顺序表功能实现(入手版详解)
🍉博客主页:阿博历练记
📖文章专栏:数据结构与算法
🚚代码仓库:阿博编程日记
🌹欢迎关注:欢迎友友们点赞收藏+关注哦

文章目录
- 🍓前言
- ✨顺序表
- 🔍1.顺序表的整体框架
- 🔍2.打印顺序表的菜单
- 🔍3.主函数的创建
- ⭐第一个case后面加中括号
- ⭐枚举变量和函数名同名
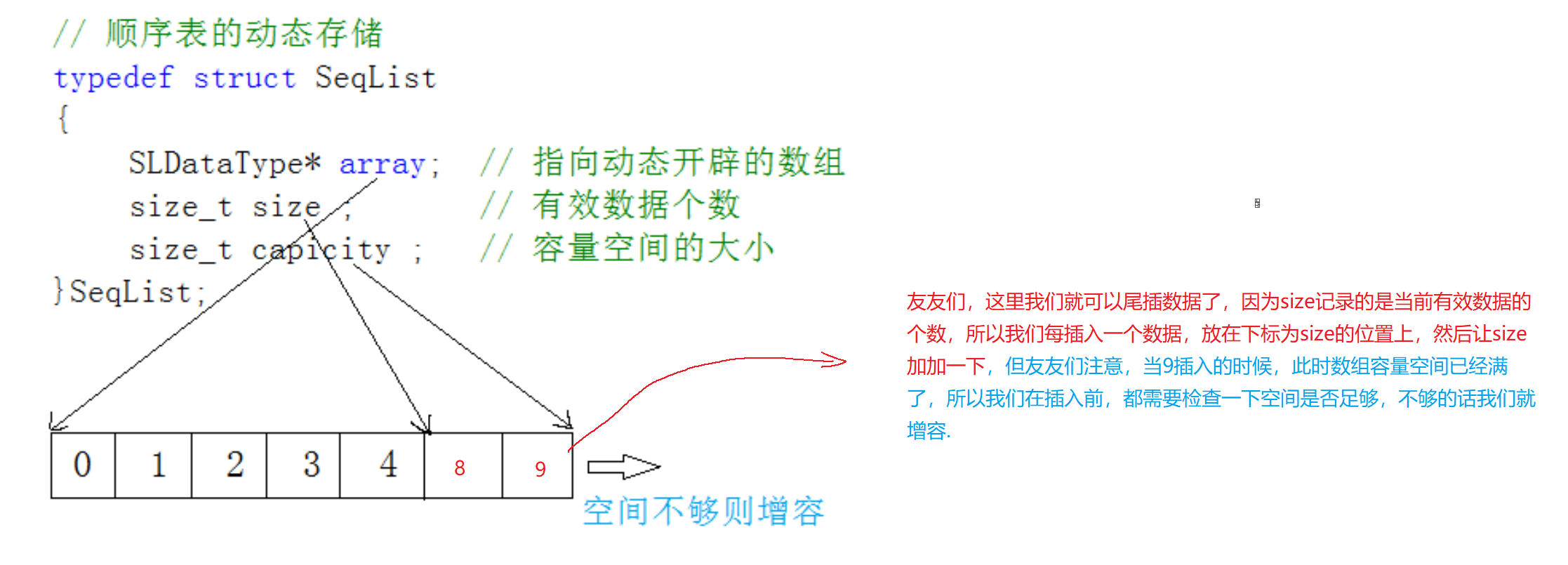
- 🔍4.顺序表的定义
- 🔍5.顺序表的初始化
- ⭐传结构体本身还是它的地址
- 🔍6.顺序表的尾插
- 🔍7.顺序表的打印
- 🔍8.顺序表的头插
- ⭐挪动数据(从后往前)
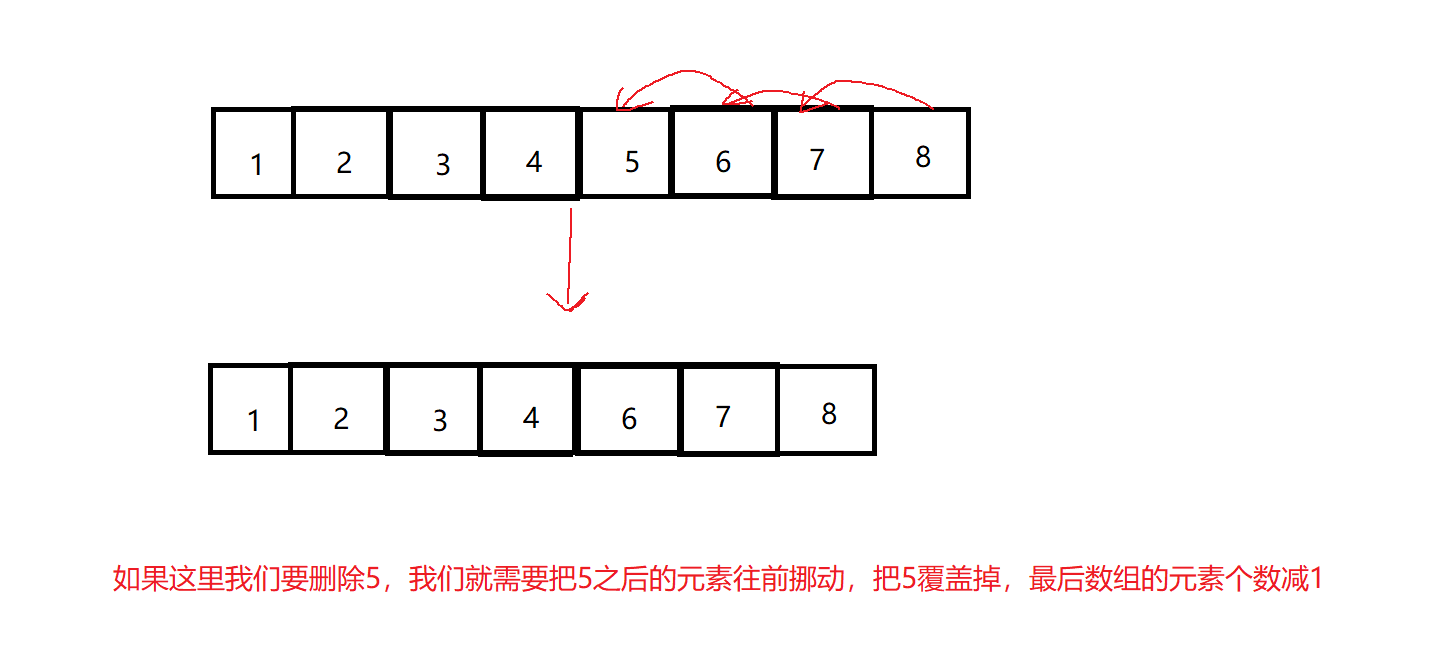
- 🔍9.顺序表的尾删
- ⭐assert的声明
- ⭐数组越界不一定报错
- 🔍10.顺序表的头删
- ⭐挪动数据(从前往后)
- 🔍11.顺序表任意位置的插入
- 🔍12.顺序表任意位置的删除
- ⭐assert声明的改变&&函数的附用
- 🔍13.顺序表数据的查找
- 🔍13.顺序表数据的修改
- 🔍14.顺序表的销毁
- 👻Seqlist.h代码
- 👻Seqlist.c代码
- 👻test.c代码
🍓前言
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
顺序表一般可以分为:
1.静态顺序表:使用定长数组存储元素.
2.动态顺序表:使用动态开辟的数组存储.
友友们,这里虽然顺序表删除需要挪动大量的元素很不方便,但是顺序表有个绝对的优势就是下标的随机访问,比如:二分查找、还有一些排序都需要作用到数组之上.
✨顺序表
🔍1.顺序表的整体框架
1.创建一个test.c文件:测试顺序表的相关功能
2.创建一个SeqList.c文件:实现顺序表功能的定义
3.创建一个SeqList.h文件:实现顺序表功能的声明
🔍2.打印顺序表的菜单
void menu()
{printf("***************************\n");printf("****1.尾插数据 2.尾删数据****\n");printf("****3.头插数据 4.头删数据****\n");printf("****5.打印数据 0.退出 ****\n");printf("***************************\n");
