2、RabbitMQ的5种模式基本使用(Maven项目)
本文案例中的代码没有对队列和消息设置为持久化,在实际开发中应该把队列和消息设置为持久化
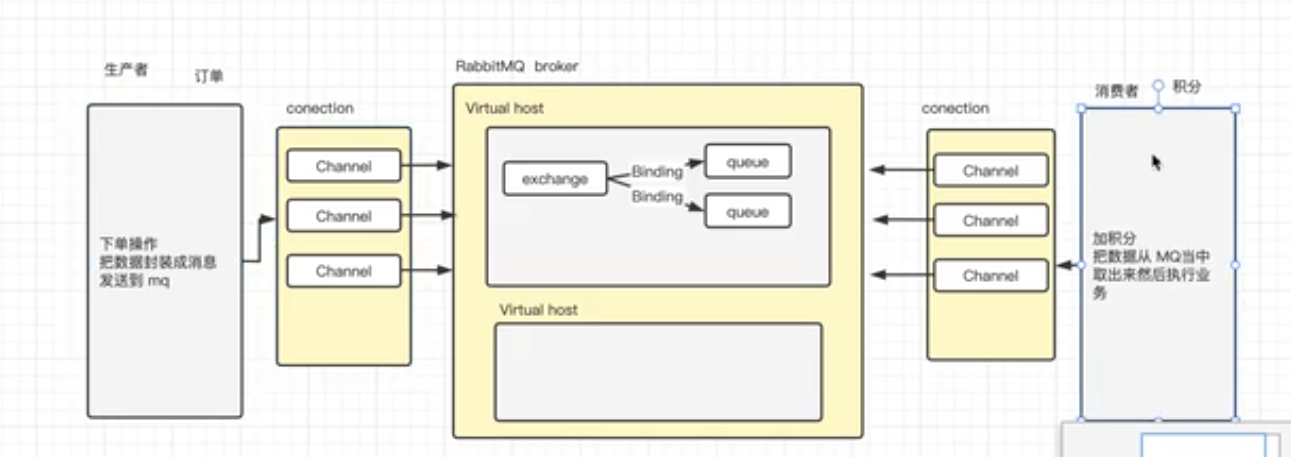
作为一名开发者,主要关心的就是生产者如何发送消息,消费者如何消费消息。
1、创建普通maven项目
1.1 创建项目
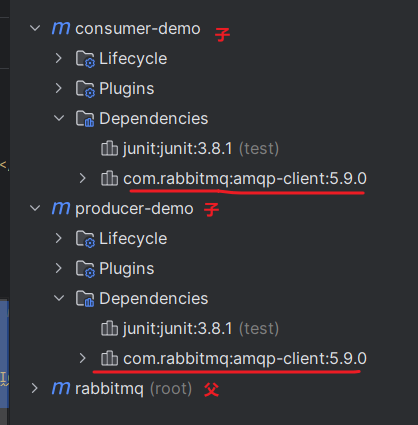
1.2 父pom导入依赖
<!-- rabbitmq --><dependency><groupId>com.rabbitmq</groupId><artifactId>amqp-client</artifactId><version>5.9.0</version></dependency><!-- 不导入这个依赖,控制台会报错 --><!-- slf4j --><dependency><groupId>org.slf4j</groupId><artifactId>slf4j-nop</artifactId><version>1.7.2</version></dependency>1.3 maven查看
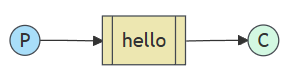
2、简单模式
简单模式实现Hello World
2.1 生产者
先编写生产者,想发送消息:
- 创建连接工厂对象(connectFactory)
- 设置rabbitmq的Ip地址
- 用连接工厂创建连接对象Connection
- 用连接对象创建channel
- 设置channel属性,例如队列名字,是否持久化等等
- channel调用basicPublish方法发送消息
- 关闭消息
2.1.1 代码实现
/*** 生产者,生产消息 Hello World*/
@Slf4j
public class Producer {/*** main方法* @param args* @throws IOException* @throws TimeoutException*/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {// 1.创建连接工厂对象(connectFactory)ConnectionFactory connectFactory = new ConnectionFactory();// 2.设置rabbitmq的Ip地址connectFactory.setHost(HOST);connectFactory.setPort(PORT);connectFactory.setUsername(USER_NAME);connectFactory.setPassword(PASS_WORD);connectFactory.setVirtualHost(VIRTUAL_HOST);// 3.用连接工厂创建连接对象ConnectionConnection connection = connectFactory.newConnection();// 4.用连接对象创建channelChannel channel = connection.createChannel();// 5.设置channel属性,例如队列名字,是否持久化等等/*** 第一个参数:队列名字* 第二个参数:是否持久化* 第三个参数:是否排他性(设置true独占队列)* 第四个参数:是否自动删除(设置true就删除)* 第五个参数:是否设置其他额外参数*/channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);// 6.channel调用basicPublish方法发送消息/*** 第一个参数:交换机名字* 第二个参数:路由key* 第三个参数:消息属性* 第四个参数:消息内容*/channel.basicPublish("", QUEUE_NAME, null, "Hello RabbitMQ".getBytes());// 7.关闭消息channel.close();connection.close();}}2.1.2 实现效果
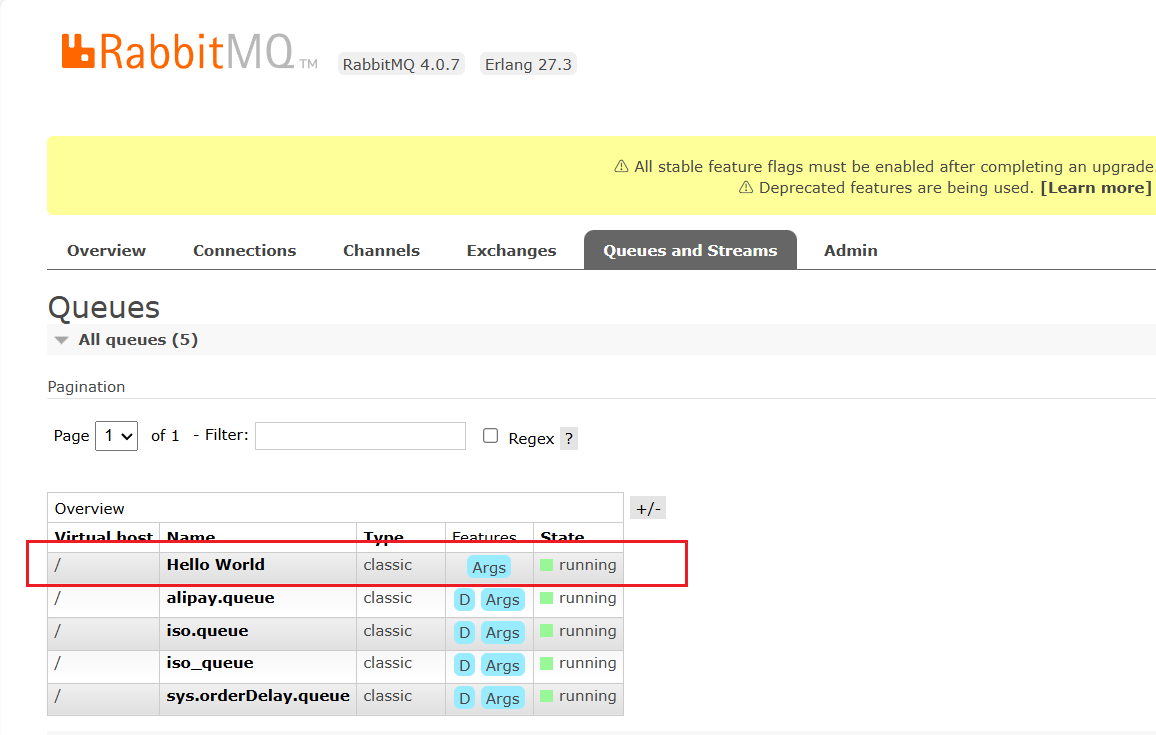
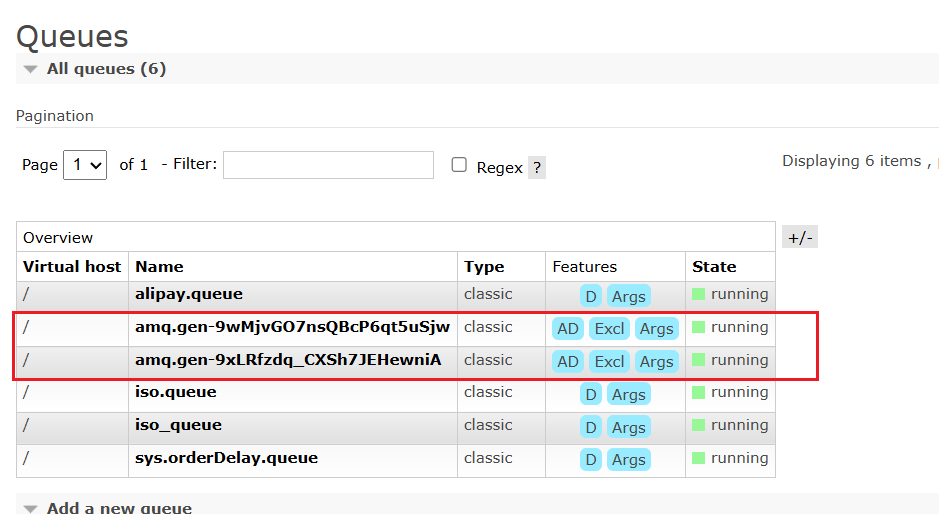
运行生产者后,看mq界面的queue
2.2 消费者
在编写消费者,签收消费消息:
- 创建连接工厂对象(connectFactory)
- 设置rabbitmq的Ip地址
- 用连接工厂创建连接对象Connection
- 用连接对象创建channel
- 设置channel属性,例如队列名字,是否持久化等等
- channel调用basicPublish方法发送消息
- 关闭消息
2.2.1 代码实现
/*** 消费者,接收消息 Hello World*/
public class Consumer {/*** main方法* @param args* @throws IOException* @throws TimeoutException*/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {// 1.创建连接工厂对象(connectFactory)ConnectionFactory connectFactory = new ConnectionFactory();// 2.设置rabbitmq的Ip地址connectFactory.setHost(HOST);connectFactory.setPort(PORT);connectFactory.setUsername(USER_NAME);connectFactory.setPassword(PASS_WORD);connectFactory.setVirtualHost(VIRTUAL_HOST);// 3.用连接工厂创建连接对象ConnectionConnection connection = connectFactory.newConnection();// 4.用连接对象创建channelChannel channel = connection.createChannel();// 5.设置channel属性,例如队列名字,是否持久化等等/*** 第一个参数:队列名字* 第二个参数:是否持久化* 第三个参数:是否排他性(设置true独占队列)* 第四个参数:是否自动删除(设置true就删除)* 第五个参数:是否设置其他额外参数*/channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);// 6.使用channel去rabbitmq中取消息进行消费/*** 第一个参数:队列名字* 第二个参数:是否自动确认(签收)*/channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, true, new DeliverCallback() {/*** 当消息从mq中取出来会回调这个函数* 消费者消费消息在handle处理* @param consumerTag the <i>consumer tag</i> associated with the consumer* @param message the delivered message* @throws IOException*/public void handle(String consumerTag, Delivery message) throws IOException {System.out.println("消费者接收到的消息是:" + new String(message.getBody()));}}, new CancelCallback() {/*** 消费者取消消费的回调这个方法* @param consumerTag the <i>consumer tag</i> associated with the consumer*/public void handle(String consumerTag) {System.out.println("消费者取消消费的回调这个方法");}});}}2.2.2 实现效果
