【RabbitMQ】SpringBoot整合RabbitMQ、实现RabbitMQ五大工作模式(万字长文)
目录
一、准备
1、创建SpringBoot项目
2、添加配置信息
3、创建配置类
二、RabbitMQ的配置类里创建队列
三、RabbitMQ的配置类里创建交换机及绑定队列
四、SpringBoot整合RabbitMQ入门案例
1、生产者
2、消费者
四、SpringBoot里实现RabbitMQ五大工作模式
1、简单模式
2、work queues工作队列模式
3、pub/sub订阅模式
4、routing路由模式
5、topic通配符模式
一、准备
1、创建SpringBoot项目
我们需要创建一个生产者项目与消费者项目
【Java】两张图帮你的社区版IDEA创建SpringBoot项目_1373i的博客-CSDN博客![]() https://blog.csdn.net/qq_61903414/article/details/130174514?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_61903414/article/details/130174514?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
如何创建SpringBoot项目在该文章里,项目创建完成后即可进行后续操作
2、添加配置信息
项目创建完成后,需要在各自的配置文件里添加RabbitMQ的相关配置

在该文件里添加以下配置信息
spring:rabbitmq:host: 127.0.0.1 # IPport: 5672 # 端口username: guest # 用户名password: guest # 密码virtual-host: /learn # 虚拟机名3、创建配置类
完成上述操作后我们还需要创建一个RabbitMQ的配置类,后续会通过这个类来创建队列等,此时我们就可以编写RabbitMQ代码了

二、RabbitMQ的配置类里创建队列
在之前Spring项目里我们是通过xml文件来创建队列,此时我们可以通过@Bean注解在这个配置类来创建队列并注入Spring容器里,有两种方式
import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;/*** 配置RabbitMQ* 配置交换机、队列、绑定队列与交换机*/
@Configuration
public class RabbitMQConfig {// 定义队列名private static final String QUEUE1_NAME = "queue1";private static final String QUEUE2_NAME = "queue2";// 注入队列@Beanpublic Queue queue1 () {// 通过QueueBuiller.durable(队列名).build();return QueueBuilder.durable(QUEUE1_NAME).build();}@Beanpublic Queue queue2() {// 直接通过Queue来创建return new Queue(QUEUE2_NAME);}}
注意此处的队列Queue不是我们之前在Java集合类里学过的Queue而是Rabbit MQ 里的Queue,他在 org.springframework.amqp.core这个包底下
三、RabbitMQ的配置类里创建交换机及绑定队列
同样交换机我们也可以通过注解来创建并注入Spring容器

 创建交换机也有两种方法
创建交换机也有两种方法
import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;/*** 配置RabbitMQ* 配置交换机、队列、绑定队列与交换机*/
@Configuration
public class RabbitMQConfig {// 定义交换机名称private static final String EXCHANGE = "ex";@Beanpublic Exchange exchange() {// ExchangeBuilder.fanoutExchange(交换机名).durable(是否持久化).build()return ExchangeBuilder.fanoutExchange(EXCHANGE).durable(true).build();}@Bean public Exchange exchange2() {return new FanoutExchange("交换机名");}}
将之前创建的两个队列与该交换机进行绑定
import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;/*** 配置RabbitMQ* 配置交换机、队列、绑定队列与交换机*/
@Configuration
public class RabbitMQConfig {// 定义队列名private static final String QUEUE1_NAME = "queue1";// 定义交换机名称private static final String EXCHANGE = "ex";// 注入队列@Beanpublic Queue queue1 () {// QueueBuilder.durable(队列名).build()return QueueBuilder.durable(QUEUE1_NAME).build();}// 注入交换机@Beanpublic Exchange exchange() {// ExchangeBuilder.fanoutExchange(交换机名).durable(是否持久化).build()return ExchangeBuilder.fanoutExchange(EXCHANGE).durable(true).build();}// 绑定@Beanpublic Binding binding(@Qualifier("queue1") Queue queue1,@Qualifier("exchange") FanoutExchange exchange) {// BindingBuilder.bind(队列).to(交换机).with(队列路由) 此处交换机类型为fanout所以不需要设置路由其他类型需要设置路由return BindingBuilder.bind(queue1).to(exchange);}}
四、SpringBoot整合RabbitMQ入门案例
创建了队列与交换机,我们来实现一个简单的案例,生产者生产一条消息,消费者进行消费
1、生产者
我们在生产者项目里需要在配置类里创建队列
package com.example.demo.config;import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;/*** 配置RabbitMQ* 配置交换机、队列、绑定队列与交换机*/
@Configuration
public class RabbitMQConfig {// 创建demo队列public static final String QUEUE = "demoQueue";@Beanpublic Queue demoQueue() {return QueueBuilder.durable(QUEUE).build();}
