基于PD控制器的四旋翼无人机群飞行控制系统simulink建模与仿真
目录
1.课题概述
2.系统仿真结果
3.核心程序
4.系统原理简介
5.参考文献
6.完整工程文件
1.课题概述
使用simulink建模四旋翼无人机,然后结合MATLAB实现基于PD控制器的四旋翼无人机群飞行控制系统,仿真输出无人机的飞行模拟,无人机位置变化曲线,速度变化曲线,角度变化曲线等指标。
2.系统仿真结果
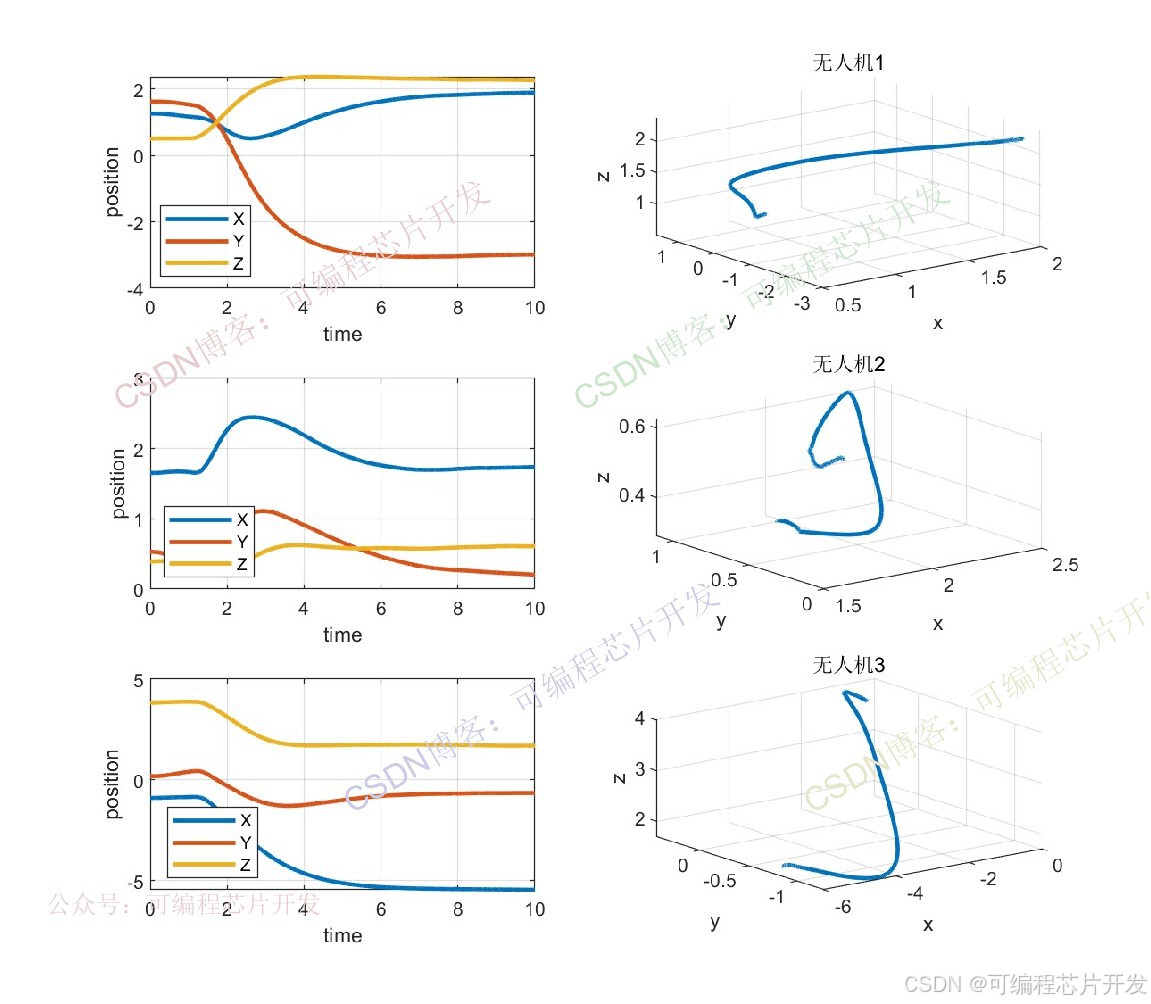
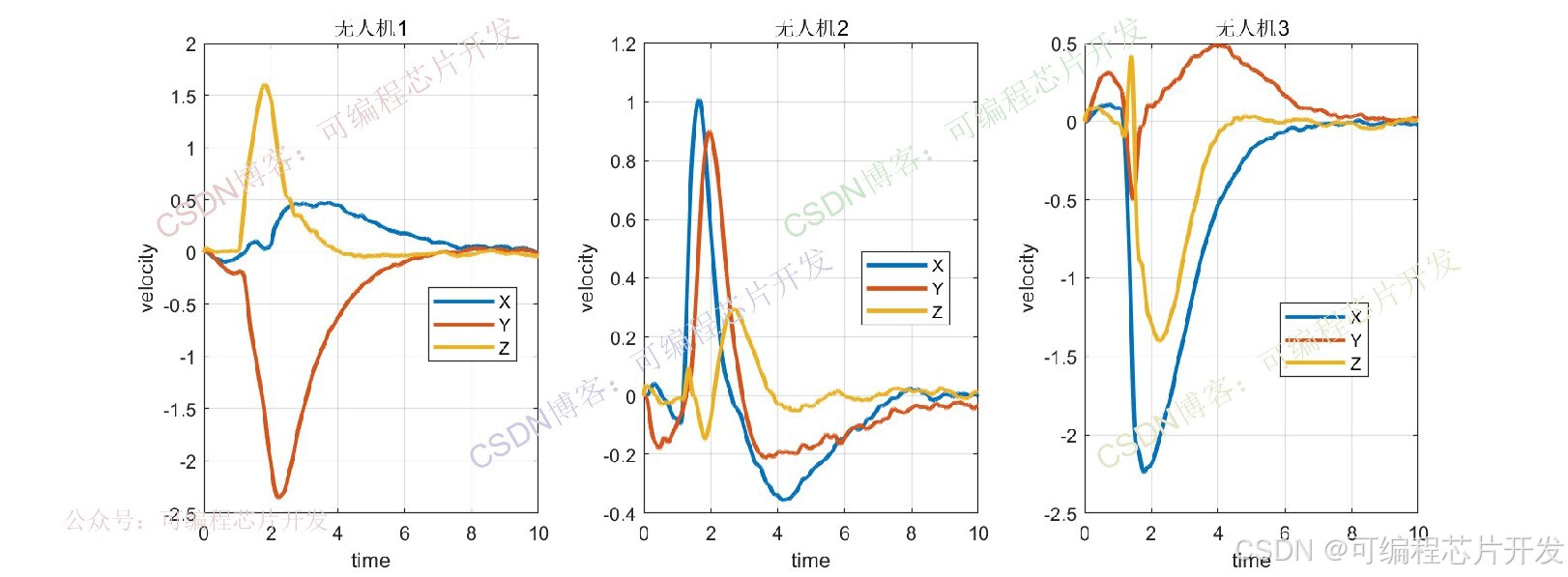
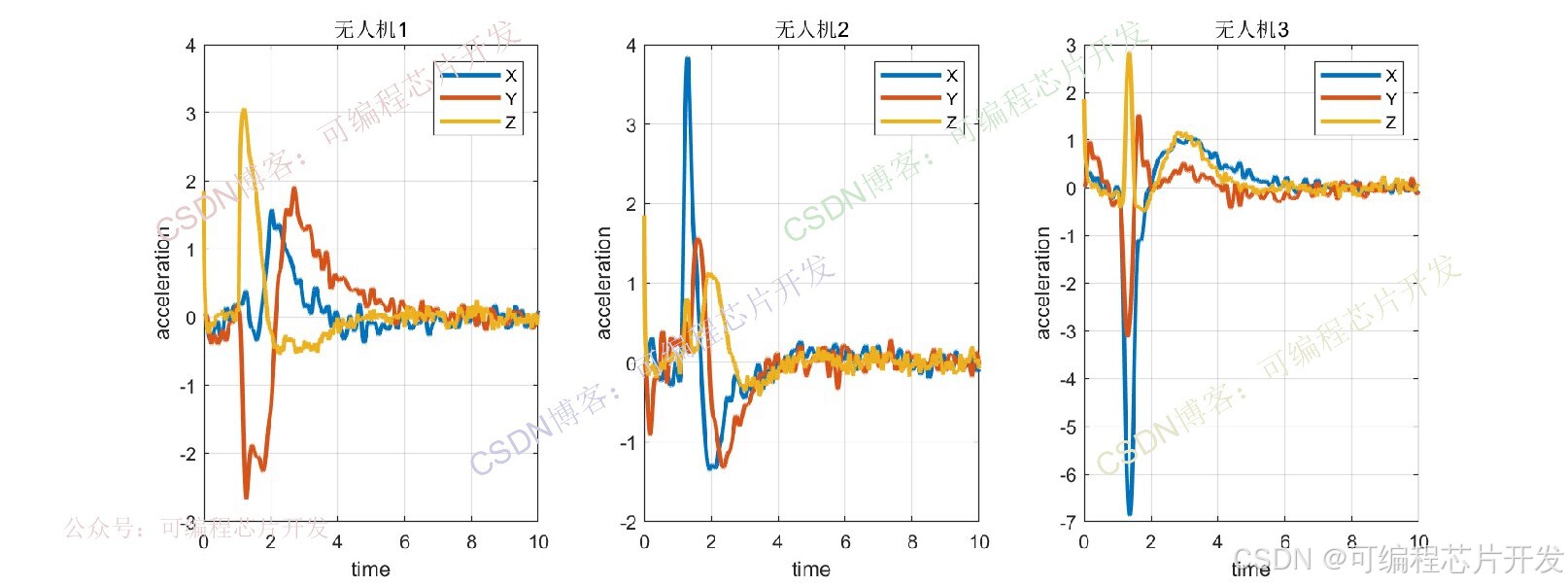
3.核心程序
matlab2024b
out = sim("tops.slx");func_plots(out, simkey, ['b'])load position1.mat
t1=ans.Time;
for i = 1:length(t1)posx1(i)=ans.Data(1,:,i);posy1(i)=ans.Data(2,:,i);posz1(i)=ans.Data(3,:,i);
end
load position2.mat
t2=ans.Time;
for i = 1:length(t2)posx2(i)=ans.Data(1,:,i);posy2(i)=ans.Data(2,:,i);posz2(i)=ans.Data(3,:,i);
end
load position3.mat
t3=ans.Time;
for i = 1:length(t1)posx3(i)=ans.Data(1,:,i);posy3(i)=ans.Data(2,:,i);posz3(i)=ans.Data(3,:,i);
endfigure;
subplot(321);
plot(t1,posx1,'LineWidth',2);
hold on
plot(t1,posy1,'LineWidth',2);
hold on
plot(t1,posz1,'LineWidth',2);
grid on
xlabel('time');