执行消费者
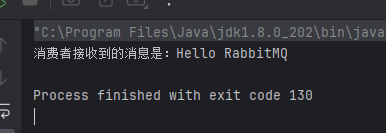
2.3 生产者中用到的属性
属性的设置,生产者和消费者要保持一致
2.3.1 持久化
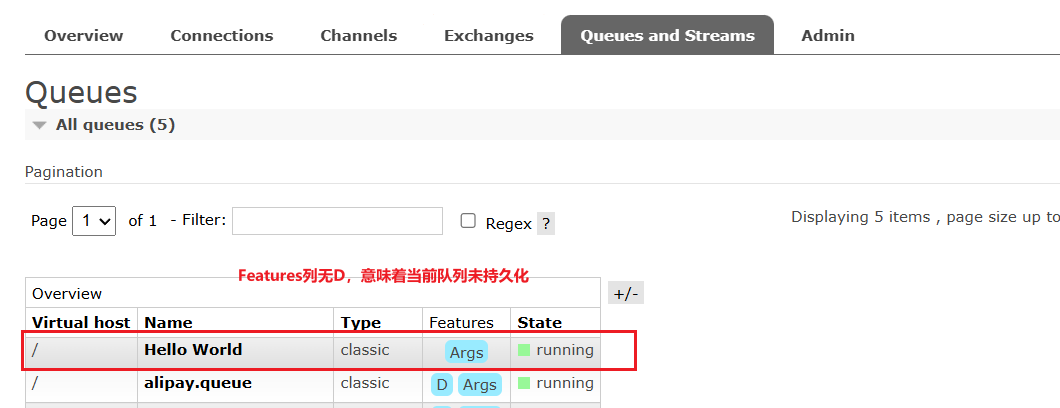
Queues界面对应的消息Features列无D,意味着当前队列未持久化。
没有持久化,关掉消费者并且重新启动mq,消息队列会消失不见
// Producer类和Consumer类保持一致
/*** 第一个参数:队列名字* 第二个参数:是否持久化,设置为true,即持久化* 第三个参数:是否排他性(设置true独占队列)* 第四个参数:是否自动删除(设置true就删除)* 第五个参数:是否设置其他额外参数*/channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, true, false, false, null);2.3.2 排他性
设置为true,只能在一个连接对象,才能操作队列。生产者会创建一个连接对象,消费者也会创建一个连接对象,两个对象同时操作队列,会产生问题。开发中很少会创建于一个连接对象,一般是false
如果设置为true,只能在一个类中同时写生产者和消费者代码// Producer类和Consumer类保持一致
/*** 第一个参数:队列名字* 第二个参数:是否持久化,设置为true,即持久化* 第三个参数:是否排他性(设置true独占队列)* 第四个参数:是否自动删除(设置true就删除)* 第五个参数:是否设置其他额外参数*/channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, true, true, false, null);2.3.3 自动删除
设置为true,如果没有消费者连接这个队列(断开消费者连接),就自动删除掉
// Producer类和Consumer类保持一致
/*** 第一个参数:队列名字* 第二个参数:是否持久化,设置为true,即持久化* 第三个参数:是否排他性(设置true独占队列)* 第四个参数:是否自动删除(设置true就删除)* 第五个参数:是否设置其他额外参数*/channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, true, false, true, null);2.3.4 消息持久化
队列持久化和消息持久化不是一个东西。
- 队列持久化,保证队列重启是存在的,
- 消息持久化是队列重启,消息不一定存在
/*** 第一个参数:交换机名字* 第二个参数:路由key* 第三个参数:消息属性* 第四个参数:消息内容*/
// 设置消息持久化:MessageProperties.PERSISTENT_TEXT_PLAIN 是程序提供,不是人为编辑
channel.basicPublish("", QUEUE_NAME, MessageProperties.PERSISTENT_TEXT_PLAIN, "Hello RabbitMQ".getBytes());2.3.5 消息内容
rabbitmq发送的消息内容是字符串,但并不是简简单单的字符串,可以把对象、集合等等转成字符串
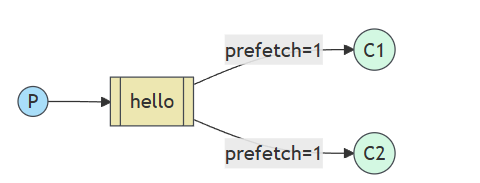
3、Work模式(工作模式)
解决简单模式所产生的问题:生产者生产的消息,消费者来不及处理,导致消息中间件累积消息,为了避免消息中间件累计消息,多添加消费者进行消息接收。
3.1 生产者
3.1.1 代码实现
/*** 生产者,生产消息 Hello RabbitMQ*/
public class Producer {/*** main方法* @param args* @throws IOException* @throws TimeoutException*/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {// 1.创建连接工厂对象(connectFactory)ConnectionFactory connectFactory = new ConnectionFactory();// 2.设置rabbitmq的Ip地址connectFactory.setHost(HOST);connectFactory.setPort(PORT);connectFactory.setUsername(USER_NAME);connectFactory.setPassword(PASS_WORD);connectFactory.setVirtualHost(VIRTUAL_HOST);// 3.用连接工厂创建连接对象ConnectionConnection connection = connectFactory.newConnection();// 4.用连接对象创建channelChannel channel = connection.createChannel();// 5.设置channel属性,例如队列名字,是否持久化等等/*** 第一个参数:队列名字* 第二个参数:是否持久化* 第三个参数:是否排他性(设置true独占队列)* 第四个参数:是否自动删除(设置true就删除)* 第五个参数:是否设置其他额外参数*/channel.queueDeclare(WORK_QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);// 6.channel调用basicPublish方法发送消息/*** 第一个参数:交换机名字* 第二个参数:路由key* 第三个参数:消息属性* 第四个参数:消息内容*/for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {String mesage = "Hello RabbitMQ" + i;channel.basicPublish("", WORK_QUEUE_NAME, null, mesage.getBytes());}// 7.关闭消息channel.close();connection.close();}}3.1.2 实现效果
3.2 消费者
work模式,有两个消费者
3.2.1 代码实现
/*** 消费者01,接收消息 Hello RabbitMQ*/
