二叉树相关算法
1、二叉树基本操作
二叉树的定义就不在这里多说了,下面这个图就是一个简单的二叉树:
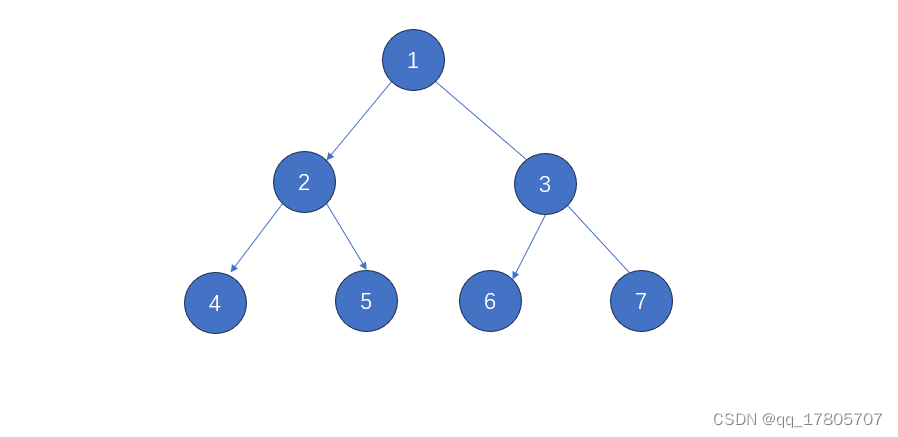 二叉树的三种遍历方式:
二叉树的三种遍历方式:
前序遍历:头左右,也就是先头后左再右:1245367
public static void prePrint(BinaryTreeNode root) {if (root != null) {System.err.print(root.val);prePrint(root.left);prePrint(root.right);}}中序遍历:左头右,也就是先左后头再右:4251637
public static void midPrint(BinaryTreeNode root) {if (root != null) {midPrint(root.left);System.err.print(root.val);midPrint(root.right);}}后序遍历:左头右,也就是先左后右再头:4526731
public static void posPrint(BinaryTreeNode root) {if (root != null) {posPrint(root.left);posPrint(root.right);System.err.print(root.val);}}测试代码:
class BinaryTreeNode {int val;BinaryTreeNode left;BinaryTreeNode right;public BinaryTreeNode(int val) {this.val = val;}public BinaryTreeNode(int val, BinaryTreeNode left, BinaryTreeNode right) {this.val = val;this.left = left;this.right = right;}
} public static void main(String[] args) {BinaryTreeNode one = new BinaryTreeNode(1,new BinaryTreeNode(2, new BinaryTreeNode(4, null, null), new BinaryTreeNode(5, null, null)),new BinaryTreeNode(3, new BinaryTreeNode(6, null, null), new BinaryTreeNode(7, null, null)));prePrint(one);System.err.println();midPrint(one);System.err.println();posPrint(one);}那么我们可以看出来,不论是哪种遍历方式,其在处理左右子节点的时候,逻辑都是一样的,都是要递归处理,不同的只是头结点的输出时机,那么可以优化成下面的代码:
public static void print(BinaryTreeNode root, int type) {switch (type) {case 1:if (root != null) {System.err.print(root.val);print(root.left, 1);print(root.right, 1);}break;case 2:if (root != null) {print(root.left, 2);System.err.print(root.val);print(root.right, 2);}break;case 3:if (root != null) {print(root.left, 3);print(root.right, 3);System.err.print(root.val);}break;}}2、两棵树是否结构一样
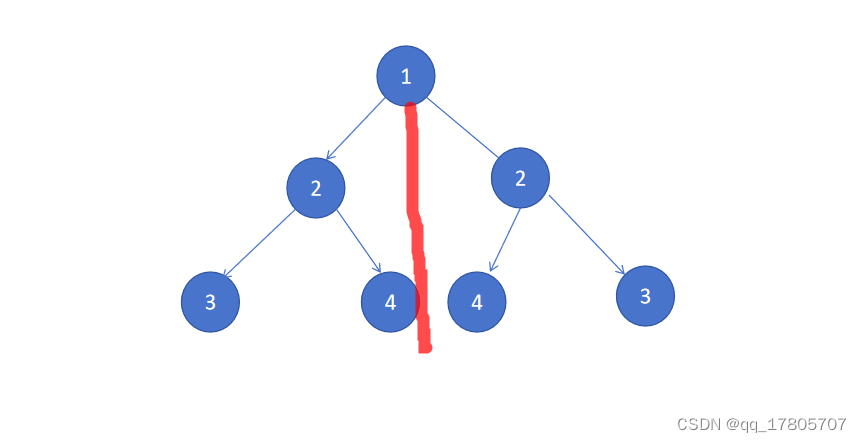
如下面的图中,只有左上角和右上角两棵树的结构是一样的,才算符合条件:

Java实现判断两棵树是否一样:
public static boolean isSameTree(BinaryTreeNode node1, BinaryTreeNode node2) {if (node1 == null ^ node2 == null) {return false;}if (node1 == null && node2 == null) {return true;}return node1.val == node2.val && isSameTree(node1.left, node2.left) && isSameTree(node1.right, node2.right);}@Testpublic void testSame() {BinaryTreeNode one = new BinaryTreeNode(1,new BinaryTreeNode(2, new BinaryTreeNode(4, null, null), new BinaryTreeNode(5, null, null)),new BinaryTreeNode(3, new BinaryTreeNode(6, null, null), new BinaryTreeNode(7, null, null)));BinaryTreeNode two = new BinaryTreeNode(1,new BinaryTreeNode(2, new BinaryTreeNode(4, null, null), new BinaryTreeNode(5, null, null)),new BinaryTreeNode(3, new BinaryTreeNode(6, null, null), new BinaryTreeNode(7, null, null)));System.err.println(isSameTree(one, two));}3、镜面树
镜面树有两种情况:
- 两棵树互为镜面:按照红线对折,可以重叠

- 单棵树两边互为镜面:
 代码实现:
