【机器学习】Gradient Descent for Logistic Regression
Gradient Descent for Logistic Regression
- 1. 数据集(多变量)
- 2. 逻辑梯度下降
- 3. 梯度下降的实现及代码描述
- 3.1 计算梯度
- 3.2 梯度下降
- 4. 数据集(单变量)
- 附录
导入所需的库
import copy, math
import numpy as np
%matplotlib widget
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from lab_utils_common import dlc, plot_data, plt_tumor_data, sigmoid, compute_cost_logistic
from plt_quad_logistic import plt_quad_logistic, plt_prob
plt.style.use('./deeplearning.mplstyle')
1. 数据集(多变量)
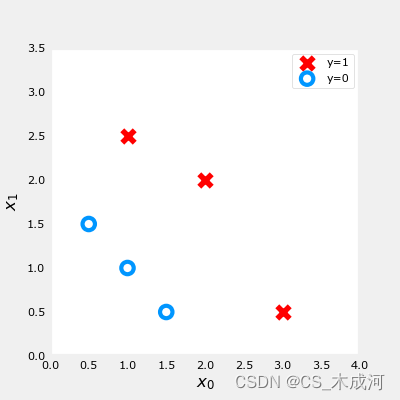
X_train = np.array([[0.5, 1.5], [1,1], [1.5, 0.5], [3, 0.5], [2, 2], [1, 2.5]])
y_train = np.array([0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1])
fig,ax = plt.subplots(1,1,figsize=(4,4))
plot_data(X_train, y_train, ax)ax.axis([0, 4, 0, 3.5])
ax.set_ylabel('$x_1$', fontsize=12)
ax.set_xlabel('$x_0$', fontsize=12)
plt.show()
2. 逻辑梯度下降
梯度下降计算公式:
repeat until convergence: { w j = w j − α ∂ J ( w , b ) ∂ w j for j := 0..n-1 b = b − α ∂ J ( w , b ) ∂ b } \begin{align*} &\text{repeat until convergence:} \; \lbrace \\ & \; \; \;w_j = w_j - \alpha \frac{\partial J(\mathbf{w},b)}{\partial w_j} \tag{1} \; & \text{for j := 0..n-1} \\ & \; \; \; \; \;b = b - \alpha \frac{\partial J(\mathbf{w},b)}{\partial b} \\ &\rbrace \end{align*} repeat until convergence:{wj=wj−α∂wj∂J(w,b)b=b−α∂b∂J(w,b)}for j := 0..n-1(1)
其中,对于所有的 j j j 每次迭代同时更新 w j w_j wj ,
∂ J ( w , b ) ∂ w j = 1 m ∑ i = 0 m − 1 ( f w , b ( x ( i ) ) − y ( i ) ) x j ( i ) ∂ J ( w , b ) ∂ b = 1 m ∑ i = 0 m − 1 ( f w , b ( x ( i ) ) − y ( i ) ) \begin{align*} \frac{\partial J(\mathbf{w},b)}{\partial w_j} &= \frac{1}{m} \sum\limits_{i = 0}^{m-1} (f_{\mathbf{w},b}(\mathbf{x}^{(i)}) - y^{(i)})x_{j}^{(i)} \tag{2} \\ \frac{\partial J(\mathbf{w},b)}{\partial b} &= \frac{1}{m} \sum\limits_{i = 0}^{m-1} (f_{\mathbf{w},b}(\mathbf{x}^{(i)}) - y^{(i)}) \tag{3} \end{align*} ∂wj∂J(w,b)∂b∂J(w,b)=m1i=0∑m−1(fw,b(x(i))−y(i))xj(i)=m1i=0∑m−1(fw,b(x(i))−y(i))(2)(3)
- m 是训练集样例的数量
- f w , b ( x ( i ) ) f_{\mathbf{w},b}(x^{(i)}) fw,b(x(i)) 是模型预测值, y ( i ) y^{(i)} y(i) 是目标值
- 对于逻辑回归模型
z = w ⋅ x + b z = \mathbf{w} \cdot \mathbf{x} + b z=w⋅x+b
f w , b ( x ) = g ( z ) f_{\mathbf{w},b}(x) = g(z) fw,b(x)=g(z)
其中 g ( z ) g(z) g(z) 是 sigmoid 函数: g ( z ) = 1 1 + e − z g(z) = \frac{1}{1+e^{-z}} g(z)=1+e−z1
3. 梯度下降的实现及代码描述
实现梯度下降算法需要两步:
- 循环实现上面等式(1). 即下面的
gradient_descent - 当前梯度的计算等式(2, 3). 即下面的
compute_gradient_logistic
3.1 计算梯度
对于所有的 w j w_j wj 和 b b b,实现等式 (2),(3)
-
初始化变量计算
dj_dw和dj_db -
对每个样例:
- 计算误差 g ( w ⋅ x ( i ) + b ) − y ( i ) g(\mathbf{w} \cdot \mathbf{x}^{(i)} + b) - \mathbf{y}^{(i)} g(w⋅x(i)+b)−y(i)
