【LeetCode】链表练习 9 道题
第一题:移除链表元素
题目描述:
给你一个链表的头节点head和一个整数val,请你删除链表中所有满足Node.val == val的节点,并返回新的头节点 。
列表中的节点数目在范围 [0, 10^4] 内1 <= Node.val <= 500 <= val <= 50
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*///题目框架
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){
}
方法一:
利用链表删除的思路。定义一个prev和一个cur指针变量,如果cur指向的值不是val,prev和cur都向后移动;cur指向的值是val,就进行删除操作。但如果是第一个结点的删除,需要额外处理。
参考代码如下:
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val)
{struct ListNode* prev = NULL;struct ListNode* cur = head;while (cur != NULL){if (cur->val != val){prev = cur;cur = cur->next;}else//cur->val == val{//第一个结点的删除if (NULL == prev){head = cur->next;free(cur);cur=head;}else//中间结点的删除{prev->next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = prev->next;}}}return head;
}
方法二:
通过定义指针变量cur对给定的链表进行遍历,如果cur->val != val,就将该节点尾插到新链表;如果cur->val == val,就将该节点进行删除。
参考代码如下:
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val)
{struct ListNode* cur = head;struct ListNode* tail = NULL;struct ListNode* del = NULL;head = NULL;while (cur != NULL){//插入情况if (cur->val != val){//头插情况if (NULL == tail){head = tail = cur;}else//尾插情况{tail->next = cur;tail = tail->next;}cur = cur->next;}else//删除情况{del = cur;cur = cur->next;free(del);del=NULL;}}if(tail != NULL){tail->next = NULL;}//返回新链表return head;
}
第二题:反转链表
题目描述:
给你单链表的头节点head,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
链表中节点的数目范围是 [0, 5000]-5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*///题目框架
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head{
}
方法一:
直接颠倒节点指针指向进行反转。
定义三个指针变量prev,cur,next。prev记录cur的上一个节点,next记录cur的下一个节点。
参考代码如下:
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{struct ListNode* prev = NULL;struct ListNode* cur = head;struct ListNode* next = NULL;while (cur != NULL){next = cur->next;//进行指针指向的反转cur->next = prev;prev = cur;cur = next;}return prev;
}
第三题:链表的中间结点
题目描述:
给你单链表的头结点head,请你找出并返回链表的中间结点。
如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点。
链表的结点数范围是 [1, 100]1 <= Node.val <= 100
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*///题目框架
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head){
}
方法一:
可以使用快慢指针来解决这道题。
可以定义一个快指针fast和一个慢指针slow,快指针一次走 2 步,慢指针一次走 1 步,当快指针走到结束,慢指针正好走到一半。
参考代码如下:
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head)
{struct ListNode* slow = head;struct ListNode* fast = head;//fast==NULL和fast->next==NULL,都代表走到结束位置while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;}return slow;
}
第四题:链表中倒数第k个结点
这道题用的是牛客网的。
题目描述:
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
/*** struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*//*** * @param pListHead ListNode类 * @param k int整型 * @return ListNode类*///题目框架
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k ) {
}
方法一:
这道题也是可以使用快反指针的方法来解决。
定义一个快指针fast,定义一个慢指针slow,快指针先走k步,然后快指针和慢指针一起走,直到快指针走到结束,慢指针就走到倒数第k个位置。
参考代码如下:
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k )
{struct ListNode* slow = pListHead;struct ListNode* fast = pListHead;//fast先走k步while (k--){//如果pListHead.length < k,出错返回NULLif(NULL == fast){return NULL;}fast = fast->next;}//fast走到NULL算结束while (fast != NULL){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next;}return slow;
}
第五题:合并两个有序链表
题目描述:
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
两个链表的节点数目范围是 [0, 50]-100 <= Node.val <= 100l1 和 l2 均按 非递减顺序 排列
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*///题目框架
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2){
}
方法一:
要将两个链表合并为一个链表,可以尝试将其中一个链表中的所有值全部插入到另一个链表中。这种方法看似简单,但其实会有很多细节性的处理。
参考代码如下:
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2)
{//存在空链表的情况if (NULL == list1){return list2;}else if (NULL == list2){return list1;}//找出第一个结点值最小的链表,让其做被插入的链表struct ListNode* head = NULL;struct ListNode* cur = NULL;if ((list1->val) < (list2->val)){head = list1;cur = list2;}else{head = list2;cur = list1;}//cur链表节点不断插入到head链表struct ListNode* prev = head;struct ListNode* pnext = prev->next;//cur==NULL代表插入完成while (cur != NULL){//pnext!=NULL意味着在两个节点中间进行插入if (pnext != NULL){if ((cur->val) >= pnext->val){//不符合升序的条件,继续向后查找prev = prev->next;pnext = pnext->next;}else if ((cur->val) >= (prev->val) && (cur->val) <= (pnext->val)){//符合升序条件,进行插入prev->next = cur;prev = prev->next;cur = cur->next;prev->next = pnext;}}else //在链表尾进行插入{prev->next = cur;break;}}return head;
}
方法二:
可以采用归并的思想将两个链表归并到一个新链表之中。
//采用设置头结点的方式解决
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2)
{struct ListNode* head = NULL;struct ListNode* tail = NULL;//头结点head = tail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));while ((list1 != NULL) && (list2 != NULL)){if((list1->val) < (list2->val)){tail->next = list1;tail = tail->next;list1 = list1->next;}else{tail->next = list2;tail = tail->next;list2 = list2->next;}}if(NULL == list1){tail->next = list2;}else{tail->next = list1;}struct ListNode* fNode = head;head = head->next;free(fNode);fNode = NULL;return head;
