chapter 3 Free electrons in solid - 3.2 量子自由电子理论对一些现象的解释
3.2 自由电子气的热容 Heat capacity of free electron gas
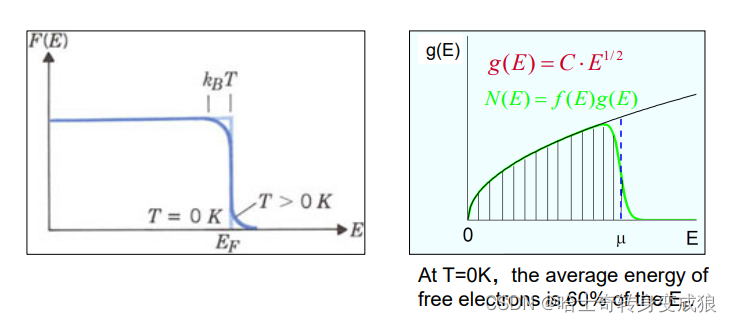
3.2.1 计算自由电子的热容 Calculation of Heat Capacity of free Electrons
T>0K, total energy of free electrons:
E = ∫ E d N = 3 5 N e E F 0 [ 1 + 5 12 π 2 ( k B T E F 0 ) 2 ] E= \int EdN = \frac{3}{5} N_e E_F^0 [1+\frac{5}{12}\pi^2 (\frac{k_B T}{E_F^0})^2] E=∫EdN=53NeEF0[1+125π2(EF0kBT)2]
C V e = ∂ E ∂ T = γ T C_V^e = \frac{\partial E}{\partial T} = \gamma T CVe=∂T∂E=γT
γ = π 2 N e k B 2 2 E F 0 , N e = N Z \gamma = \frac{\pi^2 N_e k_B^2}{2E_F^0},\ \ N_e = NZ γ=2EF0π2NekB2, Ne=NZ
N e N_e Ne: 自由电子数 the total number of free electrons
N: 原子数 the number of atoms
Z: 每个原子提供的价电子数 the number of free electrons provided by one atom
3.2.2 电子热容与声子热容的对比 Comparison of C V e C_V^e CVe and C V l C_V^l CVl
The total heat capacity of a metal includes electron contribution and phonon contribution:
C V = C V e + C V l C_V = C_V^e +C_V^l CV=CVe+CVl
high temperature ( T > Θ D T > \Theta_D T>ΘD): C V e ≪ C V l , C V ≈ C V l C_V^e\ll C_V^l,\ \ C_V \approx C_V^l CVe≪CVl, CV≈CVl
low temperature ( T ≪ Θ D T \ll \Theta_D T≪ΘD): C V = C V e + C V l = γ T + b T 3 C_V = C_V^e + C_V^l = \gamma T+b T^3 CV=CVe+CVl=γT+bT3
3.2.3 固体热容 Heat Capacity of Metal
At low temperature, the electronic contribution may be comparable with the phonon’s contribution.
低温物理中,电子热熔具有重要意义。
C V M e t a l = { C V P h o n o n = b T 3 C V E l e c t r o n = γ T C_V^{Metal}= \begin{cases} C_V^{Phonon} = bT^3 \\ C_V^{Electron} = \gamma T \end{cases} CVMetal={CVPhonon=bT3CVElectron=γT
3.3 电子传输特性 Transport properties of conductive electron
3.3.1 电导率与温度的关系Electrical conductivity vs Temperature
根据德鲁德自由电子模型: σ ∝ T − 1 / 2 \sigma \propto T^{-1/2} σ∝T−1/2
实验结果表明: σ ∝ T − 1 \sigma \propto T^{-1} σ∝T−1
What is the key factor affecting the theoretical electrical conductivity of metals?
Electrical conductivity depends on the DOS at E F E_F EF and the size of the Fermi surface. —Related to its crystal structure and its valent electrons!
影响金属理论电导率的关键因素:态密度和费米面的大小—与晶体结构和价电子有关!