}
然后设置消息发送情景为当前端访问/send接口时进行发送,此时我们编写该接口
package com.example.demo.controller;import com.example.demo.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;@Controller
@ResponseBody
public class Producer {@Autowiredprivate RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;@RequestMapping("/send")public void sendMessage() {rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitMQConfig.QUEUE,"hello demo");}
}
运行项目,在浏览器访问该接口查看控制台![]()
消息已发送
2、消费者
我们需要在消费者项目里创建一个监听该队列的类,将他通过类注解注入Spring容器,让他能随着项目的启动而启动去监听
我们在类里定义一个监听方法加上RabbitListener注解进行监听
package com.example.demo.controller;import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component
public class DemoQueueListener {@RabbitListener(queues = "demoQueue")public void listener(Message message) {System.out.println("消费消息" + new String(message.getBody()));}
}

运行代码查看控制台![]()
四、SpringBoot里实现RabbitMQ五大工作模式
1、简单模式
简单模式的实现与上述代码相同
2、work queues工作队列模式
工作队列模式与简单模式相同,只不过多了一个消费者监听队列,在实现时创建两个消费者即可
3、pub/sub订阅模式
实现订阅模式我们需要先在RabbitMQ配置类里创建两个队列以及fanout类型的交换机,并将他们绑定
package com.example.demo.config;import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;/*** 配置RabbitMQ* 配置交换机、队列、绑定队列与交换机*/
@Configuration
public class RabbitMQConfig {/*** pub/sub订阅模式*/// 定义队列与交换机private static final String F_QUEUE1 = "fQueue1";private static final String F_QUEUE2 = "fQueue2";private static final String F_EXCHANGE = "fEx";@Beanpublic Queue fQueue1() {// 创建队列1return QueueBuilder.durable(F_QUEUE1).build();}@Beanpublic Queue fQueue2() {// 创建队列2return new Queue(F_QUEUE2);}@Beanpublic Exchange fEx() {// 创建交换机return ExchangeBuilder.fanoutExchange(F_EXCHANGE).durable(true).build();}@Beanpublic Binding binding1(@Qualifier("fQueue1")Queue fQueue1,@Qualifier("fEx") FanoutExchange exchange) {// 绑定队列1return BindingBuilder.bind(fQueue1).to(exchange);}@Beanpublic Binding binding2(@Qualifier("fQueue2")Queue fQueue2,@Qualifier("fEx") FanoutExchange exchange) {// 绑定队列1return BindingBuilder.bind(fQueue2).to(exchange);}}
此时访问fEx接口时发送消息
package com.example.demo.controller;import com.example.demo.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;@Controller
@ResponseBody
public class Producer {@Autowiredprivate RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;@RequestMapping("/send")public void sendMessage() {rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitMQConfig.QUEUE,"hello demo");}@RequestMapping("/fEx")public void sendByF() {rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("fEx","","hello mq");}
}
运行代码查看MQ控制台
消费者只需监听对应的队列即可
4、routing路由模式
首先我们需要在RabbitMQ配置类里面创建队列以及direct类型的交换机,并将他们绑定指定队列路由key
package com.example.demo.config;import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;/*** 配置RabbitMQ* 配置交换机、队列、绑定队列与交换机*/
@Configuration
public class RabbitMQConfig {// 创建队列与交换机private static final String D_QUEUE1 = "dQueue1";private static final String D_QUEUE2 = "dQueue2";private static final String D_EXCHANGE = "dEx";@Beanpublic Queue dQueue1() {// 创建队列1return QueueBuilder.durable(D_QUEUE1).build();}@Beanpublic Queue dQueue2() {// 创建队列2return new Queue(D_QUEUE2);}@Beanpublic DirectExchange dEx() {// 创建交换机return ExchangeBuilder.directExchange(D_EXCHANGE).durable(true).build();}@Beanpublic Binding binding1(@Qualifier("dQueue1")Queue dQueue1,DirectExchange dEx) {// 绑定交换机通过with指定路由return BindingBuilder.bind(dQueue1).to(dEx).with("error");}@Beanpublic Binding binding2(@Qualifier("dQueue2")Queue dQueue2,DirectExchange dEx) {// 绑定交换机通过with指定路由return BindingBuilder.bind(dQueue2).to(dEx).with("info");}
