C++学习————第十天(string的基本使用)
1、string 对象类的常见构造

(constructor)函数名称 功能说明:
string() (重点) 构造空的string类对象,即空字符串
string(const char* s) (重点) 用C-string来构造string类对象
string(size_t n, char c) string类对象中包含n个字符c
string(const string&s) (重点) 拷贝构造函数void test_string1() {//常用string s1; //定义string s2("hello world"); //拷贝构造string s3(s2);//不常用 了解 //从s2的第三个字符开始拷贝,拷贝5个字符,如果5大于后面的字符数,到'\0'停止string s4(s2, 3, 5);string s5(s2, 3); //从s2的第三个字符开始拷贝string s6(s2, 3, 30);string s7("hello world", 5);string s8(10, 'x');cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl;cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl;cout << "s3 = " << s3 << endl;cout << "s4 = " << s4 << endl;cout << "s5 = " << s5 << endl;cout << "s6 = " << s6 << endl;cout << "s7 = " << s7 << endl;cout << "s8 = " << s8 << endl; }
2、string的隐式类型转换和构造

void test_string2()
{string s1("hello world"); //构造string s2 = "hello world"; //隐式类型转换const string& s3 = "hello world";// 临时对象具有常性,加const}3、string类对象的容量操作
void test_string3()
{string s1("hello world");cout << s1.size() << endl;
//capacity 比 实际空间少一个,有一个多的是预留给\0cout << s1.capacity() << endl;cout << s1.max_size() << endl;
}4、string的遍历
void test_string4() {// 遍历方式:下标 + []string s1 = "hello world";for (int i = 0; s1[i]; i++){cout << s1[i] << " ";}cout << endl;//遍历方式2:迭代器string::iterator it1 = s1.begin();while (it1 != s1.end()) { cout << *it1 << " ";++it1;}cout << endl;cout << typeid(it1).name() << endl;//遍历方式3:范围for// 底层:就是迭代器for (auto e : s1) {cout << e << " ";}
}注意:迭代器中的begin和end

5、reverse逆置
void test_string5() //反向迭代器
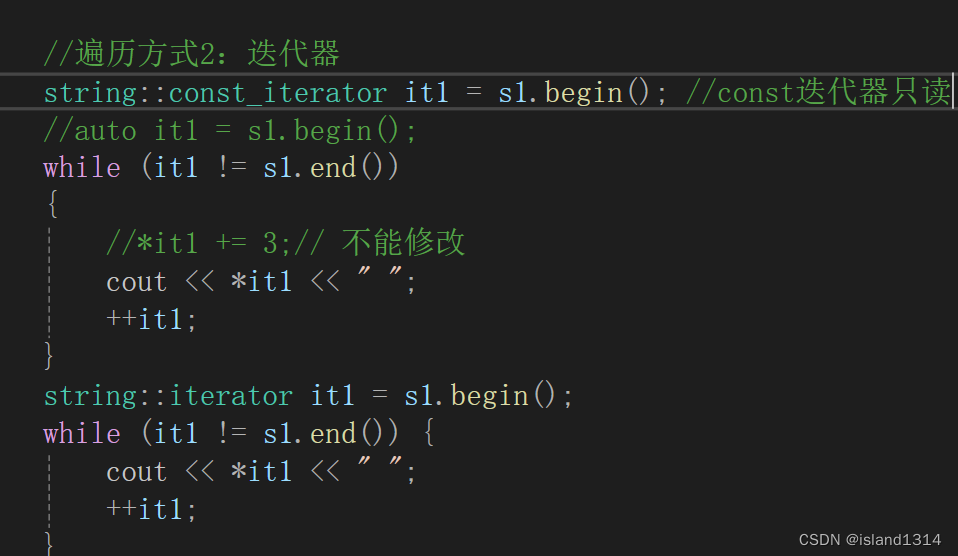
{string s1("hello world");string::const_iterator it1 = s1.begin();//auto it1 = s1.begin();while (it1 != s1.end()){//*it1 += 3;// 不能修改cout << *it1 << " ";++it1;}string s2("hello world");string::reverse_iterator it2 = s2.rbegin();while (it2 != s2.rend()) {*it2 += 3;cout << *it2 << " ";++it2;}
}
6、const
7、sort排序
void test_string6()
{string s1("hello world");cout << s1 <<endl;//按字典序排序sort(s1.begin(), s1.end());//第一个和最后一个参与排序sort(++s1.begin(), --s1.end());//前五个排序sort(s1.begin(), s1.begin() + 5);cout << s1 << endl;
}8、插入删除
a、push_back、append的后插
void test_string7()
{string s1("hello world");cout << s1 << endl;s1.push_back('x');cout << s1 << endl;s1.append(" yyyyyy!! ");cout << s1 << endl;s1 += 'z';s1 += "wwwwww";cout << s1 << endl;
}b、insert插入、erase删除
s.insert(1, "111");//在1位置后插入111
s.erase(1, 2);//从1位置开始删两个
9、resize和reserve
注意:
resize : 影响size 、capacity
reserve : 只影响capacity
void test_string11()
{string s1;s1.resize(5, '0'); //初始值cout << s1 << endl;// 再扩容s1.reserve(100);cout << s1.size() << " " << s1.capacity() << endl;//reserve 在vs下不会缩容,没有规定s1.reserve(20);cout << s1.size() << " " << s1.capacity() << endl;s1.resize(10);cout << s1.size() << " " << s1.capacity() << endl;s1.resize(120);cout << s1.size() << " " << s1.capacity() << endl;//由此发现resize影响capacity、size(当再开辟空间大于原先capacity才会影响capacity), reserve不影响size//插入(空间不够扩容)string s2("hello world");s2.resize(20, 'x'); //不会清掉之前的字符,在后面填写cout << s2 << endl;// 删除s2.resize(5);
}10、查找

