Java8之Stream操作
Java8之Stream操作
- stream干啥用的?
- 创建流
- 中间操作
- 终结操作
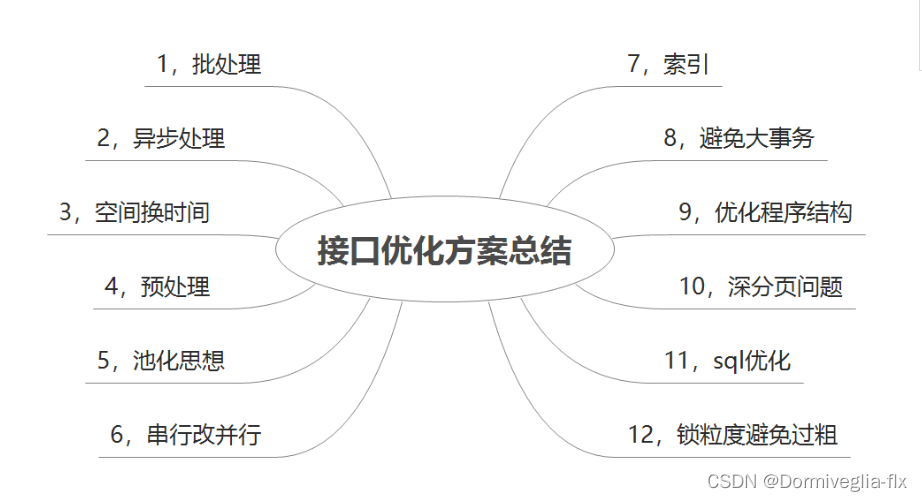
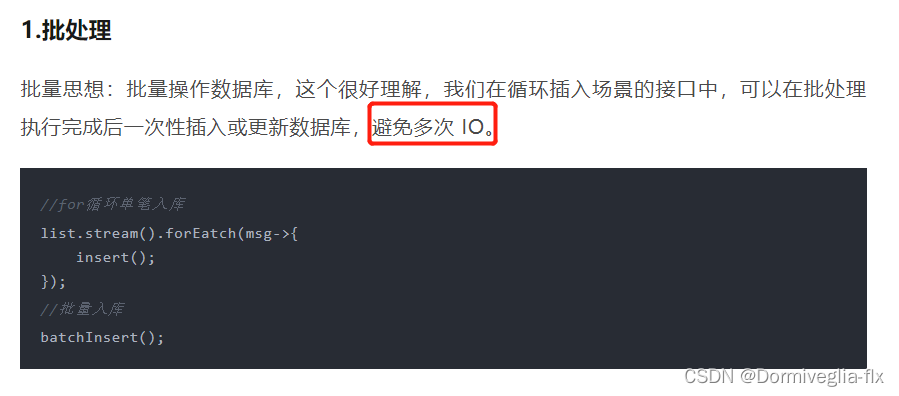
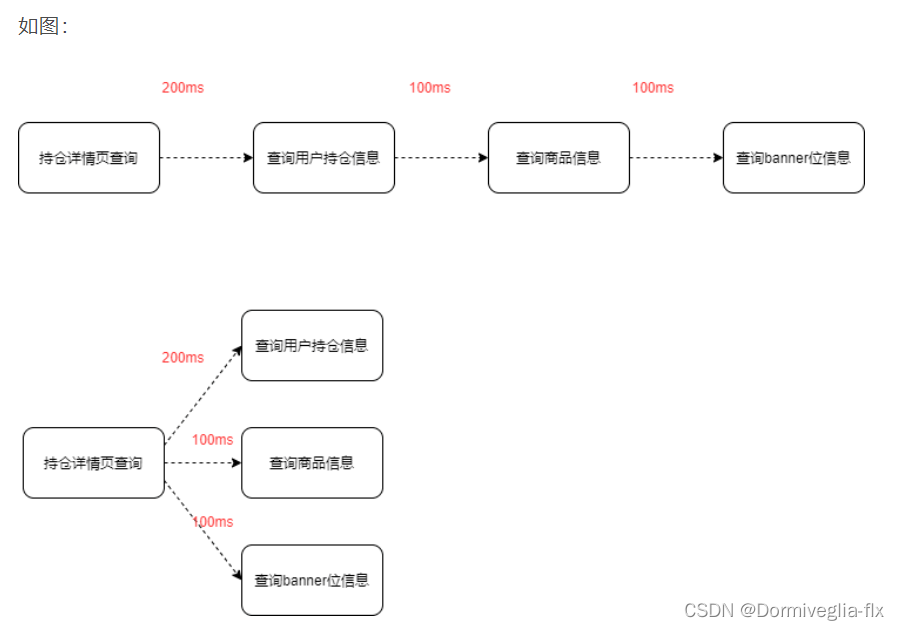
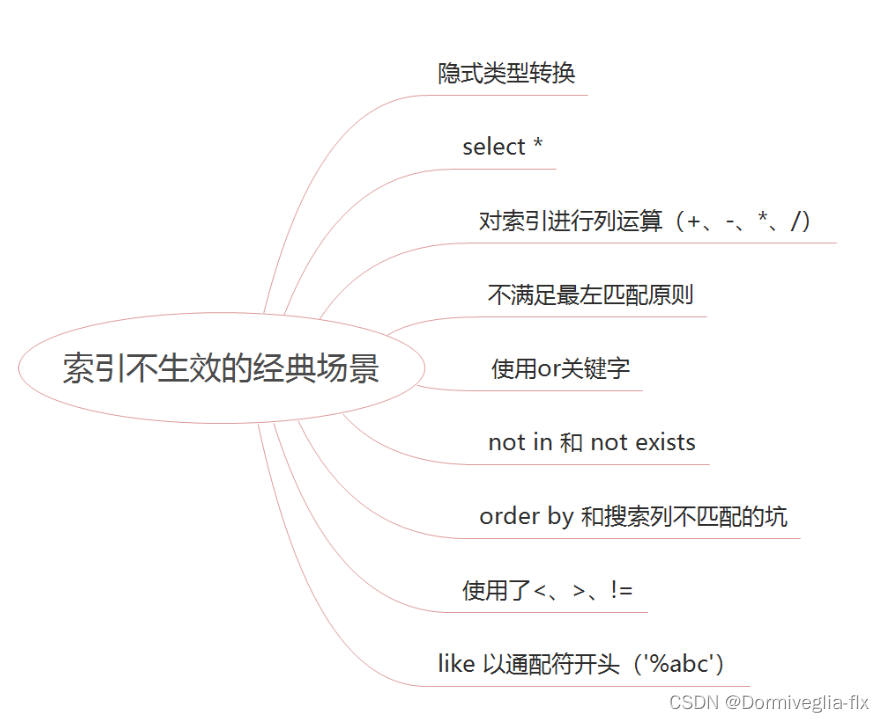
- 好文推荐----接口优化思想
stream干啥用的?
Stream 就是操作数据用的。使用起来很方便
创建流 → 中间操作 → 终结操作
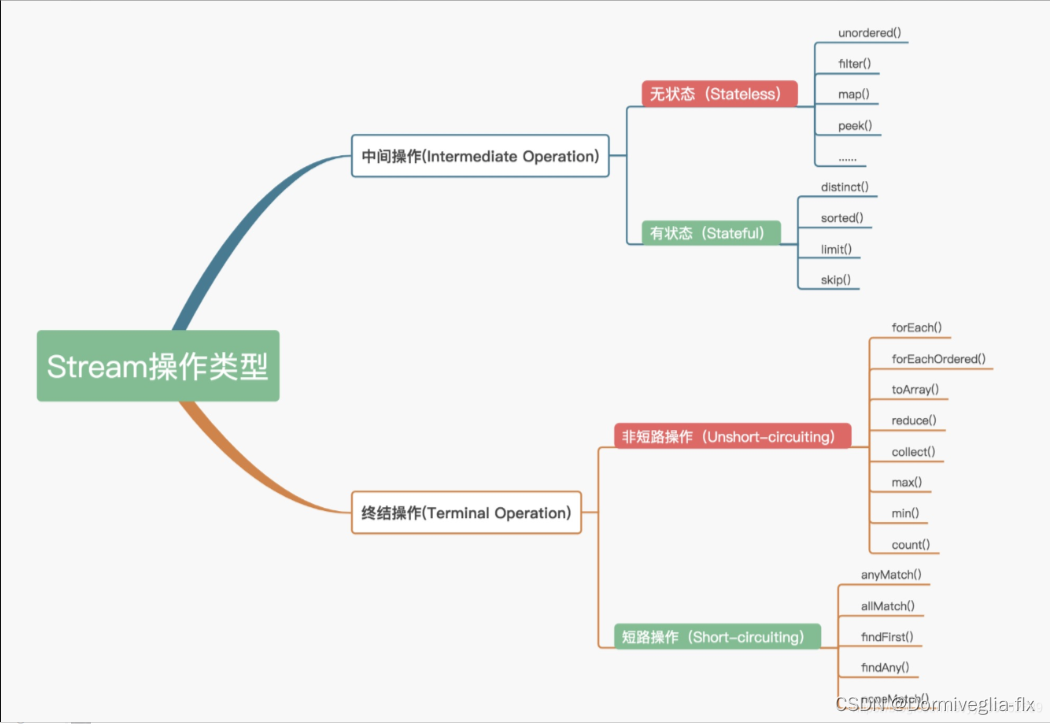
Stream的操作可以分为两大类:中间操作、终结操作
中间操作可分为:
- 无状态(Stateless)操作:指元素的处理不受之前元素的影响
- 有状态(Stateful)操作:指该操作只有拿到所有元素之后才能继续下去
终结操作可分为:
- 短路(Short-circuiting)操作:指遇到某些符合条件的元素就可以得到最终结果
- 非短路(Unshort-circuiting)操作:指必须处理完所有元素才能得到最终结果
创建流
- 单列集合
通过.stream()方法即可。
// 例如:List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<>();// 创建流Stream pstream = personList.stream();
- 双列集合
转成单列集合,再创建流
//例如:Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();map.entrySet() //转成与List一样的单列集合,只是取值不一样。.stream()
中间操作
-
filter过滤
List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<>();personList.add(new Person(10,"flx"));personList.add(new Person(11,"flx"));personList.add(new Person(12,"cxy"));personList.add(new Person(13,"cxy"));personList.add(new Person(10,"flx"));//filter操作----过滤。比如过滤出年龄大于10的人。personList.stream().filter(person -> person.age>10).forEach(person -> System.out.println(person.getName()));
-
map对整体流的操作
//最常用的操作是取某一些值personList.stream().map(person -> person.getName()).forEach(name -> System.out.println(name));// 计算的话,一般用不到personList.stream().map(person -> person.age = person.age+10).forEach(person -> System.out.println(person));
flatMap扁平化List。重点是扁平化对象中有List的数据,且要返回流数据
Friend friend1 = new Friend("张三");Friend friend2 = new Friend("李四");Friend friend3 = new Friend("王五");List<Friend> friends = new ArrayList<>();friends.add(friend1);friends.add(friend2);friends.add(friend3);List<Person> personList2 = new ArrayList<>();personList2.add(new Person(10,"flx",friends));personList2.add(new Person(11,"cxy",friends));personList2.stream().flatMap(person -> person.getFriendList().stream()).forEach(friend -> System.out.println(friend.getName()));
distinct去重。重点是需要重写对象中equals()方法
// distinct操作----去重。personList.stream().distinct().forEach(person -> System.out.println(person.getName()));