根据德鲁德模型: σ = n e 2 m τ \sigma =\frac{ne^2}{m}\tau σ=mne2τ
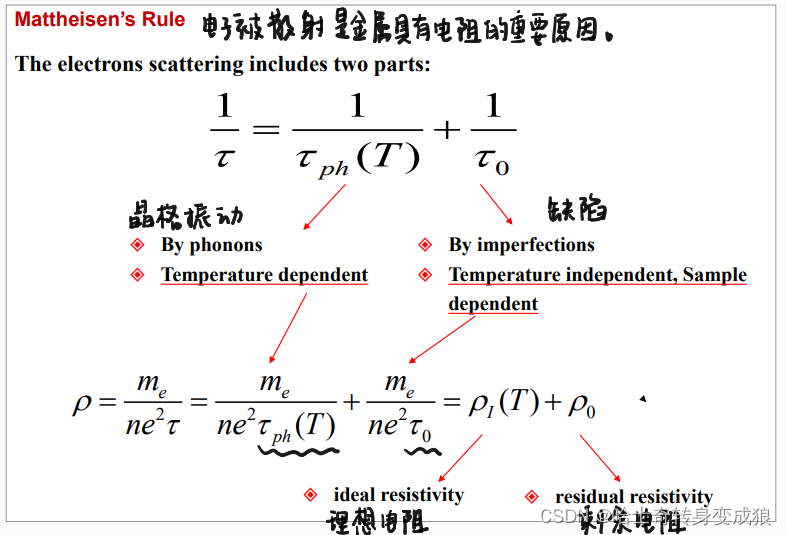
经典理论中, τ \tau τ与温度无关。
τ = 平均自由程 l v R M S \tau = \frac{平均自由程l}{v_{RMS}} τ=vRMS平均自由程l,而 1 2 v ˉ 2 = 3 2 k B T \frac{1}{2}\bar v^2 =\frac{3}{2}k_BT 21vˉ2=23kBT,所以 σ ∝ T − 1 / 2 \sigma \propto T^{-1/2} σ∝T−1/2
根据量子力学的观点,对外界电场产生响应的仅仅为费米能附近的电子,这里的速度 v R M S v_{RMS} vRMS应当为费米速度,而费米速度与温度无关,因此关键在于平均自由程与温度的关系。
晶体中的电子具有波粒二象性,波长不满足布拉格定律,所以电子不会与离子实发生碰撞,而是自由传播(索末菲模型与德鲁德模型之间的差异)。对于理想晶体,电子波在晶体中畅行无阻, l = ∞ l=\infty l=∞。由于晶体缺陷和晶格振动, l ∝ T − 1 l \propto T^{-1} l∝T−1,所以 σ ∝ T − 1 \sigma \propto T^{-1} σ∝T−1。
Mattheisen’s Rule
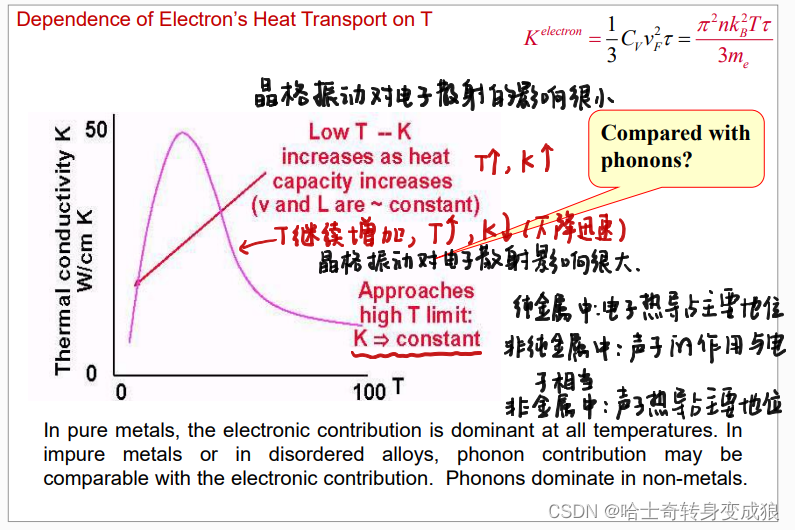
3.3.2 导热系数 Thermal conductivity
Electrons’ Heat Transport
电子热导: K e l e c t r o n = 1 3 C V e ⋅ v ⋅ l = 1 3 C V e ⋅ v F 2 ⋅ τ = π 2 n k B T τ 3 m e K^{electron} = \frac{1}{3}C_V^e \cdot v \cdot l =\frac{1}{3}C_V^e \cdot v_F^2 \cdot \tau = \frac{\pi^2 n k_B T \tau}{3m_e} Kelectron=31CVe⋅v⋅l=31CVe⋅vF2⋅τ=3meπ2nkBTτ
声子热导: K p h o n o n = 1 3 C V l ⋅ v 0 ⋅ λ K^{phonon} = \frac{1}{3}C_V^l \cdot v_0 \cdot \lambda Kphonon=31CVl⋅v0⋅λ
电子热容比声子热容小两个数量级,但费米速度比 v 0 v_0 v0大三个数量级,所以电子热导大于声子热导
The speed of conductive electrons is in the Fermi velocity, which is much higher than that of phonons.