public class ConsumerOne {/*** main方法* @param args* @throws IOException* @throws TimeoutException*/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {// 1.创建连接工厂对象(connectFactory)ConnectionFactory connectFactory = new ConnectionFactory();// 2.设置rabbitmq的Ip地址connectFactory.setHost(HOST);connectFactory.setPort(PORT);connectFactory.setUsername(USER_NAME);connectFactory.setPassword(PASS_WORD);connectFactory.setVirtualHost(VIRTUAL_HOST);// 3.用连接工厂创建连接对象ConnectionConnection connection = connectFactory.newConnection();// 4.用连接对象创建channelChannel channel = connection.createChannel();// 5.设置channel属性,例如队列名字,是否持久化等等/*** 第一个参数:队列名字* 第二个参数:是否持久化* 第三个参数:是否排他性(设置true独占队列)* 第四个参数:是否自动删除(设置true就删除)* 第五个参数:是否设置其他额外参数*/channel.queueDeclare(WORK_QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);// 6.使用channel去rabbitmq中取消息进行消费/*** 第一个参数:队列名字* 第二个参数:是否自动确认(签收)*/channel.basicConsume(WORK_QUEUE_NAME, true, new DeliverCallback() {/*** 当消息从mq中取出来会回调这个函数* 消费者消费消息在handle处理* @param consumerTag the <i>consumer tag</i> associated with the consumer* @param message the delivered message* @throws IOException*/public void handle(String consumerTag, Delivery message) throws IOException {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}System.out.println("消费者01接收到的消息是:" + new String(message.getBody()));}}, new CancelCallback() {/*** 消费者取消消费的回调这个方法* @param consumerTag the <i>consumer tag</i> associated with the consumer*/public void handle(String consumerTag) {System.out.println("消费者01取消消费的回调这个方法");}});}}
/*** 消费者02,接收消息 Hello RabbitMQ*/
public class ConsumerTwo {/*** main方法* @param args* @throws IOException* @throws TimeoutException*/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {// 1.创建连接工厂对象(connectFactory)ConnectionFactory connectFactory = new ConnectionFactory();// 2.设置rabbitmq的Ip地址connectFactory.setHost(HOST);connectFactory.setPort(PORT);connectFactory.setUsername(USER_NAME);connectFactory.setPassword(PASS_WORD);connectFactory.setVirtualHost(VIRTUAL_HOST);// 3.用连接工厂创建连接对象ConnectionConnection connection = connectFactory.newConnection();// 4.用连接对象创建channelChannel channel = connection.createChannel();// 5.设置channel属性,例如队列名字,是否持久化等等/*** 第一个参数:队列名字* 第二个参数:是否持久化* 第三个参数:是否排他性(设置true独占队列)* 第四个参数:是否自动删除(设置true就删除)* 第五个参数:是否设置其他额外参数*/channel.queueDeclare(WORK_QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);// 6.使用channel去rabbitmq中取消息进行消费/*** 第一个参数:队列名字* 第二个参数:是否自动确认(签收)*/channel.basicConsume(WORK_QUEUE_NAME, true, new DeliverCallback() {/*** 当消息从mq中取出来会回调这个函数* 消费者消费消息在handle处理* @param consumerTag the <i>consumer tag</i> associated with the consumer* @param message the delivered message* @throws IOException*/public void handle(String consumerTag, Delivery message) throws IOException {try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}System.out.println("消费者02接收到的消息是:" + new String(message.getBody()));}}, new CancelCallback() {/*** 消费者取消消费的回调这个方法* @param consumerTag the <i>consumer tag</i> associated with the consumer*/public void handle(String consumerTag) {System.out.println("消费者02取消消费的回调这个方法");}});}}3.2.2 实现效果
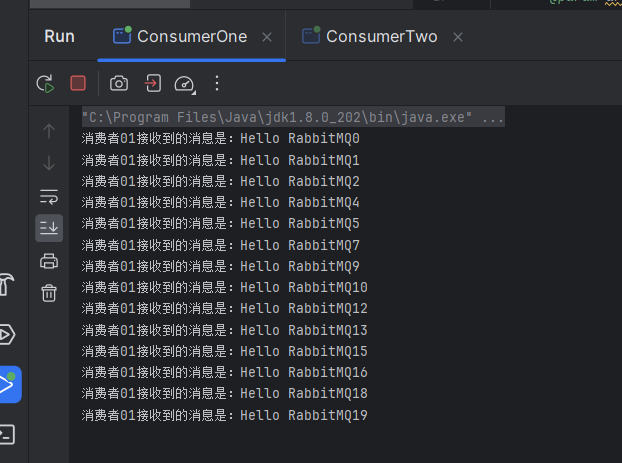
消费1,执行的速度快
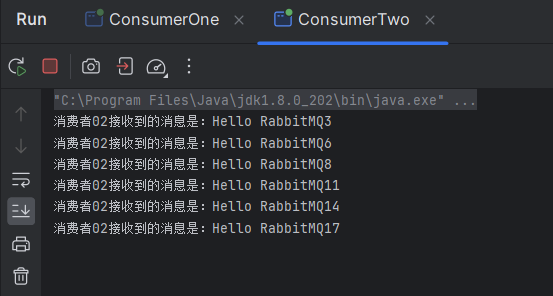
消费2,执行的速度慢
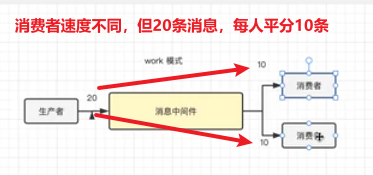
两个消费者,虽然消费的速度不同,但是处理消息数量进行平分
3.2.3 优化Work模式问题
优化:
- 设置为预期
- 签收改为手动签收
/*** 消费者01,接收消息 Hello RabbitMQ*/
