Linux下socketpair系统API调用使用说明
目录
1.socketpair函数说明
2.socketpair使用举例
在阅读nginx源码时,发现其调用socketpair来实现master和worker进程之间进行数据交互。其代码如下:
思考:master和worker进程是父子关系,有亲属关系的进程通过pipe/pipe2(匿名管道)和mkfifo(有名管道)也能实现数据传输,为什么要使用socketpair来进行数据交互?
原因:socketpair创建的全双工的一对套接字,而匿名管道和有名管道是单工的。
匿名管道和有名管道使用可以参考如下博客:
https://www.cnblogs.com/fortunely/p/14648146.html
1.socketpair函数说明
socketpair创建管道之后,fds[0]和fds[1]均可以读写,读写可发生在一个线程中,也可以发生在父子进程之间。关于socketpair使用,可参考如下说明:
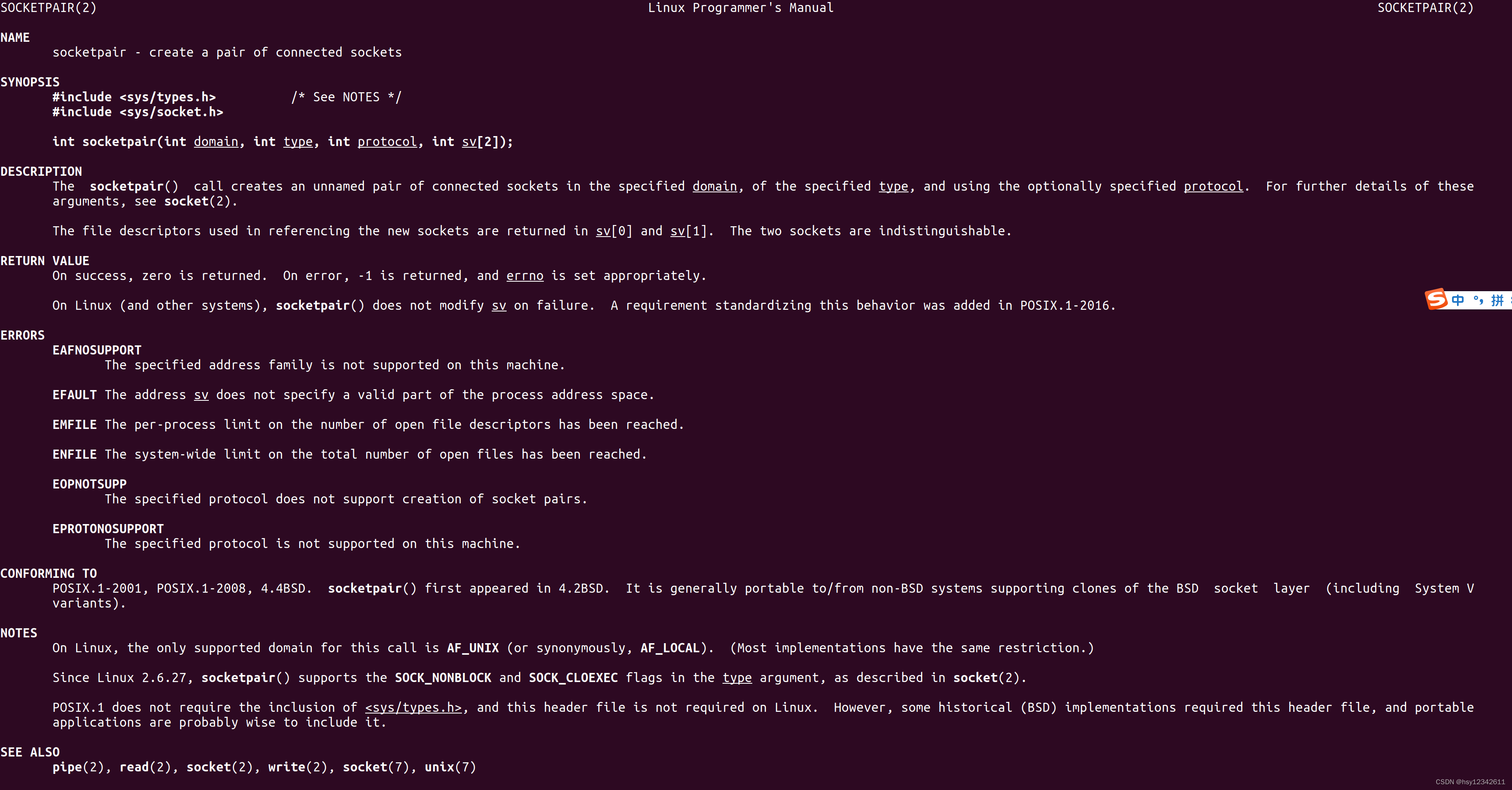
SOCKETPAIR(2) Linux Programmer's Manual SOCKETPAIR(2)
NAME
socketpair - create a pair of connected socketsSYNOPSIS
#include <sys/types.h> /* See NOTES */
#include <sys/socket.h>int socketpair(int domain, int type, int protocol, int sv[2]);
DESCRIPTION
The socketpair() call creates an unnamed pair of connected sockets in the specified domain, of the specified type, and using the optionally specified protocol. For further details of these
arguments, see socket(2).The file descriptors used in referencing the new sockets are returned in sv[0] and sv[1]. The two sockets are indistinguishable.
RETURN VALUE
On success, zero is returned. On error, -1 is returned, and errno is set appropriately.On Linux (and other systems), socketpair() does not modify sv on failure. A requirement standardizing this behavior was added in POSIX.1-2016.
ERRORS
EAFNOSUPPORT
The specified address family is not supported on this machine.EFAULT The address sv does not specify a valid part of the process address space.
EMFILE The per-process limit on the number of open file descriptors has been reached.
ENFILE The system-wide limit on the total number of open files has been reached.
EOPNOTSUPP
The specified protocol does not support creation of socket pairs.EPROTONOSUPPORT
The specified protocol is not supported on this machine.CONFORMING TO
POSIX.1-2001, POSIX.1-2008, 4.4BSD. socketpair() first appeared in 4.2BSD. It is generally portable to/from non-BSD systems supporting clones of the BSD socket layer (including System V
variants).NOTES
On Linux, the only supported domain for this call is AF_UNIX (or synonymously, AF_LOCAL). (Most implementations have the same restriction.)Since Linux 2.6.27, socketpair() supports the SOCK_NONBLOCK and SOCK_CLOEXEC flags in the type argument, as described in socket(2).
POSIX.1 does not require the inclusion of <sys/types.h>, and this header file is not required on Linux. However, some historical (BSD) implementations required this header file, and portable
applications are probably wise to include it.