代码实现: public static boolean isMirror(BinaryTreeNode node1, BinaryTreeNode node2) {if (node1 == null ^ node2 == null) {return false;}if (node1 == null && node2 == null) {return true;}return node1.val == node2.val && isMirror(node1.left, node2.right) && isMirror(node1.right, node2.left);}@Testpublic void testMirror() {BinaryTreeNode one = new BinaryTreeNode(1,new BinaryTreeNode(2, new BinaryTreeNode(4, null, null), new BinaryTreeNode(5, null, null)),new BinaryTreeNode(2, new BinaryTreeNode(5, null, null), new BinaryTreeNode(4, null, null)));BinaryTreeNode two = new BinaryTreeNode(1,new BinaryTreeNode(2, new BinaryTreeNode(4, null, null), new BinaryTreeNode(5, null, null)),new BinaryTreeNode(2, new BinaryTreeNode(5, null, null), new BinaryTreeNode(4, null, null)));System.err.println(isMirror(one, two));}
4、树的最大深度
二叉树的最大深度其实就是左子树和右子树的最大深度加一,代码实现如下:
public static int maxDepth(BinaryTreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return 0;}return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;}@Testpublic void testMaxDepth() {BinaryTreeNode two = new BinaryTreeNode(1,new BinaryTreeNode(2, new BinaryTreeNode(4, null, null), new BinaryTreeNode(5, null, null)),new BinaryTreeNode(2, new BinaryTreeNode(5, null, null), new BinaryTreeNode(4, null, null)));System.err.println(maxDepth(two));}5、还原二叉树
给定一个二叉树的前序遍历数组和中序遍历数组,两个数组中都没有重复值,根据这两个数组还原二叉树,返回头结点
解题思路:仍然是采用递归的方式,几个重要的解题点:
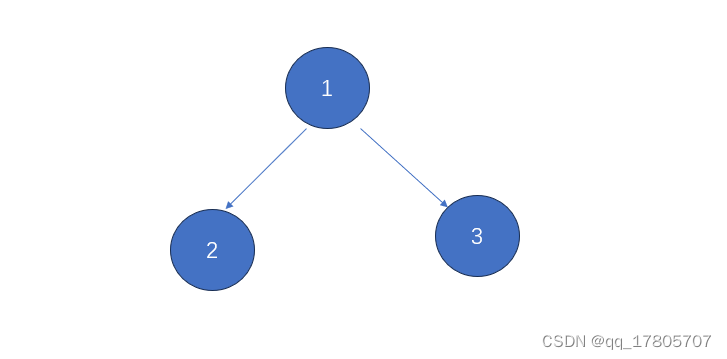
1、前序遍历的第一个元素一定是树的头结点,比如下面这个最基本的二叉树,前序遍历是1,2,3,中序遍历是2,1,3,所以树的头结点一定是1
2、找出中序遍历数组中头结点所在的位置,假设下标为A,那么在前序遍历数组中,从头结点所在下标加1到A(包括两端),以及在中序序遍历数组中从0到A减1(包括两端)的位置都是左子树的节点
比如下面这棵树的头结点是1,在中序遍历数组中的下标是1,那么2就是左子树,再比如文章最前面的第一棵二叉树,前序遍历1245367和中序遍历4251637,根据第二点我们可以得出前序遍历中的245和中序遍历中的425一定是左子树,右子树的逻辑也类似
代码实现:
public static BinaryTreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {// 构建中序遍历数组中元素与索引的映射关系Map<Integer, Integer> inorderMap = new HashMap<>();for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {inorderMap.put(inorder[i], i);}return buildTreeHelper(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1, inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1, inorderMap);}private static BinaryTreeNode buildTreeHelper(int[] preorder, int preStart, int preEnd,int[] inorder, int inStart, int inEnd, Map<Integer, Integer> inorderMap) {if (preStart > preEnd || inStart > inEnd) {return null;}int rootVal = preorder[preStart];BinaryTreeNode root = new BinaryTreeNode(rootVal);if (preStart == preEnd) {//相等的时候说明要么是根节点,要么是到了最后一个节点return root;}int rootIndex = inorderMap.get(rootVal);int leftSize = rootIndex - inStart;root.left = buildTreeHelper(preorder, preStart + 1, preStart + leftSize,inorder, inStart, rootIndex - 1, inorderMap);root.right = buildTreeHelper(preorder, preStart + leftSize + 1, preEnd,inorder, rootIndex + 1, inEnd, inorderMap);return root;}@Testpublic void testBuildTree() {int[] preorder = {1, 2, 4, 5, 3, 6, 7};int[] inorder = {4, 2, 5, 1, 6, 3, 7};
// int[] preorder = {1, 2, 3};
// int[] inorder = {2, 1, 3};BinaryTreeNode root = buildTree(preorder, inorder);print(root, 1);System.err.println();print(root, 2);System.err.println();print(root, 3);}