代码随想录算法训练营十八天|二叉树part08
LeetCode 699 修剪二叉搜索树
题目链接:669. 修剪二叉搜索树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给你二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,同时给定最小边界low 和最大边界 high。通过修剪二叉搜索树,使得所有节点的值在[low, high]中。修剪树 不应该 改变保留在树中的元素的相对结构 (即,如果没有被移除,原有的父代子代关系都应当保留)。 可以证明,存在 唯一的答案 。
所以结果应当返回修剪好的二叉搜索树的新的根节点。注意,根节点可能会根据给定的边界发生改变。
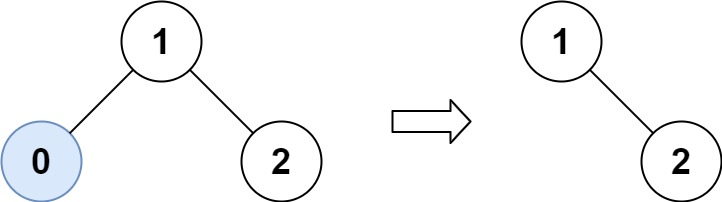
示例 1:
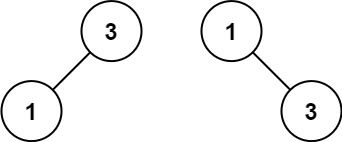
输入:root = [1,0,2], low = 1, high = 2
输出:[1,null,2]
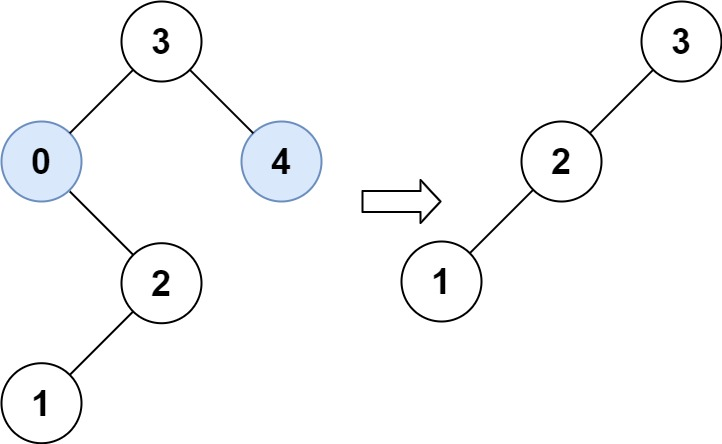
示例 2:
输入:root = [3,0,4,null,2,null,null,1], low = 1, high = 3
输出:[3,2,null,1]
递归思路:
如果根节点的值小于low,说明根节点左子树上所有的节点值都小于low,所以直接返回修剪好的右子树即可;如果根节点的值大于high,说明根节点右子树上所以得节点值都大于high,所以直接返回修剪好的左子树即可;如果根节点的值大于等于low,小于等于high,返回修剪好的左右子树。
代码如下:
class Solution {public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root,int low,int high){//递归法if(root==null)return null;//如果根节点的值小于low,说明根节点左子树都不在范围内,返回修剪好的右子树即可if(root.val<low)return trimBST(root.right,low,high);//如果根节点的值大于high,说明根节点右子树都不在范围内,返回修剪好的左子树即可if(root.val>high)return trimBST(root.left,low,high);//在范围内,递归返回修剪好的左子树和右子树root.left=trimBST(root.left,low,high);root.right=trimBST(root.right,low,high);return root;}
}迭代法:
首先判断根节点是否在范围内,如果小于low,root=root.right;如果大于high,root=root.left;如果节点在范围内,接下来处理左孩子元素小于low和右孩子元素大于high的情况。
完整代码如下:
class Solution {public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root,int low,int high){//迭代法if(root==null)return null;while(root!=null&&(root.val<low||root.val>high)){if(root.val<low)root=root.right;if(root.val>high)root=root.left;}TreeNode curr=root;while(curr!=null){while(curr.left!=null&&curr.left.val<low){curr.left=curr.left.right;}curr=curr.left;}curr=root;while(curr!=null){while(curr.right!=null&&curr.right.val>high){curr.right=curr.right.left;}curr=curr.right;}return root;}
}LeetCode 108 将有序数组转化为二叉搜索树
题目链接:108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给你一个整数数组 nums ,其中元素已经按 升序 排列,请你将其转换为一棵 平衡 二叉搜索树。
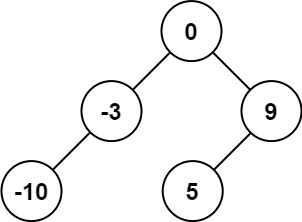
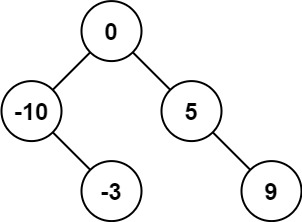
示例 1:
输入:nums = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
输出:[0,-3,9,-10,null,5]
解释:[0,-10,5,null,-3,null,9] 也将被视为正确答案:
示例 2:
输入:nums = [1,3]
输出:[3,1]
解释:[1,null,3] 和 [3,1] 都是高度平衡二叉搜索树。
思路:
从数组中间位置取值作为节点元素,把其作为分割点,然后递归左区间和右区间。是不是感觉这个思路很熟悉,就是之前在做最大二叉树、从中序和后序遍历序列构造二叉树用的方法。
那么有人就会问,如果数组的长度为偶数,中间节点有两个,选哪一个呢?
