtualService</font>定义虚拟主机及相关的路由规则,包括路由至哪个目标(集群或子集)<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">DestinationRule</font>定义集群、子集及其内部的流量分发机制
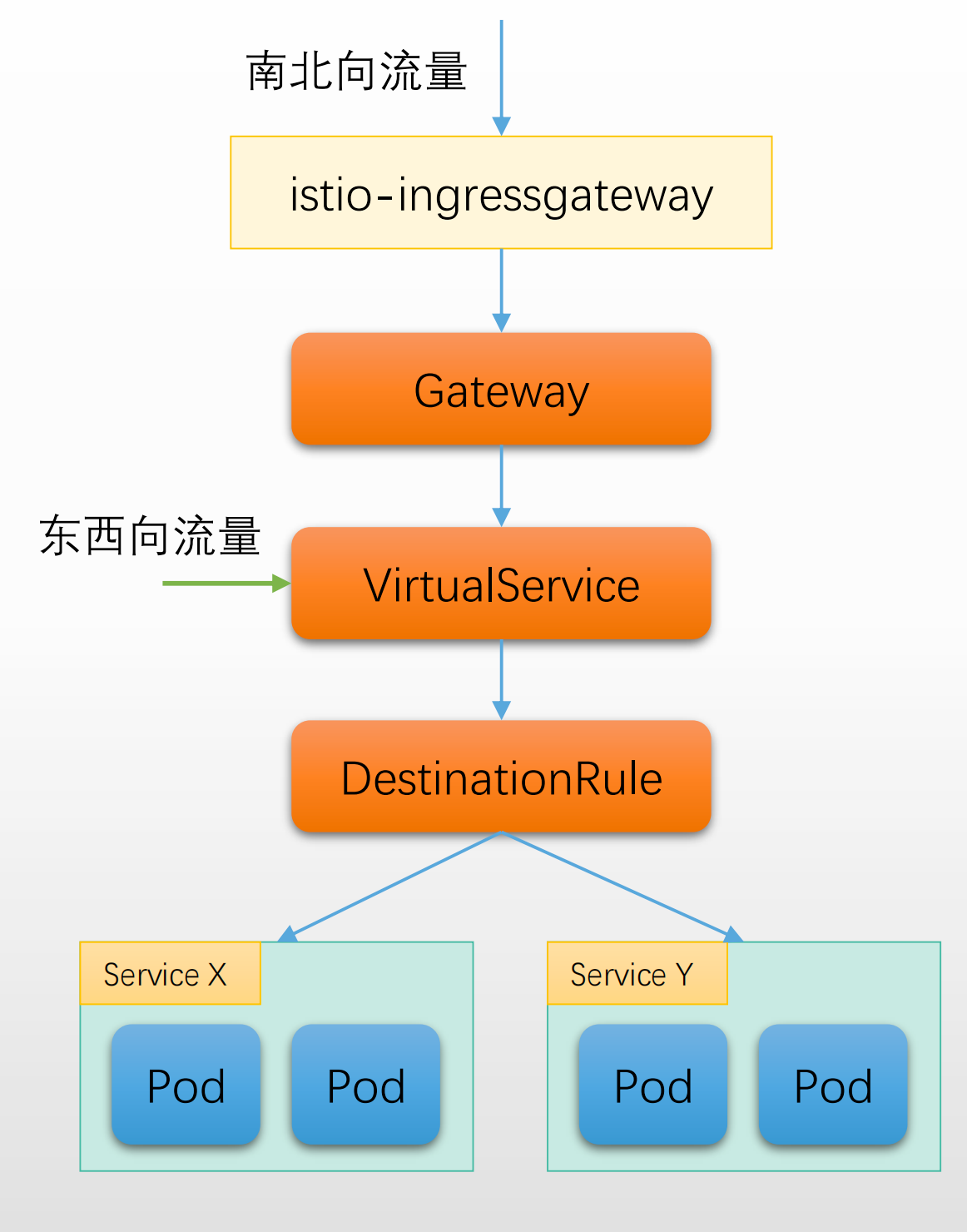
1.5.3 流量治理整体链路
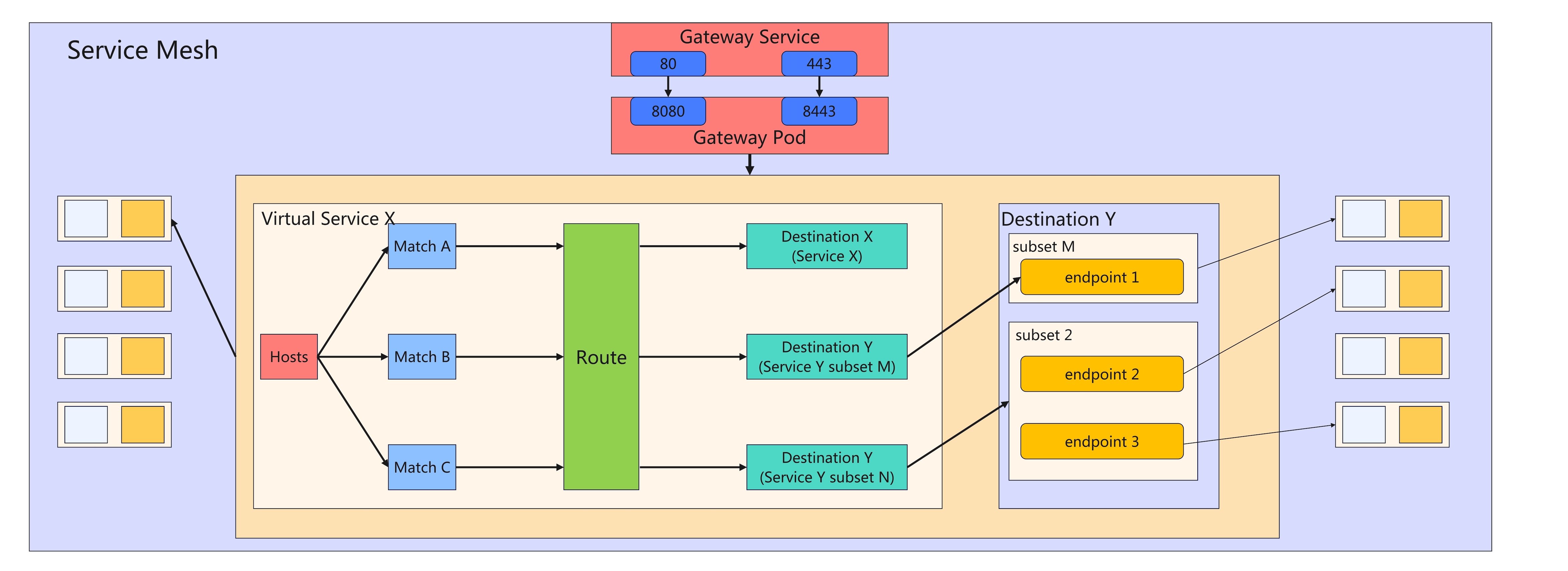
上面的图展示了 Istio 的南北、东西向流量全链路走向:
- 用户访问
**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Service Mesh</font>**的服务,外部请求首先通过入向网关( Ingress Gateway),Ingress Gateway 主要由两个对象:<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Gateway Service</font>:定义了实际对外暴露的端口和协议,比如常用的 80、443。<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Gatway Pod</font>:实际运行 Envoy 代理的 Pod,监听内部端口(入 8080、8443)
- 流量进入 Service Mesh,开始接受 Istio 的流量治理规则。
- VirtualService 流量路由
- VirtualService X 控制了"哪些主机名/请求域名" 可以被路由,以及根据请求内容(如路径、host、header 等)进行多条件匹配(MatchA/B/C)。
- 每一个 Mathc 条件对应一种流量治理策略,最终确定"Route" ,也就是实际的榴莲转发路径。
- 确定路由/服务目标
- Route 决定后,流量会被转发到相应的目标服务(Destination)
- 比如:有的流量被转发到 Destination X(ServiceX),有的被转发到 Destination Y(ServiceY 的部分子集)。
- Destination 很可能是"服务的子集"(如版本/批次等),实现灰度、蓝绿、A/B 测试等场景。
- 目标服务子集选择
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">DestinationRule</font>定义:一个服务(入 ServiceY)下有多个子集(subsets),比如 M、N,每个子集下有多个 endpoint(本质就是 pod 实例)。<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">VirtualService</font>可以结合<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">DestinationRule</font>,将精确的流量路由到指定子集(比如将 20%的流量转发到新版本的服务)。
- 实际请求到 Pod 实例
- 流量按照治理规则进入目标的 endpoint(具体的业务 Pod)。
- 返回路径同理,流量遵循路由规则返回。
1.6 配置 Istio 流量治理
集群外部的入站流量会经由 Ingress Gateway 到达集群内部:
- 需要经由 Gateway 定义的 Ingress Gateway 上的"虚拟主机"
- 包括目标流量访问的"host",以及虚拟主机监听的端口等。
集群内部的流量仅会在 Sidecar 之间流动:
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">VirtualService</font>为Sidecar Envoy定义<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Listener</font>(主要定义流量路由机制等)<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">DestinationRule</font>为Sidecar Envoy定义<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Cluster</font>(包括发现端点等)
1.7 暴露 kiali 服务访问
1.7.1 创建 Gateway
定义服务网格入向网关,告诉 istio IngressGateway 监听哪些端口、哪些 Host(域名)
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: Gateway
metadata:name: kiali-gatewaynamespace: istio-system
spec:selector:app: istio-ingressgatewayservers:- port:number: 80name: http-kialiprotocol: HTTPhosts:- "kiali.dujie.com"
---
<font style="color:rgb(251, 71, 135);">selector</font>指定应用到哪个 ingressgateway(一般是 istio 默认入口)。<font style="color:rgb(251, 71, 135);">servers</font>配置:<font style="color:rgb(251, 71, 135);">port</font>: 80,HTTP访问<font style="color:rgb(251, 71, 135);">hosts</font>: 只允许给定的 Host(域名)“kiali.dujie.com”被处理
实际面向用户:
任何流量到 IngressGateway(暴露出来的公网IP/NodePort/负载均衡),只要 Host 是 <font style="color:rgb(251, 71, 135);">kiali.dujie.com</font> 、端口80,才会进此 Gateway。
创建完成可以通过 istioctl proxy-config 查看相关集群、listener 信息
[root@k8s-master01 kiali]# kubectl get pods -n istio-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
grafana-548947586b-6f9zh 1/1 Running 0 68m
istio-egressgateway-65589498c8-g4zsx 1/1 Running 0 77m
istio-ingressgateway-8f8d6679b-nnc9l 1/1 Running 0 77m
istiod-846896755-6drrb 1/1 Running 0 77m
jaeger-b8465f948-xnhkw 1/1 Running 0 66m
kiali-7cbdf5689-25c42 1/1 Running 0 69m
prometheus-66bf456d8-h5m49 2/2 Running 0 66m
[root@k8s-master01 kiali]#
# 可以看到这里就是我们上面创建的gateway
[root@k8s-master01 kiali]# istioctl proxy-config cluster istio-ingressgateway-8f8d6679b-nnc9l -n istio-system
...
