单链表应用实践
目录
移除链表元素(力扣)
思路:
代码形成:
注意:
反转链表(力扣)
思路:
代码:
注意:
迭代法
链表的中间结点(力扣)(快慢指针法)
思路:编辑
快慢指针实现代码
循环逻辑:
注意事项
边界情况处理:
偶数长度的中间节点定义:
合并两个有序链表
思路:
代码实现:
核心循环
申请空间,要释放
优势:
改进:
链表的回文结构
思路1:
代码实现:
潜在改进点
思路2:
代码
相交链表
思路:
代码:
环形链表
思路:编辑
代码:
环形链表2
思路:编辑
代码:
移除链表元素(力扣)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/description/
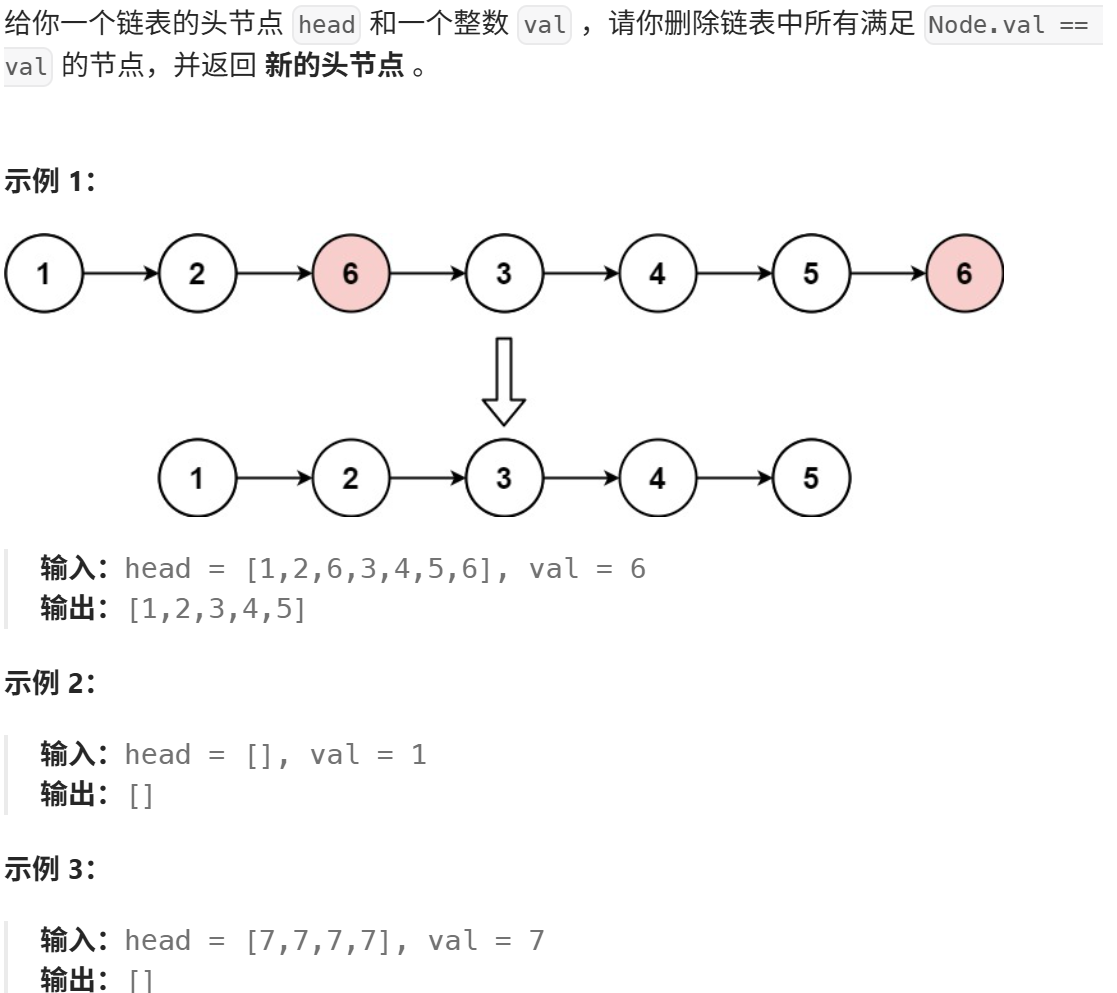
思路:
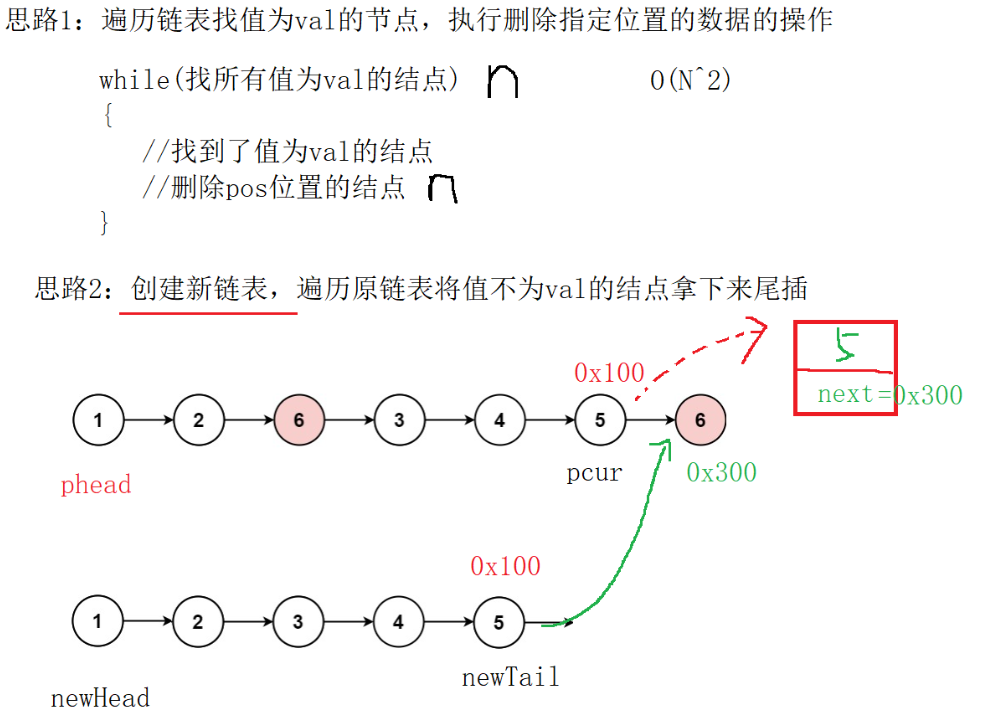
代码形成:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val) {//创建空链表ListNode*newHead,*newtail;newHead=newtail=NULL;ListNode*pcur=head;while(pcur){//把不为val的值插入新链表中if(pcur->val!=val){//尾插//链表为空if(newHead==NULL){newHead=newtail=pcur;}else{newtail->next=pcur;newtail=newtail->next;}}pcur=pcur->next;}if(newtail)newtail->next=NULL;return newHead;