2.socketpair使用举例
2.1 如下代码演示阻塞和非阻塞socketpair使用:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>int parentProcess(int* fds, int num) {if (num < 2) {return -1;}char buf[128] {0};recv(fds[0], buf, 128, 0);printf("parent:: %s\n", buf);recv(fds[0], buf, 128, 0);printf("parent:: %s\n", buf);sleep(1);recv(fds[0], buf, 128, 0);printf("parent:: %s\n", buf);sleep(1);memset(buf, 0x00, sizeof(buf));strcpy(buf, "hello child, I am parent !");send(fds[1], buf, strlen(buf), 0);close(fds[0]);close(fds[1]);return 0;
}int childProcess(int* fds, int num) {if (num < 2) {return -1;}char buf[128] = "hello parent, I am child";send(fds[1], buf, strlen(buf), 0);sleep(1);send(fds[1], buf, strlen(buf), 0);sleep(1);char *pStr = (char*)"给父进程再发一次消息";send(fds[1], pStr, strlen(pStr), 0);memset(buf, 0x00, sizeof(buf));sleep(1);recv(fds[0], buf, 128, 0);printf("child:: %s\n", buf);close(fds[0]);close(fds[1]);return 0;
}//设置文件描述符非阻塞
int fd_nonblocking(int s)
{int nb;nb = 1;//方法一/*int flag = fcntl(s, F_GETFL);flag |= O_NONBLOCK;return fcntl(s, F_SETFL, flag);*///方法二return ioctl(s, FIONBIO, &nb);
}int close_channel(int* fds) {if (close(fds[0]) == -1) {printf("close() channel fds[0] failed\n");}if (close(fds[1]) == -1) {printf("close() channel fds[1] failed\n");}return 0;
}void testNonblockingSocketFd(int* fds) {if (-1 == fd_nonblocking(fds[0])) {printf("fd_nonblocking fds[0] failed\n");close_channel(fds);}if (-1 == fd_nonblocking(fds[1])) {printf("fd_nonblocking fds[1] failed\n");close_channel(fds);}
}int main()
{int fds[2];// fds[0]: 读 fds[1]: 写 socketpair(PF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0, fds);