kiali.istio-system.svc.cluster.local 9090 - outbound EDS kiali.istio-system
kiali.istio-system.svc.cluster.local 20001 - outbound EDS kiali.istio-system1.7.2 创建 virtualservice
- 针对被 Gateway “放行”的流量,进一步解析“路径/条件”,决定转发给 Mesh 内哪台服务,甚至可以做多级路由、A/B测试、灰度等。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:name: kiali-virtualservicenamespace: istio-system
spec:hosts:- "kiali.dujie.com"gateways:- kiali-gatewayhttp:- match:- uri:prefix: /route:- destination:host: kialiport:number: 20001
---<font style="color:rgb(251, 71, 135);">hosts</font>:匹配<font style="color:rgb(251, 71, 135);">kiali.dujie.com</font>内容,和Gateway一致<font style="color:rgb(251, 71, 135);">gateways</font>: 指定受哪几个 Gateway 管控(此处为kiali-gateway)<font style="color:rgb(251, 71, 135);">http.match</font>: 匹配所有 URI(<font style="color:rgb(251, 71, 135);">/</font>开头,即所有路径)<font style="color:rgb(251, 71, 135);">route.destination.host</font>: 匹配到的请求,直接发送给 Service 名为<font style="color:rgb(251, 71, 135);">kiali</font>的服务,端口20001。- 用户访问(假设公网 IP、域名已解析好):
- 浏览器请求
<font style="color:rgb(251, 71, 135);">http://kiali.dujie.com/</font> - IngressGateway 监听规则中匹配到 hosts
- VirtualService 进一步匹配(URI全部OK),流量被转发到 kiali:20001
- 浏览器请求
定义了 <font style="color:#DF2A3F;">kiali-virtualService</font> 资源后,<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">kiali-gateway</font> 的流量将由<font style="color:#DF2A3F;"> kiali-virtualservice.istio-system</font> 进行路由:
[root@k8s-master01 kiali]# kubectl get pods -n istio-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
grafana-548947586b-6f9zh 1/1 Running 0 86m
istio-egressgateway-65589498c8-g4zsx 1/1 Running 0 95m
istio-ingressgateway-db8dcb984-4zc6x 1/1 Running 0 5m13s
istiod-846896755-6drrb 1/1 Running 0 95m
jaeger-b8465f948-xnhkw 1/1 Running 0 85m
kiali-7cbdf5689-25c42 1/1 Running 0 87m
prometheus-66bf456d8-h5m49 2/2 Running 0 84m
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# istioctl proxy-config route istio-ingressgateway-db8dcb984-4zc6x -n istio-system
NAME VHOST NAME DOMAINS MATCH VIRTUAL SERVICE
http.8080 kiali.dujie.com:80 kiali.dujie.com /* kiali-virtualservice.istio-systembackend * /healthz/ready* backend * /stats/prometheus*
kiali-virtualservice.istio-system 会从相应的流量路由到"kiali"这一目标,而该目标所代表的 Cluster 会由 Istio 控制平面从同已给名称空间 istio-system 下的 services/kiali 资源发现并自动创建,只是这个 cluster 并不属于人嗯 DestinationRule:
[root@k8s-master01 kiali]# kubectl get pods -n istio-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
grafana-548947586b-6f9zh 1/1 Running 0 86m
istio-egressgateway-65589498c8-g4zsx 1/1 Running 0 95m
istio-ingressgateway-db8dcb984-4zc6x 1/1 Running 0 5m13s
istiod-846896755-6drrb 1/1 Running 0 95m
jaeger-b8465f948-xnhkw 1/1 Running 0 85m
kiali-7cbdf5689-25c42 1/1 Running 0 87m
prometheus-66bf456d8-h5m49 2/2 Running 0 84m[root@k8s-master01 kiali]# istioctl proxy-config listener -n istio-system istio-ingressgateway-db8dcb984-4zc6x
ADDRESSES PORT MATCH DESTINATION
0.0.0.0 8080 ALL Route: http.8080
0.0.0.0 15021 ALL Inline Route: /healthz/ready*
0.0.0.0 15090 ALL Inline Route: /stats/prometheus*
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# istioctl proxy-config cluster istio-ingressgateway-db8dcb984-4zc6x -n istio-system |grep kiali
kiali.istio-system.svc.cluster.local 9090 - outbound EDS kiali.istio-system
kiali.istio-system.svc.cluster.local 20001 - outbound EDS kiali.istio-system
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# istioctl proxy-config endpoint istio-ingressgateway-db8dcb984-4zc6x -n istio-system |grep kiali
172.16.58.238:9090 HEALTHY OK outbound|9090||kiali.istio-system.svc.cluster.local
172.16.58.238:20001 HEALTHY OK outbound|20001||kiali.istio-system.svc.cluster.local
1.7.3 创建destinationrule
- 针对流向某个 Service(即