- 对于这个样例中的每个输入值 x j ( i ) x_{j}^{(i)} xj(i) ,
- 误差乘以输入值 x j ( i ) x_{j}^{(i)} xj(i), 然后加到对应的
dj_dw中. (上述等式2)
- 误差乘以输入值 x j ( i ) x_{j}^{(i)} xj(i), 然后加到对应的
- 累加误差到
dj_db(上述等式3)
-
dj_db和dj_dw都除以样例总数 m m m -
在Numpy中 x ( i ) \mathbf{x}^{(i)} x(i) 是
X[i,:]或者X[i], x j ( i ) x_{j}^{(i)} xj(i) 是X[i,j]
代码描述:
def compute_gradient_logistic(X, y, w, b): """Computes the gradient for linear regression Args:X (ndarray (m,n): Data, m examples with n featuresy (ndarray (m,)): target valuesw (ndarray (n,)): model parameters b (scalar) : model parameterReturnsdj_dw (ndarray (n,)): The gradient of the cost w.r.t. the parameters w. dj_db (scalar) : The gradient of the cost w.r.t. the parameter b. """m,n = X.shapedj_dw = np.zeros((n,)) #(n,)dj_db = 0.for i in range(m):f_wb_i = sigmoid(np.dot(X[i],w) + b) #(n,)(n,)=scalarerr_i = f_wb_i - y[i] #scalarfor j in range(n):dj_dw[j] = dj_dw[j] + err_i * X[i,j] #scalardj_db = dj_db + err_idj_dw = dj_dw/m #(n,)dj_db = dj_db/m #scalarreturn dj_db, dj_dw
测试一下
X_tmp = np.array([[0.5, 1.5], [1,1], [1.5, 0.5], [3, 0.5], [2, 2], [1, 2.5]])
y_tmp = np.array([0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1])
w_tmp = np.array([2.,3.])
b_tmp = 1.
dj_db_tmp, dj_dw_tmp = compute_gradient_logistic(X_tmp, y_tmp, w_tmp, b_tmp)
print(f"dj_db: {dj_db_tmp}" )
print(f"dj_dw: {dj_dw_tmp.tolist()}" )

3.2 梯度下降
实现上述公式(1),代码为:
def gradient_descent(X, y, w_in, b_in, alpha, num_iters): """Performs batch gradient descentArgs:X (ndarray (m,n) : Data, m examples with n featuresy (ndarray (m,)) : target valuesw_in (ndarray (n,)): Initial values of model parameters b_in (scalar) : Initial values of model parameteralpha (float) : Learning ratenum_iters (scalar) : number of iterations to run gradient descentReturns:w (ndarray (n,)) : Updated values of parametersb (scalar) : Updated value of parameter """# An array to store cost J and w's at each iteration primarily for graphing laterJ_history = []w = copy.deepcopy(w_in) #avoid modifying global w within functionb = b_infor i in range(num_iters):# Calculate the gradient and update the parametersdj_db, dj_dw = compute_gradient_logistic(X, y, w, b) # Update Parameters using w, b, alpha and gradientw = w - alpha * dj_dw b = b - alpha * dj_db # Save cost J at each iterationif i<100000: # prevent resource exhaustion J_history.append( compute_cost_logistic(X, y, w, b) )# Print cost every at intervals 10 times or as many iterations if < 10if i% math.ceil(num_iters / 10) == 0:print(f"Iteration {i:4d}: Cost {J_history[-1]} ")return w, b, J_history #return final w,b and J history for graphing
运行一下:
w_tmp = np.zeros_like(X_train[0])
b_tmp = 0.
