JavaSE-String类
String在Java中是一种应用类型,用于表示一串字符,在基础语法中,我们只学习了使用String表示文本的用法,但String类的用处实际上很多。
常用方法
字符串的构造
String提供许多种常用的构造方式,可以将String视为数据类型,也可以视为一个类,常用的有三种:
public class test {public static void main(String[] args) {// 使用常量串构造String s1 = "hello world";System.out.println(s1);// 直接newString对象String s2 = new String("hello world");System.out.println(s1);// 使用字符数组进行构造char[] array = {'h','e','l','l','o','w','o','r','l','d'};String s3 = new String(array);System.out.println(s1);}}注意:
String是引用对象,在内部并不储存字符串本身,而是以字符数组的形式存储:
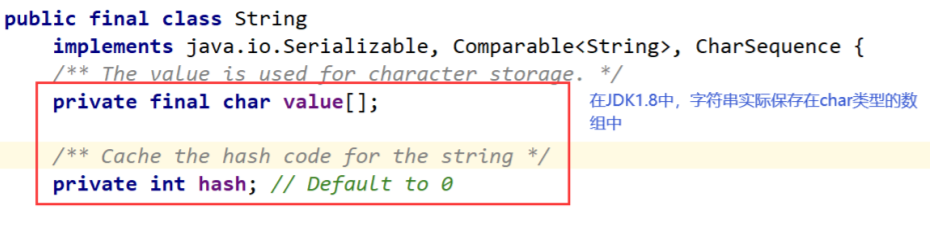
在更高版本的JDK中,以byte数组的形式存储:

String对象的比较
字符串之间的比较用于字符串排序,java提供了四种方法:
1.‘==’比较是否引用自同一个对象
对于基础数据类型,‘==’比较的是变量中的值,对于引用数据类型,‘==’比较的是应用对象的地址。
public static void main(String[] args) {int a = 10;int b = 20;int c = 10;// 对于基本类型变量,==比较两个变量中存储的值是否相同System.out.println(a == b); // falseSystem.out.println(a == c); // true// 对于引用类型变量,==比较两个引用变量引用的是否为同一个对象String s1 = new String("hello");String s2 = new String("hello");String s3 = new String("world");String s4 = s1;System.out.println(s1 == s2); // falseSystem.out.println(s2 == s3); // falseSystem.out.println(s1 == s4); // true}
2.boolean equals(Object anObject)方法按照字典序比较
字典序:字符大小的顺序
String类重写了Object类中的equals方法,Object类中采用'=='比较,而String中采用如下方法比较,比如s1.equals(s2):
public boolean equals(Object anObject) {// 1. 先检测this 和 anObject 是否为同一个对象比较,如果是返回trueif (this == anObject) {return true;}// 2. 检测anObject是否为String类型的对象,如果是继续比较,否则返回falseif (anObject instanceof String) {// 将anObject向下转型为String类型对象String anotherString = (String) anObject;int n = value.length;// 3. this和anObject两个字符串的长度是否相同,是继续比较,否则返回falseif (n == anotherString.value.length) {char v1[] = value;char v2[] = anotherString.value;int i = 0;// 4. 按照字典序,从前往后逐个字符进行比较while (n-- != 0) {if (v1[i] != v2[i])return false;i++;}return true;}}return false;}public static void main(String[] args) {String s1 = new String("hello");String s2 = new String("hello");String s3 = new String("Hello");// s1、s2、s3引用的是三个不同对象,因此==比较结果全部为falseSystem.out.println(s1 == s2); // falseSystem.out.println(s1 == s3); // false// equals比较:String对象中的逐个字符// 虽然s1与s2引用的不是同一个对象,但是两个对象中放置的内容相同,因此输出true// s1与s3引用的不是同一个对象,而且两个对象中内容也不同,因此输出falseSystem.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); // trueSystem.out.println(s1.equals(s3)); // false}3.int compareTo(String s) 方法: 按照字典序进行比较
与equals不同的是,equals返回的是boolean类型,而compareTo返回的是int类型。具体比较方式:
1. 先按照字典次序大小比较,如果出现不等的字符,直接返回这两个字符的大小差值
2。如果前k个字符相等(k为两个字符长度最小值),返回两个字符串长度差值
public static void main(String[] args) {String s1 = new String("abc");String s2 = new String("ac");String s3 = new String("abc");String s4 = new String("abcdef");System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2)); // 不同输出字符差值-1System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s3)); // 相同输出 0System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s4)); // 前k个字符完全相同,输出长度差值}
4.int compareToIgnoreCase(String str) 方法:与compareTo方式相同,但是忽略大小写比较
public static void main(String[] args) {String s1 = new String("abc");String s2 = new String("ac");String s3 = new String("ABc");String s4 = new String("abcdef");System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s2)); // 不同输出字符差值-1System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s3)); // 相同输出 0System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s4)); // 前k个字符完全相同,输出长度差值 -3}
字符串的查找
| 方法 | 功能 |
| char charAt(int index) | 返回index位置上字符,如果index为负数或者越界,抛出 IndexOutOfBoundsException异常 |
| int indexOf(int ch) | 返回ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
| int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) | 从fromIndex位置开始找ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
| int indexOf(String str) | 返回str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
| int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) | 从fromIndex位置开始找str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
| int lastIndexOf(int ch) | 从后往前找,返回ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
| int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) | 从fromIndex位置开始找,从后往前找ch第一次出现的位置,没有返 回-1 |
| int lastIndexOf(String str) | 从后往前找,返回str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