热流密度: J t h e r m a l = − K d T d x J_{thermal} = -K\frac{dT}{dx} Jthermal=−KdxdT
K m e t a l s ≫ K n o n − m e t a l s K_{metals} \gg K_{non-metals} Kmetals≫Knon−metals
3.3.3 魏德曼·弗朗兹定理 Wiedemann-Franz Law
In physics, the Wiedemann–Franz law states that the ratio of the electronic contribution to the thermal conductivity (κ) and the electrical conductivity (σ) of a metal is proportional to the temperature (T).
电导率高,热导率也高。
K σ = L T \frac{K}{\sigma} = LT σK=LT
L:洛伦兹常数,The proportionality constant L is known as the Lorentz number
理论值: L = 2.45 × 1 0 − 8 ( V / K ) 2 L= 2.45\times 10^{-8}(V/K)^2 L=2.45×10−8(V/K)2
K e σ = π 2 3 ( k B e ) 2 T \frac{K_e}{\sigma} = \frac{\pi^2}{3}\left (\frac{k_B}{e} \right)^2 T σKe=3π2(ekB)2T
3.3.4 霍尔效应 Hall effect
In a conductor, an associated electric field (Hall field) is built in the direction J×B when a current J flows across a magnetic field B.
在导体中,当电流J流过磁场B时,会在J×B方向上产生相关的电场(霍尔场)。
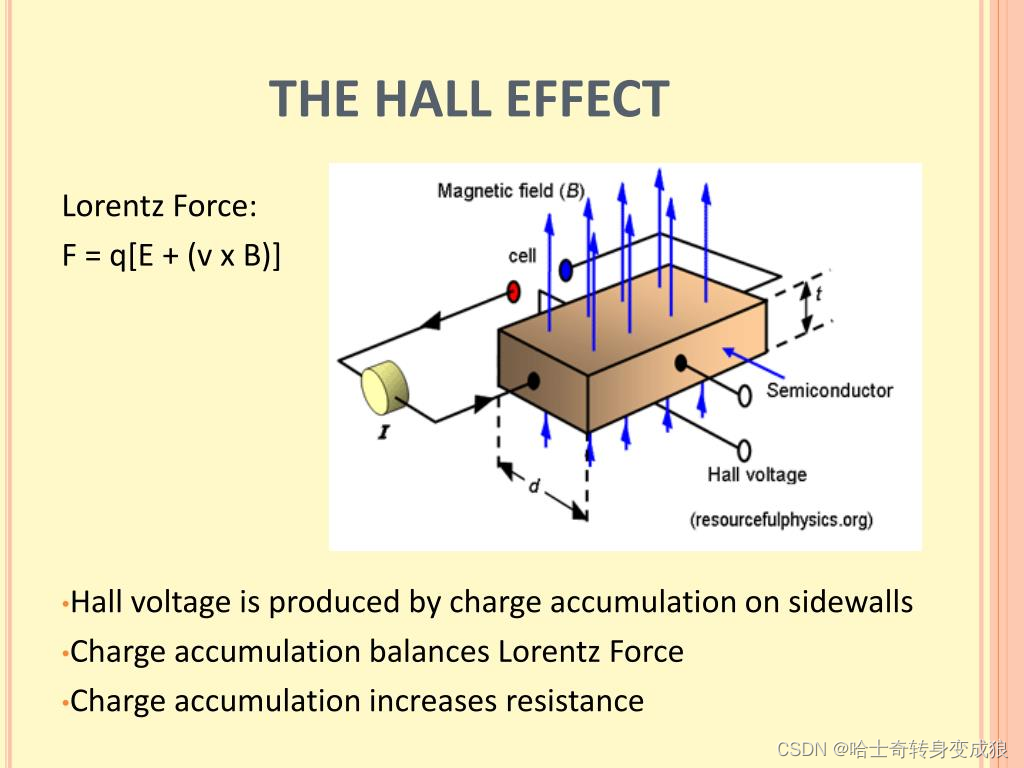
Lorentz force causes the deflection of electrons and then accumulate electrons on one face of the conductor. At stable state, the electrostatic force of Hall field just cancels the Lorentz force duo to magnetic field.