<font style="color:rgb(251, 71, 135);">host: kiali</font>)的通信,设定具体的流量管理(比如子集选择、负载均衡、mTLS、安全设置等)。 - 这里最主要是关闭 TLS(某些后端服务原生不支持TLS时需要,尤其kiali常这样配)。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:name: kialinamespace: istio-system
spec:host: kialitrafficPolicy:tls:mode: DISABLE
---
1.7.4 访问 kiali 服务
1.7.5 查 kiali 仪表盘
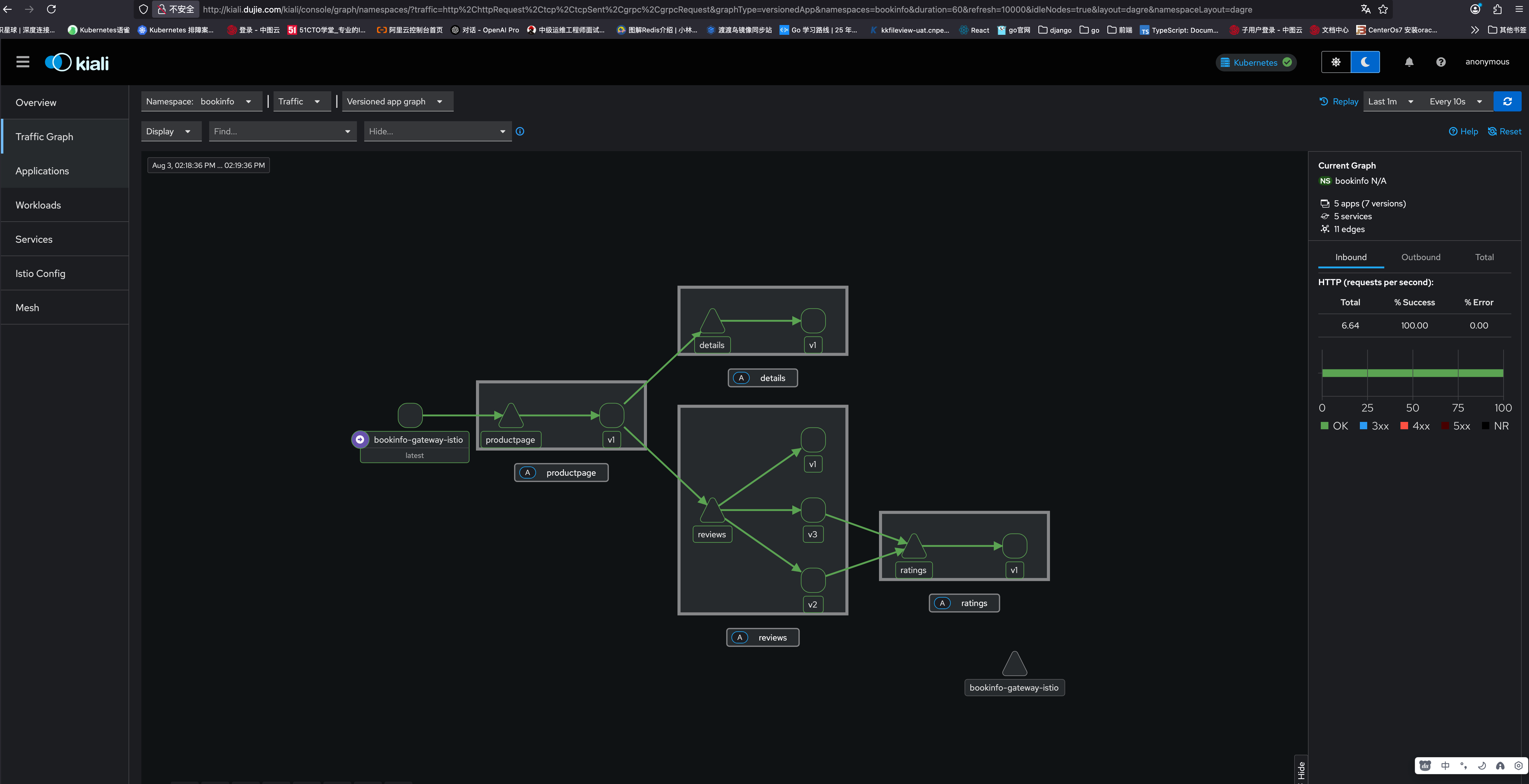
左侧导航菜单中选择图形,命名空间列表选择 booinfo
若要查看跟踪数据,必须向服务发送请求。请求数量取决于 Istio 的采样率,可以使用 Telemetry API 进行配置。默认采样率为 1%,需要发送至少 100 个请求,然后第一个跟踪才能可见。要向
<font style="color:rgb(41, 54, 85);">productpage</font>服务发送 100 个请求,请使用以下命令:
[root@k8s-master01 kiali]# for i in $(seq 1 100); do curl -s -o /dev/null "http://bookinfo.test.com/productpage"; done
Kiali 仪表板显示网格的概述以及**** **<font style="color:rgb(41, 54, 85);">Bookinfo</font>** ****示例应用程序中服务之间的关系。它还提供过滤器来可视化交通流。
1.8 暴露 Grafana 至集群外部
和上面的 kiali 一样,需要创建对应的 gateway、virtualservice、destintionRule 资源
1.8.1 创建 Gateway
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: Gateway
metadata:name: grafana-gatewaynamespace: istio-system
spec:selector:app: istio-ingressgatewayservers:- port:number: 80name: httpprotocol: HTTPhosts:- "grafana.dujie.com"
1.8.2 创建 VirtualService
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:name: grafana-virtualservicenamespace: istio-system
spec:hosts:- "grafana.dujie.com"gateways:- grafana-gatewayhttp:- match:- uri:prefix: /route:- destination:host: grafanaport:number: 3000
[root@k8s-master01 grafana]# istioctl proxy-config cluster istio-ingressgateway-db8dcb984-4zc6x -n istio-system |grep grafana
grafana.istio-system.svc.cluster.local 3000 - outbound EDS
[root@k8s-master01 grafana]# istioctl proxy-config endpoint istio-ingressgateway-db8dcb984-4zc6x -n istio-system |grep grafana
172.16.58.235:3000 HEALTHY OK outbound|3000||grafana.istio-system.svc.cluster.local
[root@k8s-master01 grafana]# istioctl proxy-config route istio-ingressgateway-db8dcb984-4zc6x -n istio-system
NAME VHOST NAME DOMAINS MATCH VIRTUAL SERVICE
http.8080 grafana.dujie.com:80 grafana.dujie.com /* grafana-virtualservice.istio-system
http.8080 kiali.dujie.com:80 kiali.dujie.com /* kiali-virtualservice.istio-systembackend * /healthz/ready* backend * /stats/prometheus*
1.8.3 创建 destintionRule
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:name: grafananamespace: istio-system
spec:host: grafanatrafficPolicy:tls:mode: DISABLE1.8.4 访问测试
二、Istio 流量治理
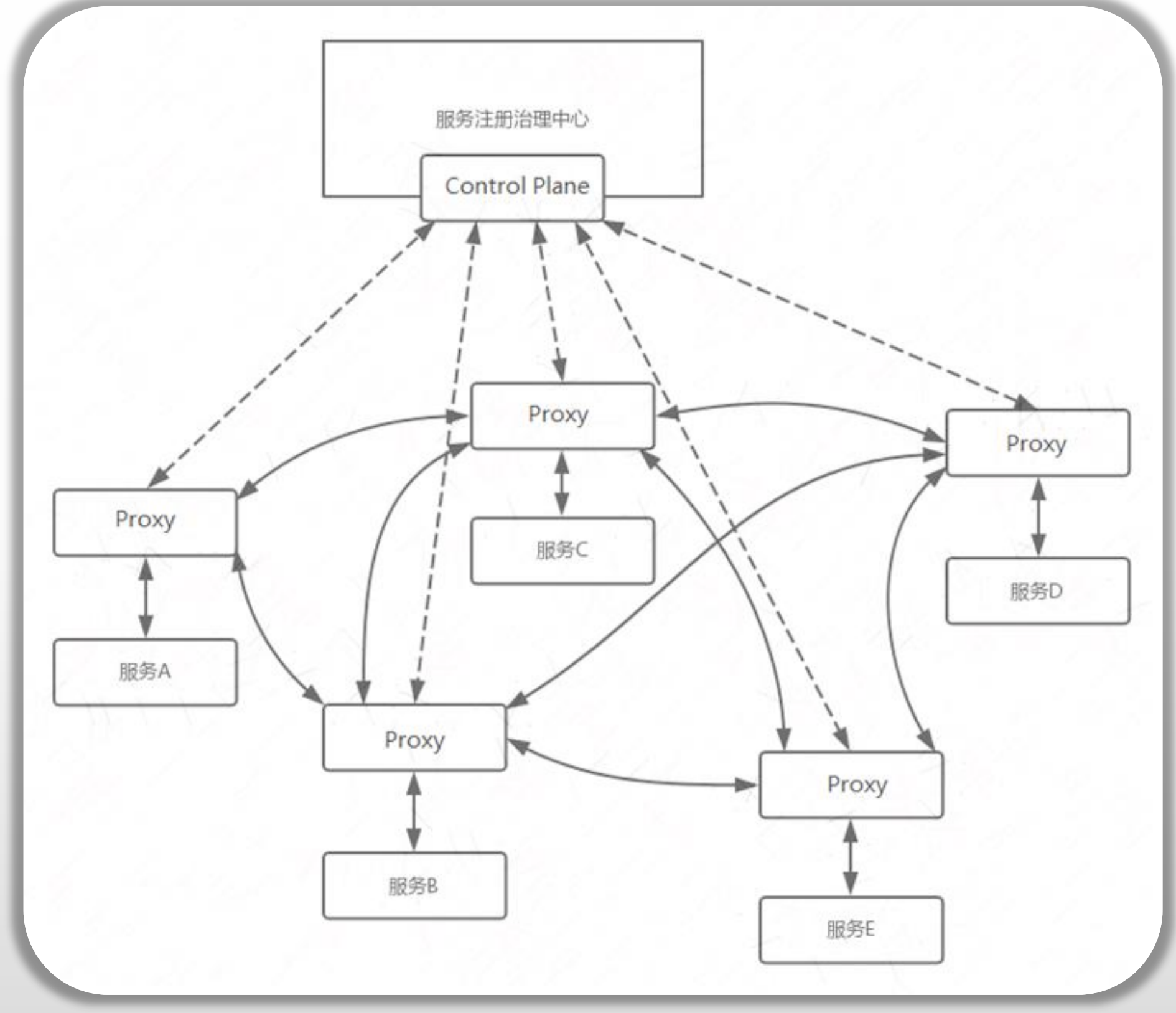
2.1 网格流量治理与服务发现
- 网格内服务发送和接收的所有流量(DataPlane流量)都要经由
**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Envoy</font>**代理进行- 绑定到服务的所有流量都会通过
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Sidecar Envoy</font>自动进行重新路由
- 绑定到服务的所有流量都会通过
- Istio借助于服务注册中心完成服务发现
- Istio自身并不进行服务发现功能,它需要借助于服务注册中心发现所有的Service及相应的各Endpoint
- Istio还假设服务的新实例会自动注册到服务注册表,并且会自动删除不健康的实例
- Kubernetes、Mesos 等平台能够为基于容器的应用程序提供服务发现功能,另外也存在大量针对基于 VM 的应用程序的解决方案
- Kubernetes系统上,Istio会将网格中的
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">每个Service的端口</font>创建为<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Listener</font>,而其匹配到的<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">endpoint</font>将组合成为一个<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Cluster</font>- 这些
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Listener</font>和<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Cluster</font>将配置在网格内的每个<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Sidecar Envoy</font>之上 - 对于某个特定Sidecar Envoy来说,仅其自身所属的 Service生成的
**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Listener</font>**为**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Inbound Listener</font>**,而所有 Service生成Listener都将配置为其上的**<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Outbound Listener </font>**<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);">Inbound Listener</font>:接收其所属Service的部分或全部流量<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);">Outbound Listener</font>:代理本地应用访问集群内的其它服务
- 进出应用的所有流量都将被