#ifdef NOBLOCKFDtestNonblockingSocketFd(fds);
#endifint pid = fork();printf("parent: %d, child: %d\n", getpid(), pid);switch (pid) {case -1: // errorreturn -1;case 0: // childchildProcess(fds, 2);printf("child exit \n");break;default: // parentparentProcess(fds, 2);printf("parent exit \n");break;}return 0;
}
阻塞应用:

非阻塞应用:
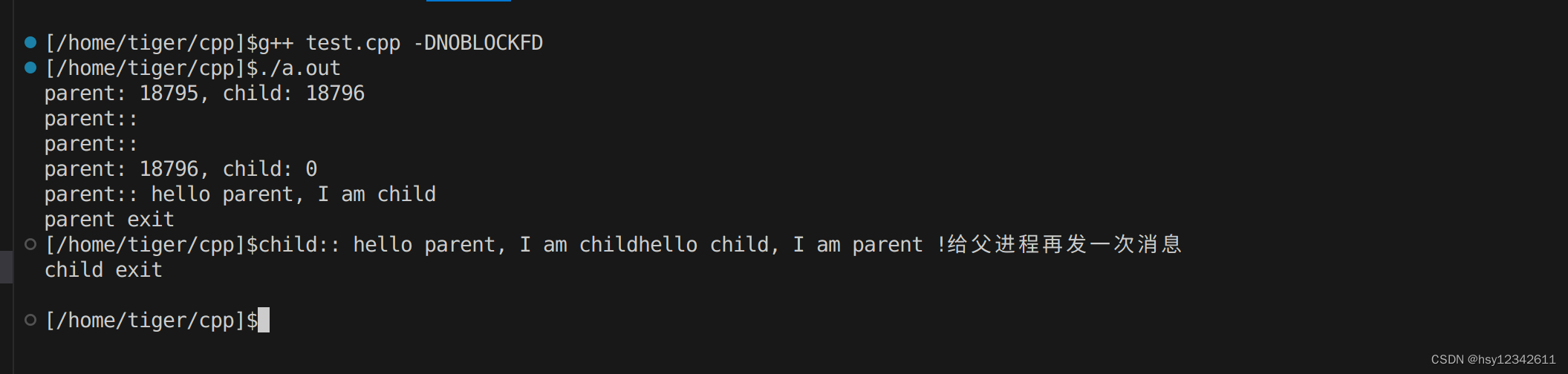
通过非阻塞应用发现, 父进程退出后,子进程往管道发送数据后,接着自己读到了发送的数据。
2.2只使用一端进行读写
如2.1可以发现fds[0]和fds[1]均可以读写,那么自己进程读到的可能是别的进程发来的数据,也可能是自己进程发来的数据,编程逻辑很不清晰。
常用的方式是:
(1) 父进程 close(fd[0]),使用fd[1]读写,子进程close(fd[1]),使用fd[0]读写
(1) 父进程 close(fd[1]),使用fd[0]读写,子进程close(fd[0]),使用fd[1]读写
如下代码显示情形(1)
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>int parentProcess(int* fds, int num) {if (num < 2) {return -1;}close(fds[0]); // 关闭fds[0] 使用fds[1]读写,子进程中关闭fds[1] 使用fds[0]读写char buf[128] {0};char *pStr = (char*)"hello child, I am parent";int inum = 0;while (inum++ < 10) {memset(buf, 0x00, sizeof(buf));//写write(fds[1], pStr, strlen(pStr));//读read(fds[1], buf, 128);printf("parent收到child的招呼 %d :: %s\n", inum, buf);sleep(1);}close(fds[1]);return 0;
}int childProcess(int* fds, int num) {if (num < 2) {return -1;}close(fds[1]);char buf[128] {0};char *pStr = (char*)"hello parent, I am child";int inum = 0;while (inum++ < 10) {memset(buf, 0x00, sizeof(buf));//读read(fds[0], buf, 128);printf("child收到paren的招呼 %d :: %s\n", inum, buf);//写write(fds[0], pStr, strlen(pStr));sleep(1);}close(fds[0]);return 0;
}//设置文件描述符非阻塞
int fd_nonblocking(int s)
{int nb;nb = 1;//方法一/*int flag = fcntl(s, F_GETFL);flag |= O_NONBLOCK;return fcntl(s, F_SETFL, flag);*///方法二return ioctl(s, FIONBIO, &nb);