}
🔍3.主函数的创建
enum option
{ Destory,PushBack,PopBack,PushFront,PopFront,Print,
};
int main()
{SL s;SLInit(&s);int option = 0;do{menu();printf("请输入你的选择:\n");scanf("%d", &option);switch (option){case PushBack:{printf("请输入要尾插数据的个数,再依次输入要插入的数据:\n");int n = 0;scanf("%d", &n);int x = 0;while (n > 0){scanf("%d", &x);SLPushBack(&s, x);n--;}break;}case PopBack:printf("尾删成功\n");SLPopBack(&s);break;case PushFront:printf("请输入要头插数据的个数,在依次输入要插入的数据:\n");int n = 0;scanf("%d", &n);int x = 0;while (n > 0){scanf("%d", &x);SLPushFront(&s, x);n--;}break;case PopFront:printf("头删成功\n");SLPopFront(&s);break;case Print:SLPrint(&s);break;case Destory:SLDestory(&s);break;default:printf("选择错误,请重新选择:\n");break;}} while (option);return 0;
}
⭐第一个case后面加中括号
友友们,这里我们加中括号是因为我们需要把它里面的n和x变成
局部变量,防止和下面的x和n出现变量的重定义
⭐枚举变量和函数名同名
函数名代表函数的地址,可以认为是函数指针类型,如果我们用它当作枚举变量的话,这里我们就会改变它的类型,当再次调用函数的时候,程序就会报错.