ylabel('position');
legend('X','Y','Z');
subplot(322);
plot3(posx1,posy1,posz1,'LineWidth',2);
grid on
xlabel('x');
ylabel('y');
zlabel('z');
title('无人机1')subplot(323);
plot(t2,posx2,'LineWidth',2);
hold on
plot(t2,posy2,'LineWidth',2);
hold on
plot(t2,posz2,'LineWidth',2);
grid on
xlabel('time');
ylabel('position');
legend('X','Y','Z');
subplot(324);
plot3(posx2,posy2,posz2,'LineWidth',2);
grid on
xlabel('x');
ylabel('y');
zlabel('z');
title('无人机2')subplot(325);
plot(t3,posx3,'LineWidth',2);
hold on
plot(t3,posy3,'LineWidth',2);
hold on
plot(t3,posz3,'LineWidth',2);
grid on
xlabel('time');
ylabel('position');
legend('X','Y','Z');
subplot(326);
plot3(posx3,posy3,posz3,'LineWidth',2);
grid on
xlabel('x');
ylabel('y');
zlabel('z');
title('无人机3')load body_velocity1.mat
t1=ans.Time;
for i = 1:length(t1)Vx1(i)=ans.Data(1,:,i);Vy1(i)=ans.Data(2,:,i);Vz1(i)=ans.Data(3,:,i);
end
load body_velocity2.mat
t2=ans.Time;
