CompletableFuture 详解
目录
简单介绍
常见操作
创建 CompletableFuture
new 关键字
静态工厂方法
处理异步结算的结果
简单介绍
CompletableFuture 同时实现了 Future 和 CompletionStage 接口。
public class CompletableFuture<T> implements Future<T>, CompletionStage<T> {
}
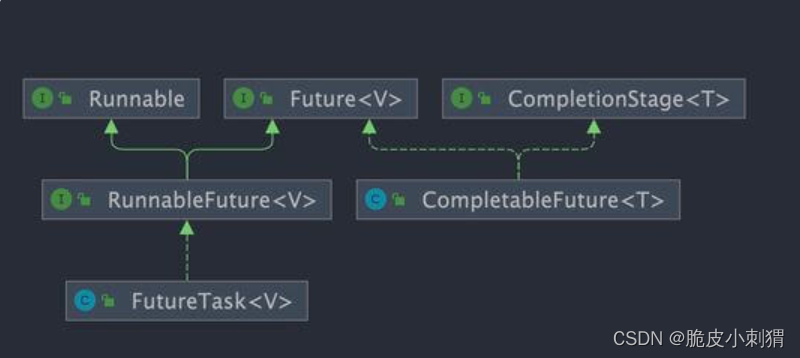
CompletableFuture 除了提供了更为好用和强大的 Future 特性之外,还提供了函数式编程的能力。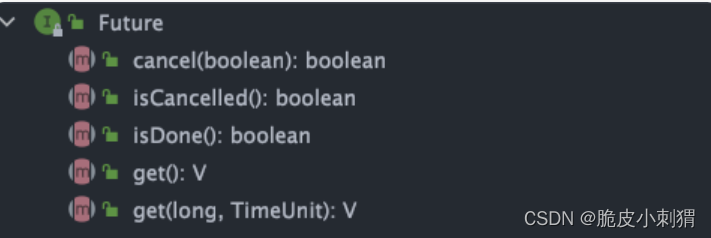
Future 接口有 5 个方法:
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning):尝试取消执行任务。boolean isCancelled():判断任务是否被取消。boolean isDone():判断任务是否已经被执行完成。get():等待任务执行完成并获取运算结果。get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit):多了一个超时时间。
CompletionStage 接口描述了一个异步计算的阶段。很多计算可以分成多个阶段或步骤,此时可以通过它将所有步骤组合起来,形成异步计算的流水线。
CompletionStage 接口中的方法比较多,CompletableFuture 的函数式能力就是这个接口赋予的。从这个接口的方法参数你就可以发现其大量使用了 Java8 引入的函数式编程。
常见操作
创建 CompletableFuture
常见的创建 CompletableFuture 对象的方法如下:
- 通过 new 关键字。
- 基于
CompletableFuture自带的静态工厂方法:runAsync()、supplyAsync()。
new 关键字
通过 new 关键字创建 CompletableFuture 对象这种使用方式可以看作是将 CompletableFuture 当做 Future 来使用。
下面咱们来看一个简单的案例。
我们通过创建了一个结果值类型为 RpcResponse<Object> 的 CompletableFuture,你可以把 resultFuture 看作是异步运算结果的载体。
CompletableFuture<RpcResponse<Object>> resultFuture = new CompletableFuture<>();
假设在未来的某个时刻,我们得到了最终的结果。这时,我们可以调用 complete() 方法为其传入结果,这表示 resultFuture 已经被完成了。
// complete() 方法只能调用一次,后续调用将被忽略。
resultFuture.complete(rpcResponse);
你可以通过 isDone() 方法来检查是否已经完成。
public boolean isDone() {return result != null;
}
获取异步计算的结果也非常简单,直接调用 get() 方法即可。调用 get() 方法的线程会阻塞直到 CompletableFuture 完成运算。
rpcResponse = completableFuture.get();
如果你已经知道计算的结果的话,可以使用静态方法 completedFuture() 来创建 CompletableFuture 。
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("hello!");
assertEquals("hello!", future.get());
completedFuture() 方法底层调用的是带参数的 new 方法,只不过,这个方法不对外暴露。
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> completedFuture(U value) {return new CompletableFuture<U>((value == null) ? NIL : value);
}
静态工厂方法
这两个方法可以帮助我们封装计算逻辑。
static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier);
// 使用自定义线程池(推荐)
static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor);
static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable);
// 使用自定义线程池(推荐)
static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor);
runAsync() 方法接受的参数是 Runnable ,这是一个函数式接口,不允许返回值。当你需要异步操作且不关心返回结果的时候可以使用 runAsync() 方法。
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {public abstract void run();
}
supplyAsync() 方法接受的参数是 Supplier<U> ,这也是一个函数式接口,U 是返回结果值的类型。
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Supplier<T> {/*** Gets a result.** @return a result*/T get();
}
当你需要异步操作且关心返回结果的时候,可以使用 supplyAsync() 方法。
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> System.out.println("hello!"));
future.get();// 输出 "hello!"
CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "hello!");
assertEquals("hello!", future2.get());
处理异步结算的结果
当我们获取到异步计算的结果之后,还可以对其进行进一步的处理,比较常用的方法有下面几个:
thenApply()thenAccept()thenRun()whenComplete()
thenApply() 方法接受一个 Function 实例,用它来处理结果。
// 沿用上一个任务的线程池
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) {return uniApplyStage(null, fn);
}//使用默认的 ForkJoinPool 线程池(不推荐)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) {return uniApplyStage(defaultExecutor(), fn);
}
// 使用自定义线程池(推荐)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn, Executor executor) {return uniApplyStage(screenExecutor(executor), fn);
}
如果你不需要从回调函数中获取返回结果,可以使用 thenAccept() 或者 thenRun()。这两个方法的区别在于 thenRun() 不能访问异步计算的结果。
thenAccept() 方法的参数是 Consumer<? super T> 。
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action) {return uniAcceptStage(null, action);
}public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action) {return uniAcceptStage(defaultExecutor(), action);
}public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action,Executor executor) {return uniAcceptStage(screenExecutor(executor), action);
}