public class ConsumerOne {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {........// 4.用连接对象创建channelfinal Channel channel = connection.createChannel();// 5.设置channel属性,例如队列名字,是否持久化等等channel.queueDeclare(WORK_QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);// 预取,告诉rabbitmq,在从mq中取消息的时候,一次取多少条// 设置为1,一次只能拿1条数据channel.basicQos(1);// 6.使用channel去rabbitmq中取消息进行消费channel.basicConsume(WORK_QUEUE_NAME, false, new DeliverCallback() {public void handle(String consumerTag, Delivery message) throws IOException {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}System.out.println("消费者01接收到的消息是:" + new String(message.getBody()));channel.basicAck(message.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), false);}}, new CancelCallback() {public void handle(String consumerTag) {System.out.println("消费者01取消消费的回调这个方法");}});}}/*** 消费者02,接收消息 Hello RabbitMQ*/
public class ConsumerTwo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {........// 4.用连接对象创建channelfinal Channel channel = connection.createChannel();// 5.设置channel属性,例如队列名字,是否持久化等等channel.queueDeclare(WORK_QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);// 预取,告诉rabbitmq,在从mq中取消息的时候,一次取多少条// 设置为1,一次只能拿1条数据channel.basicQos(1);// 6.使用channel去rabbitmq中取消息进行消费channel.basicConsume(WORK_QUEUE_NAME, false, new DeliverCallback() {public void handle(String consumerTag, Delivery message) throws IOException {try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}System.out.println("消费者02接收到的消息是:" + new String(message.getBody()));channel.basicAck(message.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), false);}}, new CancelCallback() {public void handle(String consumerTag) {System.out.println("消费者02取消消费的回调这个方法");}});}}3.3 消费者签收模式说明
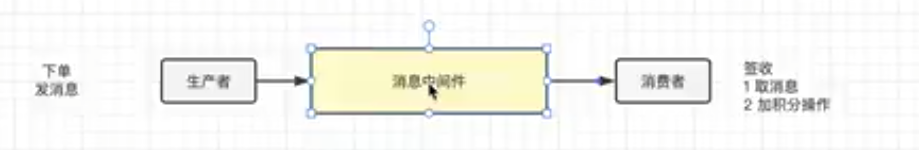
用户做下单逻辑,生产者进行发消息,把消息存储到中间件,消费者从中间件取消息,立马进行签收,然后执行加积分逻辑,但是加积分操作失败了,消费者把消息签收了,mq把消息删除了,造成数据不一致。
签收应该在业务逻辑执行成功后,消费者手动签收消息。自动签收可能会存在数据不一致情况,手动签收即使是失败了,也能让生产者重新投递
4、Pub/Sub(发布/订阅模式)
生产者生产消息,多个消费者可同时消费消息。适用于发送短信、发送邮件等操作
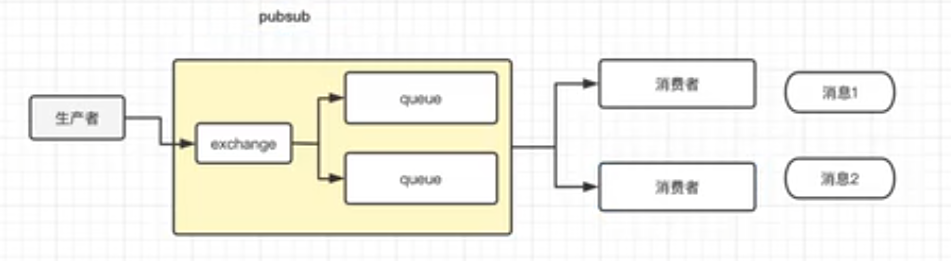
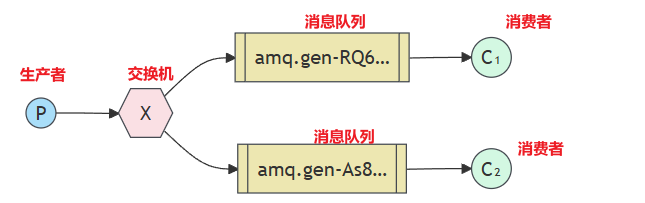
P:生产者,发送消息的程序,但是不在发送到队列中,而是发给X(交换机)。
C:消费者,消息的接收者,会一直等待消息到来。
Queue:消息队列,接收消息,缓存消息。
Exchange:交换机(X),一方面,接收生产者发送的消息,另一方面,知道如何处理消息,例如递给某个特别队列,递给所有队列,或者将消息丢弃,到底如何操作,取决于Exchange的类型
Exchange有常见以下3种类型:
- Fanout:广播,把消息交给所有绑定到交换机的队列(Pub/Sub模式使用)
- Direct:定向,把消息交给符合指定routing key 的队列(Routing模式使用)
- Topic:通配符,把消息交给符合routing pattern(路由模式)的队列(Topic模式使用)
Exchange(交换机)只负责转发消息,不具备存储消息的能力,因此如果没有任何队列与Exchange绑定,或者没有符合路由规则的队列,那么消息会丢失!
4.1 代码实现
4.1.1 生产者
/*** 生产者,生产消息 Hello RabbitMQ*/
public class Producer {/*** main方法* @param args* @throws IOException* @throws TimeoutException*/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {// 1.创建连接工厂对象(connectFactory)ConnectionFactory connectFactory = new ConnectionFactory();// 2.设置rabbitmq的Ip地址connectFactory.setHost(HOST);connectFactory.setPort(PORT);connectFactory.setUsername(USER_NAME);connectFactory.setPassword(PASS_WORD);connectFactory.setVirtualHost(VIRTUAL_HOST);// 3.用连接工厂创建连接对象ConnectionConnection connection = connectFactory.newConnection();// 4.用连接对象创建channelChannel channel = connection.createChannel();// 5.设置channel属性/*** 第一个参数:交换机名字* 第二个参数:交换机类型*/channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "fanout");// 6.channel调用basicPublish方法发送消息/*** 第一个参数:交换机名字* 第二个参数:路由key* 第三个参数:消息属性* 第四个参数:消息内容*/
// String message = "info: Hello World!";channel.basicPublish(EXCHANGE_NAME, "", null, QUEUE_MESSAGE.getBytes());// 7.关闭消息channel.close();connection.close();}}4.1.2 消费者1
/*** 消费者,接收消息 Hello RabbitMQ*/