for i = 1:length(t2)Vx2(i)=ans.Data(1,:,i);Vy2(i)=ans.Data(2,:,i);Vz2(i)=ans.Data(3,:,i);
end
load body_velocity3.mat
t3=ans.Time;
for i = 1:length(t3)Vx3(i)=ans.Data(1,:,i);Vy3(i)=ans.Data(2,:,i);Vz3(i)=ans.Data(3,:,i);
endfigure;
subplot(131);
plot(t1,Vx1,'LineWidth',2);
hold on
plot(t1,Vy1,'LineWidth',2);
hold on
plot(t1,Vz1,'LineWidth',2);
grid on
xlabel('time');
ylabel('velocity');
legend('X','Y','Z');
title('无人机1')subplot(132);
plot(t1,Vx2,'LineWidth',2);
hold on
plot(t1,Vy2,'LineWidth',2);
hold on
plot(t1,Vz2,'LineWidth',2);
grid on
xlabel('time');
ylabel('velocity');
legend('X','Y','Z');
title('无人机2')subplot(133);
plot(t1,Vx3,'LineWidth',2);
hold on
plot(t1,Vy3,'LineWidth',2);
hold on
plot(t1,Vz3,'LineWidth',2);
grid on
xlabel('time');
ylabel('velocity');
legend('X','Y','Z');
title('无人机3')load acceleration1.mat
t1=ans.Time;
for i = 1:length(t1)accx1(i)=ans.Data(1,:,i);accy1(i)=ans.Data(2,:,i);accz1(i)=ans.Data(3,:,i);
end
load acceleration2.mat
t2=ans.Time;
