【java基础】Java常用类———包装类
包装类
wrapper
装箱与拆箱
- 装箱:基本类型->包装类; 拆箱: 包装类->基本类型
public class Integer01 {public static void main(String[] args) {//演示int <--> Integer 的装箱和拆箱//jdk5前是手动装箱和拆箱//手动装箱 int->Integerint n1 = 100;Integer integer = new Integer(n1);Integer integer1 = Integer.valueOf(n1);//手动拆箱//Integer -> intint i = integer.intValue();//jdk5后,就可以自动装箱和自动拆箱int n2 = 200;//自动装箱 int->IntegerInteger integer2 = n2; //底层使用的是 Integer.valueOf(n2)//自动拆箱 Integer->intint n3 = integer2; //底层仍然使用的是 intValue()方法}}如果频繁拆装箱的话,也会严重影响系统的性能。我们应该尽量避免不必要的拆装箱操作。
8种包装类
针对8种基本数据类型相应的引用类型——包装类
| 基本数据类型 | 包装类 |
|---|---|
| byte | Byte |
| short | Short |
| int | Integer |
| long | Long |
| char | Character |
| float | Float |
| double | Double |
| boolean | Boolean |
所有包装类都是抽象类Number的子类
缓存机制
Java 基本数据类型的包装类型的大部分都用到了缓存机制来提升性能。
Byte,Short,Integer,Long 这 4 种包装类默认创建了数值 [-128,127] 的相应类型的缓存数据,
只有自动装箱的才有缓存
Character 创建了数值在 [0,127] 范围的缓存数据,
Boolean 直接返回 True or False。
两种浮点数类型的包装类 Float,Double 并没有实现缓存机制。
Integer a1=new Integer(1);
Integer a2=new Integer(1);
System.out.println(a1==a2);//false Integer b1=2;
Integer b2=2;
System.out.println(b1==b2);//true,在[-128,127]之间的自动装箱valueOf使用了缓冲机制,不会创建新的对象 Integer c1=200;
Integer c2=200;
System.out.println(c1==c2);//false
//因此,包装类对象的比较要用equals
System.out.println(c1.equals(c2));//trueBoolean d1=true;
Boolean d2=true;
System.out.println(d1==d2);//true
Integer 缓存源码:
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];return new Integer(i);
}
private static class IntegerCache {static final int low = -128;static final int high;static {// high value may be configured by propertyint h = 127;}
}Character 缓存源码:
public static Character valueOf(char c) {if (c <= 127) { // must cachereturn CharacterCache.cache[(int)c];}return new Character(c);
}private static class CharacterCache {private CharacterCache(){}static final Character cache[] = new Character[127 + 1];static {for (int i = 0; i < cache.length; i++)cache[i] = new Character((char)i);}}如果超出对应范围仍然会去创建新的对象,缓存的范围区间的大小只是在性能和资源之间的权衡。
常用方法
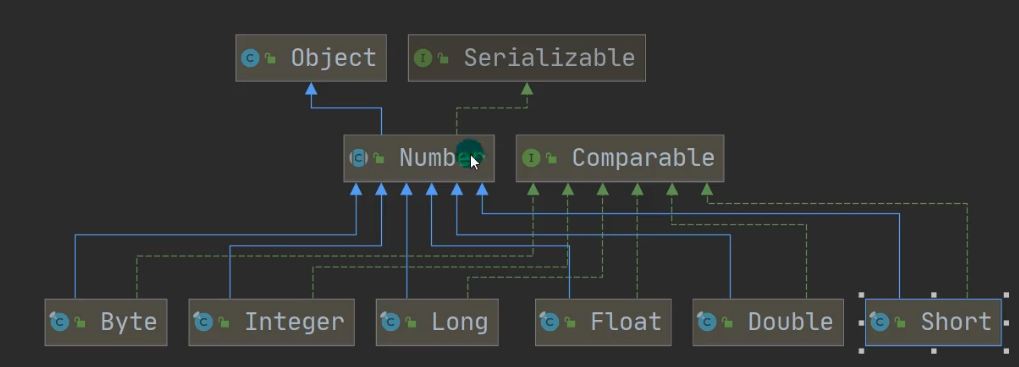
- Number子类实现的方法
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
byte byteValue() , short shortValue(), int intValue() , long longValue(), float floatValue(), double doubleValue() | Converts the value of this Number object to the primitive data type returned.把包装类对象转换成基本数据类型 |
int compareTo(Byte anotherByte) , int compareTo(Double anotherDouble), int compareTo(Float anotherFloat), int compareTo(Integer anotherInteger), int compareTo(Long anotherLong), int compareTo(Short anotherShort) | Compares this Number object to the argument.比较函数 |
boolean equals(Object obj) | Determines whether this number object is equal to the argument. The methods return true if the argument is not null and is an object of the same type and with the same numeric value. There are some extra requirements for Double and Float objects that are described in the Java API documentation.是否相等 |
Integer的方法
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
static Integer decode(String s) | Decodes a string into an integer. Can accept string representations of decimal, octal, or hexadecimal numbers as input. |
static int parseInt(String s) | Returns an integer (decimal only). |
static int parseInt(String s, int radix) | Returns an integer, given a string representation of decimal, binary, octal, or hexadecimal (radix equals 10, 2, 8, or 16 respectively) numbers as input. |
String toString() | Returns a String object representing the value of this Integer. |
static String toString(int i) | Returns a String object representing the specified integer. |
static Integer valueOf(int i) | Returns an Integer object holding the value of the specified primitive. |
static Integer valueOf(String s) | Returns an Integer object holding the value of the specified string representation. |
static Integer valueOf(String s, int radix) | Returns an Integer object holding the integer value of the specified string representation, parsed with the value of radix. For example, if s = “333” and radix = 8, the method returns the base-ten integer equivalent of the octal number 333. |
eg
public class WrapperMethod {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(Integer.MIN_VALUE); //返回最小值System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE);//返回最大值System.out.println(Character.isDigit('a'));//判断是不是数字System.out.println(Character.isLetter('a'));//判断是不是字母System.out.println(Character.isUpperCase('a'));//判断是不是大写System.out.println(Character.isLowerCase('a'));//判断是不是小写System.out.println(Character.isWhitespace('a'));//判断是不是空格System.out.println(Character.toUpperCase('a'));//转成大写System.out.println(Character.toLowerCase('A'));//转成小写}
}