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Sidecar Envoy</font>拦截并基于重定向的方式进行处理
- 这些
- Sidecar Envoy的功能
- 在负载均衡池中的实例之间分配流量
- 对后端端点进行健康状态检测
- ……
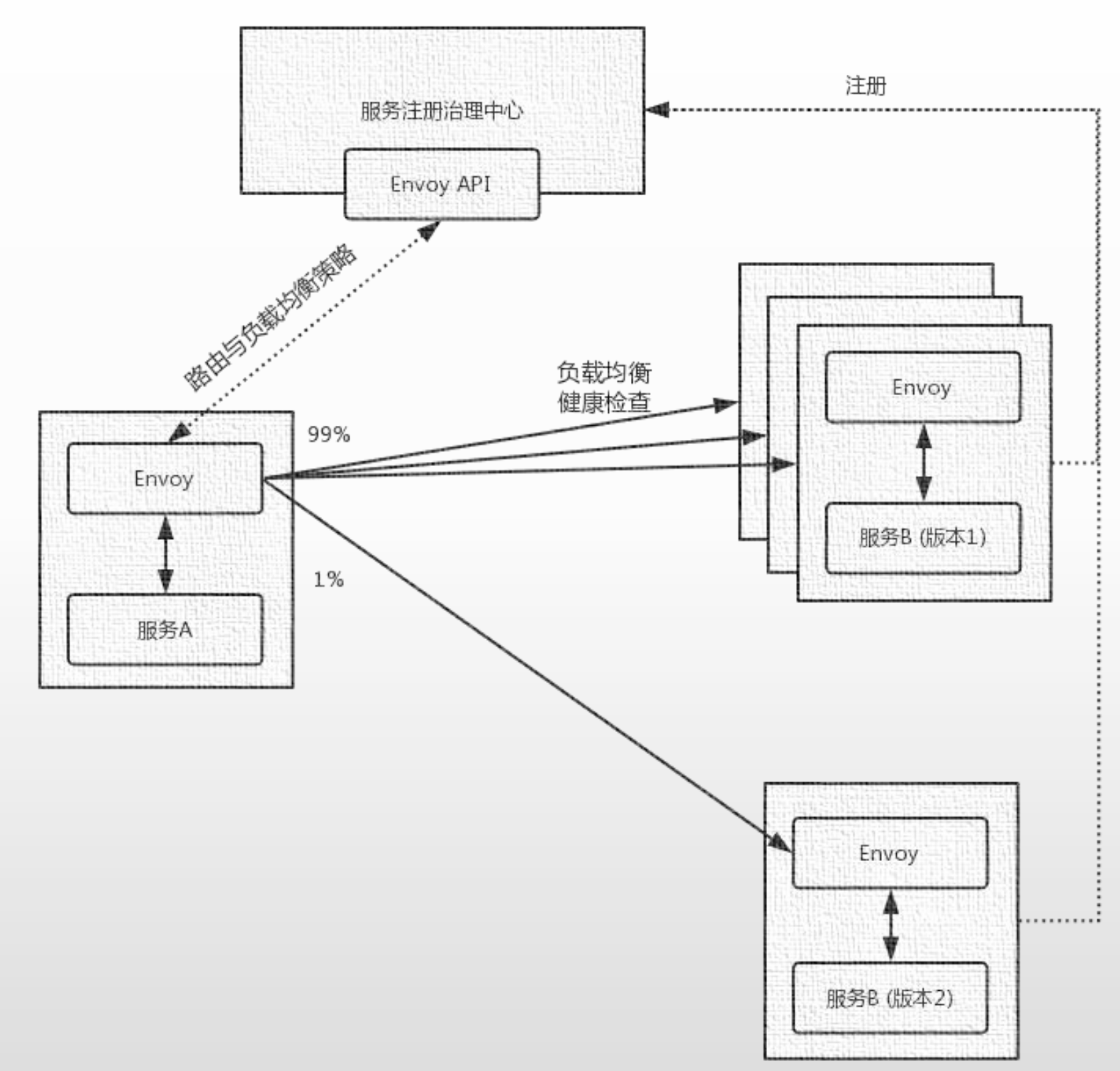
2.2 流量治理案例
这里准备两个应用:
frontend:前端应用,是后端服务 demoapp 的客户端,service: frontenddemapp:后端应用,service: demoapp
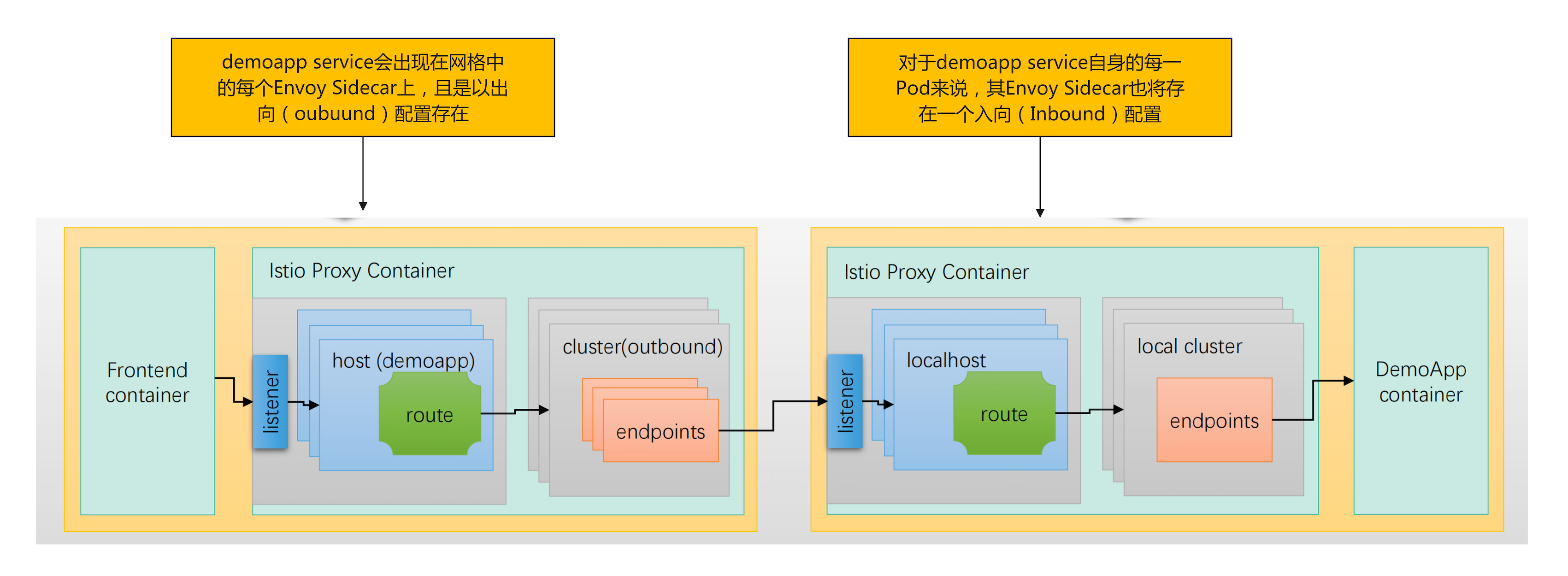
流量路径及代理发生的位置
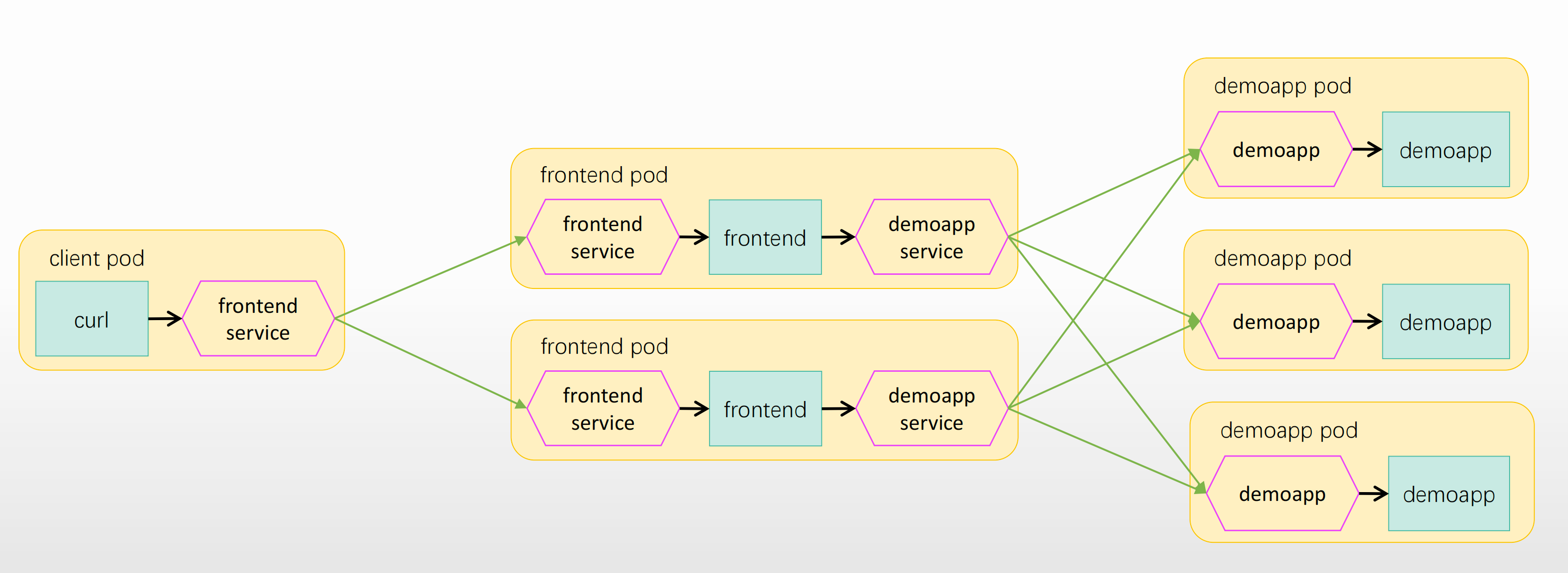
2.2.1 创建命名空间并添加自动注入 sidecar
[root@k8s-master01 ms-demo]# kubectl create ns app
namespace/app created
[root@k8s-master01 ms-demo]#
[root@k8s-master01 ms-demo]# kubectl label namespace app istio-injection=enabled
namespace/app labeled
2.2.2 客户端应用准备(curl)
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:labels:app: clientname: client
spec:replicas: 1selector:matchLabels:app: clientversion: v1.2template:metadata:labels:app: clientversion: v1.2spec:hostAliases:- hostnames: ["nginx.dujie.com", "nginx"]ip: '172.29.1.201'containers:- image: swr.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com/ddn-k8s/docker.io/ikubernetes/admin-box:v1.2name: admin-boxcommand: ['/bin/sh', '-c', 'sleep INFINITE']
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:labels:app: clientname: client
spec:ports:- name: http-80appProtocol: httpport: 80protocol: TCPtargetPort: 80selector:app: clientversion: v1.2type: ClusterIP
2.2.3 前端应用准备
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:name: frontend
spec:progressDeadlineSeconds: 600replicas: 2selector:matchLabels:app: frontendversion: v2.3template:metadata:labels:app: frontendversion: v2.3spec:containers:- env:- name: BACKEND_URLvalue: 'http://demoapp:8080'- name: PORTvalue: '80'image: ikubernetes/frontend:v2.3.1imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresentname: frontendports:- containerPort: 80name: httpprotocol: TCPresources:limits:cpu: 50m
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:name: frontend
spec:ports:- name: httpport: 80protocol: TCPtargetPort: 80selector:app: frontend
2.2.4 后端应用准备(demoapp)
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:labels:app: demoappversion: v2.1name: demoapp
spec:progressDeadlineSeconds: 600replicas: 3selector:matchLabels:app: demoappversion: v2.1template:metadata:labels:app: demoappversion: v2.1spec:containers:- image: ikubernetes/demoapp:v2.1imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresentname: demoappenv:- name: "PORT"value: "8080"- name: "VERSION"value: "v2.1"ports:- containerPort: 8080name: webprotocol: TCPresources:limits:cpu: 50m
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:name: demoapp
spec:ports:- name: httpport: 8080protocol: TCPtargetPort: 8080selector:app: demoapptype: ClusterIP
等待 Pod 启动完成
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl get pods -n app
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
client-d44cdc4b7-9dl8s 2/2 Running 0 9m39s
demoapp-68575f5545-djqsh 2/2 Running 0 2m3s
demoapp-68575f5545-q8cv2 2/2 Running 0 2m3s
demoapp-68575f5545-rdc8z 2/2 Running 0 2m3s
frontend-7c55c868cf-fhd87 2/2 Running 0 2m3s
frontend-7c55c868cf-p5rrv 2/2 Running 0 2m3s
启动就可以查看 fronted 对流量的转发方式,
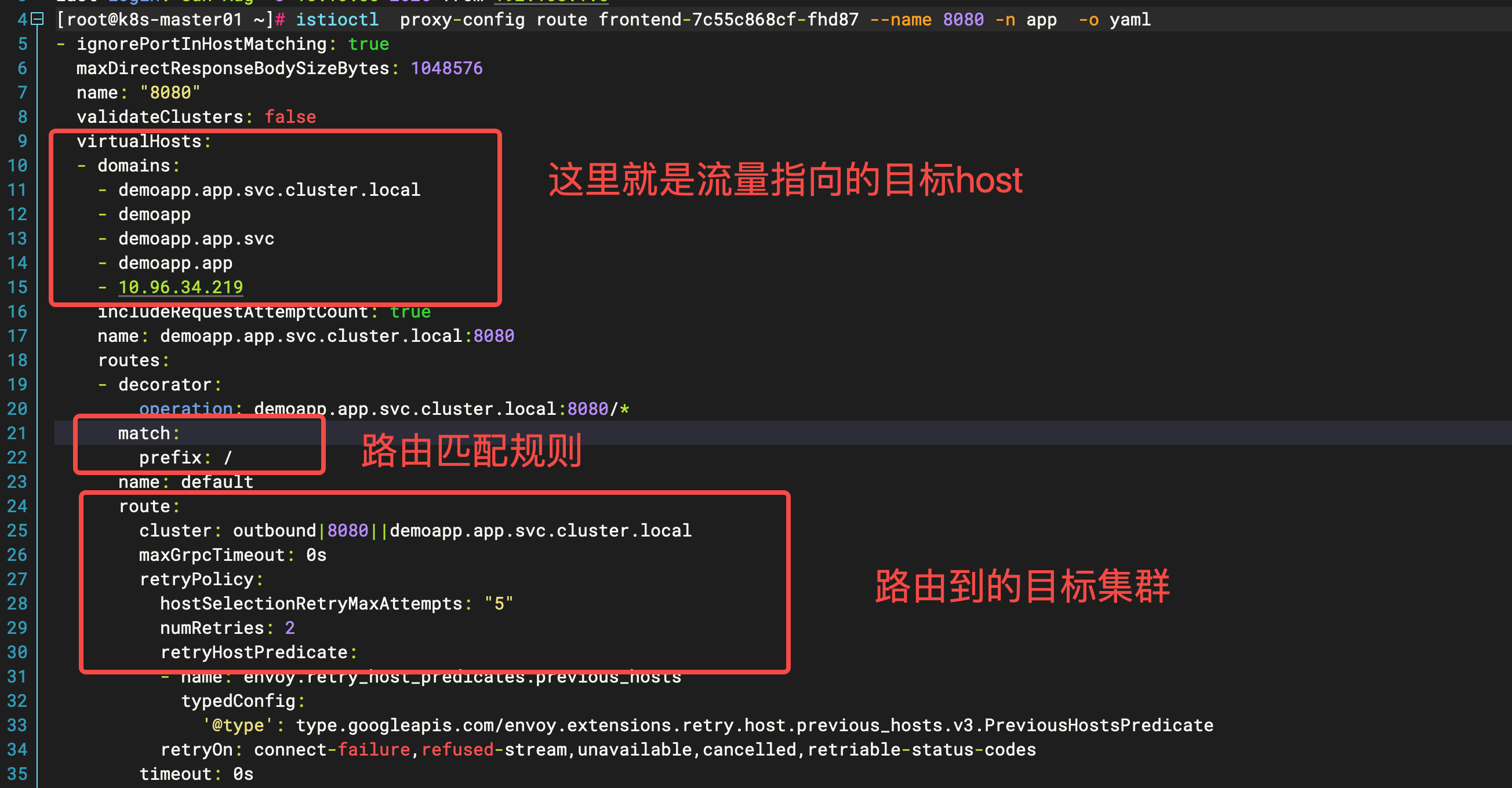
[root@k8s-master01 01-demoapp-deployment]# istioctl proxy-config route frontend-7c55c868cf-fhd87 --name 8080 -n app
NAME VHOST NAME DOMAINS MATCH VIRTUAL SERVICE
8080 demoapp.app.svc.cluster.local:8080 demoapp, demoapp.app + 1 more... /*
8080 higress-console.higress-system.svc.cluster.local:8080 higress-console.higress-system, 10.96.213.72 /*
执行下面的命令就可以看到前端应用对流量的转发方式,实际上其实就是 envoy 配置,所以要理解 istio 之前一定要学 envoy!!!