🔍4.顺序表的定义
//typedef int SLDatatype;
//
//struct Seqlist
//{
// SLDatatype a[N]; //静态的顺序表 给小了不够用,给大了浪费,这里我们考虑动态顺序表
// int size;
//};typedef int SLDatatype;typedef struct Seqlist
{SLDatatype * a; //动态的顺序表int size; //存储的有效数据个数int capcity; //容量空间
}SL;
🔍5.顺序表的初始化
void SLInit(SL* ps1)
{assert(ps1);ps1->a =(SLDatatype*)malloc(sizeof(SLDatatype)*4);if (ps1->a == NULL){perror("malloc");return;}ps1->capcity = 4;ps1->size = 0;
}
⭐传结构体本身还是它的地址
1.传结构体本身
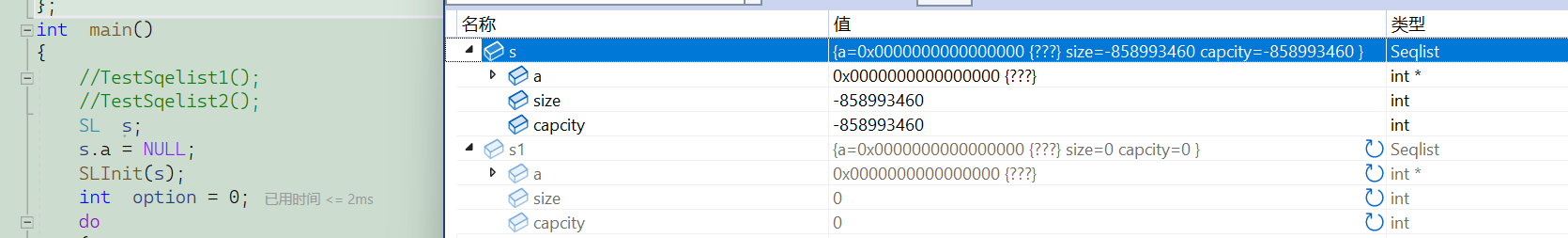
2.传结构体的地址
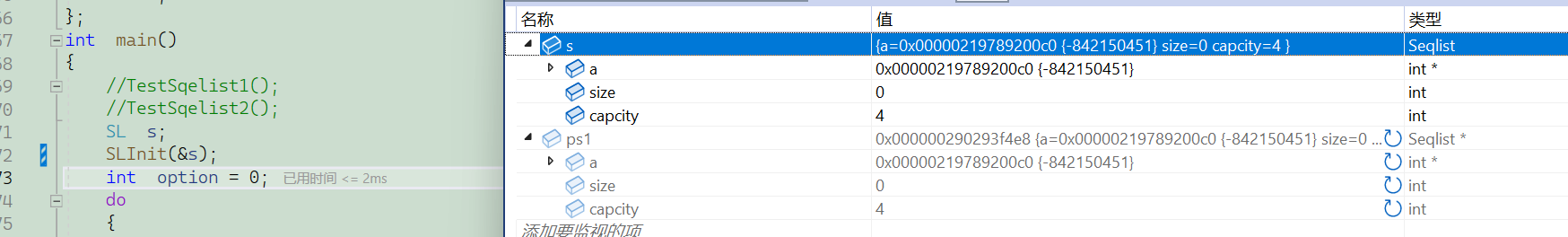
友友们,这里传结构体本身,形参相当于实参的一份
临时拷贝,形参的改变不会影响实参,所以如果如果我们要改变它,就要传它的地址,这样我们解引用就可以改变它了.
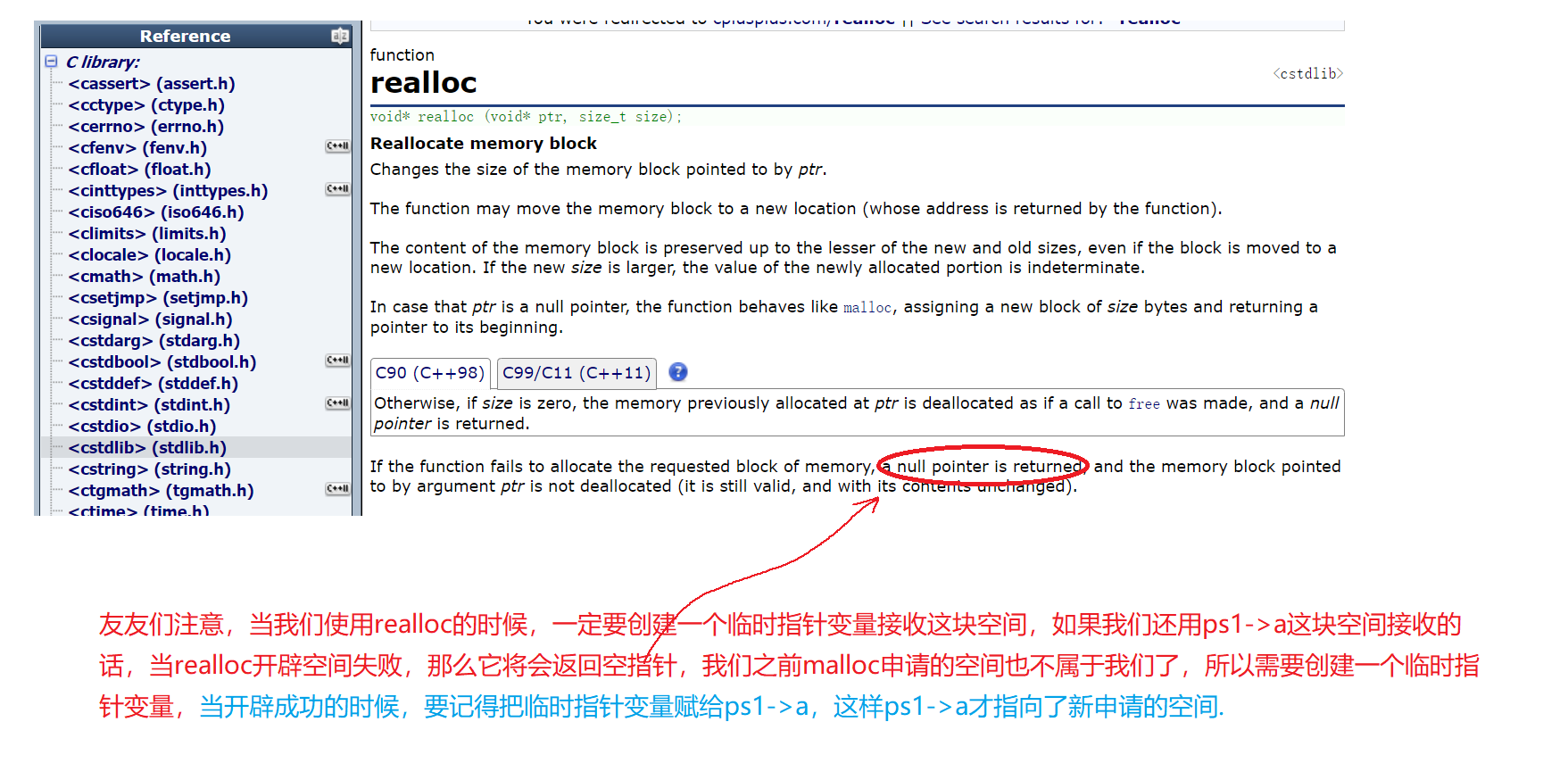
