动态规划-树形DP
树的重心
题目
链接:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/848/
给定一颗树,树中包含 n n n 个结点(编号 1 ∼ n 1 \sim n 1∼n)和 n − 1 n-1 n−1 条无向边。
请你找到树的重心,并输出将重心删除后,剩余各个连通块中点数的最大值。
重心定义:重心是指树中的一个结点,如果将这个点删除后,剩余各个连通块中点数的最大值最小,那么这个节点被称为树的重心。
输入格式
第一行包含整数 n n n,表示树的结点数。
接下来 n − 1 n-1 n−1 行,每行包含两个整数 a a a 和 b b b,表示点 a a a 和点 b b b 之间存在一条边。
输出格式
输出一个整数 m m m,表示将重心删除后,剩余各个连通块中点数的最大值。
数据范围
1 ≤ n ≤ 1 0 5 1 \le n \le 10^5 1≤n≤105
输入样例
9
1 2
1 7
1 4
2 8
2 5
4 3
3 9
4 6
输出样例:
4
思路
任取一点u,如果以u为重心,则分为如下两类:
- u的子树
- u上面的部分
需要算出这两者的节点数,取最大值。具体细节见代码
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>#define int long long
using namespace std;const int N = 1e5 + 10;
vector<int> e[N];
int n;
int sz[N]; //记录u的最大子树的节点数
int ans = 1e9;void dfs(int u, int fa) { //u:当前点,fa:父节点sz[u] = 1;int mx = 0; //记录u上面的点和子节点连通块的最大值for (auto j: e[u]) {if (j == fa) continue; //防止向上搜索dfs(j, u);sz[u] += sz[j];mx = max(mx, sz[j]);}mx = max(mx, n - sz[u]);ans = min(ans, mx);
}signed main() {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGEfreopen("test.in", "r", stdin);freopen("test.out", "w", stdout);
#endifcin >> n;for (int i = 1; i <= n - 1; i++) {int x, y;cin >> x >> y;e[x].push_back(y);e[y].push_back(x);}dfs(1, 0);cout << ans << endl;return 0;
}
树的最长直径
题目
链接:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/1074/
给定一棵树,树中包含 $ n $ 个结点(编号$ 1 ~ n $)和 $ n-1 $ 条无向边,每条边都有一个权值。
现在请你找到树中的一条最长路径。
换句话说,要找到一条路径,使得使得路径两端的点的距离最远。
注意:路径中可以只包含一个点。
输入格式
第一行包含整数 $ n $。
接下来 $ n-1 $ 行,每行包含三个整数 $ a_i,b_i,c_i $,表示点 $ a_i $ 和 $ b_i $ 之间存在一条权值为 $ c_i $ 的边。
输出格式
输出一个整数,表示树的最长路径的长度。
数据范围
$ 1 \le n \le 10000 $,
$ 1 \le a_i,b_i \le n $,
$ -10^5 \le c_i \le 10^5 $
输入样例:
6
5 1 6
1 4 5
6 3 9
2 6 8
6 1 7
输出样例:
22
思路
任取一点u,从u点向下搜索,返回时收集边的权值,记录两条路径:
- d1:记录从u点往下走的最长路径的长度
- d2:记录从u点往下走的次长路径的长度
更新答案:ans=max(ans,d1+d2)
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>#define int long long
using namespace std;const int N = 10010;