istioctl proxy-config route frontend-7c55c868cf-fhd87 --name 8080 -n app
2.2.5 测试访问网格内的服务
进入到 client pod,进行循环访问测试
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl exec -it client-d44cdc4b7-9dl8s bash -n app
root@client-d44cdc4b7-9dl8s /# while true; do curl frontend; sleep 1; done
Demoapp by iKubernetes! App Version: v2.1, Client IP: 127.0.0.6, Server Name: demoapp-68575f5545-djqsh, Server IP: 172.16.58.248 ~
Demoapp by iKubernetes! App Version: v2.1, Client IP: 127.0.0.6, Server Name: demoapp-68575f5545-djqsh, Server IP: 172.16.58.248 ~
Demoapp by iKubernetes! App Version: v2.1, Client IP: 127.0.0.6, Server Name: demoapp-68575f5545-q8cv2, Server IP: 172.16.85.195 ~然后可以到 kiali 页面查看
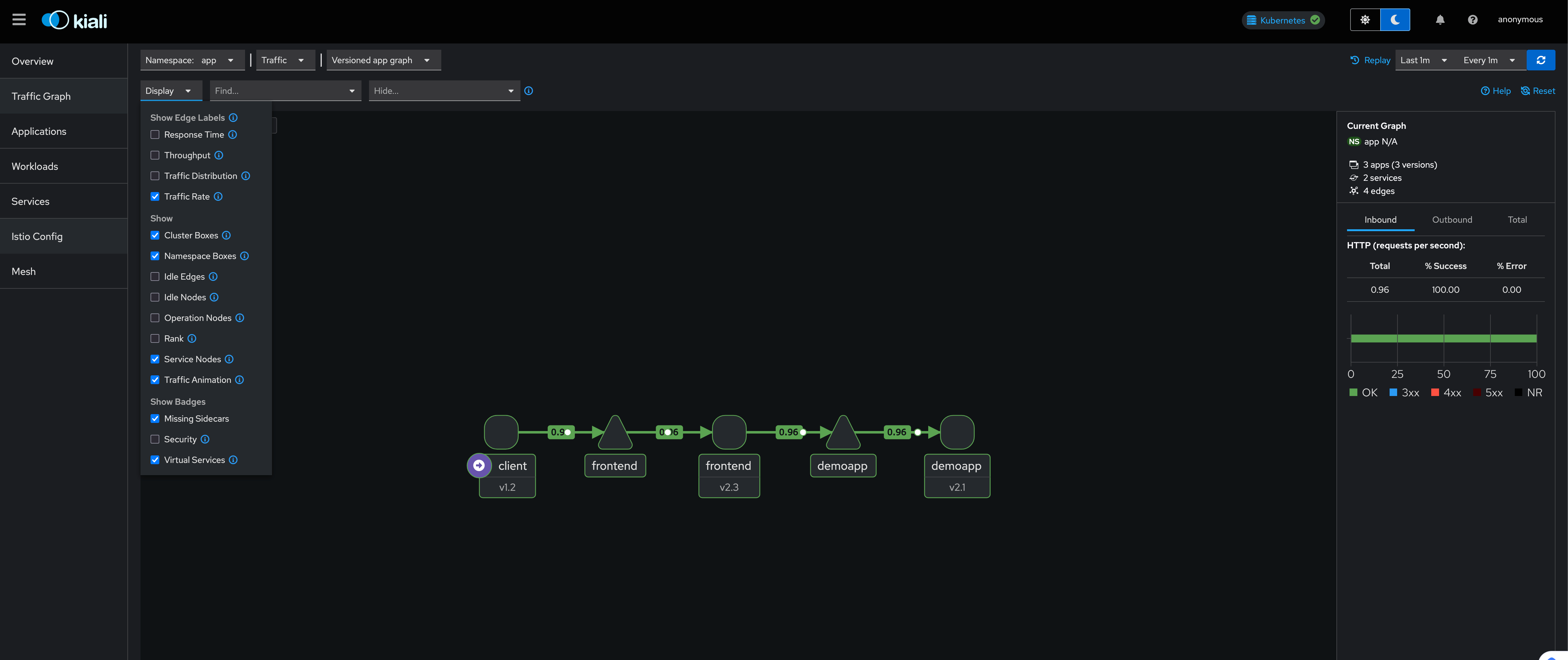
2.2.6 添加 canary 版本的后端
- demoapp:后端应用
- 两个版本:原有的v2.0外,再部署一个v2-canary版本
- 两个版本的pod属于同一个Service(frontend)
◼ 默认情况下,流量被无差别地分发给<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">frontend Service</font>的所有后端Pod
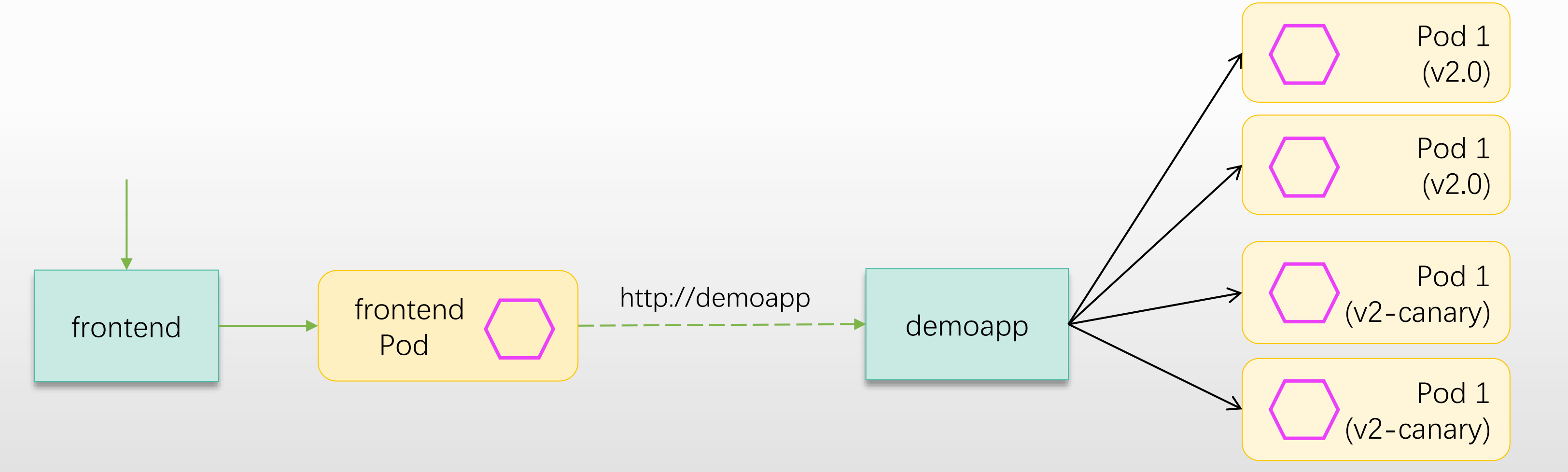
添加一个 canary 版本的后端
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:labels:app: demoappversion: v2.1-canaryname: demoapp-canary
spec:progressDeadlineSeconds: 600replicas: 3selector:matchLabels:app: demoappversion: v2.1-canarytemplate:metadata:labels:app: demoappversion: v2.1-canaryspec:containers:- image: ikubernetes/demoapp:v2.1imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresentname: demoappenv:- name: "PORT"value: "8080"- name: "VERSION"value: "v2.1-canary"ports:- containerPort: 8080name: webprotocol: TCPresources:limits:cpu: 50m
部署
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl apply -f deploy-demoapp-canary.yaml -n app
deployment.apps/demoapp-canary created
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl get pods -n app
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
client-d44cdc4b7-9dl8s 2/2 Running 0 28m
demoapp-68575f5545-djqsh 2/2 Running 0 21m
demoapp-68575f5545-q8cv2 2/2 Running 0 21m
demoapp-68575f5545-rdc8z 2/2 Running 0 21m
demoapp-canary-54954bd447-8rjzd 2/2 Running 0 37s
demoapp-canary-54954bd447-htnzs 2/2 Running 0 37s
demoapp-canary-54954bd447-l9l8h 2/2 Running 0 37s
frontend-7c55c868cf-fhd87 2/2 Running 0 21m
frontend-7c55c868cf-p5rrv 2/2 Running 0 21m