}此时访问/dEx接口时发送消息到路由为error队列,不给路由为info队列发送
package com.example.demo.controller;import com.example.demo.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;@Controller
@ResponseBody
public class Producer {@Autowiredprivate RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;@RequestMapping("/send")public void sendMessage() {rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("","hello demo");}@RequestMapping("/fEx")public void sendByF() {rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("fEx","","hello mq");}@RequestMapping("/dEx")public void sendByD() {rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("dEx","error","hello mq");}
}
运行代码访问接口查看MQ控制台
消费者相同只需修改监听队列名即可
5、topic通配符模式
首先需要在RabbitMQ配置类里创建队列与topic类型的交换机,并将它们进行绑定设置通配符匹配规则
package com.example.demo.config;import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;/*** 配置RabbitMQ* 配置交换机、队列、绑定队列与交换机*/
@Configuration
public class RabbitMQConfig {/*** topic通配符模式*/private static final String T_QUEUE1 = "tQueue1";private static final String T_QUEUE2 = "tQueue2";private static final String T_EXCHANGE = "tEx";@Beanpublic Queue tQueue1() {return QueueBuilder.durable(T_QUEUE1).build(); // 创建队列}@Beanpublic Queue tQueue2() {return new Queue(T_QUEUE2); // 创建队列}@Bean public TopicExchange tEx() {return ExchangeBuilder.topicExchange(T_EXCHANGE).durable(true).build();//创建交换机}@Beanpublic Binding binding1(@Qualifier("tQueue1") Queue tQueue1,@Qualifier("tEx") TopicExchange tEx) {return BindingBuilder.bind(tQueue1).to(tEx).with("A.*"); //绑定并配置通配符匹配规则}@Beanpublic Binding binding2(@Qualifier("tQueue2") Queue tQueue2,@Qualifier("tEx") TopicExchange tEx) {return BindingBuilder.bind(tQueue2).to(tEx).with("#.error");}
}此时访问/tEx接口,给tQueue2发送消息不给tQueue1发送,具体匹配规则可查看之前文章
【RabbitMQ】RabbbitMQ的六种工作模式以及代码实现_1373i的博客-CSDN博客![]() https://blog.csdn.net/qq_61903414/article/details/130156097?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_61903414/article/details/130156097?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
package com.example.demo.controller;import com.example.demo.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;@Controller
@ResponseBody
public class Producer {@Autowiredprivate RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;@RequestMapping("/send")public void sendMessage() {rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("","hello demo");}@RequestMapping("/fEx")public void sendByF() {rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("fEx","","hello mq");}@RequestMapping("/dEx")public void sendByD() {rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("dEx","error","hello mq");}@RequestMapping("/tEx")public void sendByT() {rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("tEx","B.error","hello mq");}
}
运行程序访问接口查看MQ控制台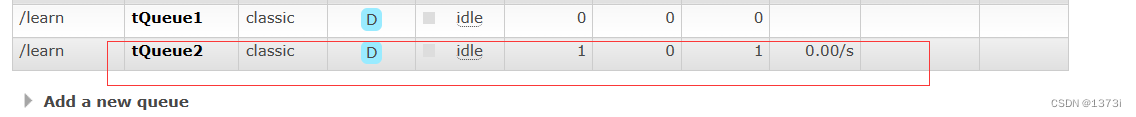
同理消费者也只需修改监听队列名即可