public class ConsumerOne {/*** main方法* @param args* @throws IOException* @throws TimeoutException*/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {// 1.创建连接工厂对象(connectFactory)ConnectionFactory connectFactory = new ConnectionFactory();// 2.设置rabbitmq的Ip地址connectFactory.setHost(HOST);connectFactory.setPort(PORT);connectFactory.setUsername(USER_NAME);connectFactory.setPassword(PASS_WORD);connectFactory.setVirtualHost(VIRTUAL_HOST);// 3.用连接工厂创建连接对象ConnectionConnection connection = connectFactory.newConnection();// 4.用连接对象创建channelfinal Channel channel = connection.createChannel();// 5.设置channel属性/*** 第一个参数:交换机名字* 第二个参数:交换机类型*/channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "fanout");// 6.消费者绑定队列// 匿名String queueName = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();/*** 第一个参数:队列名字* 第二个参数:交换机名称* 第三个参数:路由key*/channel.queueBind(queueName, EXCHANGE_NAME, "");// 7.使用channel去rabbitmq中取消息进行消费/*** 第一个参数:队列名字* 第二个参数:是否自动确认(签收)*/channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, new DeliverCallback() {/*** 当消息从mq中取出来会回调这个函数* 消费者消费消息在handle处理* @param consumerTag the <i>consumer tag</i> associated with the consumer* @param message the delivered message* @throws IOException*/public void handle(String consumerTag, Delivery message) throws IOException {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}System.out.println("消费者01接收到的消息是:" + new String(message.getBody()));channel.basicAck(message.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), false);}}, new CancelCallback() {/*** 消费者取消消费的回调这个方法* @param consumerTag the <i>consumer tag</i> associated with the consumer*/public void handle(String consumerTag) {System.out.println("消费者01取消消费的回调这个方法");}});}}4.1.3 消费者2
/*** 消费者02,接收消息 Hello RabbitMQ*/
public class ConsumerTwo {/*** main方法* @param args* @throws IOException* @throws TimeoutException*/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {// 1.创建连接工厂对象(connectFactory)ConnectionFactory connectFactory = new ConnectionFactory();// 2.设置rabbitmq的Ip地址connectFactory.setHost(HOST);connectFactory.setPort(PORT);connectFactory.setUsername(USER_NAME);connectFactory.setPassword(PASS_WORD);connectFactory.setVirtualHost(VIRTUAL_HOST);// 3.用连接工厂创建连接对象ConnectionConnection connection = connectFactory.newConnection();// 4.用连接对象创建channelfinal Channel channel = connection.createChannel();// 5.设置channel属性/*** 第一个参数:交换机名字* 第二个参数:交换机类型*/channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "fanout");// 6.消费者绑定队列// 匿名String queueName = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();/*** 第一个参数:队列名字* 第二个参数:交换机名称* 第三个参数:路由key*/channel.queueBind(queueName, EXCHANGE_NAME, "");// 7.使用channel去rabbitmq中取消息进行消费/*** 第一个参数:队列名字* 第二个参数:是否自动确认(签收)*/channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, new DeliverCallback() {/*** 当消息从mq中取出来会回调这个函数* 消费者消费消息在handle处理* @param consumerTag the <i>consumer tag</i> associated with the consumer* @param message the delivered message* @throws IOException*/public void handle(String consumerTag, Delivery message) throws IOException {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}System.out.println("消费者02接收到的消息是:" + new String(message.getBody()));channel.basicAck(message.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), false);}}, new CancelCallback() {/*** 消费者取消消费的回调这个方法* @param consumerTag the <i>consumer tag</i> associated with the consumer*/public void handle(String consumerTag) {System.out.println("消费者02取消消费的回调这个方法");}});}}4.2 实现效果
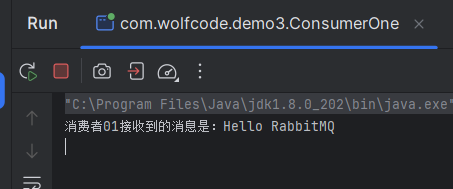