🔍6.顺序表的尾插
void SLCheckcapcity(SL*ps1)
{assert(ps1);if (ps1->size == ps1->capcity){SLDatatype* temp =(SLDatatype*) realloc(ps1->a, sizeof(SLDatatype) * ps1->capcity * 2); if (temp == NULL){perror("realloc");return;}ps1->a = temp;ps1->capcity *= 2;}
}
void SLPushBack(SL* ps1, SLDatatype x)
{assert(ps1);SLCheckcapcity(ps1);ps1->a[ps1->size++] = x;
}
🔍7.顺序表的打印
void SLPrint(SL* ps1)
{assert(ps1);for (int i = 0; i < ps1->size; i++){printf("%d ", ps1->a[i]);}printf("\n");
}
🔍8.顺序表的头插
1.方法一:
void SLPushFront(SL* ps1, SLDatatype x)
{assert(ps1);SLCheckcapcity(ps1);//挪动数据int end = ps1->size - 1;while (end >= 0){ps1->a[end + 1] = ps1->a[end];end--;}ps1->a[0] = x;ps1->size++;
}
⭐挪动数据(从后往前)
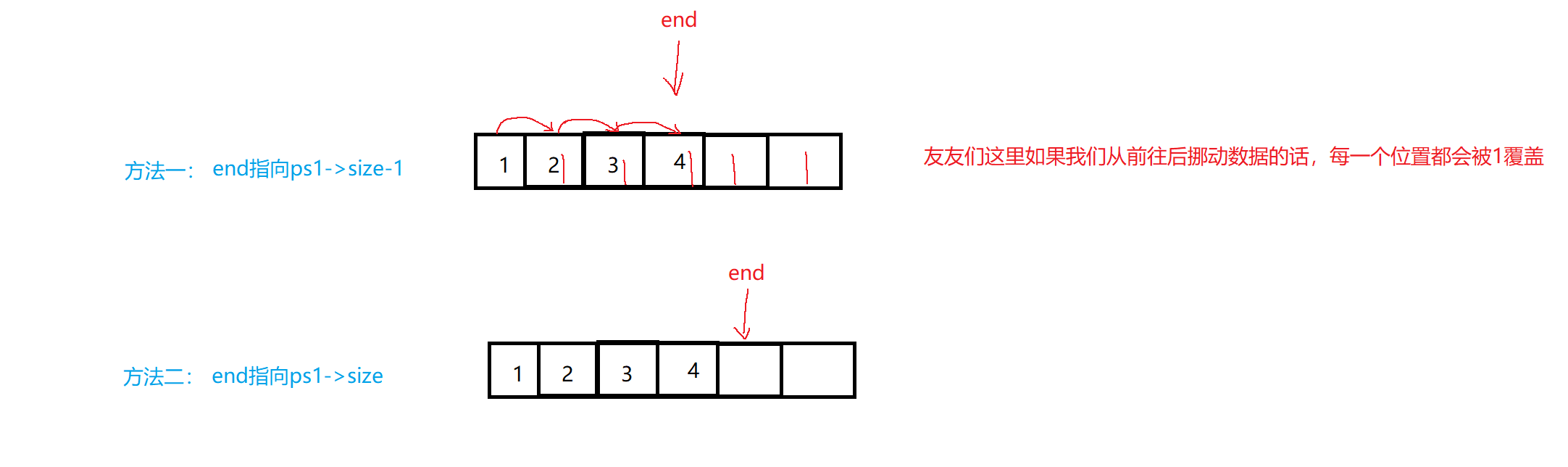
2.方法二:
void SLPushFront(SL* ps1, SLDatatype x)
{assert(ps1);SLCheckcapcity(ps1);//挪动数据int end = ps1->size;while (end > 0){ps1->a[end] = ps1->a[end-1];end--;}ps1->a[0] = x;ps1->size++;
}
🔍9.顺序表的尾删
void SLPopBack(SL* ps1)
{assert(ps1->size > 0&&ps1); //暴力检查ps1->size--;
}
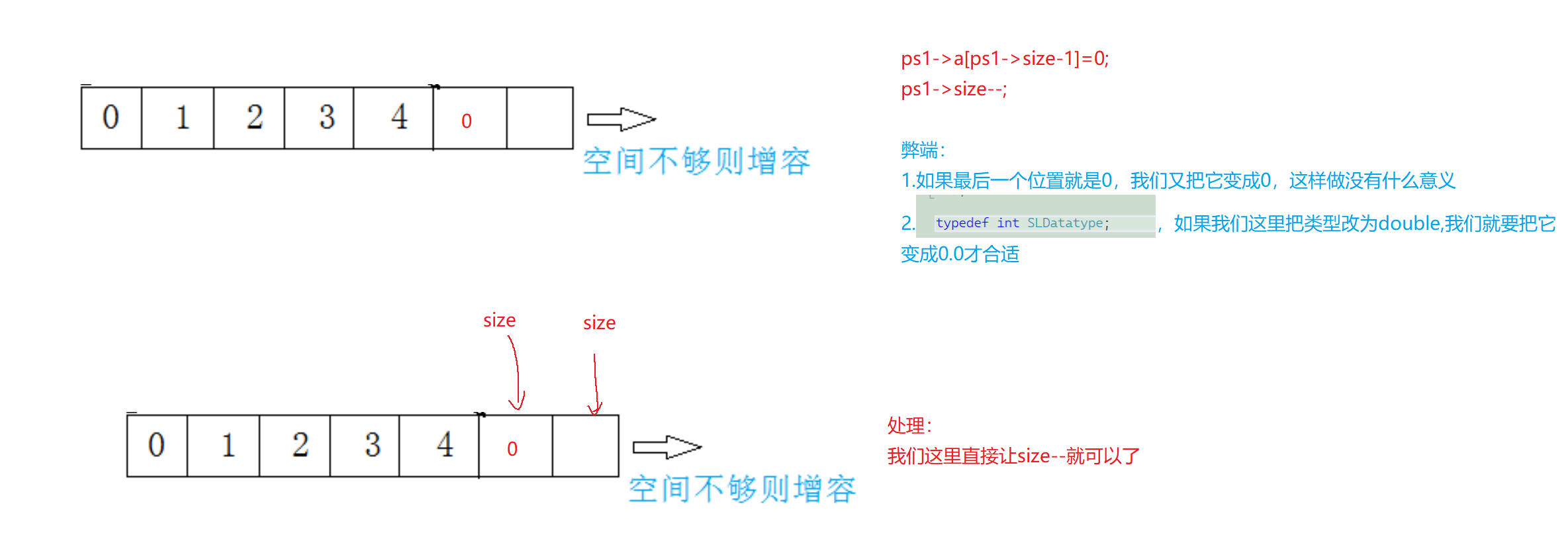
⭐assert的声明
友友们注意,如果我们顺序表里面有5个数据,而我们尾删6次,这时候ps1->size就变成-1了,就会出现数组越界,就是第一个数据放到下标为-1的位置上了,导致结果出错. 所以这里我们就需要assert来声明一下:如果顺序表为空,就不需要再尾删了.
⭐数组越界不一定报错
友友们一定要清楚越界本身就是一个抽查,并不是一定会报错的,如果数组下标越界了,那么它会自动接着那块内存往后写,如果界外的空间暂时没有被利用,那么我们就可以占用那块内存,但是如果界外的内存已经存放了数据,我们越界过去就会覆盖那块内存,则就有可能导致错误的产生.