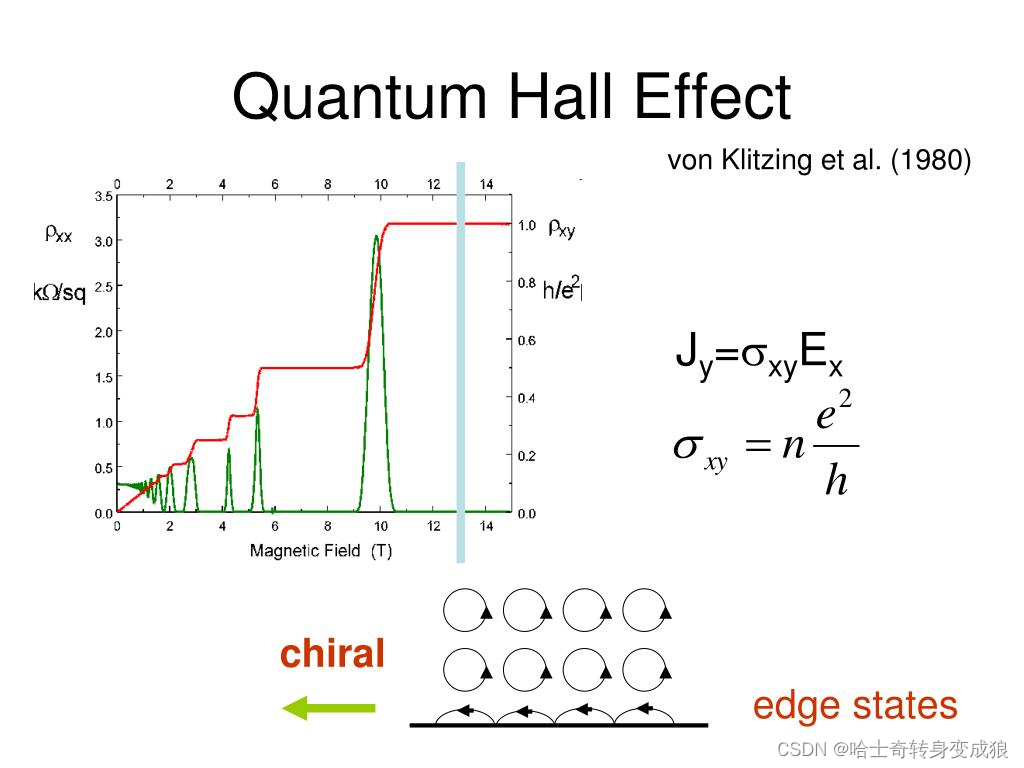
Quantum Hall Effect
In 1985 Klaus von Klitzing won the Nobel Prize for discovery of the quantized Hall effect. In a two-dimensional metal or semiconductor, the Hall effect is also observed, but at low temperatures a series of steps appear in the Hall resistance as a function of magnetic field instead of the monotonic increase. What is more, these steps occur at incredibly precise values of resistance which are the same no matter what sample is investigated. The resistance is quantized in units of h / e 2 h/e^2 h/e2 divided by an integer. This is the QUANTUM HALL EFFECT.
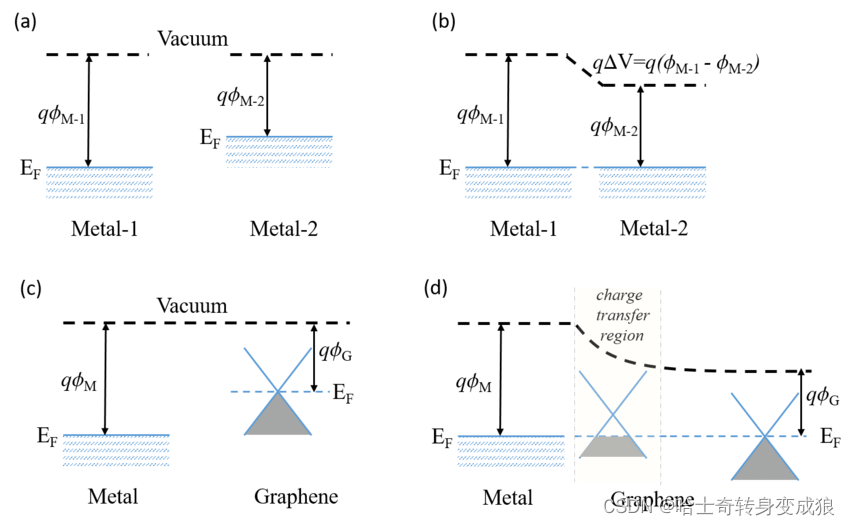
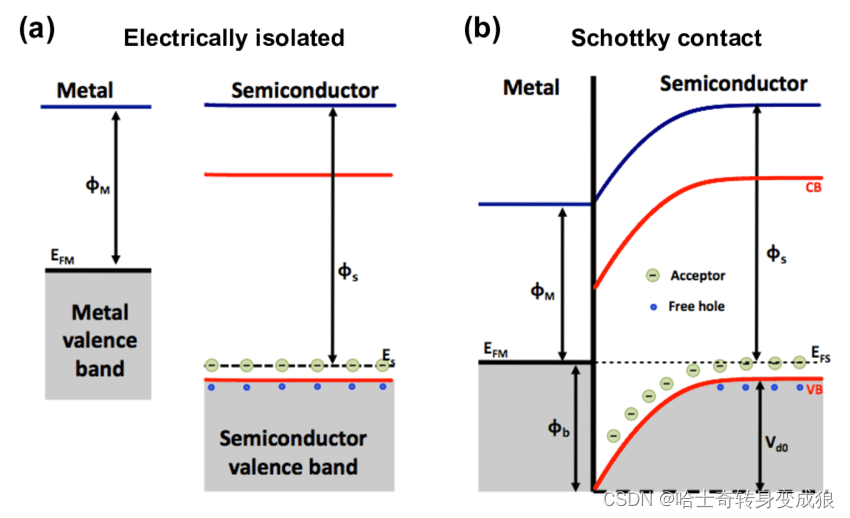
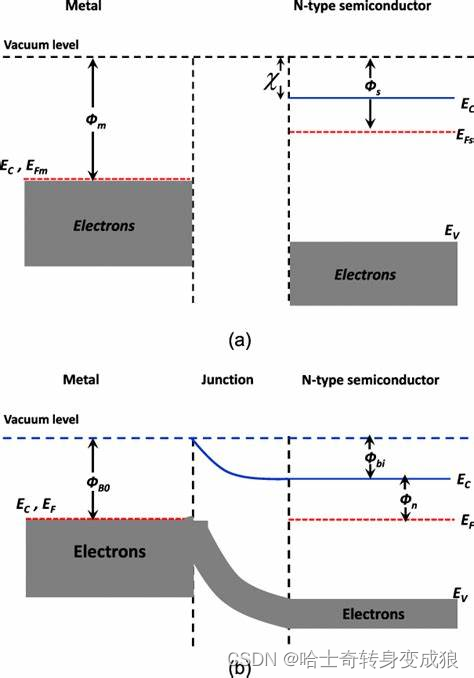
3.4 电子发射与接触电势 Electron emission and contacting voltage