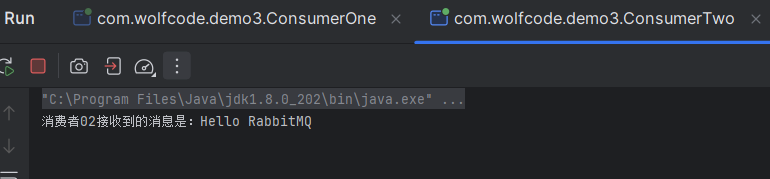
先启动消费者代码,在启动生产者代码,消费者关闭启动后,队列消失
5、Routing模式(路由模式)
队列与交换机的绑定,不能是任意绑定了,而是要指定一个RoutingKey(路由key)
消息的发送方在向Exchange发送消息时,也必须指定消息的RoutingKey
Exchange不再把消息交给每一个绑定的队列,而是根据消息的Routing Key进行判断,只有队列的Routing Key与信息的Routing Key完全一致,才会接收到消息
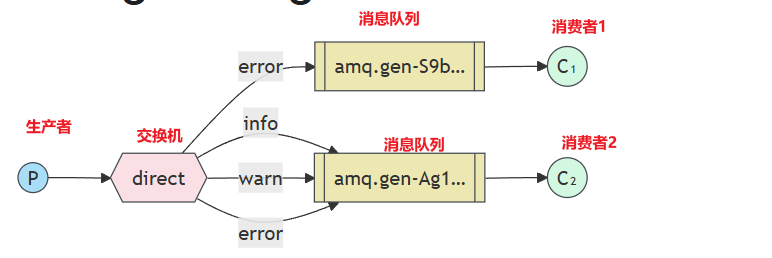
P:生产者,向Exchange发送消息,发送消息时,会指定一个routing key
X:Exchange(交换机),接收生产者的消息,然后把消息递给与routing key完全匹配的队列
C1:消费者,其所在队列指定了需要routing key为error的消息
C2:消费者,其所在队列指定了需要routing key为info、warn、error的消息
Exchange有常见以下3种类型:
- Fanout:广播,把消息交给所有绑定到交换机的队列(Pub/Sub模式使用)
- Direct:定向,把消息交给符合指定routing key 的队列(Routing模式使用)
- Topic:通配符,把消息交给符合routing pattern(路由模式)的队列(Topic模式使用)
5.1 代码实现
5.1.1 生产者
/*** 生产者,生产消息 Hello RabbitMQ*/
public class Producer {/*** main方法* @param args* @throws IOException* @throws TimeoutException*/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {// 1.创建连接工厂对象(connectFactory)ConnectionFactory connectFactory = new ConnectionFactory();// 2.设置rabbitmq的Ip地址connectFactory.setHost(HOST);connectFactory.setPort(PORT);connectFactory.setUsername(USER_NAME);connectFactory.setPassword(PASS_WORD);connectFactory.setVirtualHost(VIRTUAL_HOST);// 3.用连接工厂创建连接对象ConnectionConnection connection = connectFactory.newConnection();// 4.用连接对象创建channelChannel channel = connection.createChannel();// 5.设置channel属性/*** 第一个参数:交换机名字* 第二个参数:交换机类型*/channel.exchangeDeclare(ROUTING_NAME, "direct");// 6.channel调用basicPublish方法发送消息/*** 第一个参数:交换机名字* 第二个参数:路由key* 第三个参数:消息属性* 第四个参数:消息内容*/channel.basicPublish(ROUTING_NAME, "info", null, QUEUE_MESSAGE.getBytes());// 7.关闭消息channel.close();connection.close();}}5.1.2 消费者1
/*** 消费者,接收消息 Hello RabbitMQ*/
public class ConsumerOne {/*** main方法* @param args* @throws IOException* @throws TimeoutException*/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {// 1.创建连接工厂对象(connectFactory)ConnectionFactory connectFactory = new ConnectionFactory();// 2.设置rabbitmq的Ip地址connectFactory.setHost(HOST);connectFactory.setPort(PORT);connectFactory.setUsername(USER_NAME);connectFactory.setPassword(PASS_WORD);connectFactory.setVirtualHost(VIRTUAL_HOST);// 3.用连接工厂创建连接对象ConnectionConnection connection = connectFactory.newConnection();// 4.用连接对象创建channelfinal Channel channel = connection.createChannel();// 5.设置channel属性/*** 第一个参数:交换机名字* 第二个参数:交换机类型*/channel.exchangeDeclare(ROUTING_NAME, "direct");// 6.消费者绑定队列// 匿名String queueName = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();/*** 第一个参数:队列名字* 第二个参数:交换机名称* 第三个参数:路由key*/channel.queueBind(queueName, ROUTING_NAME, "info");channel.queueBind(queueName, ROUTING_NAME, "error");channel.queueBind(queueName, ROUTING_NAME, "warn");// 7.使用channel去rabbitmq中取消息进行消费/*** 第一个参数:队列名字* 第二个参数:是否自动确认(签收)*/channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, new DeliverCallback() {/*** 当消息从mq中取出来会回调这个函数* 消费者消费消息在handle处理* @param consumerTag the <i>consumer tag</i> associated with the consumer* @param message the delivered message* @throws IOException*/public void handle(String consumerTag, Delivery message) throws IOException {System.out.println("消费者01接收到的消息是:" + new String(message.getBody()));}}, new CancelCallback() {/*** 消费者取消消费的回调这个方法* @param consumerTag the <i>consumer tag</i> associated with the consumer*/public void handle(String consumerTag) {System.out.println("消费者01取消消费的回调这个方法");}});}}5.1.3 消费者2
/*** 消费者,接收消息 Hello RabbitMQ*/