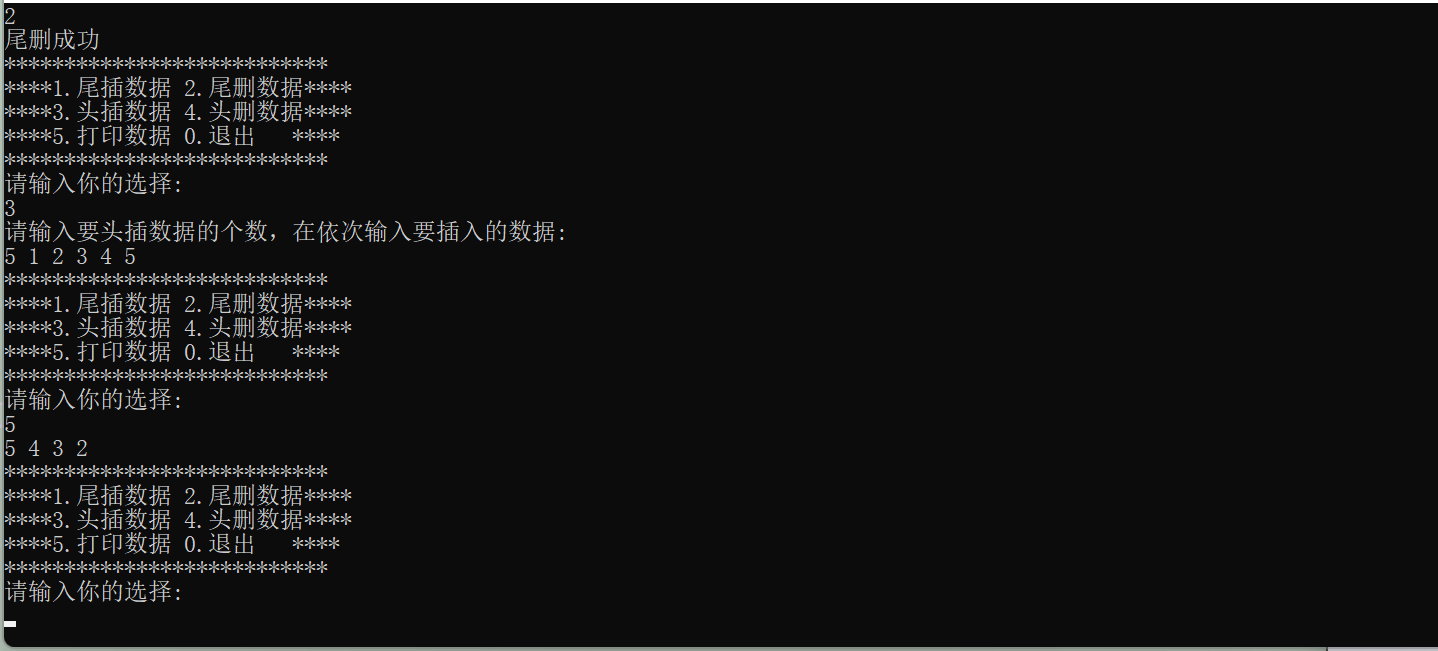
🔍10.顺序表的头删
1.方法一:start为1
void SLPopFront(SL* ps1)
{assert(ps1);assert(ps1->size > 0);int start = 1;while (start < ps1->size){ps1->a[start - 1] = ps1->a[start];start++;}ps1->size--;
}
2.方法二:start为0
void SLPopFront(SL* ps1)
{assert(ps1);assert(ps1->size > 0);int start = 0;while (start < ps1->size-1){ps1->a[start] = ps1->a[start+1];start++;}ps1->size--;
}
⭐挪动数据(从前往后)
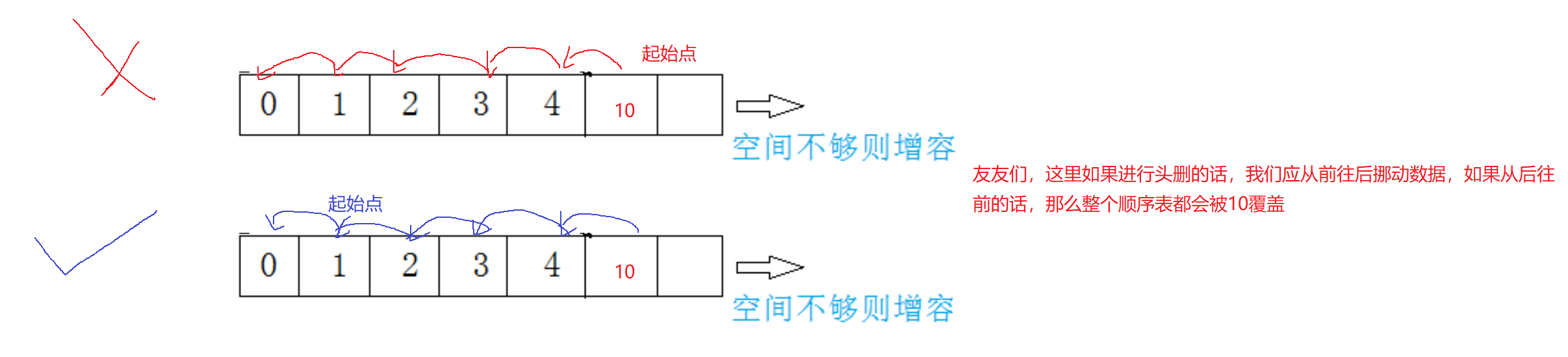
🔍11.顺序表任意位置的插入
void SLInsert(SL* ps1, int pos,SLDatatype x)
{assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps1->size&&ps1); //防止越界访问SLCheckcapcity(ps1);int end = ps1->size - 1;while (end >= pos){ps1->a[end + 1] = ps1->a[end];end--;}ps1->a[pos] = x;ps1->size++;
}
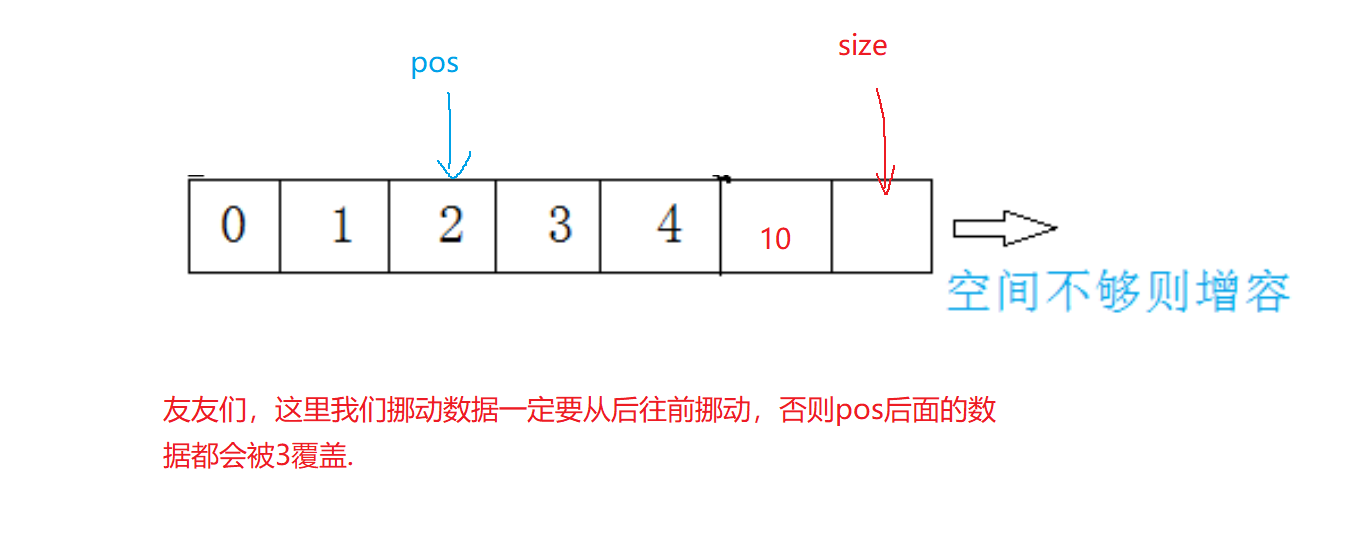
友友们,这里我们的
头插和尾插其实就是两种特殊位置的任意插入,这时候我们就可以附用这个函数,比如头插:SLInsert(ps1,0,x),尾插:SLInsert(ps1,ps1->size,x).
🔍12.顺序表任意位置的删除
1.方法一:start为pos+1
void SLErase(SL* ps1, int pos)
{assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps1->size&&ps1); //注意这里不能等于ps1->size,因为这里是删除,它本身就没有那么多的元素int start = pos + 1;while (start < ps1->size){ps1->a[start - 1] = ps1->a[start];start++;}ps1->size--;
}
2.方法二:start为pos
void SLErase(SL* ps1, int pos)
{assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps1->size&&ps1); //注意这里不能等于ps1->size,因为这里是删除,它本身就没有那么多的元素int start = pos;while (start < ps1->size-1){ps1->a[start] = ps1->a[start+1];start++;}ps1->size--;
}
⭐assert声明的改变&&函数的附用
友友们注意,这里pos就不能等于ps1->size了,因为我们要删除顺序表中的数据,它最多下标为ps1->size-1.这里我们的
头删和尾删就可以附用这个函数,头删就是:SLErase(ps1,0),尾删就是:(ps1,ps1->size-1).
🔍13.顺序表数据的查找
int SLFind(SL* ps1, SLDatatype x)
{assert(ps1);for (int i = 0; i < ps1->size; i++){if (ps1->a[i] == x){return i;}}return -1;
}
友友们注意,因为下标不可能是负数,所以我们没有找到就可以返回负数,一般我们都使用-1.
🔍13.顺序表数据的修改
void Modify(SL* ps1, int pos, SLDatatype x)
{assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps1->size&&ps1);ps1->a[pos] = x;
}
🔍14.顺序表的销毁
1.free之后需要置空
void SLDestory(SL*ps1)
{assert(ps1);free(ps1->a);ps1->a = NULL;ps1->size = 0;ps1->capcity = 0;
}
友友们,这里我们把ps1->a释放之后,因为它不是在函数内部创建的指针变量,它存放的是顺序表的地址,所以释放之后,函数外部可能会调用到它,所以我们这里需要及时置空.
2.free之后不需要置空
void rate(int* nums, int numsSize, int k)
{if (k > numsSize){k %= numsSize;}int* temp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * numsSize);memcpy(temp + k, nums, sizeof(int) * numsSize - k);memcpy(temp, nums + numsSize - k, sizeof(int) * k);memcpy(nums, temp, sizeof(int) * numsSize);free(temp);temp = NULL;
}
友友们注意了,这里的temp是我们在这个函数内部创建的指针变量,它是一个局部变量,它出完函数作用域就销毁了,所以我们free释放之后,就还给操作系统了,以后它也不会被调用了,所以这里我们不置空也是可以的.