| int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex) | 从fromIndex位置开始找,从后往前找str第一次出现的位置,没有返 回-1 |
public static void main(String[] args) {String s = "aaabbbcccaaabbbccc";System.out.println(s.charAt(3)); // 'b'System.out.println(s.indexOf('c')); // 6System.out.println(s.indexOf('c', 10)); // 15System.out.println(s.indexOf("bbb")); // 3System.out.println(s.indexOf("bbb", 10)); // 12System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf('c')); // 17System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf('c', 10)); // 8System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf("bbb")); // 12System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf("bbb", 10)); // 3}
字符串的转化
1.数值和字符串转化
public static void main(String[] args) {// 数字转字符串String s1 = String.valueOf(1234);String s2 = String.valueOf(12.34);String s3 = String.valueOf(true);String s4 = String.valueOf(new Student("Hanmeimei", 18));System.out.println(s1);System.out.println(s2);System.out.println(s3);System.out.println(s4);System.out.println("=================================");// 字符串转数字// 注意:Integer、Double等是Java中的包装类型int data1 = Integer.parseInt("1234");double data2 = Double.parseDouble("12.34");System.out.println(data1);System.out.println(data2);}2.大小写转换
public static void main(String[] args) {String s1 = "hello";String s2 = "HELLO";// 小写转大写System.out.println(s1.toUpperCase());// 大写转小写System.out.println(s2.toLowerCase());
}
3.字符串转数组
public static void main(String[] args) {String s = "hello";// 字符串转数组char[] ch = s.toCharArray();for (int i = 0; i < ch.length; i++) {System.out.print(ch[i]);}System.out.println();// 数组转字符串String s2 = new String(ch);System.out.println(s2);}4.格式化
public static void main(String[] args) {String s = String.format("%d-%d-%d", 2019, 9,14);System.out.println(s);}字符串的替换
| 方法 | 功能 |
| String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement) | 替换所有的指定内容 |
| String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement) | 替换首个内容 |
public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "helloworld" ;System.out.println(str.replaceAll("l", "_"));System.out.println(str.replaceFirst("l", "_"));}
字符串的拆分
| 方法 | 功能 |
| String[] split(String regex) | 将字符串全部拆分 |
| String[] split(String regex, int limit) | 将字符串以指定格式拆分为limit组 |
public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "hello world hello bit";String[] result = str.split(" "); // 按照空格拆分for (String s : result) {System.out.println(s);}}
字符串的截取
| 方法 | 功能 |
| String substring(int beginIndex) | 从指定索引截取到结尾 |
| String substring(int beginIndex,int endIndex) | 截取部分内容 |
public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "helloworld" ;System.out.println(str.substring(5));System.out.println(str.substring(0, 5));}
其他操作方法
| 方法 | 功能 |
| String trim() | 去掉字符串中的左右空格,保留中间空格 |
| String toUpperCase() | 字符串转大写 |
| String toLowerCase() | 字符串转小写 |
StringBuilder和StringBuffer
由于String的不可更改特性,为了方便字符串的修改,Java中又提供StringBuilder和StringBuffer类。
public static void main(String[] args) {StringBuilder sb1 = new StringBuilder("hello");StringBuilder sb2 = sb1;// 追加:即尾插-->字符、字符串、整形数字sb1.append(' '); // hellosb1.append("world"); // hello worldsb1.append(123); // hello world123System.out.println(sb1); // hello world123System.out.println(sb1 == sb2); // trueSystem.out.println(sb1.charAt(0)); // 获取0号位上的字符 hSystem.out.println(sb1.length()); // 获取字符串的有效长度14System.out.println(sb1.capacity()); // 获取底层数组的总大小sb1.setCharAt(0, 'H'); // 设置任意位置的字符 Hello world123sb1.insert(0, "Hello world!!!"); // Hello world!!!Hello world123System.out.println(sb1);System.out.println(sb1.indexOf("Hello")); // 获取Hello第一次出现的位置System.out.println(sb1.lastIndexOf("hello")); // 获取hello最后一次出现的位置sb1.deleteCharAt(0); // 删除首字符sb1.delete(0,5); // 删除[0, 5)范围内的字符String str = sb1.substring(0, 5); // 截取[0, 5)区间中的字符以String的方式返回System.out.println(str);sb1.reverse(); // 字符串逆转str = sb1.toString(); // 将StringBuffer以String的方式返回System.out.println(str);}从上述例子可以看出:String和StringBuilder最大的区别在于String的内容无法修改,而StringBuilder的内容可 以修改。频繁修改字符串的情况考虑使用StringBuilder,而StringBuilder和StringBuffer的区别是StringBuffer采用同步处理,属于线程安全操作;而StringBuilder未采用同步处理,属于线程不安全操作。