int n, ans;
typedef struct edge {int v, w;
} edge;vector<edge> e[N];int dfs(int u, int fa) {int d1 = 0, d2 = 0;//最长和次长for (auto j: e[u]) {auto [v, w] = j;if (v == fa) continue;int d = dfs(v, u) + w;if (d >= d1) d2 = d1, d1 = d;else if (d > d2) d2 = d;}ans= max(ans,d1+d2);return d1;
}signed main() {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGEfreopen("test.in", "r", stdin);freopen("test.out", "w", stdout);
#endifcin >> n;for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {int a, b, c;cin >> a >> b >> c;e[a].push_back({b, c});e[b].push_back({a, c});}dfs(1, 0);cout << ans << endl;return 0;
}
树的中心
题目
链接:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/1075/
给定一棵树,树中包含 $ n $ 个结点(编号$ 1 ~ n $)和 $ n-1 $ 条无向边,每条边都有一个权值。
请你在树中找到一个点,使得该点到树中其他结点的最远距离最近。
输入格式
第一行包含整数 $ n $。
接下来 $ n-1 $ 行,每行包含三个整数 $ a_i,b_i,c_i $,表示点 $ a_i $ 和 $ b_i $ 之间存在一条权值为 $ c_i $ 的边。
输出格式
输出一个整数,表示所求点到树中其他结点的最远距离。
数据范围
$ 1 \le n \le 10000 $,
$ 1 \le a_i,b_i \le n $,
$ 1 \le c_i \le 10^5 $
输入样例:
5
2 1 1
3 2 1
4 3 1
5 1 1
输出样例:
2
思路
开一个数组p:p[u]记录从u点向下走点最长路径是从哪个点下去的
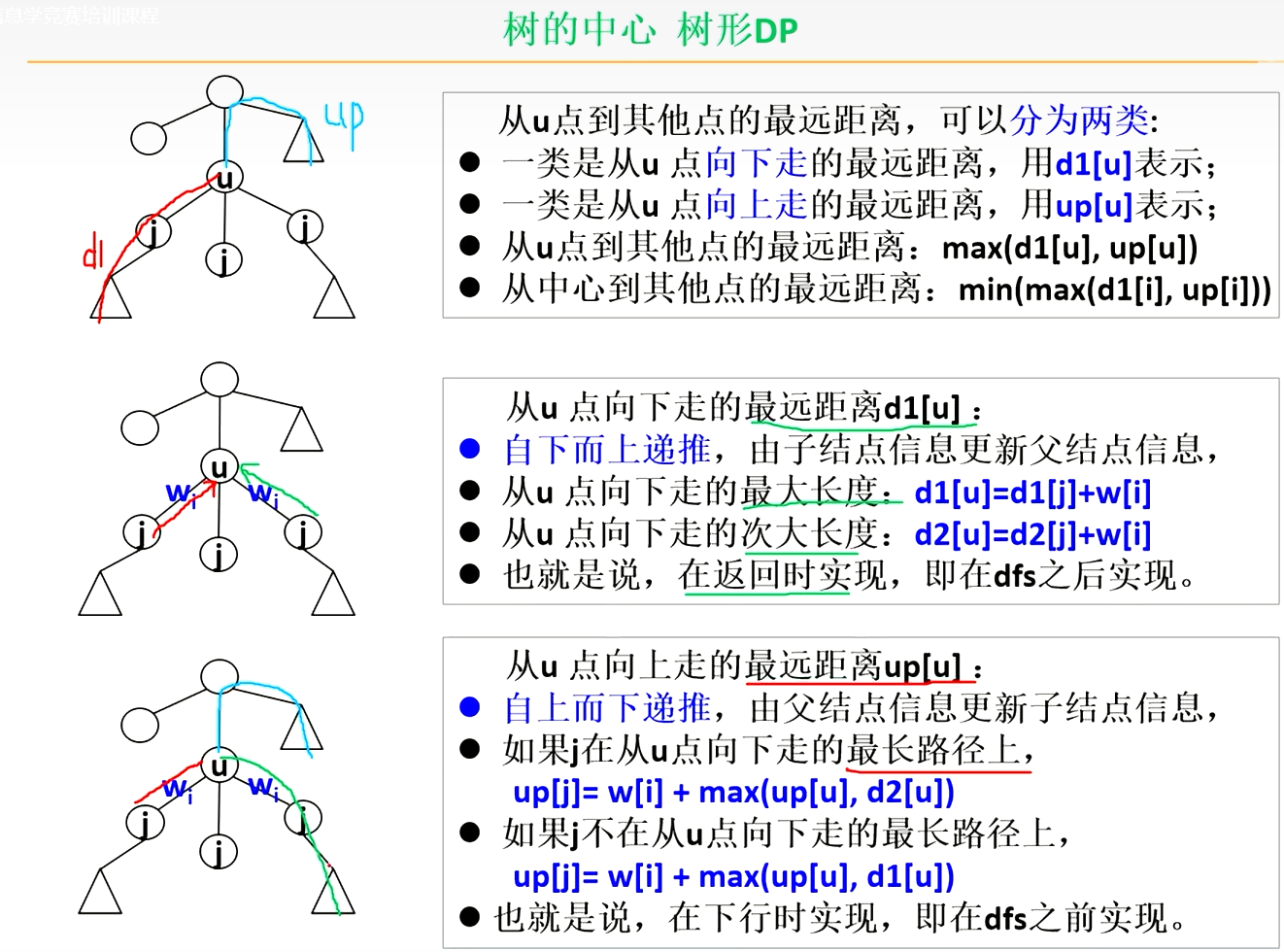
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>#define int long long
using namespace std;const int N = 100010;
int ans = 2e9;
int n;
typedef struct edge {int v, w;
} edge;vector<edge> e[N];
int d1[N], d2[N], up[N], p[N];void dfs1(int x, int fa) {for (auto item: e[x]) {int y = item.v, w = item.w;if (y == fa) continue;dfs1(y, x);if (d1[y] + w > d1[x]) {d2[x] = d1[x], d1[x] = d1[y] + w, p[x] = y;} else if (d1[y] + w > d2[x]) d2[x] = d1[y] + w;}
}void dfs2(int x, int fa) {for (auto item: e[x]) {int y = item.v, w = item.w;if (y == fa)continue;else if (y == p[x]) up[y] = max(up[x], d2[x]) + w;else up[y] = max(up[x], d1[x]) + w;dfs2(y, x);}
}signed main() {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGEfreopen("test.in", "r", stdin);freopen("test.out", "w", stdout);