然后可以通过<font style="color:#DF2A3F;"> istioctl proxy-config endpoint </font>命令查看 frontend 出向网关都有哪些,可以看到下面基于<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">outbound|8080||demoapp.app.svc.cluster.local </font>这个集群的 endpoint 一共由 6 个,如果没有配置负载均衡策略,他们将会是随机或轮询访问
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# istioctl proxy-config endpoint frontend-7c55c868cf-fhd87 -n app --port 8080
ENDPOINT STATUS OUTLIER CHECK CLUSTER
172.16.29.4:8080 HEALTHY OK outbound|8080||demoapp.app.svc.cluster.local
172.16.29.8:8080 HEALTHY OK outbound|8080||demoapp.app.svc.cluster.local
172.16.58.231:8080 HEALTHY OK outbound|80||istio-ingressgateway.istio-system.svc.cluster.local
172.16.58.244:8080 HEALTHY OK outbound|80||istio-egressgateway.istio-system.svc.cluster.local
172.16.58.248:8080 HEALTHY OK outbound|8080||demoapp.app.svc.cluster.local
172.16.58.251:8080 HEALTHY OK outbound|8080||demoapp.app.svc.cluster.local
172.16.85.194:8080 HEALTHY OK outbound|8080||higress-console.higress-system.svc.cluster.local
172.16.85.195:8080 HEALTHY OK outbound|8080||demoapp.app.svc.cluster.local
172.16.85.197:8080 HEALTHY OK outbound|8080||demoapp.app.svc.cluster.local[root@k8s-master01 ~]# istioctl proxy-config endpoint frontend-7c55c868cf-fhd87 -n app --cluster "outbound|8080||demoapp.app.svc.cluster.local"
ENDPOINT STATUS OUTLIER CHECK CLUSTER
172.16.29.4:8080 HEALTHY OK outbound|8080||demoapp.app.svc.cluster.local
172.16.29.8:8080 HEALTHY OK outbound|8080||demoapp.app.svc.cluster.local
172.16.58.248:8080 HEALTHY OK outbound|8080||demoapp.app.svc.cluster.local
172.16.58.251:8080 HEALTHY OK outbound|8080||demoapp.app.svc.cluster.local
172.16.85.195:8080 HEALTHY OK outbound|8080||demoapp.app.svc.cluster.local
172.16.85.197:8080 HEALTHY OK outbound|8080||demoapp.app.svc.cluster.local
2.2.7 再次测试访问网格内的服务
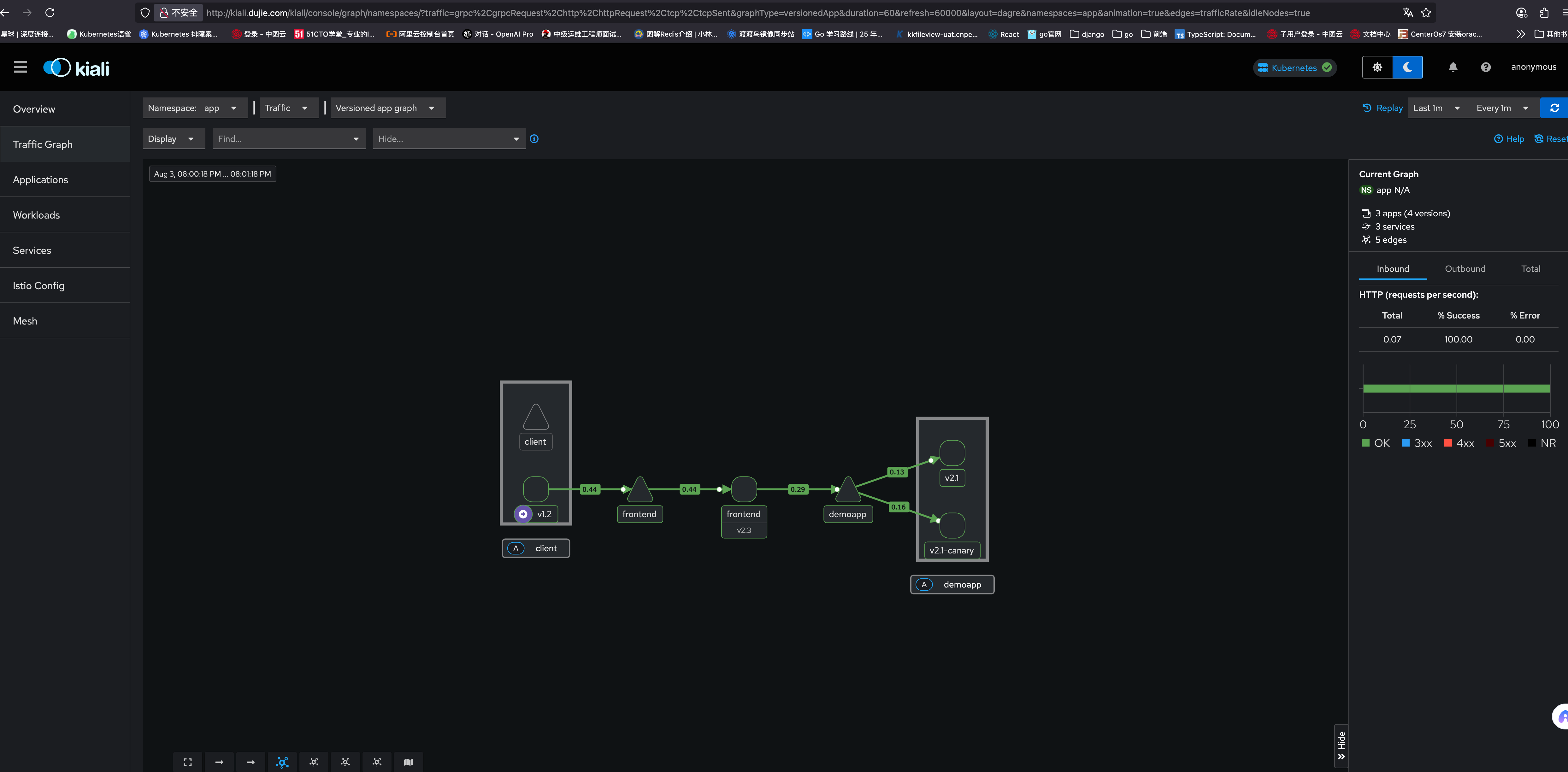
2.3 流量治理案例升级——基于多版本子集
基于上面的案例,默认情况下,流量如果进行规则配置,会被无差别的分发给 frontend Service 下所有的 pod,现在可以使用 <font style="color:#DF2A3F;">DestinationRule</font> 定义不同的子集,然后使用 <font style="color:#DF2A3F;">virtualService</font> 按照权重分配给不同的子集。
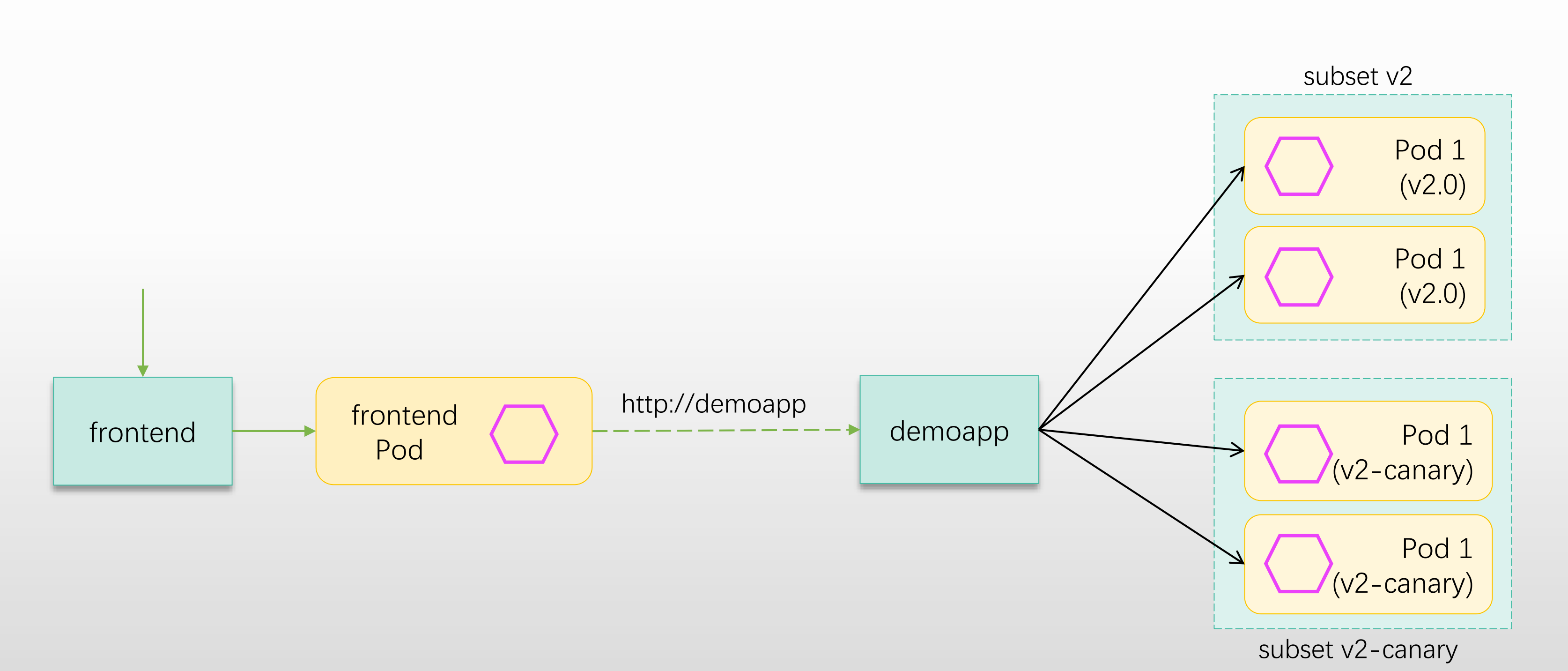
2.3.1 定义 VirtualService 资源
下面定了两两个 route 规则,按照权重比例 9:1 匹配不同的子集
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:name: demoapp
