快速了解MyBatis---映射关系多对一
文章目录
- 映射关系多对一
- 映射关系-官方文档
- 映射关系多对1-基本介绍
- 基本介绍
- 注意细节
- 映射关系多对1-映射方式
- 映射方式
- 配置Mapper.xml 方式-应用实例
- 注解实现多对1 映射-应用实例
映射关系多对一
映射关系-官方文档
文档地址: https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/sqlmap-xml.html
映射关系多对1-基本介绍
基本介绍
- 项目中多对1 的关系是一个基本的映射关系, 多对1, 也可以理解成是1 对多.
- User — Pet: 一个用户可以养多只宠物
- Dep —Emp : 一个部门可以有多个员工
注意细节
- 我们直接讲双向的多对一的关系,单向的多对一比双向的多对一简单。
- 在实际的项目开发中, 要求会使用双向的多对一的映射关系
- 什么是双向的多对一的关系: 比如通过User 可以查询到对应的Pet, 反过来,通过Pet 也可以级联查询到对应的User 信息.
- 多对多的关系,是在多对1 的基础上扩展.
映射关系多对1-映射方式
映射方式
方式1:通过配置XxxMapper.xml 实现多对1
方式2:通过注解的方式实现多对1
配置Mapper.xml 方式-应用实例
需求说明: 实现级联查询,通过user 的id 可以查询到用户信息,并可以查询到关联的pet信息,
反过来,通过Pet 的id 可以查询到Pet 的信息,并且可以级联查询到它的主人User对象信息。
- 创建mybatis_user 和mybatis_pet 表
CREATE TABLE mybatis_user
(id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,NAME VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL DEFAULT ''
)CHARSET=utf8 ;CREATE TABLE mybatis_pet
(id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,nickname VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',user_id INT ,FOREIGN KEY (user_id) REFERENCES mybatis_user(id)
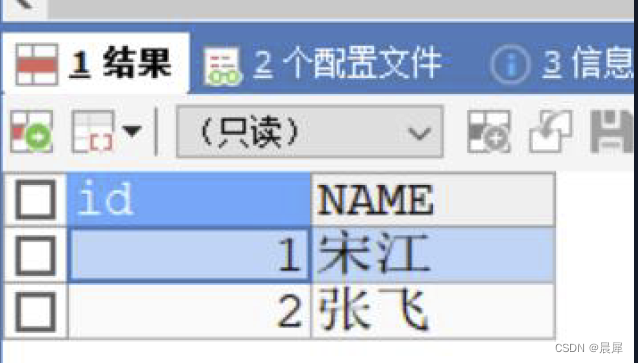
)CHARSET=utf8 ;INSERT INTO mybatis_user
VALUES(NULL,'宋江'),(NULL,'张飞');
INSERT INTO mybatis_pet
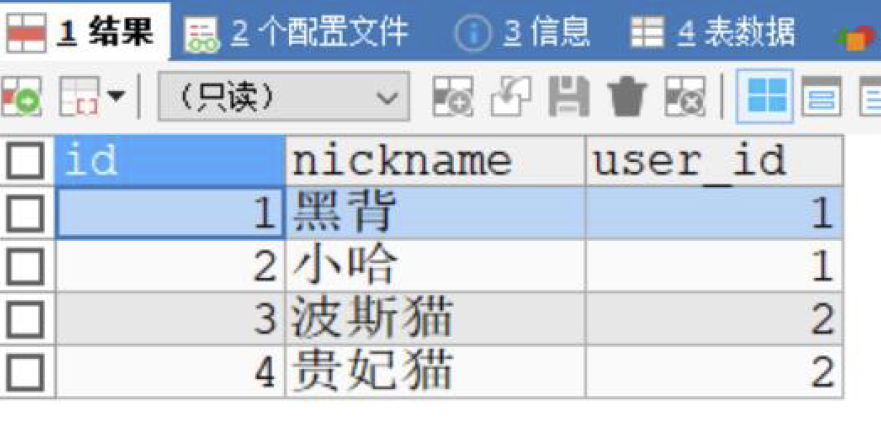
VALUES(1,'黑背',1),(2,'小哈',1);
INSERT INTO mybatis_pet
VALUES(3,'波斯猫',2),(4,'贵妃猫',2);SELECT * FROM mybatis_user;
SELECT * FROM mybatis_pet;
- 创建src\main\java\com\nlc\entity\Pet.java
public class Pet {private Integer id;private String nickname;//一个pet对应一个主人 User对象private User user;public Integer getId() {return id;}public void setId(Integer id) {this.id = id;}public String getNickname() {return nickname;}public void setNickname(String nickname) {this.nickname = nickname;}public User getUser() {return user;}public void setUser(User user) {this.user = user;}}创建src\main\java\com\nlc\entity\User.java
public class User {private Integer id;private String name;//因为一个user可以养多个宠物,mybatis 使用集合List<Pet>体现这个关系private List<Pet> pets;public Integer getId() {return id;}public void setId(Integer id) {this.id = id;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public List<Pet> getPets() {return pets;}public void setPets(List<Pet> pets) {this.pets = pets;}//这toString会带来麻烦=>会造成StackOverFlow//@Override//public String toString() {// return "User{" +// "id=" + id +// ", name='" + name + '\'' +// ", pets=" + pets +// '}';//}
}
-
创建PetMapper.java
public interface PetMapper {//通过User的id来获取pet对象,可能有多个,因此使用List接收public List<Pet> getPetByUserId(Integer userId);//通过pet的id获取Pet对象, 同时会查询到pet对象关联的user对象public Pet getPetById(Integer id); }创建UserMapper.java
public interface UserMapper {//通过id获取User对象public User getUserById(Integer id);}
-
创建UserMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper nameNlcace="com.nlc.mapper.UserMapper"><!--解读1、一定要想一想我们前面1-1是如何实现2、配置/实现 public User getUserById(Integer id);3、思路(1) 先通过user-id 查询得到user信息 (2) 再根据user-id查询对应的pet信息并映射到User-List<Pet> pets--><resultMap id="UserResultMap" type="User"><id property="id" column="id"/><result property="name" column="name"/><!--解读:因为pets属性是集合,因此这里需要是collection标签来处理1. ofType="Pet" 指定返回的集合中存放的数据类型Pet2. collection 表示 pets 是一个集合3. property="pets" 是返回的user对象的属性 pets4. column="id" SELECT * FROM `mybatis_user` WHERE `id` = #{id} 返回的id字段对应的值--><collection property="pets" column="id" ofType="Pet"select="com.nlc.mapper.PetMapper.getPetByUserId"/></resultMap><select id="getUserById" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="UserResultMap">SELECT * FROM `mybatis_user` WHERE `id` = #{id}</select></mapper> -