sorted排序。重点是对象需要实现Comparable接口
// sorted操作----排序。personList.stream().sorted().forEach(person -> System.out.println(person.getAge()));
limit与skip。limit是截取前n个元素。skip是跳过前n个,剩下的截取
// limit操作----截取。personList.stream().limit(2).forEach(person -> System.out.println(person.getAge()));// skip操作----跳过并截取personList.stream().skip(2).forEach(person -> System.out.println(person.getAge()));
终结操作
collect转成集合forEach遍历count、max、min统计、最大、最小
long count = personList.stream().flatMap(person -> person.getFriendList().stream()).count();System.out.println(count);Optional<Integer> max = personList.stream().map(person -> person.getAge()).max((o1,o2) -> o1-o2);System.out.println(max.get());
-
anyMatch与allMatch
// anyMatch 只要有一个匹配,就返回true// allMatch 所有都匹配,才返回trueBoolean b = personList.stream().anyMatch(person -> person.getAge()>10);System.out.println(b);-
findAny与findFirst
// findAny 查找任意一个满足条件的元素// findFirst 查找满足条件元素的第一个Optional<Person> first = personList.stream().filter(person -> person.getAge() > 10).findFirst();first.ifPresent(person -> System.out.println(person.getName()));
-
reduce一般会先map一下,再执行reduce ( 我们熟悉的mapReduce()操作 )
// reduce(params1,params2)// params1:初始化的第一个值// params2: 要执行的操作。// 里面有两个参数 result、element// result 每一步返回的结果// element 当前的元素// 例如,计算所有的年龄的和Integer reduce = personList.stream().map(person -> person.getAge()).reduce(0, (result, element) -> result = result + element);System.out.println(reduce);
中间操作常用的是 filter、map、flatmap
终结操作常用的是foreach、collect、reduce
整体代码示例
package com.face;import lombok.val;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;@SpringBootTest
class FaceEasyApplicationTests {@Testvoid contextLoads() {}/** 中间操作* */@Testvoid testStreamMiddle() {List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<>();personList.add(new Person(10,"flx"));personList.add(new Person(11,"flx"));personList.add(new Person(12,"cxy"));personList.add(new Person(13,"cxy"));personList.add(new Person(10,"flx"));//filter操作----过滤。比如过滤出年龄大于10的人。personList.stream().filter(person -> person.age>10).forEach(person -> System.out.println(person.getName()));//map操作----对整体流中数据的计算或者转换。