spec:hosts:- demoapphttp:- name: weight-based-routingroute:- destination:host: demoappsubset: v2weight: 90- destination:host: demoappsubset: v2-canaryweight: 10
2.3.2 定义 DestinationRule 资源
在<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);">service/demoapp</font>的基础上,将其匹配到端点根据<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">version</font>标签进一步细分
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:name: demoapp
spec:host: demoappsubsets:- name: v2labels:version: v2.1- name: v2-canarylabels:version: v2.1-canary
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl apply -f destinationrule-demoapp.yaml -n app
destinationrule.networking.istio.io/demoapp create
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl apply -f virtualservice-demoapp.yaml -n app
virtualservice.networking.istio.io/demoapp created
2.3.3 测试访问网格内的服务,查看流量分配结果
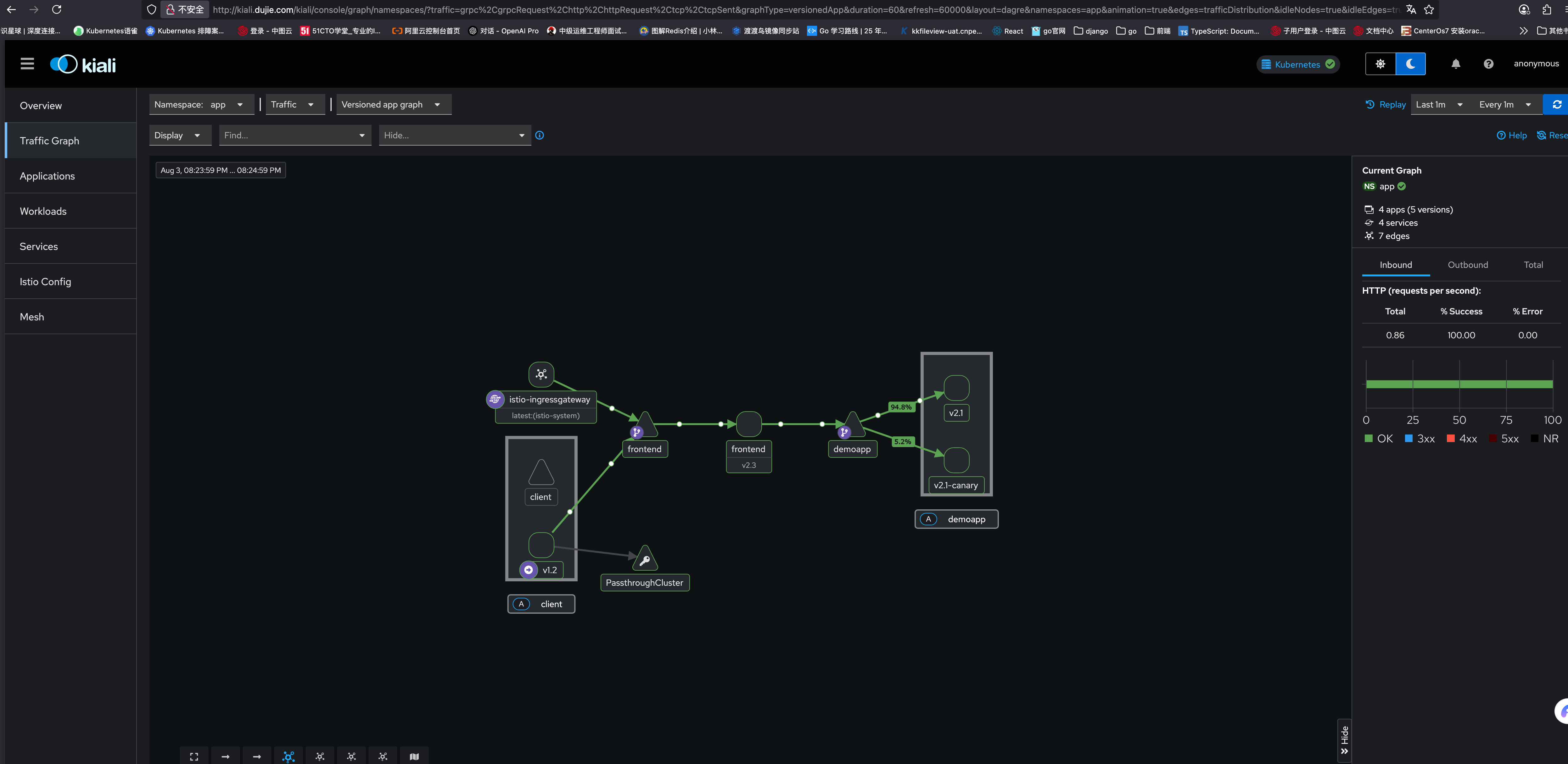
可以看到,访问请求已经是 9:1 的比例了
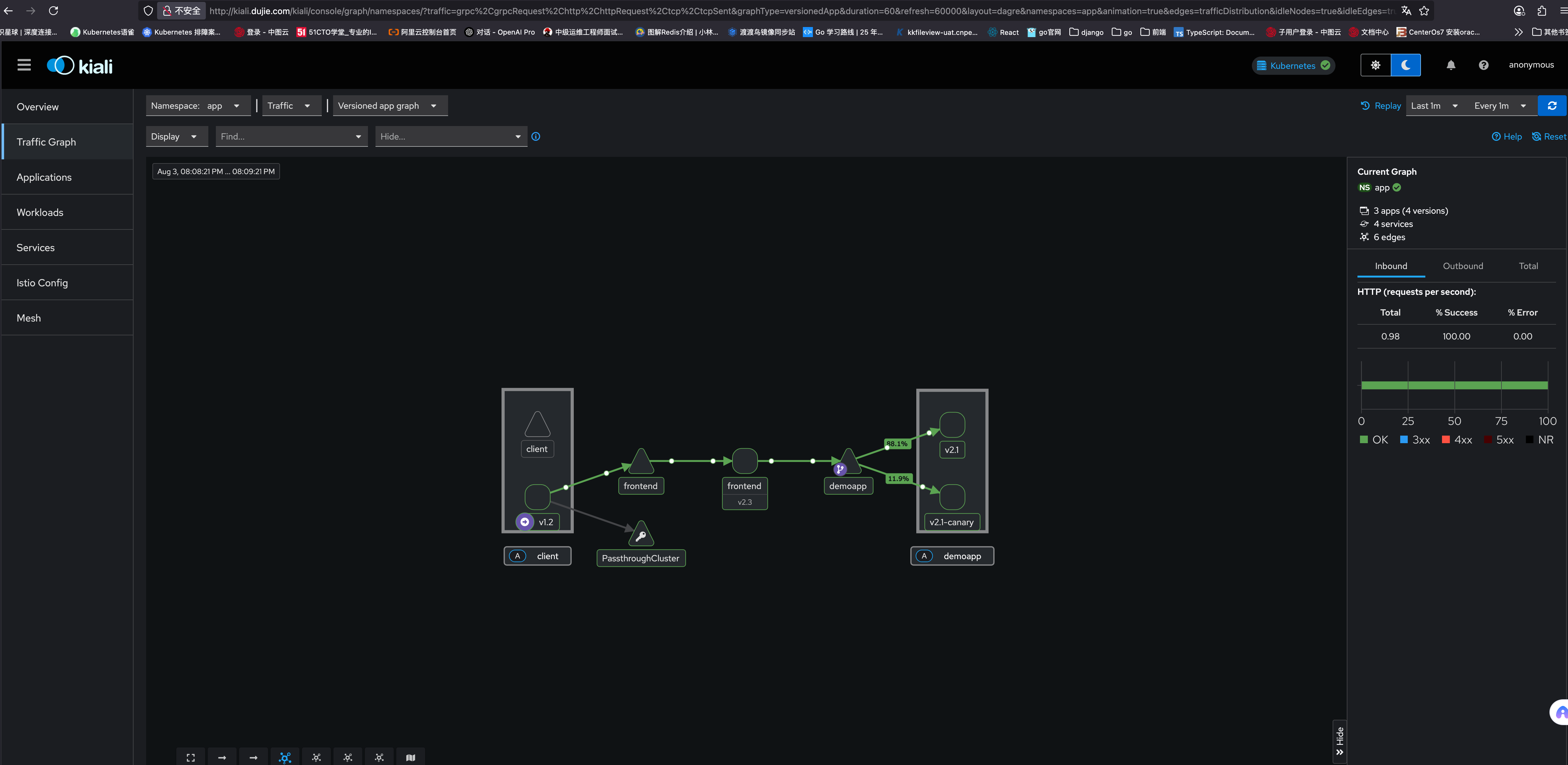
2.3.4 查看 demoapp 的路由配置
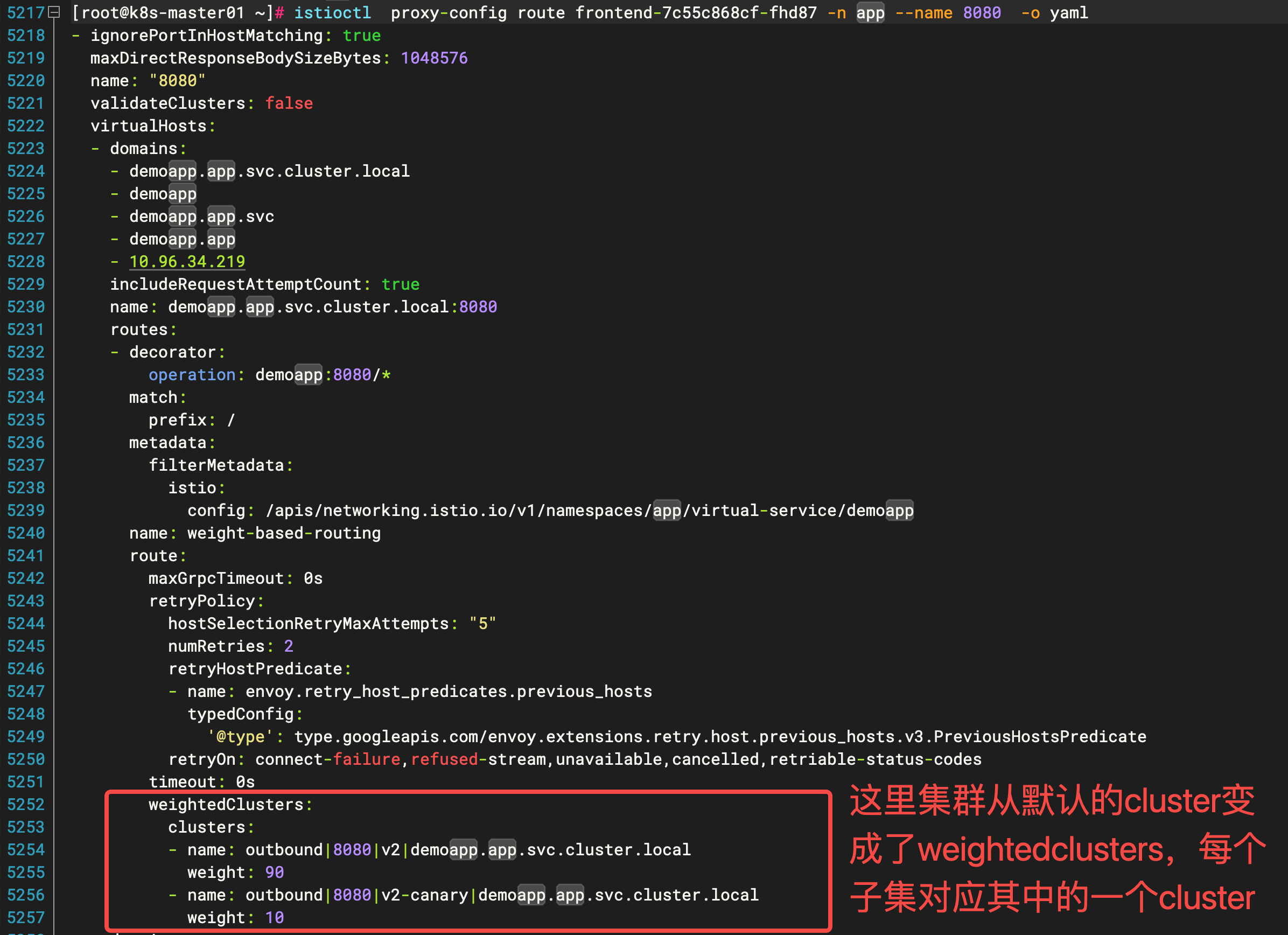
现在还可以查看 demoapp 的路由配置来验证路由是否已经变动
istioctl proxy-config route frontend-7c55c868cf-fhd87 -n app --name 8080 -o yaml
2.4 使用 Gateway 暴露 proxy 服务
上面的案例都是基于服务网格内的 client 服务来访问 frontend,而实际使用中, 一般客户端都是在集群外部访问,所以可以通过使用 <font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Gateway</font>、<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">VirtualService</font> 和 <font style="color:#DF2A3F;">DestinationRule</font> 配置 frontend,将他开放到集群外部
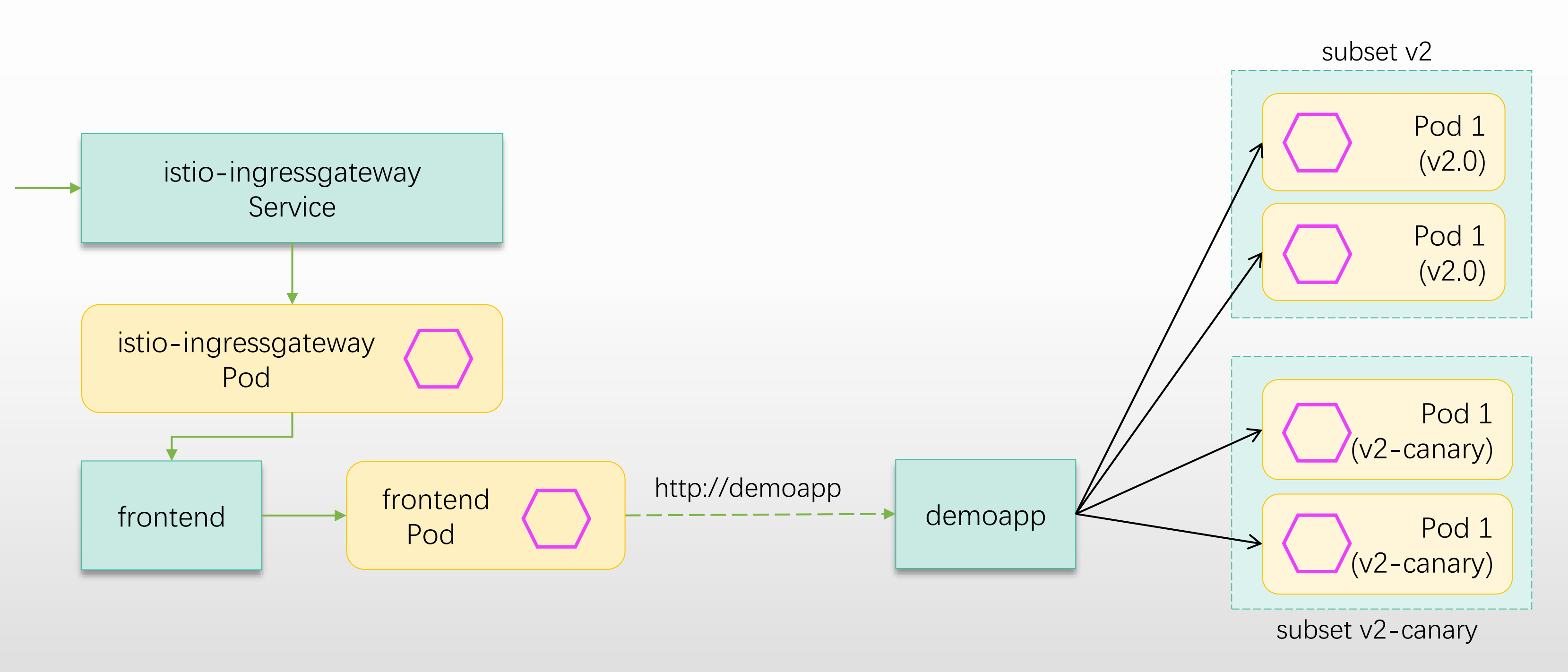
流量路径及代理发生的位置:
2.4.1 开放 frontend 给 k8s 集群外部的客户端访问
创建Gateway资源,配置在<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">IngressGateway Pod</font>上为<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">frontend</font>引入集群外部的流量
- 接入的流量需要由
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">frontend</font>专用的<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">VirtualService</font>指明他在网格内的路由目标- 那些由
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">IngressGateway</font>接入的访问<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">frontend</font>的流量,要由<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">VirtualService</font>指定路由目标 - 相应的路由目标的后端端点,同样可由