#endifcin >> n;for (int i = 1; i <= n - 1; i++) {int a, b, c;cin >> a >> b >> c;e[a].push_back({b, c});e[b].push_back({a, c});}dfs1(1, 0);dfs2(1, 0);for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {ans = min(ans, max(d1[i], up[i]));}cout<<ans<<endl;return 0;
}
数字转换
题目
链接:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/1077/
如果一个数 $ x $ 的约数之和 $ y $(不包括他本身)比他本身小,那么 $ x $ 可以变成 $ y , , , y $ 也可以变成 $ x $。
例如,$ 4 $ 可以变为 $ 3 , , , 1 $ 可以变为 $ 7 $。
限定所有数字变换在不超过 $ n $ 的正整数范围内进行,求不断进行数字变换且不出现重复数字的最多变换步数。
输入格式
输入一个正整数 $ n $。
输出格式
输出不断进行数字变换且不出现重复数字的最多变换步数。
数据范围
$ 1 \le n \le 50000 $
输入样例:
7
输出样例:
3
样例解释
一种方案为:$ 4 \to 3 \to 1 \to 7 $。
思路
因为每个数x的约数之和y是固定的,但是一个约数之和y有可能是很多数x产生的,因此我们可以从y向x连边,这样就可以构成一棵树了,反之就不会构成树
这样建图的方式会构造出很多的树
如何求每个数的约数:
可以使用试除法求约数,这样的时间复杂度为 O ( n n ) O(n\sqrt{n}) O(nn)本题应该可以过
也可以利用晒法的思想,对于一个数x,去枚举它的倍数(2倍,3倍…),把这些倍数的数都加上数x,这样做的时间复杂度为调和级数 l n n + C lnn+C lnn+C,因此时间复杂度为 O ( n l o g n ) O(nlogn) O(nlogn)
构造完树之后,求最多的变换次数即变成了求树的最长直径,可以参考代码模版。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>#define int long long
using namespace std;const int N = 5e4 + 10;vector<int> e[N];
int res = 0;
int d1[N], d2[N];
bool st[N];
int n;
int sum[N];void dfs(int x, int fa) {for (auto y: e[x]) {if (y == fa) continue;dfs(y, x);if (d1[y] + 1 > d1[x]) d2[x] = d1[x], d1[x] = d1[y] + 1;else if (d1[y] + 1 > d2[x]) d2[x] = d1[y] + 1;}res = max(res, d1[x] + d2[x]);
}signed main() {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGEfreopen("test.in", "r", stdin);freopen("test.out", "w", stdout);
#endifcin >> n;//统计每个数的约数之和for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {for (int j = 2; j <= n / i; j++) {sum[i * j] += i;}}//建图for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {if (sum[i] < i) {e[sum[i]].push_back(i);st[i] = true;}}for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)if (!st[i]) dfs(i, i);cout << res << endl;return 0;
}