比如给所有作家+10岁//常用的操作是取某一些值personList.stream().map(person -> person.getName()).forEach(name -> System.out.println(name));// 计算的话,一般用不到personList.stream().map(person -> person.age = person.age+10).forEach(person -> System.out.println(person));// distinct操作----去重。重点是重写equals方法。personList.stream().distinct().forEach(person -> System.out.println(person.getName()));// sorted操作----排序。personList.stream().sorted().forEach(person -> System.out.println(person.getAge()));// limit操作----截取。例如截取前两个。可以结合排序使用,比如排序后,截取元素personList.stream().limit(2).forEach(person -> System.out.println(person.getAge()));// skip操作----跳过。跳过前n个元素,返回剩下的。可以结合排序使用,比如排序后,跳过某些元素,返回剩下的personList.stream().skip(2).forEach(person -> System.out.println(person.getAge()));// flatMap操作----扁平化处理。扁平化对象中的List,并且把她们作为流返回Friend friend1 = new Friend("张三");Friend friend2 = new Friend("李四");Friend friend3 = new Friend("王五");List<Friend> friends = new ArrayList<>();friends.add(friend1);friends.add(friend2);friends.add(friend3);List<Person> personList2 = new ArrayList<>();personList2.add(new Person(10,"flx",friends));personList2.add(new Person(11,"cxy",friends));personList2.stream().flatMap(person -> person.getFriendList().stream()).forEach(friend -> System.out.println(friend.getName()));}/** 终结操作* */@Testvoid testStreamFinish() {Friend friend1 = new Friend("张三");Friend friend2 = new Friend("李四");Friend friend3 = new Friend("王五");List<Friend> friends = new ArrayList<>();friends.add(friend1);friends.add(friend2);friends.add(friend3);List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<>();personList.add(new Person(10,"flx",friends));personList.add(new Person(11,"cxy",friends));// forEachpersonList.stream().map(person -> person.getName()).forEach(name -> System.out.println(name));// count操作----统计数量。例如统计personList中,所有朋友的数量long count = personList.stream().flatMap(person -> person.getFriendList().stream()).count();System.out.println(count);// max和min操作----取最大值与最小值。例如取personList中年龄的最大值与最小值Optional<Integer> max = personList.stream().map(person -> person.getAge()).max((o1,o2) -> o1-o2);System.out.println(max.get());// collect操作----转换成集合。