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">DestinationRule</font>进行配置,也要使用网格发现<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">frontend service</font>生成的默认配置
- 那些由
- 集群外部的流量应该从
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">istio-system</font>名称空间中的<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">services/istio-ingressgateway</font>的入口进行访问- 该Service通常应该是
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">LoadBalancer</font>类型的<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">Service</font>
- 该Service通常应该是
2.4.2 创建 gateway
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:name: frontend-gateway
spec:selector:istio: ingressgateway # 选择哪个ingress gateway pod来监听(istio系统自带的ingressgateway)servers:- port:number: 80name: httpprotocol: HTTPhosts:- "frontend.dujie.com"- "fe.dujie.com"
2.4.3 创建 virtualService
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:name: frontend
spec:hosts:- "fe.dujie.com"- "frontend.dujie.com"gateways:- frontend-gateway # 自定义 Gateway,主要是为“集群外部流量(进来的请求)”提供入口- mesh # 这是 Istio 的内置关键字,代表 Service Mesh 内部的所有Pod间的相互调用(不通过入口网关的内部流量)。http:- name: defaultmatch:- uri: prefix: /route:- destination:host: frontendport:number: 80
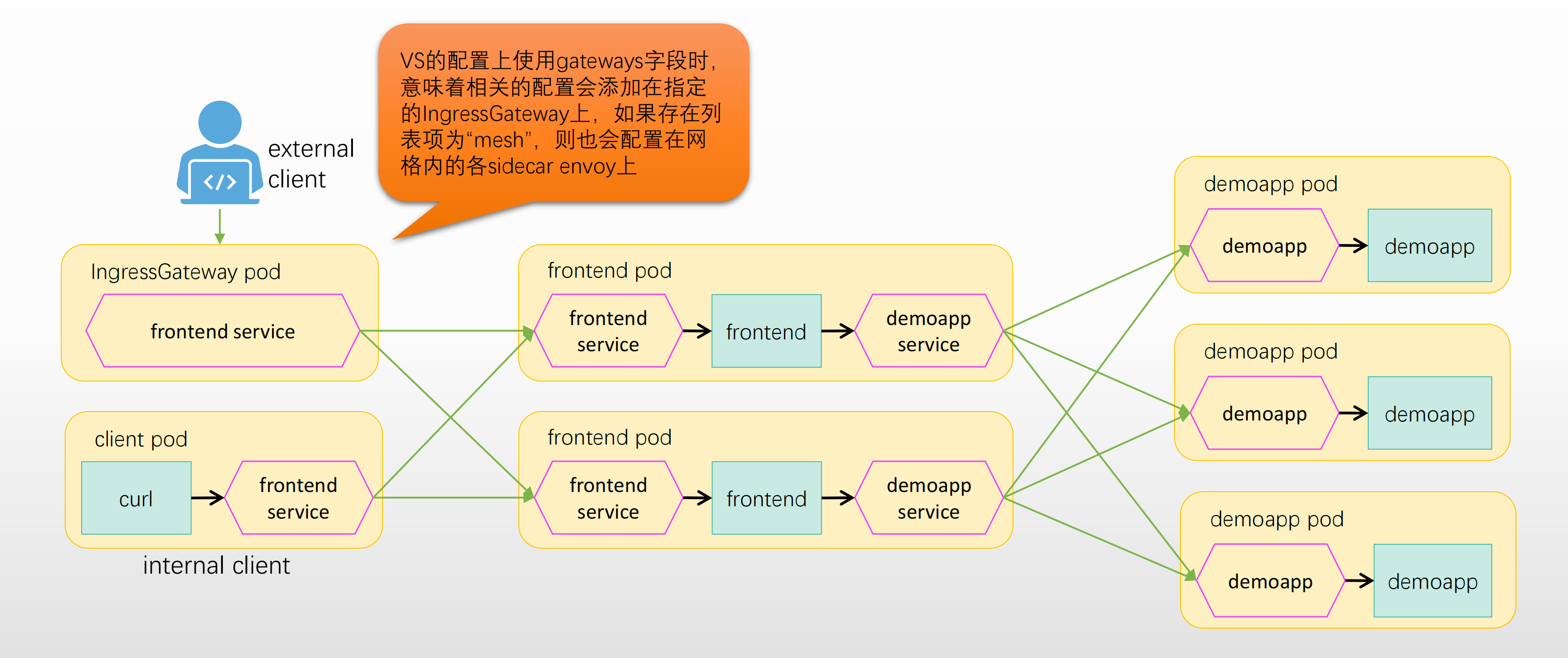
这里在 gateways 中配置了两个:
<font style="color:rgb(251, 71, 135);">frontend-gateway</font>: 自定义 Gateway,主要是为“集群外部流量(进来的请求)”提供入口。<font style="color:rgb(251, 71, 135);">mesh</font>: 这是 Istio 的内置关键字,代表 Service Mesh 内部的所有Pod间的相互调用(不通过入口网关的内部流量)。- 如果只写 frontend-gateway:
- 这条 VirtualService 只对通过
<font style="color:rgb(251, 71, 135);">frontend-gateway</font>进入的外部流量生效。 - 集群内部 Pod 直接访问
<font style="color:rgb(251, 71, 135);">frontend</font>服务的流量不会受它影响。
- 这条 VirtualService 只对通过
- 如果只写 mesh:
- 只影响 mesh 内部调用
- 外部流量不通过入口 gateway 也访问不到
- 都写上:
- 无论外部流量(进来经过 gateway)还是 mesh 内部流量(服务间直接调用),都按照这套规则路由!
- 这样一份
<font style="color:#DF2A3F;">VirtualService</font>能统一管理服务的所有入口流量,无论是 mesh 内外。
2.4.4 创建 destintionRule
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:name: frontend
spec:host: frontendtrafficPolicy:tls:mode: DISABLE
2.4.5 从集群外部测试访问网格内的服务
在集群外部,于交互式接口中重新发起持续访问请求,以生成新的请求流量,例如
while true; do curl frontend.dujie.com; sleep 0.$RANDOM; done
此时再次查看 kiali,可以看到集群内外都有访问的请求,并且流量比例还是上面设置的 9:1