【abc417】E - A Path in A Dictionary
Problem Statement
You are given a simple connected undirected graph G with N vertices and M edges.
The vertices of G are numbered vertex 1, vertex 2, …, vertex N, and the i-th (1≤i≤M) edge connects vertices Ui and Vi.Find the lexicographically smallest simple path from vertex X to vertex Y in G.
That is, find the lexicographically smallest among the integer sequences P=(P1,P2,…,P∣P∣) that satisfy the following conditions:
1≤Pi≤N
If i
j, then Pi
Pj.
P1=X and
For 1≤i≤∣P∣−1, there exists an edge connecting vertices Pi and Pi+1.
One can prove that such a path always exists under the constraints of this problem.
You are given T test cases, so find the answer for each.
Lexicographic order on integer sequencesAn integer sequence S=(S1,S2,…,S∣S∣) is lexicographically smaller than an integer sequence T=(T1,T2,…,T∣T∣) if either of the following 1. or 2. holds. Here, ∣S∣ and ∣T∣ represent the lengths of S and T, respectively.
∣S∣<∣T∣ and (S1,S2,…,S∣S∣)=(T1,T2,…,T∣S∣).
There exists some 1≤i≤min(∣S∣,∣T∣) such that (S1,S2,…,Si−1)=(T1,T2,…,Ti−1) and Si<Ti.
Constraints
1≤T≤500
2≤N≤1000
N−1≤M≤min(2N(N−1),5×104)
1≤X,Y≤N
X
Y
1≤Ui<Vi≤N
If i
j, then (Ui,Vi)
(Uj,Vj).
The given graph is connected.
The sum of N over all test cases in each input is at most 1000.
The sum of M over all test cases in each input is at most 5×104.
All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
T
case1
case2
⋮
caseTcasei represents the i-th test case. Each test case is given in the following format:
N M X Y
U1 V1
U2 V2
⋮
UM VMOutput
Output T lines.
The i-th line (1≤i≤T) should contain the vertex numbers on the simple path that is the answer to the i-th test case, in order, separated by spaces.
That is, when the answer to the i-th test case is P=(P1,P2,…,P∣P∣), output P1, P2, …, P∣P∣ on the i-th line in this order, separated by spaces.
Sample Input 1
2
6 10 3 5
1 2
1 3
1 5
1 6
2 4
2 5
2 6
3 4
3 5
5 6
3 2 3 2
1 3
2 3Sample Output 1
3 1 2 5
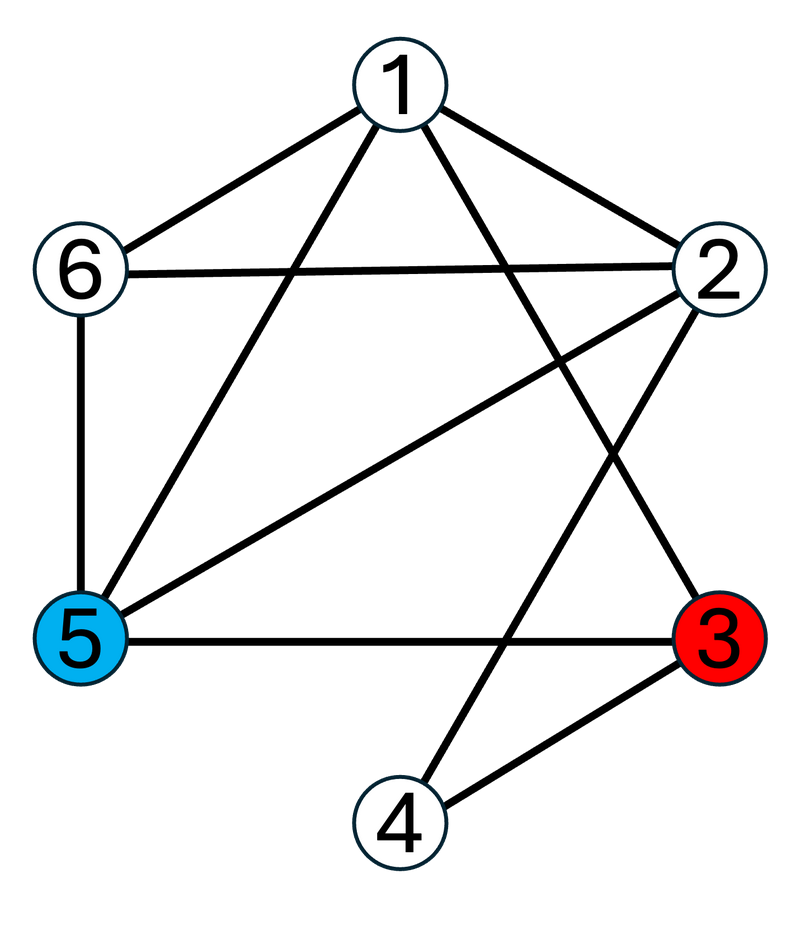
3 2For the first test case, graph G is as follows:
The simple paths from vertex 3 to vertex 5 on G, listed in lexicographic order, are as follows:
- (3,1,2,5)
- (3,1,2,6,5)
- (3,1,5)
- (3,1,6,2,5)
- (3,1,6,5)
- (3,4,2,1,5)
- (3,4,2,1,6,5)
- (3,4,2,5)
- (3,4,2,6,1,5)
- (3,4,2,6,5)
- (3,5)
Among these, the lexicographically smallest is (3,1,2,5), so output 3,1,2,5 separated by spaces on the first line.
For the second test case, (3,2) is the only simple path from vertex 3 to vertex 2.
题目大意:找到从x到y的最小字典序通路
用邻接图存储,排序,dfs搜索,回溯,注意回溯的时候,不用把状态再改回false,因为我们在dfs到该点时,已经发现它是构不成连通的,所以下次就不需要再到达这个节点了,这样可以减少很大一部分运算,从而将TLE的代码变成AC
AC代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll=long long;
const ll N=200010;
int n,m,x,y;
vector<int>path;
bool found;
void dfs(int current,vector<vector<int>>&graph,vector<bool>&visit){path.push_back(current);visit[current]=true;if (current==y){found=true;for (int i:path) cout<<i<<" ";cout<<"\n";return ; }sort(graph[current].begin(),graph[current].end());for (auto i:graph[current]){if (!visit[i]&&!found){visit[i]=true;dfs(i,graph,visit);if (found)return ;path.pop_back();}}
}
void solve(){cin>>n>>m>>x>>y;vector<vector<int>>graph(n+1);for (int i=1;i<=m;i++){int u,v;cin>>u>>v;graph[u].push_back(v);graph[v].push_back(u);}path.clear();vector<bool>visit(n+1,false);found=false;dfs(x,graph,visit);
}
int main() {ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);int T;cin>>T;while(T--){solve();}
}