a、find、rfind
find : 从前往后查找,并且返回所在下标
rfind : 从后往前查找
substr : 获得子串
void test_string12()
{string s = "aabaabaab";cout << s.find("aa") << endl;//查找字符串“aa”首次出现位置 0cout << s.find("aa", 3) << endl;//查找下标3开始(即第四个字符开始)字符串“aa”首次出现位置 3cout << s.find('a') << endl;//查找字符串'a'首次出现位置 0cout << s.find('a', 3) << endl;//查找下标3开始(即第四个字符开始)字符串“aa”首次出现位置 3cout << s.rfind("aa") << endl;//查找字符串“aa”最后一次出现位置 6
}b、查找第一个大于或大于等于的字符
x=lower_bound(b+1,b+m+1,y)-b;//从[first,last)中找第一个大于等于y的元素的地址,-b是转化为下标
x=upper_bound(b+1,b+m+1,y)-b;//同理,只不过找第一个大于的
c、查找某一字符串中任意字符首次/末次出现位置
cout << s.find_first_of("hark") << endl;
cout << s.find_last_of("a") << endl;
d、查找不是某一字符串中字符的首次/末次出现位置
cout << s.find_first_not_of("hark") << endl;
cout << s.find_last_not_of("hark") << endl;
11、c_str
1、用处可以用在文件使用上,如:
// 文件操作
void TestFile()
{string file("test.cpp");FILE* fout = fopen(file.c_str(), "r");//.c_str()作用是吧一个string串转换成一个C - style的串,// 以"/0"null character结尾,返回的是一个指向该C - style串的常指针。char ch = fgetc(fout);while (ch != EOF){cout << ch;ch = fgetc(fout);}
}2、c_str比较
void test_string13()
{string a = "abc";string b = a;//a.c_str() == b.c_str()比较的是存储字符串位置的地址,// a和b是两个不同的对象,内部数据存储的位置也不相同,因此不相等if (a.c_str() == b.c_str())cout << "True" << endl;else cout << "False" << endl;
}
12、substr 取子串
str = str.substr(cnt); //取从cnt下标开始一直到结束的所有字符
str = str.substr(cnt,m); //取从cnt下标开始的m个字符
13、字符串与数字的相互转化
a、字符串转数字
string s="12";
int y=stoi(s);
b、数字转字符串
string x=to_string(12);
14、大小写转化
transform(s.begin(),s.end(),s.begin(),::tolower);
transform(s.begin(),s.end(),s.begin(),::toupper);
15、sizeof 和strlen在char*和string中的使用
void test_string17()
{char buff1[] = "abcd";char buff2[] = "瓦特";string s1("abcd");cout << sizeof(buff1) << endl; // 5, '\0'算一个字节cout << sizeof(buff2) << endl; // 5,一个汉字两个字节,'\0'算一个字节cout << sizeof(s1) << endl; // 40cout << strlen(buff1) << endl; // 4cout << strlen(buff2) << endl; // 4,一个汉字两个字节//cout << strlen(s1) << endl; // 不能计算
}
16、string的底层实现
类域定义:
namespace bit
{class string {public: //迭代器实现typedef char* iterator;iterator begin();iterator end();//string(); //无参构造//string(const char* str);string(const char* str = ""); //全缺省~string();const char* c_str() const;size_t size() const; //长度char& operator[](size_t pos); //打印private:// char _buff[16];char* _str;size_t _size;size_t _capacity;};
}函数实现:
namespace bit
{//string::string() //{// _str = new char[1] {'\0'};// _size = 0;// _capacity = 0;//}string::iterator string::begin() {return _str;}string::iterator string::end(){return _str + _size;}string::string(const char* str):_str(new char[strlen(str) + 1]), _size(strlen(str)), _capacity(strlen(str)){strcpy(_str, str);}string::~string(){delete[] _str;_str = nullptr;_size = _capacity = 0;}const char* string:: c_str() const{return _str;}size_t string::size() const{return _size;}char& string::operator[](size_t pos){assert(pos < _size);return _str[pos];}}函数测试:
namespace bit{void test_string1(){bit::string s1("hello world");cout << s1.c_str() << endl;bit::string s2;cout << s2.c_str() << endl;for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++){s1[i]++;cout << s1[i] << " ";}cout << endl;//封装:屏蔽了底层实现细节,提供了一种简单通用访问容器的方式string::iterator it1 = s1.begin();while (it1 != s1.end()){cout << *it1 << " ";++it1;}cout << endl;//范围for底层也是迭代器for (auto e : s1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}
}string相关题型:
1、字符串相加
2、仅仅反转字母
3、字符串中第一个唯一字符
4、字符串中最后一个单词长度
5、验证回文串
6、字符串相加
7、反转字符串II
8、反转字符串III
9、字符串相乘
10、找出字符串中第一个只出现一次的字符