alph = 0.1
iters = 10000w_out, b_out, _ = gradient_descent(X_train, y_train, w_tmp, b_tmp, alph, iters)
print(f"\nupdated parameters: w:{w_out}, b:{b_out}")

梯度下降的结果可视化:
fig,ax = plt.subplots(1,1,figsize=(5,4))
# plot the probability
plt_prob(ax, w_out, b_out)# Plot the original data
ax.set_ylabel(r'$x_1$')
ax.set_xlabel(r'$x_0$')
ax.axis([0, 4, 0, 3.5])
plot_data(X_train,y_train,ax)# Plot the decision boundary
x0 = -b_out/w_out[1]
x1 = -b_out/w_out[0]
ax.plot([0,x0],[x1,0], c=dlc["dlblue"], lw=1)
plt.show()
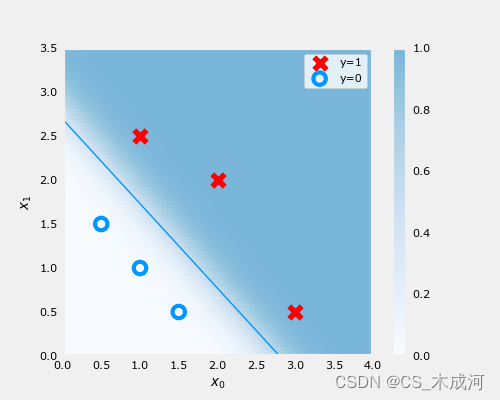
在上图中,阴影部分表示概率 y=1,决策边界是概率为0.5的直线。
4. 数据集(单变量)
导入数据绘图可视化,此时参数为 w w w, b b b:
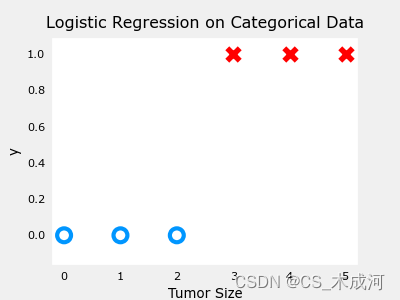
x_train = np.array([0., 1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
y_train = np.array([0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1])fig,ax = plt.subplots(1,1,figsize=(4,3))
plt_tumor_data(x_train, y_train, ax)
plt.show()
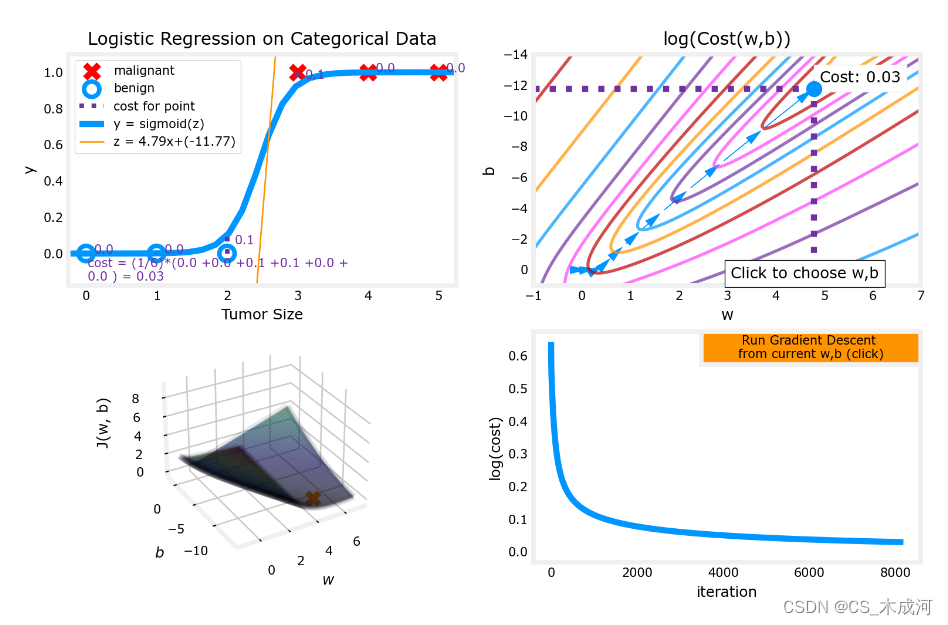
w_range = np.array([-1, 7])
b_range = np.array([1, -14])
quad = plt_quad_logistic( x_train, y_train, w_range, b_range )
附录
lab_utils_common.py 源码:
"""
lab_utils_commoncontains common routines and variable definitionsused by all the labs in this week.by contrast, specific, large plotting routines will be in separate filesand are generally imported into the week where they are used.those files will import this file
"""
import copy
import math
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.patches import FancyArrowPatch
from ipywidgets import Outputnp.set_printoptions(precision=2)dlc = dict(dlblue = '#0096ff', dlorange = '#FF9300', dldarkred='#C00000', dlmagenta='#FF40FF', dlpurple='#7030A0')
dlblue = '#0096ff'; dlorange = '#FF9300'; dldarkred='#C00000'; dlmagenta='#FF40FF'; dlpurple='#7030A0'
dlcolors = [dlblue, dlorange, dldarkred, dlmagenta, dlpurple]
plt.style.use('./deeplearning.mplstyle')def sigmoid(z):"""Compute the sigmoid of zParameters----------z : array_likeA scalar or numpy array of any size.Returns-------g : array_likesigmoid(z)"""z = np.clip( z, -500, 500 ) # protect against overflowg = 1.0/(1.0+np.exp(-z))return g##########################################################
# Regression Routines
##########################################################def predict_logistic(X, w, b):""" performs prediction """return sigmoid(X @ w + b)def predict_linear(X, w, b):""" performs prediction """return X @ w + bdef compute_cost_logistic(X, y, w, b, lambda_=0, safe=False):"""Computes cost using logistic loss, non-matrix versionArgs:X (ndarray): Shape (m,n) matrix of examples with n featuresy (ndarray): Shape (m,) target valuesw (ndarray): Shape (n,) parameters for predictionb (scalar): parameter for predictionlambda_ : (scalar, float) Controls amount of regularization, 0 = no regularizationsafe : (boolean) True-selects under/overflow safe algorithmReturns:cost (scalar): cost"""m,n = X.shapecost = 0.0for i in range(m):z_i = np.dot(X[i],w) + b #(n,)(n,) or (n,) ()if safe: #avoids overflowscost += -(y[i] * z_i ) + log_1pexp(z_i)else:f_wb_i = sigmoid(z_i) #(n,)cost += -y[i] * np.log(f_wb_i) - (1 - y[i]) * np.log(1 - f_wb_i) # scalarcost = cost/mreg_cost = 0if lambda_ != 0:for j in range(n):reg_cost += (w[j]**2) # scalarreg_cost = (lambda_/(2*m))*reg_costreturn cost + reg_costdef log_1pexp(x, maximum=20):''' approximate log(1+exp^x)https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/475589/numerical-computation-of-cross-entropy-in-practiceArgs:x : (ndarray Shape (n,1) or (n,) inputout : (ndarray Shape matches x output ~= np.log(1+exp(x))'''out = np.zeros_like(x,dtype=float)i = x <= maximumni = np.logical_not(i)out[i] = np.log(1 + np.exp(x[i]))out[ni] = x[ni]return outdef compute_cost_matrix(X, y, w, b, logistic=False, lambda_=0, safe=True):"""Computes the cost using using matricesArgs:X : (ndarray, Shape (m,n)) matrix of examplesy : (ndarray Shape (m,) or (m,1)) target value of each examplew : (ndarray Shape (n,) or (n,1)) Values of parameter(s) of the modelb : (scalar ) Values of parameter of the modelverbose : (Boolean) If true, print out intermediate value f_wbReturns:total_cost: (scalar) cost"""m = X.shape[0]y = y.reshape(-1,1) # ensure 2Dw = w.reshape(-1,1) # ensure 2Dif logistic:if safe: #safe from overflowz = X @ w + b #(m,n)(n,1)=(m,1)cost = -(y * z) + log_1pexp(z)cost = np.sum(cost)/m # (scalar)else:f = sigmoid(X @ w + b) # (m,n)(n,1) = (m,1)cost = (1/m)*(np.dot(-y.T, np.log(f)) - np.dot((1-y).T, np.log(1-f))) # (1,m)(m,1) = (1,1)cost = cost[0,0] # scalarelse:f = X @ w + b # (m,n)(n,1) = (m,1)cost = (1/(2*m)) * np.sum((f - y)**2) # scalarreg_cost = (lambda_/(2*m)) * np.sum(w**2) # scalartotal_cost = cost + reg_cost # scalarreturn total_cost # scalardef compute_gradient_matrix(X, y, w, b, logistic=False, lambda_=0):"""Computes the gradient using matricesArgs:X : (ndarray, Shape (m,n)) matrix of examplesy : (ndarray Shape (m,) or (m,1)) target value of each examplew : (ndarray Shape (n,) or (n,1)) Values of parameters of the modelb : (scalar ) Values of parameter of the modellogistic: (boolean) linear if false, logistic if truelambda_: (float) applies regularization if non-zeroReturnsdj_dw: (array_like Shape (n,1)) The gradient of the cost w.r.t. the parameters wdj_db: (scalar) The gradient of the cost w.r.t. the parameter b"""m = X.shape[0]y = y.reshape(-1,1) # ensure 2Dw = w.reshape(-1,1) # ensure 2Df_wb = sigmoid( X @ w + b ) if logistic else X @ w + b # (m,n)(n,1) = (m,1)err = f_wb - y # (m,1)dj_dw = (1/m) * (X.T @ err) # (n,m)(m,1) = (n,1)dj_db = (1/m) * np.sum(err) # scalardj_dw += (lambda_/m) * w # regularize # (n,1)return dj_db, dj_dw # scalar, (n,1)def gradient_descent(X, y, w_in, b_in, alpha, num_iters, logistic=False, lambda_=0, verbose=True):"""Performs batch gradient descent to learn theta. Updates theta by takingnum_iters gradient steps with learning rate alphaArgs:X (ndarray): Shape (m,n) matrix of examplesy (ndarray): Shape (m,) or (m,1) target value of each examplew_in (ndarray): Shape (n,) or (n,1) Initial values of parameters of the modelb_in (scalar): Initial value of parameter of the modellogistic: (boolean) linear if false, logistic if truelambda_: (float) applies regularization if non-zeroalpha (float): Learning ratenum_iters (int): number of iterations to run gradient descentReturns:w (ndarray): Shape (n,) or (n,1) Updated values of parameters; matches incoming shapeb (scalar): Updated value of parameter"""# An array to store cost J and w's at each iteration primarily for graphing laterJ_history = []w = copy.deepcopy(w_in) #avoid modifying global w within functionb = b_inw = w.reshape(-1,1) #prep for matrix operationsy = y.reshape(-1,1)for i in range(num_iters):# Calculate the gradient and update the parametersdj_db,dj_dw = compute_gradient_matrix(X, y, w, b, logistic, lambda_)# Update Parameters using w, b, alpha and gradientw = w - alpha * dj_dwb = b - alpha * dj_db# Save cost J at each iterationif i<100000: # prevent resource exhaustionJ_history.append( compute_cost_matrix(X, y, w, b, logistic, lambda_) )# Print cost every at intervals 10 times or as many iterations if < 10if i% math.ceil(num_iters / 10) == 0:if verbose: print(f"Iteration {i:4d}: Cost {J_history[-1]} ")return w.reshape(w_in.shape), b, J_history #return final w,b and J history for graphingdef zscore_normalize_features(X):"""computes X, zcore normalized by columnArgs:X (ndarray): Shape (m,n) input data, m examples, n featuresReturns:X_norm (ndarray): Shape (m,n) input normalized by columnmu (ndarray): Shape (n,) mean of each featuresigma (ndarray): Shape (n,) standard deviation of each feature"""# find the mean of each column/featuremu = np.mean(X, axis=0) # mu will have shape (n,)# find the standard deviation of each column/featuresigma = np.std(X, axis=0) # sigma will have shape (n,)# element-wise, subtract mu for that column from each example, divide by std for that columnX_norm = (X - mu) / sigmareturn X_norm, mu, sigma#check our work
#from sklearn.preprocessing import scale
#scale(X_orig, axis=0, with_mean=True, with_std=True, copy=True)######################################################
# Common Plotting Routines
######################################################def plot_data(X, y, ax, pos_label="y=1", neg_label="y=0", s=80, loc='best' ):""" plots logistic data with two axis """# Find Indices of Positive and Negative Examplespos = y == 1neg = y == 0pos = pos.reshape(-1,) #work with 1D or 1D y vectorsneg = neg.reshape(-1,)# Plot examplesax.scatter(X[pos, 0], X[pos, 1], marker='x', s=s, c = 'red', label=pos_label)ax.scatter(X[neg, 0], X[neg, 1], marker='o', s=s, label=neg_label, facecolors='none', edgecolors=dlblue, lw=3)ax.legend(loc=loc)ax.figure.canvas.toolbar_visible = Falseax.figure.canvas.header_visible = Falseax.figure.canvas.footer_visible = Falsedef plt_tumor_data(x, y, ax):""" plots tumor data on one axis """pos = y == 1neg = y == 0ax.scatter(x[pos], y[pos], marker='x', s=80, c = 'red', label="malignant")ax.scatter(x[neg], y[neg], marker='o', s=100, label="benign", facecolors='none', edgecolors=dlblue,lw=3)ax.set_ylim(-0.175,1.1)ax.set_ylabel('y')ax.set_xlabel('Tumor Size')ax.set_title("Logistic Regression on Categorical Data")ax.figure.canvas.toolbar_visible = Falseax.figure.canvas.header_visible = Falseax.figure.canvas.footer_visible = False# Draws a threshold at 0.5
def draw_vthresh(ax,x):""" draws a threshold """ylim = ax.get_ylim()xlim = ax.get_xlim()ax.fill_between([xlim[0], x], [ylim[1], ylim[1]], alpha=0.2, color=dlblue)ax.fill_between([x, xlim[1]], [ylim[1], ylim[1]], alpha=0.2, color=dldarkred)ax.annotate("z >= 0", xy= [x,0.5], xycoords='data',xytext=[30,5],textcoords='offset points')d = FancyArrowPatch(posA=(x, 0.5), posB=(x+3, 0.5), color=dldarkred,arrowstyle='simple, head_width=5, head_length=10, tail_width=0.0',)ax.add_artist(d)ax.annotate("z < 0", xy= [x,0.5], xycoords='data',xytext=[-50,5],textcoords='offset points', ha='left')f = FancyArrowPatch(posA=(x, 0.5), posB=(x-3, 0.5), color=dlblue,arrowstyle='simple, head_width=5, head_length=10, tail_width=0.0',)ax.add_artist(f)
plt_quad_logistic.py 源码:
"""
plt_quad_logistic.pyinteractive plot and supporting routines showing logistic regression
"""import time
from matplotlib import cm
import matplotlib.colors as colors
from matplotlib.gridspec import GridSpec
from matplotlib.widgets import Button