创建PetMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper nameNlcace="com.nlc.mapper.PetMapper"><!--1、通过User的id来获取pet对象,可能有多个,因此使用List接收2、public List<Pet> getPetByUserId(Integer userId);3. 完成的思路和前面大体相同.--><resultMap id="PetResultMap" type="Pet"><id property="id" column="id"/><result property="nickname" column="nickname"/><association property="user" column="user_id"select="com.nlc.mapper.UserMapper.getUserById" /></resultMap><select id="getPetByUserId" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="PetResultMap">SELECT * FROM `mybatis_pet` WHERE `user_id` = #{userId}</select><!--说明1. 注意体会resultMap带来好处, 直接复用2. 实现/配置public Pet getPetById(Integer id);3. 通过pet的id获取Pet对象--><select id="getPetById" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="PetResultMap">SELECT * FROM `mybatis_pet` WHERE `id` = #{id}</select>
</mapper>
-
创建PetMapperTest.java 完成测试
public class PetMapperTest {//属性private SqlSession sqlSession;private PetMapper petMapper;//初始化@Beforepublic void init() {//获取到sqlSessionsqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession();petMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(PetMapper.class);}@Testpublic void getPetByUserId() {List<Pet> pets = petMapper.getPetByUserId(2);for (Pet pet : pets) {System.out.println("pet信息-" + pet.getId() + "-" + pet.getNickname());User user = pet.getUser();System.out.println("user信息 name-" + user.getName());}if(sqlSession != null) {sqlSession.close();}}@Testpublic void getPetById() {Pet pet = petMapper.getPetById(2);System.out.println("pet信息-" + pet.getId() + "-" + pet.getNickname());User user = pet.getUser();System.out.println("user信息-" + user.getId() + "-" + user.getName());if(sqlSession != null) {sqlSession.close();}} } -
创建UserMapperTest.java 完成测试
public class UserMapperTest {//属性private SqlSession sqlSession;private UserMapper userMapper;//初始化@Beforepublic void init() {//获取到sqlSessionsqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession();userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);}@Testpublic void getUserById() {User user = userMapper.getUserById(2);System.out.println("user信息-" + user.getId() + "-" + user.getName());List<Pet> pets = user.getPets();for (Pet pet : pets) {System.out.println("养的宠物信息-" + pet.getId() + "-" + pet.getNickname());}if(sqlSession != null) {sqlSession.close();}} }
注解实现多对1 映射-应用实例
需求说明: 通过注解的方式来实现下面的多对1 的映射关系,实现级联查询,
完成前面完成的任务,通过User–>Pet 也可Pet->User , 在实际开发中推荐使用配置方式来做
- 创建UserMapperAnnotation.java
// UserMapperAnnotation:以注解的方式来配置多对一
public interface UserMapperAnnotation {//通过id获取User对象/*** 1. 注解的配置就是对应的Mapper.xml文件配置的,改写* 2.* 1、一定要想一想我们前面1-1是如何实现* 2、配置/实现 public User getUserById(Integer id);* 3、思路(1) 先通过user-id 查询得到user信息 (2) 再根据user-id查询对应的pet信息* 并映射到User-List<Pet> pets* <resultMap id="UserResultMap" type="User">* <id property="id" column="id"/>* <result property="name" column="name"/>* 1. ofType="Pet" 指定返回的集合中存放的数据类型Pet* 2. collection 表示 pets 是一个集合* 3. property="pets" 是返回的user对象的属性 pets* 4. column="id" SELECT * FROM `mybatis_user` WHERE `id` = #{id} 返回的id字段对应的值* <collection property="pets" column="id" ofType="Pet"* select="com.nlc.mapper.PetMapper.getPetByUserId"/>* </resultMap>* <select id="getUserById" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="UserResultMap">* SELECT * FROM `mybatis_user` WHERE `id` = #{id}* </select>*/@Select("SELECT * FROM `mybatis_user` WHERE `id` = #{id}")@Results({@Result(id = true, property = "id", column = "id"),@Result(property = "name", column = "name"),//这里注意,pets属性对应的是集合@Result(property = "pets",column = "id",many = @Many(select = "com.nlc.mapper.PetMapperAnnotation.getPetByUserId"))})public User getUserById(Integer id);