其实选哪一个都可以,只是构成了不同的平衡二叉搜索树,大家随便画个图就知道了。
class Solution {public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {return build(nums,0,nums.length);}public TreeNode build(int[] arr,int start,int end){if(start==end)return null;int n=end-start;int index=start+n/2;TreeNode root=new TreeNode(arr[index]);root.left=build(arr,start,index);root.right=build(arr,index+1,end);return root;}
}LeetCode 538 把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
题目链接:538. 把二叉搜索树转换为累加树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给出二叉 搜索 树的根节点,该树的节点值各不相同,请你将其转换为累加树(Greater Sum Tree),使每个节点 node 的新值等于原树中大于或等于 node.val 的值之和。
提醒一下,二叉搜索树满足下列约束条件:
节点的左子树仅包含键 小于 节点键的节点。
节点的右子树仅包含键 大于 节点键的节点。
左右子树也必须是二叉搜索树。
示例 1:
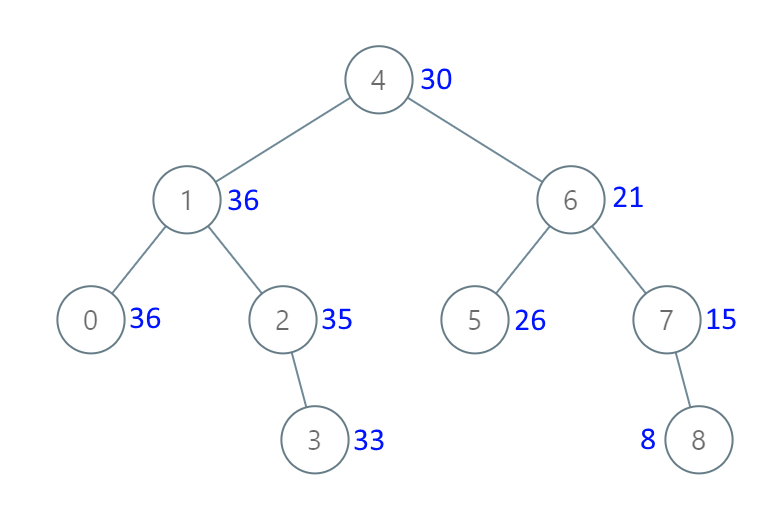
输入:[4,1,6,0,2,5,7,null,null,null,3,null,null,null,8]
输出:[30,36,21,36,35,26,15,null,null,null,33,null,null,null,8]
示例 2:输入:root = [0,null,1]
输出:[1,null,1]
示例 3:输入:root = [1,0,2]
输出:[3,3,2]
示例 4:输入:root = [3,2,4,1]
输出:[7,9,4,10]
思路:
其实这个题相当于是对一个有序数组,求从后到前的累加数组。所以我们只要按照右中左的顺序遍历二叉树,然后顺序累加就行了。
这里依旧要用到和之前做过的二叉搜索树的最小绝对差、求二叉树的众数一样的技巧,那就是引入一个pre节点保留前序节点。
class Solution {public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {//递归if(root==null)return null;return inorder(root);}TreeNode pre=null;public TreeNode inorder(TreeNode node){if(node==null)return null;inorder(node.right);if(pre!=null)node.val+=pre.val;pre=node;inorder(node.left);return node;}
}迭代法如下:
class Solution {public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {//迭代if(root==null)return null;Stack<TreeNode> st=new Stack<>();TreeNode pre=null;st.push(root);while(!st.isEmpty()){TreeNode tmp=st.pop();if(tmp!=null){if(tmp.left!=null)st.push(tmp.left);st.push(tmp);st.push(null);if(tmp.right!=null)st.push(tmp.right);}else{tmp=st.pop();if(pre!=null)tmp.val+=pre.val;pre=tmp;}}return root;}
}之后会出一个二叉树这部分的总结,把这些做题思路整合一下。