电子发射:电子脱离材料的束缚成为自由电子
- 冷发射Cold electron emission:low pressure , high voltage(尖端放电,场发射)
- 热发射Thermal electron emission: high temperature (高温热钨电镜)
功函数 work function:每个电子脱离晶体发射出来需要的能量the amount of energy per electron is required to emit (i.e. removing from a material). (Analogous to ionization potential)
The work functions of metals change with the temperature.
W = ϕ = V 0 − E F W = \phi = V_0 -E_F W=ϕ=V0−EF
W ~ several eV
V 0 V_0 V0: free electron energy in vacuum
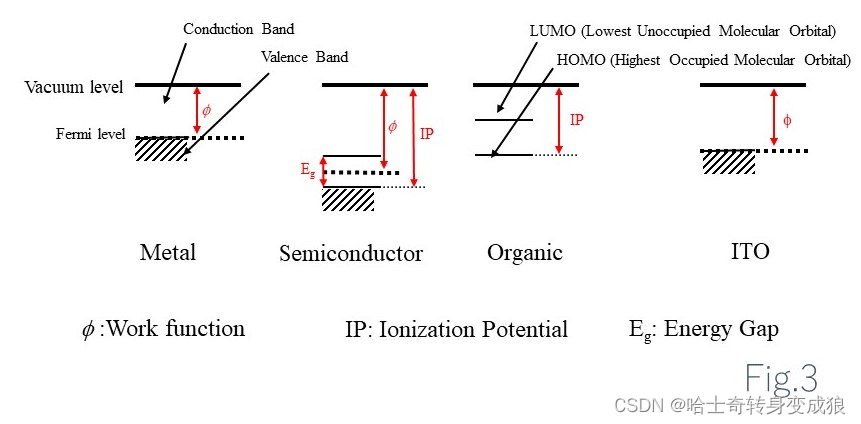
接触电势 contacting voltage:两个不同材料相接触,在界面上产生接触电势
费米能不同,电子自发跃迁,在同一系统中拉平费米能,进而去研究。
接触电势差等于两种材料的功函数之差除以e。
V 12 = 1 e ( W 2 − W 1 ) = 1 2 ( E 1 F − E 2 F ) V_{12}= \frac{1}{e} (W_2 - W_1) = \frac{1}{2}(E_{1F} - E_{2F}) V12=e1(W2−W1)=21(E1F−E2F)