public class ConsumerTwo {/*** main方法* @param args* @throws IOException* @throws TimeoutException*/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {// 1.创建连接工厂对象(connectFactory)ConnectionFactory connectFactory = new ConnectionFactory();// 2.设置rabbitmq的Ip地址connectFactory.setHost(HOST);connectFactory.setPort(PORT);connectFactory.setUsername(USER_NAME);connectFactory.setPassword(PASS_WORD);connectFactory.setVirtualHost(VIRTUAL_HOST);// 3.用连接工厂创建连接对象ConnectionConnection connection = connectFactory.newConnection();// 4.用连接对象创建channelfinal Channel channel = connection.createChannel();// 5.设置channel属性/*** 第一个参数:交换机名字* 第二个参数:交换机类型*/channel.exchangeDeclare(ROUTING_NAME, "direct");// 6.消费者绑定队列// 匿名String queueName = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();/*** 第一个参数:队列名字* 第二个参数:交换机名称* 第三个参数:路由key*/channel.queueBind(queueName, ROUTING_NAME, "trace");// 7.使用channel去rabbitmq中取消息进行消费/*** 第一个参数:队列名字* 第二个参数:是否自动确认(签收)*/channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, new DeliverCallback() {/*** 当消息从mq中取出来会回调这个函数* 消费者消费消息在handle处理* @param consumerTag the <i>consumer tag</i> associated with the consumer* @param message the delivered message* @throws IOException*/public void handle(String consumerTag, Delivery message) throws IOException {System.out.println("消费者02接收到的消息是:" + new String(message.getBody()));}}, new CancelCallback() {/*** 消费者取消消费的回调这个方法* @param consumerTag the <i>consumer tag</i> associated with the consumer*/public void handle(String consumerTag) {System.out.println("消费者02取消消费的回调这个方法");}});}}5.2 实现效果
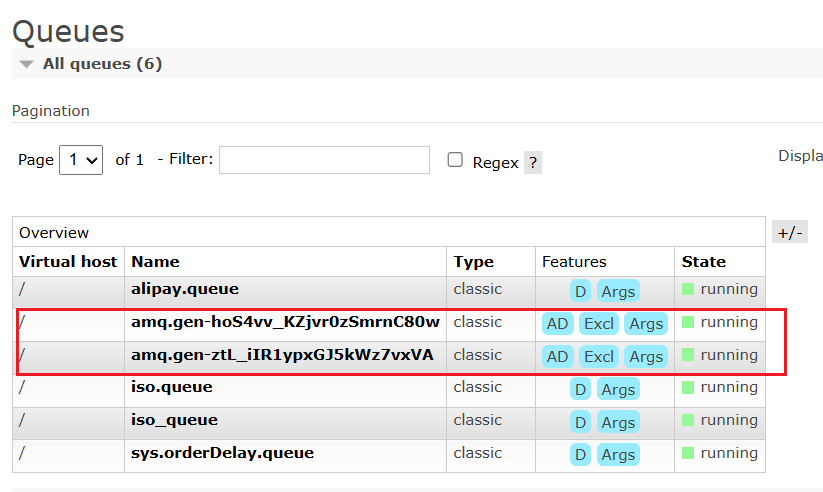
先启动消费者,在启动生产者。
生产者的routing key 是info,消费者1的routing key有info,消费者2的routing key没有info
6、Topic模式
Topic类型与Direct相比,都是可以根据Routing Key把消息路由到不同的队列,只不过Topic类型
Exchange可以让队列在绑定Routing Key的时候使用通配符
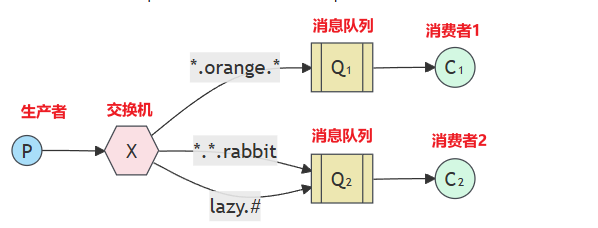
RoutingKey一般都是有一个或多个单词组成,多个单词之间以"."分割。例如:item.insert
通配符规则:
- # 匹配一个或多个词
- * 匹配不多不少恰好1个词
例如:item.# 能够匹配item.insert.abc或item.insert。item.* 只能匹配item.insert
Exchange有常见以下3种类型:
- Fanout:广播,把消息交给所有绑定到交换机的队列(Pub/Sub模式使用)
- Direct:定向,把消息交给符合指定routing key 的队列(Routing模式使用)
- Topic:通配符,把消息交给符合routing pattern(路由模式)的队列(Topic模式使用)
6.1 代码实现
6.1.1 生产者
/*** 生产者,生产消息 Hello RabbitMQ*/
public class Producer {/*** main方法* @param args* @throws IOException* @throws TimeoutException*/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {// 1.创建连接工厂对象(connectFactory)ConnectionFactory connectFactory = new ConnectionFactory();// 2.设置rabbitmq的Ip地址connectFactory.setHost(HOST);connectFactory.setPort(PORT);connectFactory.setUsername(USER_NAME);connectFactory.setPassword(PASS_WORD);connectFactory.setVirtualHost(VIRTUAL_HOST);// 3.用连接工厂创建连接对象ConnectionConnection connection = connectFactory.newConnection();// 4.用连接对象创建channelChannel channel = connection.createChannel();// 5.设置channel属性/*** 第一个参数:交换机名字* 第二个参数:交换机类型*/channel.exchangeDeclare(TOPIC_NAME, "topic");// 6.channel调用basicPublish方法发送消息/*** 第一个参数:交换机名字* 第二个参数:路由key* 第三个参数:消息属性* 第四个参数:消息内容*/channel.basicPublish(TOPIC_NAME, "employee.save", null, QUEUE_MESSAGE.getBytes());// 7.关闭消息channel.close();connection.close();}}6.1.2 消费者1
/*** 消费者,接收消息 Hello RabbitMQ*/