// anyMatch 、allMatch 、findAny、findFirst操作----见名知意,就是匹配操作与查找操作// anyMatch 只要有一个匹配,就返回true// allMatch 所有都匹配,才返回true// findAny 查找任意一个满足条件的元素// findFirst 查找满足条件元素的第一个Boolean b = personList.stream().anyMatch(person -> person.getAge()>10);System.out.println(b);// 查找年龄大于10的第一个元素Optional<Person> first = personList.stream().filter(person -> person.getAge() > 10).findFirst();first.ifPresent(person -> System.out.println(person.getName()));//reduce操作----归并。一般会先map一下,再执行reduce ( 我们熟悉的mapReduce()操作 )// reduce(params1,params2)// params1:初始化的第一个值// params2: 要执行的操作。// 里面有两个参数 result、element// result 每一步返回的结果// element 当前的元素// 例如,计算所有的年龄的和Integer reduce = personList.stream().map(person -> person.getAge()).reduce(0, (result, element) -> result = result + element);System.out.println(reduce);}}class Person implements Comparable<Person>{public int age;public String name;List<Friend> friendList;public List<Friend> getFriendList() {return friendList;}public void setFriendList(List<Friend> friendList) {this.friendList = friendList;}public Person(int age, String name, List<Friend> friendList) {this.age = age;this.name = name;this.friendList = friendList;}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o) return true;if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;Person person = (Person) o;if (age != person.age) return false;return name != null ? name.equals(person.name) : person.name == null;}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {int result = age;result = 31 * result + (name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0);return result;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public Person(int age, String name) {this.age = age;this.name = name;}@Overridepublic int compareTo(Person person) {return this.getAge() - person.getAge();}
}class Friend{public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public Friend(String name) {this.name = name;}String name;}好文推荐----接口优化思想
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/oeHLLvmKuq3zOQcRhSs8gw