}int close_channel(int* fds) {if (close(fds[0]) == -1) {printf("close() channel fds[0] failed\n");}if (close(fds[1]) == -1) {printf("close() channel fds[1] failed\n");}return 0;
}void testNonblockingSocketFd(int* fds) {if (-1 == fd_nonblocking(fds[0])) {printf("fd_nonblocking fds[0] failed\n");close_channel(fds);}if (-1 == fd_nonblocking(fds[1])) {printf("fd_nonblocking fds[1] failed\n");close_channel(fds);}
}int main()
{int fds[2];socketpair(PF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0, fds);
#ifdef NOBLOCKFDtestNonblockingSocketFd(fds);
#endifint pid = fork();printf("parent: %d, child: %d\n", getpid(), pid);switch (pid) {case -1: // errorreturn -1;case 0: // childchildProcess(fds, 2);printf("child exit \n");break;default: // parentparentProcess(fds, 2);printf("parent exit \n");break;}return 0;
}
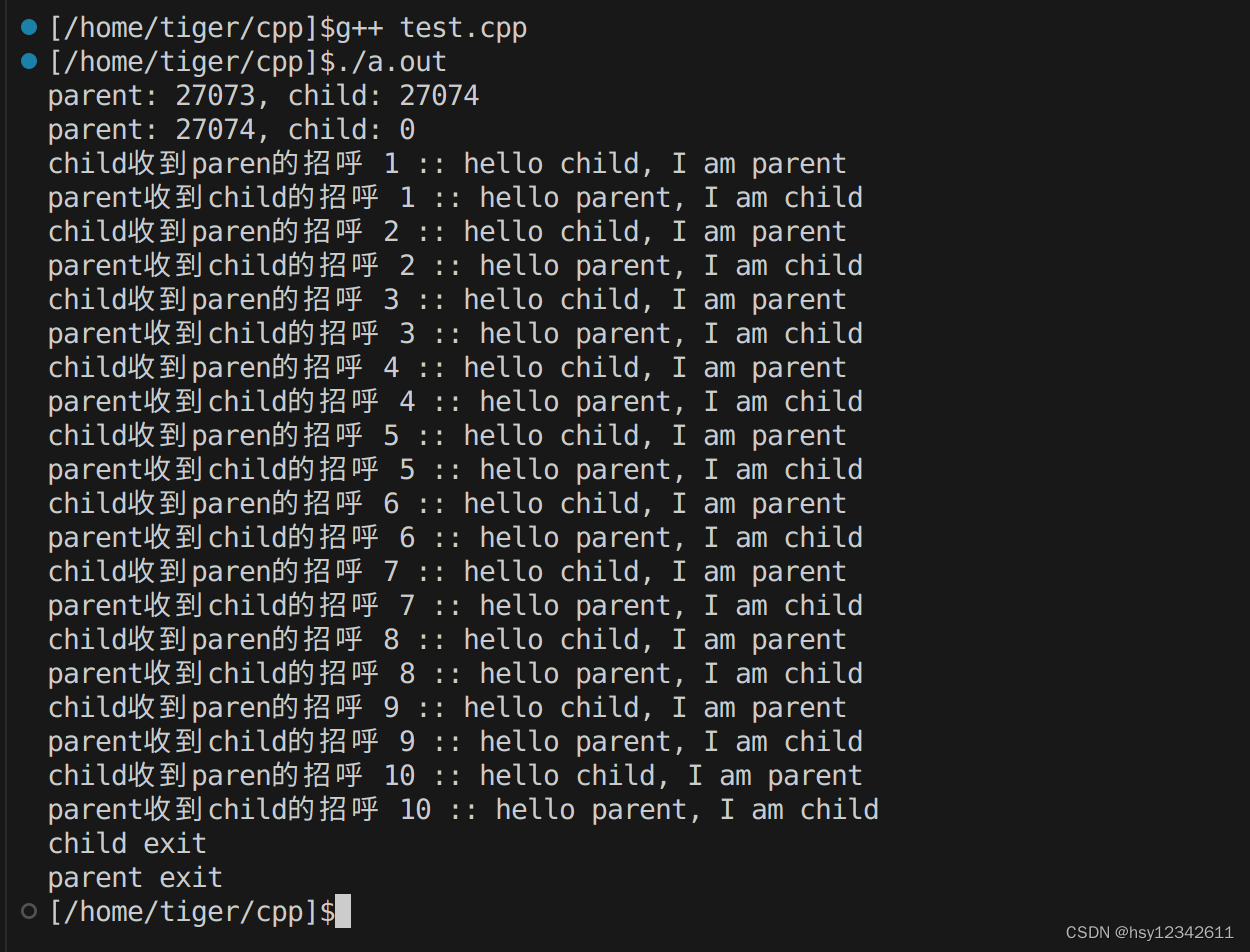
运行结果如下:
2.3一个master多个worker数据收发
如下代码模拟nginx中一个 master进程,多个worker进程进行数据交互
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>int parentProcess(int* fds, int num) {if (num < 2) {return -1;}close(fds[0]); // 关闭fds[0] 使用fds[1]读写,子进程中关闭fds[1] 使用fds[0]读写char buf[128] {0};char *pStr = (char*)"hello child, I am parent";int inum = 0;while (inum++ < 3) {memset(buf, 0x00, sizeof(buf));//写write(fds[1], pStr, strlen(pStr));//读read(fds[1], buf, 128);printf("parent [%d] %d :: %s\n", getpid(), inum, buf);sleep(1);}close(fds[1]);return 0;