}
第六题:链表分割
题目描述:
现有一链表的头指针ListNode* pHead,给一定值x,编写一段代码将所有小于x的结点排在其余结点之前,且不能改变原来的数据顺序,返回重新排列后的链表的头指针。
/*
struct ListNode {int val;struct ListNode *next;ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*///题目框架
class Partition {
public:ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {}
};
方法一:
可以定义两个都带头结点的链表:lessHead和greaterHead,将比x小的值尾插到lessHead的链表,比x大的值尾插到greaterHead的链表,最后将两个链表做一个链接。
参考代码如下:
class Partition {
public:ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {// write code herestruct ListNode* lessHead = NULL;struct ListNode* lessTail = NULL;struct ListNode* greaterHead = NULL;struct ListNode* greaterTail = NULL;lessHead = lessTail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));greaterHead = greaterTail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));struct ListNode* cur = pHead;while(cur!=NULL){if((cur->val) < x){lessTail->next = cur;lessTail = lessTail->next;cur = cur->next;}else {greaterTail->next = cur;greaterTail = greaterTail->next;cur = cur->next;}}lessTail->next = greaterHead->next;//需要将greaterTail作为合并后链表的尾结点,尾结点的next指针要置空greaterTail->next = NULL;struct ListNode* head = lessHead->next;free(lessHead);free(greaterHead);return head;}
};
第七题:回文链表
题目描述:
给你一个单链表的头节点head,请你判断该链表是否为回文链表。如果是,返回true;否则,返回false。
- 链表中节点数目在范围
[1, 10^5]内 0 <= Node.val <= 9
//题目框架
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
bool isPalindrome(struct ListNode* head){
}
方法一:
这道题可以结合链表查找中间结点和链表逆置来解决。将中间位置之后的节点都进行逆置,然后从两端遍历进行比较即可。
参考代码如下:
bool isPalindrome(struct ListNode* head)
{struct ListNode* slow = head;struct ListNode* fast = head;while(fast != NULL && (fast->next) != NULL){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;}struct ListNode* prev = slow;struct ListNode* cur = slow->next;struct ListNode* next = NULL;//相当于中间结点做两个链表的相交节点slow->next = NULL;while (cur != NULL){next = cur->next;cur->next = prev;prev = cur;cur = next;}//从两端开始比较while(prev != NULL){if(prev->val != head->val){return false;}prev = prev->next;head = head->next;}return true;
}
第八题:相交链表
题目描述:
给你两个单链表的头节点headA和headB,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回null。

listA中节点数目为mlistB中节点数目为n1 <= m, n <= 3 * 10^41 <= Node.val <= 10^5
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*///题目框架
struct ListNode* getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {
}
方法一:
这道题有一个很妙的解法。先分别遍历A链表和B链表,求出A链表和B链表的长度。根据AB链表长度的差值,决定A或B先走差值步。然后A和B一起走,如果相遇,相遇的节点就是相交的第一个结点;如果走完了都没有相遇,说明A和B没有相交节点。
参考代码如下:
struct ListNode* getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB)
{struct ListNode* curA = headA;struct ListNode* curB = headB;int countA = 0;int countB = 0;while (curA != NULL){++countA;curA = curA->next;}while (curB != NULL){++countB;curB = curB->next;}curA = headA;curB = headB;int count = 0;if (countA > countB){count = countA - countB;while(count--){curA = curA->next;}}else{count = countB-countA;while (count--){curB = curB->next;}}while (curA != NULL){if (curA == curB){return curA;}curA = curA->next;curB = curB->next;}return NULL;
}
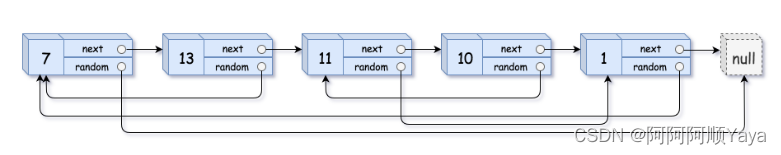
第九题:复制带随机指针的链表
题目描述:
给你一个长度为n的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针random,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
构造这个链表的 深拷贝。 深拷贝应该正好由n个 全新 节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的next指针和random`指针也都应指向复制链表中的新节点,并使原链表和复制链表中的这些指针能够表示相同的链表状态。复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点 。
返回复制链表的头节点。
0 <= n <= 1000-10^4 <= Node.val <= 10^4Node.random为null或指向链表中的节点。
/*** Definition for a Node.* struct Node {* int val;* struct Node *next;* struct Node *random;* };*///题目框架
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
}
方法一:
这道题有一个很妙的方法。在每一个节点后面都链接一个自己的copy节点,然后让copy->random=prevCopy->random->next,遇到NULL另作处理。最后把拷贝节点取下来,链接到一起,恢复原链表即可。
参考代码如下:
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head)
{struct Node* cur = head;//节点的插入while (cur != NULL){struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));newNode->val = cur->val;newNode->next = cur->next;cur->next = newNode;cur = newNode->next;}//random指针的链接cur = head;struct Node* newCur = NULL;while (cur != NULL){newCur = cur->next;if (cur->random != NULL){newCur->random = cur->random->next;}else{newCur->random = NULL;}cur = newCur->next;}//新链表的取下cur = head;struct Node* newHead = NULL;struct Node* tail = NULL;while (cur != NULL){newCur = cur->next;cur->next = newCur->next;if (NULL == newHead){newHead = tail = newCur;}else{tail->next = newCur;tail = tail->next;}cur = cur->next;}return newHead;}