from matplotlib.patches import FancyArrowPatch
from ipywidgets import Output
from lab_utils_common import np, plt, dlc, dlcolors, sigmoid, compute_cost_matrix, gradient_descent# for debug
#output = Output() # sends hidden error messages to display when using widgets
#display(output)class plt_quad_logistic:''' plots a quad plot showing logistic regression '''# pylint: disable=too-many-instance-attributes# pylint: disable=too-many-locals# pylint: disable=missing-function-docstring# pylint: disable=attribute-defined-outside-initdef __init__(self, x_train,y_train, w_range, b_range):# setup figurefig = plt.figure( figsize=(10,6))fig.canvas.toolbar_visible = Falsefig.canvas.header_visible = Falsefig.canvas.footer_visible = Falsefig.set_facecolor('#ffffff') #whitegs = GridSpec(2, 2, figure=fig)ax0 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0, 0])ax1 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0, 1])ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs[1, 0], projection='3d')ax3 = fig.add_subplot(gs[1,1])pos = ax3.get_position().get_points() ##[[lb_x,lb_y], [rt_x, rt_y]]h = 0.05 width = 0.2axcalc = plt.axes([pos[1,0]-width, pos[1,1]-h, width, h]) #lx,by,w,hax = np.array([ax0, ax1, ax2, ax3, axcalc])self.fig = figself.ax = axself.x_train = x_trainself.y_train = y_trainself.w = 0. #initial point, non-arrayself.b = 0.# initialize subplotsself.dplot = data_plot(ax[0], x_train, y_train, self.w, self.b)self.con_plot = contour_and_surface_plot(ax[1], ax[2], x_train, y_train, w_range, b_range, self.w, self.b)self.cplot = cost_plot(ax[3])# setup eventsself.cid = fig.canvas.mpl_connect('button_press_event', self.click_contour)self.bcalc = Button(axcalc, 'Run Gradient Descent \nfrom current w,b (click)', color=dlc["dlorange"])self.bcalc.on_clicked(self.calc_logistic)# @output.capture() # debugdef click_contour(self, event):''' called when click in contour '''if event.inaxes == self.ax[1]: #contour plotself.w = event.xdataself.b = event.ydataself.cplot.re_init()self.dplot.update(self.w, self.b)self.con_plot.update_contour_wb_lines(self.w, self.b)self.con_plot.path.re_init(self.w, self.b)self.fig.canvas.draw()# @output.capture() # debugdef calc_logistic(self, event):''' called on run gradient event '''for it in [1, 8,16,32,64,128,256,512,1024,2048,4096]:w, self.b, J_hist = gradient_descent(self.x_train.reshape(-1,1), self.y_train.reshape(-1,1),np.array(self.w).reshape(-1,1), self.b, 0.1, it,logistic=True, lambda_=0, verbose=False)self.w = w[0,0]self.dplot.update(self.w, self.b)self.con_plot.update_contour_wb_lines(self.w, self.b)self.con_plot.path.add_path_item(self.w,self.b)self.cplot.add_cost(J_hist)time.sleep(0.3)self.fig.canvas.draw()class data_plot:''' handles data plot '''# pylint: disable=missing-function-docstring# pylint: disable=attribute-defined-outside-initdef __init__(self, ax, x_train, y_train, w, b):self.ax = axself.x_train = x_trainself.y_train = y_trainself.m = x_train.shape[0]self.w = wself.b = bself.plt_tumor_data()self.draw_logistic_lines(firsttime=True)self.mk_cost_lines(firsttime=True)self.ax.autoscale(enable=False) # leave plot scales the same after initial setupdef plt_tumor_data(self):x = self.x_trainy = self.y_trainpos = y == 1neg = y == 0self.ax.scatter(x[pos], y[pos], marker='x', s=80, c = 'red', label="malignant")self.ax.scatter(x[neg], y[neg], marker='o', s=100, label="benign", facecolors='none',edgecolors=dlc["dlblue"],lw=3)self.ax.set_ylim(-0.175,1.1)self.ax.set_ylabel('y')self.ax.set_xlabel('Tumor