👻Seqlist.h代码
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
//typedef int SLDatatype;
//
//struct Seqlist
//{
// SLDatatype a[N]; //静态的顺序表 给小了不够用,给大了浪费,这里我们考虑动态顺序表
// int size;
//};typedef int SLDatatype;typedef struct Seqlist
{SLDatatype * a; //动态的顺序表int size; //存储的有效数据个数int capcity; //容量空间
}SL;
void SLInit(SL* ps1);
void SLDestory(SL *ps1);
void SLPushBack(SL* ps1, SLDatatype x);
void SLPushFront(SL* ps1, SLDatatype x);
void SLPopBack(SL* ps1);
void SLPopFront(SL* ps1);
void SLPrint(SL* ps1);
void SLInsert(SL* ps1, int pos,SLDatatype x);
void SLErase(SL* ps1, int pos);
//找到了返回下标,找不到返回-1
int SLFind(SL* ps1, SLDatatype x);
void Modify(SL* ps1, int pos, SLDatatype x);
👻Seqlist.c代码
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Seqlist.h"
void SLInit(SL* ps1)
{assert(ps1);ps1->a =(SLDatatype*)malloc(sizeof(SLDatatype)*4);if (ps1->a == NULL){perror("malloc");return;}ps1->capcity = 4;ps1->size = 0;
}
void SLDestory(SL*ps1)
{assert(ps1);free(ps1->a);ps1->a = NULL;ps1->size = 0;ps1->capcity = 0;
}
void SLPrint(SL* ps1)
{assert(ps1);for (int i = 0; i < ps1->size; i++){printf("%d ", ps1->a[i]);}printf("\n");
}
void SLCheckcapcity(SL*ps1)
{assert(ps1);if (ps1->size == ps1->capcity){SLDatatype* temp =(SLDatatype*) realloc(ps1->a, sizeof(SLDatatype) * ps1->capcity * 2); if (temp == NULL){perror("realloc");return;}ps1->a = temp;ps1->capcity *= 2;}
}
void SLPushBack(SL* ps1, SLDatatype x)
{assert(ps1);SLCheckcapcity(ps1);ps1->a[ps1->size++] = x;
}
void SLPushFront(SL* ps1, SLDatatype x)
{assert(ps1);SLCheckcapcity(ps1);//挪动数据int end = ps1->size;while (end >0){ps1->a[end] = ps1->a[end-1];end--;}ps1->a[0] = x;ps1->size++;/*assert(ps1);SLInsert(ps1, 0, x);*/
}
void SLPopBack(SL* ps1)
{assert(ps1->size > 0&&ps1); //暴力检查/*ps1->a[ps1->size - 1] = 0;*/ //有可能最后一个数据就是0/*if (ps1->size == 0) {return;}*/ps1->size--;/*assert(ps1);SLErase(ps1, ps1->size - 1);*/
}
void SLPopFront(SL* ps1)
{assert(ps1);assert(ps1->size > 0);int start = 0;while (start < ps1->size-1){ps1->a[start] = ps1->a[start+1];start++;}ps1->size--;
}
void SLInsert(SL* ps1, int pos,SLDatatype x)
{assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps1->size&&ps1); //防止越界访问SLCheckcapcity(ps1);int end = ps1->size - 1;while (end >= pos){ps1->a[end + 1] = ps1->a[end];end--;}ps1->a[pos] = x;ps1->size++;
}
void SLErase(SL* ps1, int pos)
{assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps1->size&&ps1); //注意这里不能等于ps1->size,因为这里是删除,它本身就没有那么多的元素int start = pos;while (start < ps1->size-1){ps1->a[start] = ps1->a[start+1];start++;}ps1->size--;
}
int SLFind(SL* ps1, SLDatatype x)
{assert(ps1);for (int i = 0; i < ps1->size; i++){if (ps1->a[i] == x){return i;}}return -1;
}
void Modify(SL* ps1, int pos, SLDatatype x)
{assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps1->size&&ps1);ps1->a[pos] = x;
}
👻test.c代码
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Seqlist.h"
void menu()
{printf("***************************\n");printf("****1.尾插数据 2.尾删数据****\n");printf("****3.头插数据 4.头删数据****\n");printf("****5.打印数据 0.退出 ****\n");printf("***************************\n");
}
enum option
{ Destory,PushBack,PopBack,PushFront,PopFront,Print,
};
int main()
{SL s;SLInit(&s);int option = 0;do{menu();printf("请输入你的选择:\n");scanf("%d", &option);switch (option){case PushBack:{printf("请输入要尾插数据的个数,再依次输入要插入的数据:\n");int n = 0;scanf("%d", &n);int x = 0;while (n > 0){scanf("%d", &x);SLPushBack(&s, x);n--;}break;}case PopBack:printf("尾删成功\n");SLPopBack(&s);break;case PushFront:printf("请输入要头插数据的个数,在依次输入要插入的数据:\n");int n = 0;scanf("%d", &n);int x = 0;while (n > 0){scanf("%d", &x);SLPushFront(&s, x);n--;}break;case PopFront:printf("头删成功\n");SLPopFront(&s);break;case Print:SLPrint(&s);break;case Destory:SLDestory(&s);break;default:printf("选择错误,请重新选择:\n");break;}} while (option);return 0;
}