public class ConsumerOne {/*** main方法* @param args* @throws IOException* @throws TimeoutException*/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {// 1.创建连接工厂对象(connectFactory)ConnectionFactory connectFactory = new ConnectionFactory();// 2.设置rabbitmq的Ip地址connectFactory.setHost(HOST);connectFactory.setPort(PORT);connectFactory.setUsername(USER_NAME);connectFactory.setPassword(PASS_WORD);connectFactory.setVirtualHost(VIRTUAL_HOST);// 3.用连接工厂创建连接对象ConnectionConnection connection = connectFactory.newConnection();// 4.用连接对象创建channelfinal Channel channel = connection.createChannel();// 5.设置channel属性/*** 第一个参数:交换机名字* 第二个参数:交换机类型*/channel.exchangeDeclare(TOPIC_NAME, "topic");// 6.消费者绑定队列// 匿名String queueName = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();/*** 第一个参数:队列名字* 第二个参数:交换机名称* 第三个参数:路由key*/channel.queueBind(queueName, TOPIC_NAME, "employee.*");// 7.使用channel去rabbitmq中取消息进行消费/*** 第一个参数:队列名字* 第二个参数:是否自动确认(签收)*/channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, new DeliverCallback() {/*** 当消息从mq中取出来会回调这个函数* 消费者消费消息在handle处理* @param consumerTag the <i>consumer tag</i> associated with the consumer* @param message the delivered message* @throws IOException*/public void handle(String consumerTag, Delivery message) throws IOException {System.out.println("消费者01 employee接收到的消息是:" + new String(message.getBody()));}}, new CancelCallback() {/*** 消费者取消消费的回调这个方法* @param consumerTag the <i>consumer tag</i> associated with the consumer*/public void handle(String consumerTag) {System.out.println("消费者01 employee取消消费的回调这个方法");}});}}6.1.3 消费者2
/*** 消费者,接收消息 Hello RabbitMQ*/
public class ConsumerTwo {/*** main方法* @param args* @throws IOException* @throws TimeoutException*/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {// 1.创建连接工厂对象(connectFactory)ConnectionFactory connectFactory = new ConnectionFactory();// 2.设置rabbitmq的Ip地址connectFactory.setHost(HOST);connectFactory.setPort(PORT);connectFactory.setUsername(USER_NAME);connectFactory.setPassword(PASS_WORD);connectFactory.setVirtualHost(VIRTUAL_HOST);// 3.用连接工厂创建连接对象ConnectionConnection connection = connectFactory.newConnection();// 4.用连接对象创建channelfinal Channel channel = connection.createChannel();// 5.设置channel属性/*** 第一个参数:交换机名字* 第二个参数:交换机类型*/channel.exchangeDeclare(TOPIC_NAME, "topic");// 6.消费者绑定队列// 匿名String queueName = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();/*** 第一个参数:队列名字* 第二个参数:交换机名称* 第三个参数:路由key*/channel.queueBind(queueName, TOPIC_NAME, "user.*");// 7.使用channel去rabbitmq中取消息进行消费/*** 第一个参数:队列名字* 第二个参数:是否自动确认(签收)*/channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, new DeliverCallback() {/*** 当消息从mq中取出来会回调这个函数* 消费者消费消息在handle处理* @param consumerTag the <i>consumer tag</i> associated with the consumer* @param message the delivered message* @throws IOException*/public void handle(String consumerTag, Delivery message) throws IOException {System.out.println("消费者02 user接收到的消息是:" + new String(message.getBody()));}}, new CancelCallback() {/*** 消费者取消消费的回调这个方法* @param consumerTag the <i>consumer tag</i> associated with the consumer*/public void handle(String consumerTag) {System.out.println("消费者02 user取消消费的回调这个方法");}});}}6.2 实现效果
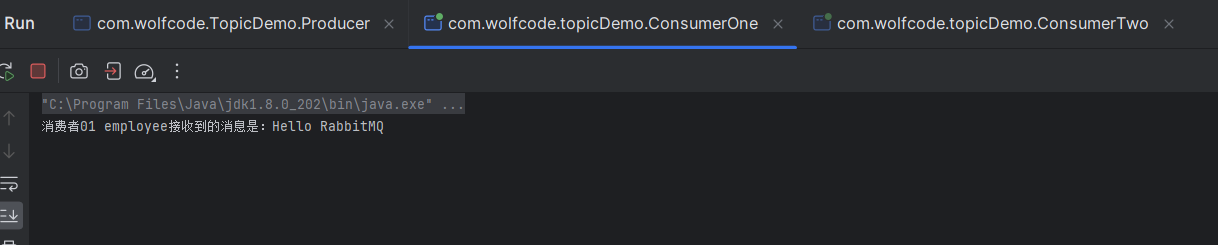
先启动消费者,在启动生产者。
生产者的routing key 是employee.save,消费者1的routing key有employee.*,消费者2的routing key没有user.*
官网:RabbitMQ tutorial - Work Queues | RabbitMQ
学习视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1HM411x7za/?spm_id_from=333.1007.top_right_bar_window_history.content.click&vd_source=94deb0bc72e4dde87140562a29a6c611