for i = 1:length(t2)accx2(i)=ans.Data(1,:,i);accy2(i)=ans.Data(2,:,i);accz2(i)=ans.Data(3,:,i);
end
load acceleration3.mat
t3=ans.Time;
for i = 1:length(t3)accx3(i)=ans.Data(1,:,i);accy3(i)=ans.Data(2,:,i);accz3(i)=ans.Data(3,:,i);
endfigure;
subplot(131);
plot(t1,accx1,'LineWidth',2);
hold on
plot(t1,accy1,'LineWidth',2);
hold on
plot(t1,accz1,'LineWidth',2);
grid on
xlabel('time');
ylabel('acceleration');
legend('X','Y','Z');
title('无人机1')subplot(132);
plot(t2,accx2,'LineWidth',2);
hold on
plot(t2,accy2,'LineWidth',2);
hold on
plot(t2,accz2,'LineWidth',2);
grid on
xlabel('time');
ylabel('acceleration');
legend('X','Y','Z');
title('无人机2')subplot(133);
plot(t3,accx3,'LineWidth',2);
hold on
plot(t3,accy3,'LineWidth',2);
hold on
plot(t3,accz3,'LineWidth',2);
grid on
xlabel('time');
ylabel('acceleration');
legend('X','Y','Z');
title('无人机3')
1224.系统原理简介
四旋翼无人机通常采用"十"字形或"X"形布局,四个旋翼对称分布在机体的四个臂上。以"X"形布局为例,四个电机分别安装在机体的前、后、左、右四个方向,其中两两旋翼的旋转方向相反。具体来说:
前、后电机:通常为顺时针旋转(CW)
左、右电机:通常为逆时针旋转(CCW)
四旋翼无人机通过调节四个旋翼的转速来实现六个自由度的运动控制,但实际控制中主要关注以下四个方向的运动:
垂直运动(高度控制):通过同时增加或减小四个旋翼的转速,改变总升力的大小,实现上升或下降。
俯仰运动(前后倾斜):通过调节前、后旋翼的转速差,使机体产生俯仰力矩,实现向前或向后倾斜飞行。
滚转运动(左右倾斜):通过调节左、右旋翼的转速差,使机体产生滚转力矩,实现向左或向右倾斜飞行。
偏航运动(旋转):通过调节顺时针和逆时针旋转旋翼的转速差,利用反扭矩差使机体产生偏航力矩,实现顺时针或逆时针旋转。
无人机旋转矩阵:
绕Z轴旋转ψ角的矩阵:
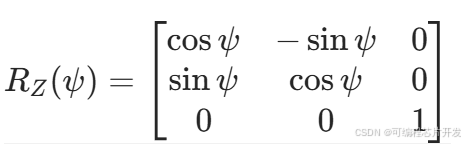
绕Y轴旋转θ角的矩阵:

绕X轴旋转ϕ角的矩阵:
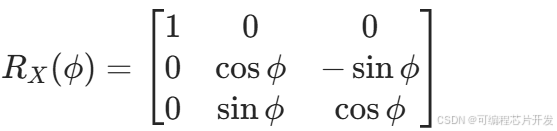
总旋转矩阵为:R=RZ(ψ)*RY(θ)*RX(ϕ)展开后得到:
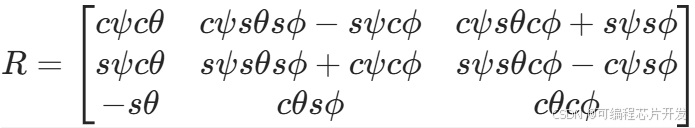
PD控制器的基本原理
PD(比例 - 微分)控制器是一种经典的线性控制器,其控制规律为:

基于PD控制器的四旋翼飞行控制系统设计
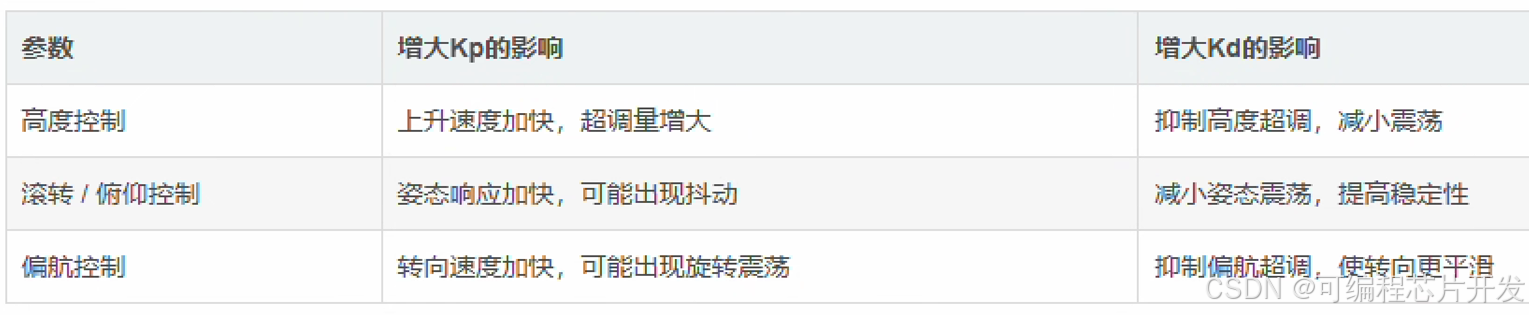
四旋翼无人机的PD控制通常采用内外环控制结构:
外环(位置环):控制无人机的空间位置(x, y, z)
内环(姿态环):控制无人机的姿态角(ϕ,θ,ψ)
这种架构的优势在于将复杂的非线性耦合系统分解为相对独立的控制环节,便于设计和调试。
控制无人机的滚转角ϕ和俯仰角θ,实现水平方向的倾斜运动,间接控制位置(x, y,z)。
5.参考文献
[1]丁少宾,肖长诗,刘金根,等.X型四旋翼无人机建模及四元数控制[J].系统仿真学报, 2015(12):6.DOI:CNKI:SUN:XTFZ.0.2015-12-027.
[2]王福,鲜斌,黄国平,等.四旋翼无人机自主悬停控制研究[C]//第三十二届中国控制会议.0[2025-07-01].
6.完整工程文件
v