}int childProcess(int* fds, int num) {if (num < 2) {return -1;}close(fds[1]);char buf[128] {0};char *pStr = (char*)"hello parent, I am child";char sendBuf[128] = {0};sprintf(sendBuf, "hello parent, I am child %d", getpid());int inum = 0;while (inum++ < 3) {memset(buf, 0x00, sizeof(buf));//读read(fds[0], buf, 128);printf("child [%d] %d :: %s\n", getpid(), inum, buf);//写write(fds[0], sendBuf, strlen(sendBuf));sleep(1);}close(fds[0]);return 0;
}//设置文件描述符非阻塞
int fd_nonblocking(int s)
{int nb;nb = 1;//方法一/*int flag = fcntl(s, F_GETFL);flag |= O_NONBLOCK;return fcntl(s, F_SETFL, flag);*///方法二return ioctl(s, FIONBIO, &nb);
}int close_channel(int* fds) {if (close(fds[0]) == -1) {printf("close() channel fds[0] failed\n");}if (close(fds[1]) == -1) {printf("close() channel fds[1] failed\n");}return 0;
}void testNonblockingSocketFd(int* fds) {if (-1 == fd_nonblocking(fds[0])) {printf("fd_nonblocking fds[0] failed\n");close_channel(fds);}if (-1 == fd_nonblocking(fds[1])) {printf("fd_nonblocking fds[1] failed\n");close_channel(fds);}
}struct TDataExchangeChannel {int fds[2];
};#define GROUP_NUM 2int main()
{
#ifdef NOBLOCKFDtestNonblockingSocketFd(fds);
#endifTDataExchangeChannel channels[GROUP_NUM];for (int i = 0; i < GROUP_NUM; i++) {socketpair(PF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0, channels[i].fds);int pid = fork();switch (pid) {case -1: // errorreturn -1;case 0: // childchildProcess(channels[i].fds, 2);printf("child exit \n");exit(0);default: // parentbreak;}}//父进程给子进程发送消息,并接收子进程发来的消息for (int i = 0; i < GROUP_NUM; i++) {parentProcess(channels[i].fds, 2);}return 0;
}
运行效果如下:
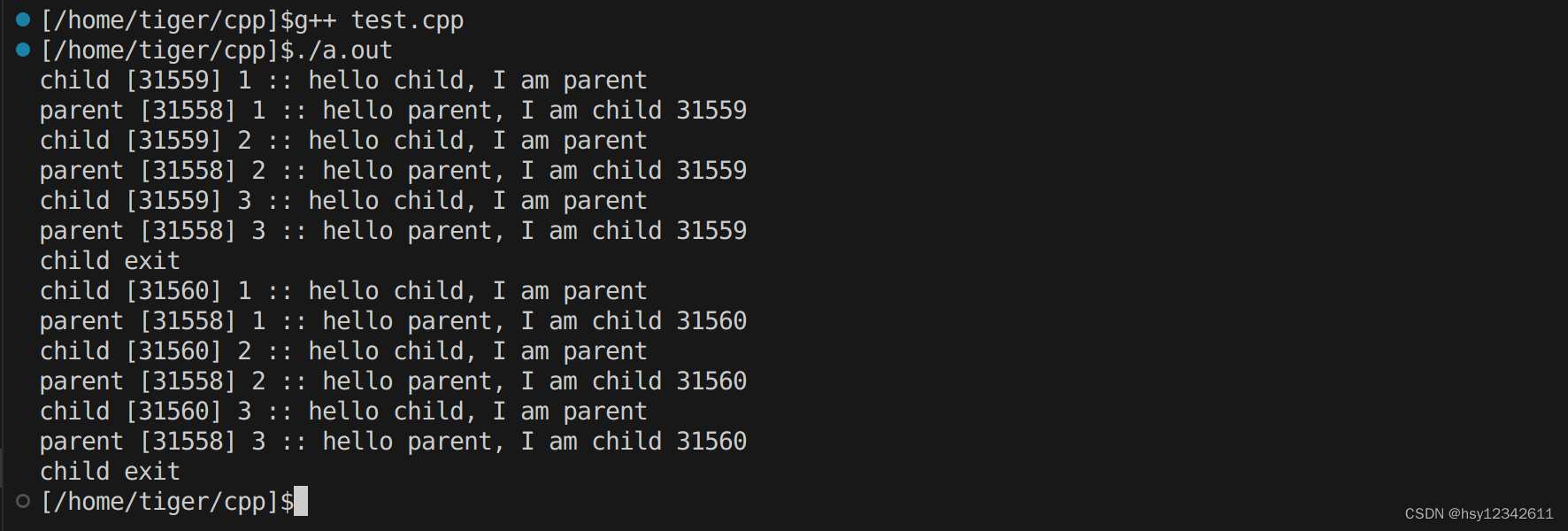
根据运行结果看,master进程为31558,两个子进程为31559,31560,master进程可以分别与两个worker进行数据收发。