Size')self.ax.set_title("Logistic Regression on Categorical Data")def update(self, w, b):self.w = wself.b = bself.draw_logistic_lines()self.mk_cost_lines()def draw_logistic_lines(self, firsttime=False):if not firsttime:self.aline[0].remove()self.bline[0].remove()self.alegend.remove()xlim = self.ax.get_xlim()x_hat = np.linspace(*xlim, 30)y_hat = sigmoid(np.dot(x_hat.reshape(-1,1), self.w) + self.b)self.aline = self.ax.plot(x_hat, y_hat, color=dlc["dlblue"],label="y = sigmoid(z)")f_wb = np.dot(x_hat.reshape(-1,1), self.w) + self.bself.bline = self.ax.plot(x_hat, f_wb, color=dlc["dlorange"], lw=1,label=f"z = {np.squeeze(self.w):0.2f}x+({self.b:0.2f})")self.alegend = self.ax.legend(loc='upper left')def mk_cost_lines(self, firsttime=False):''' makes vertical cost lines'''if not firsttime:for artist in self.cost_items:artist.remove()self.cost_items = []cstr = f"cost = (1/{self.m})*("ctot = 0label = 'cost for point'addedbreak = Falsefor p in zip(self.x_train,self.y_train):f_wb_p = sigmoid(self.w*p[0]+self.b)c_p = compute_cost_matrix(p[0].reshape(-1,1), p[1],np.array(self.w), self.b, logistic=True, lambda_=0, safe=True)c_p_txt = c_pa = self.ax.vlines(p[0], p[1],f_wb_p, lw=3, color=dlc["dlpurple"], ls='dotted', label=label)label='' #just onecxy = [p[0], p[1] + (f_wb_p-p[1])/2]b = self.ax.annotate(f'{c_p_txt:0.1f}', xy=cxy, xycoords='data',color=dlc["dlpurple"],xytext=(5, 0), textcoords='offset points')cstr += f"{c_p_txt:0.1f} +"if len(cstr) > 38 and addedbreak is False:cstr += "\n"addedbreak = Truectot += c_pself.cost_items.extend((a,b))ctot = ctot/(len(self.x_train))cstr = cstr[:-1] + f") = {ctot:0.2f}"## todo.. figure out how to get this textbox to extend to the width of the subplotc = self.ax.text(0.05,0.02,cstr, transform=self.ax.transAxes, color=dlc["dlpurple"])self.cost_items.append(c)class contour_and_surface_plot:''' plots combined in class as they have similar operations '''# pylint: disable=missing-function-docstring# pylint: disable=attribute-defined-outside-initdef __init__(self, axc, axs, x_train, y_train, w_range, b_range, w, b):self.x_train = x_trainself.y_train = y_trainself.axc = axcself.axs = axs#setup useful ranges and common linspacesb_space = np.linspace(*b_range, 100)w_space = np.linspace(*w_range, 100)# get cost for w,b ranges for contour and 3Dtmp_b,tmp_w = np.meshgrid(b_space,w_space)z = np.zeros_like(tmp_b)for i in range(tmp_w.shape[0]):for j in range(tmp_w.shape[1]):z[i,j] = compute_cost_matrix(x_train.reshape(-1,1), y_train, tmp_w[i,j], tmp_b[i,j],logistic=True, lambda_=0, safe=True)if z[i,j] == 0:z[i,j] = 1e-9### plot contour ###CS = axc.contour(tmp_w, tmp_b, np.log(z),levels=12, linewidths=2, alpha=0.7,colors=dlcolors)axc.set_title('log(Cost(w,b))')axc.set_xlabel('w', fontsize=10)axc.set_ylabel('b', fontsize=10)axc.set_xlim(w_range)axc.set_ylim(b_range)self.update_contour_wb_lines(w, b, firsttime=True)axc.text(0.7,0.05,"Click to choose w,b", bbox=dict(facecolor='white', ec = 'black'), fontsize = 10,transform=axc.transAxes, verticalalignment = 'center', horizontalalignment= 'center')#Surface plot of the cost function J(w,b)axs.plot_surface(tmp_w, tmp_b, z, cmap = cm.jet, alpha=0.3, antialiased=True)axs.plot_wireframe(tmp_w, tmp_b, z, color='k', alpha=0.1)axs.set_xlabel("$w$")axs.set_ylabel("$b$")axs.zaxis.set_rotate_label(False)axs.xaxis.set_pane_color((1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0))axs.yaxis.set_pane_color((1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0))axs.zaxis.set_pane_color((1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0))axs.set_zlabel("J(w, b)", rotation=90)axs.view_init(30, -120)axs.autoscale(enable=False)axc.autoscale(enable=False)self.path = path(self.w,self.b, self.axc) # initialize an empty path, avoids existance checkdef update_contour_wb_lines(self, w, b, firsttime=False):self.w = wself.b = bcst = compute_cost_matrix(self.x_train.reshape(-1,1), self.y_train, np.array(self.w), self.b,logistic=True, lambda_=0, safe=True)# remove lines and re-add on contour plot and 3d plotif not firsttime:for artist in self.dyn_items:artist.remove()a = self.axc.scatter(self.w, self.b, s=100, color=dlc["dlblue"], zorder= 10, label="cost with \ncurrent w,b")b = self.axc.hlines(self.b, self.axc.get_xlim()[0], self.w, lw=4, color=dlc["dlpurple"], ls='dotted')c = self.axc.vlines(self.w, self.axc.get_ylim()[0] ,self.b, lw=4, color=dlc["dlpurple"], ls='dotted')d = self.axc.annotate(f"Cost: {cst:0.2f}", xy= (self.w, self.b), xytext = (4,4), textcoords = 'offset points',bbox=dict(facecolor='white'), size = 10)#Add point in 3D surface plote = self.axs.scatter3D(self.w, self.b, cst , marker='X', s=100)self.dyn_items = [a,b,c,d,e]class cost_plot:""" manages cost plot for plt_quad_logistic """# pylint: disable=missing-function-docstring# pylint: disable=attribute-defined-outside-initdef __init__(self,ax):self.ax = axself.ax.set_ylabel("log(cost)")self.ax.set_xlabel("iteration")self.costs = []self.cline = self.ax.plot(0,0, color=dlc["dlblue"])def re_init(self):self.ax.clear()self.__init__(self.ax)def add_cost(self,J_hist):self.costs.extend(J_hist)self.cline[0].remove()self.cline = self.ax.plot(self.costs)class path:''' tracks paths during gradient descent on contour plot '''# pylint: disable=missing-function-docstring# pylint: disable=attribute-defined-outside-initdef __init__(self, w, b, ax):''' w, b at start of path '''self.path_items = []self.w = wself.b = bself.ax = axdef re_init(self, w, b):for artist in self.path_items:artist.remove()self.path_items = []self.w = wself.b = bdef add_path_item(self, w, b):a = FancyArrowPatch(posA=(self.w, self.b), posB=(w, b), color=dlc["dlblue"],arrowstyle='simple, head_width=5, head_length=10, tail_width=0.0',)self.ax.add_artist(a)self.path_items.append(a)self.w = wself.b = b#-----------
# related to the logistic gradient descent lab
#----------def truncate_colormap(cmap, minval=0.0, maxval=1.0, n=100):""" truncates color map """new_cmap = colors.LinearSegmentedColormap.from_list('trunc({n},{a:.2f},{b:.2f})'.format(n=cmap.name, a=minval, b=maxval),cmap(np.linspace(minval, maxval, n)))return new_cmapdef plt_prob(ax, w_out,b_out):""" plots a decision boundary but include shading to indicate the probability """#setup useful ranges and common linspacesx0_space = np.linspace(0, 4 , 100)x1_space = np.linspace(0, 4 , 100)# get probability for x0,x1 rangestmp_x0,tmp_x1 = np.meshgrid(x0_space,x1_space)z = np.zeros_like(tmp_x0)for i in range(tmp_x0.shape[0]):for j in range(tmp_x1.shape[1]):z[i,j] = sigmoid(np.dot(w_out, np.array([tmp_x0[i,j],tmp_x1[i,j]])) + b_out)cmap = plt.get_cmap('Blues')new_cmap = truncate_colormap(cmap, 0.0, 0.5)pcm = ax.pcolormesh(tmp_x0, tmp_x1, z,norm=cm.colors.Normalize(vmin=0, vmax=1),cmap=new_cmap, shading='nearest', alpha = 0.9)ax.figure.colorbar(pcm, ax=ax)