}
- 创建PetMapperAnnotation.java
public interface PetMapperAnnotation {//通过User的id来获取pet对象,可能有多个,因此使用List接收/*** 1、通过User的id来获取pet对象,可能有多个,因此使用List接收* 2、public List<Pet> getPetByUserId(Integer userId);* 3. 完成的思路和前面大体相同.* <resultMap id="PetResultMap" type="Pet">* <id property="id" column="id"/>* <result property="nickname" column="nickname"/>* <association property="user" column="user_id"* select="com.nlc.mapper.UserMapper.getUserById" />* </resultMap>* <select id="getPetByUserId" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="PetResultMap">* SELECT * FROM `mybatis_pet` WHERE `user_id` = #{userId}* </select>*///id = "PetResultMap" 就是给我们的Results[Result Map] 指定一个名字//目的是为了后面复用@Select("SELECT * FROM `mybatis_pet` WHERE `user_id` = #{userId}")@Results(id = "PetResultMap", value = {@Result(id = true, property = "id", column = "id"),@Result(property = "nickname", column = "nickname"),@Result(property = "user",column = "user_id",one = @One(select = "com.nlc.mapper.UserMapperAnnotation.getUserById"))})public List<Pet> getPetByUserId(Integer userId);//通过pet的id获取Pet对象, 同时会查询到pet对象关联的user对象/*** <select id="getPetById" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="PetResultMap">* SELECT * FROM `mybatis_pet` WHERE `id` = #{id}* </select>* @ResultMap("PetResultMap") 使用/引用我们上面定义的 Results[ResultMap]*/@Select("SELECT * FROM `mybatis_pet` WHERE `id` = #{id}")@ResultMap("PetResultMap")public Pet getPetById(Integer id);
}- 创建UserMapperAnnotationTest.java 完成测试
public class UserMapperAnnotationTest {//属性private SqlSession sqlSession;private UserMapperAnnotation userMapperAnnotation;//初始化@Beforepublic void init() {//获取到sqlSessionsqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession();userMapperAnnotation = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapperAnnotation.class);}@Testpublic void getUserById() {User user = userMapperAnnotation.getUserById(2);System.out.println("user信息-" + user.getId() + "-" + user.getName());List<Pet> pets = user.getPets();for (Pet pet : pets) {System.out.println("宠物信息-" + pet.getId() + "-" + pet.getNickname());}if(sqlSession != null) {sqlSession.close();}}
}
- 创建PetMapperAnnotationTest.java 完成测试
public class PetMapperAnnotationTest {//属性private SqlSession sqlSession;private PetMapperAnnotation petMapperAnnotation;//初始化@Beforepublic void init() {//获取到sqlSessionsqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession();petMapperAnnotation = sqlSession.getMapper(PetMapperAnnotation.class);}@Testpublic void getPetByUserId() {List<Pet> pets = petMapperAnnotation.getPetByUserId(1);for (Pet pet : pets) {System.out.println("宠物信息-" + pet.getId() + "-" + pet.getNickname());}if(sqlSession != null) {sqlSession.close();}}@Testpublic void getPetById() {Pet pet = petMapperAnnotation.getPetById(1);System.out.println("pet信息-" + pet.getId() + "-" +pet.getNickname());User user = pet.getUser();System.out.println("user信息-" + user.getId() + "-" + user.getName());if(sqlSession != null) {sqlSession.close();}}
}