}注意:
newHead和newtail用于维护新链表(存放所有不等于val的节点),初始为空。pcur用于遍历原链表,逐个检查节点的值- 关键:原链表中被插入新链表的节点,其
next指针可能指向原链表中的其他节点(甚至是需要删除的节点)。因此,新链表构建完成后,必须将尾节点的next置空,否则新链表可能包含不需要的节点或形成环。
反转链表(力扣)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/description/
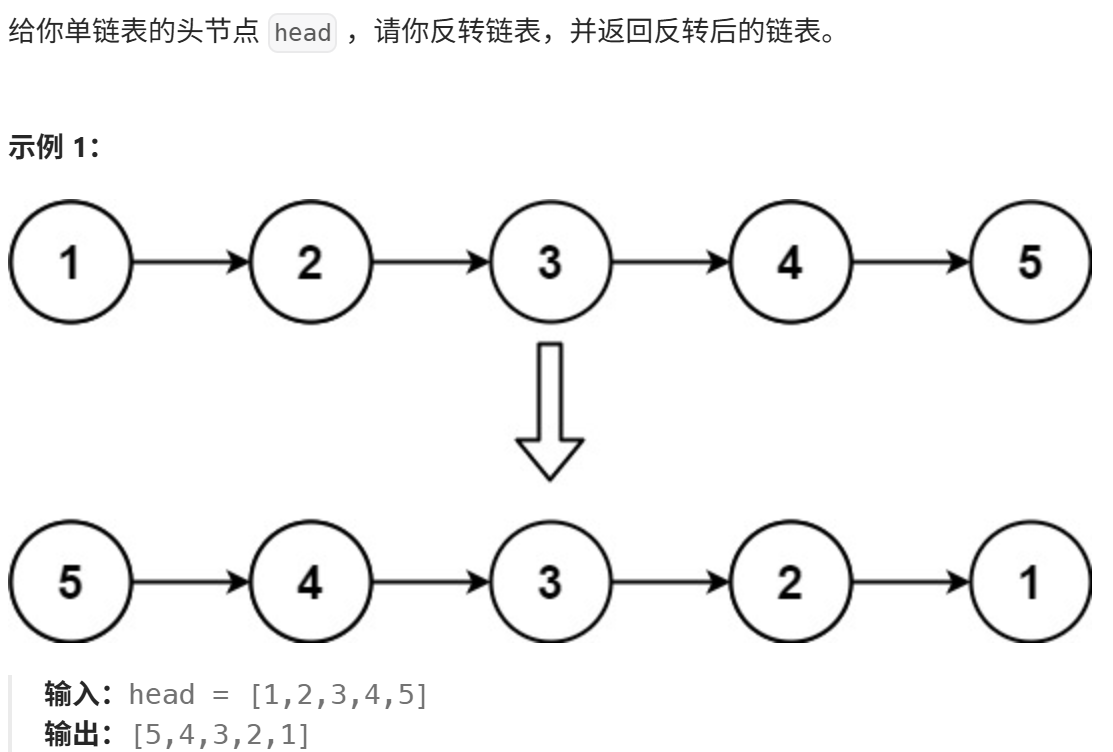
思路:

通过三个指针(n1、n2、n3)逐步遍历链表,逐个反转节点的指向关系。具体来说:
n2 指向当前需要处理的节点
n1 指向 n2 的前一个节点(反转后 n2 要指向的节点)
n3 保存 n2 的下一个节点(防止反转后丢失后续节点)
通过循环让这三个指针依次后移,直到 n2 为空(遍历完所有节点),此时 n1 就是反转后链表的头节点。
代码:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {//链表为空typedef struct ListNode ListNode;if(head==NULL){return head;}//如果原链表为空(头节点为 NULL),直接返回 NULL,避免后续操作出错。//创建三个指针ListNode*n1,*n2,*n3;//初始化n1=NULL,n2=head,n3=n2->next;while(n2){n2->next=n1;n1=n2;n2=n3;if(n3)n3=n3->next;}return n1;
}注意:
- 代码正确处理了空链表的边界情况
- 当
n3为NULL时(即n2是最后一个节点),不再执行n3 = n3->next,避免空指针访问 - 整个过程只需要三个额外指针,空间效率高
- 反转后原链表的头节点会变成尾节点(
next为NULL),符合链表规范
迭代法
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {// 终止条件:空链表或只有一个节点,直接返回if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) {return head;}// 递归反转后续节点,得到反转后的头节点ListNode* newHead = reverseList(head->next);// 反转当前节点与下一个节点的指向head->next->next = head; // 让下一个节点指向当前节点head->next = NULL; // 当前节点成为尾节点,指向NULLreturn newHead; // 始终返回反转后的头节点(原链表的最后一个节点)
}适用于理解递归思想,但不适合长链表,可能会导致栈溢出
链表的中间结点(力扣)(快慢指针法)
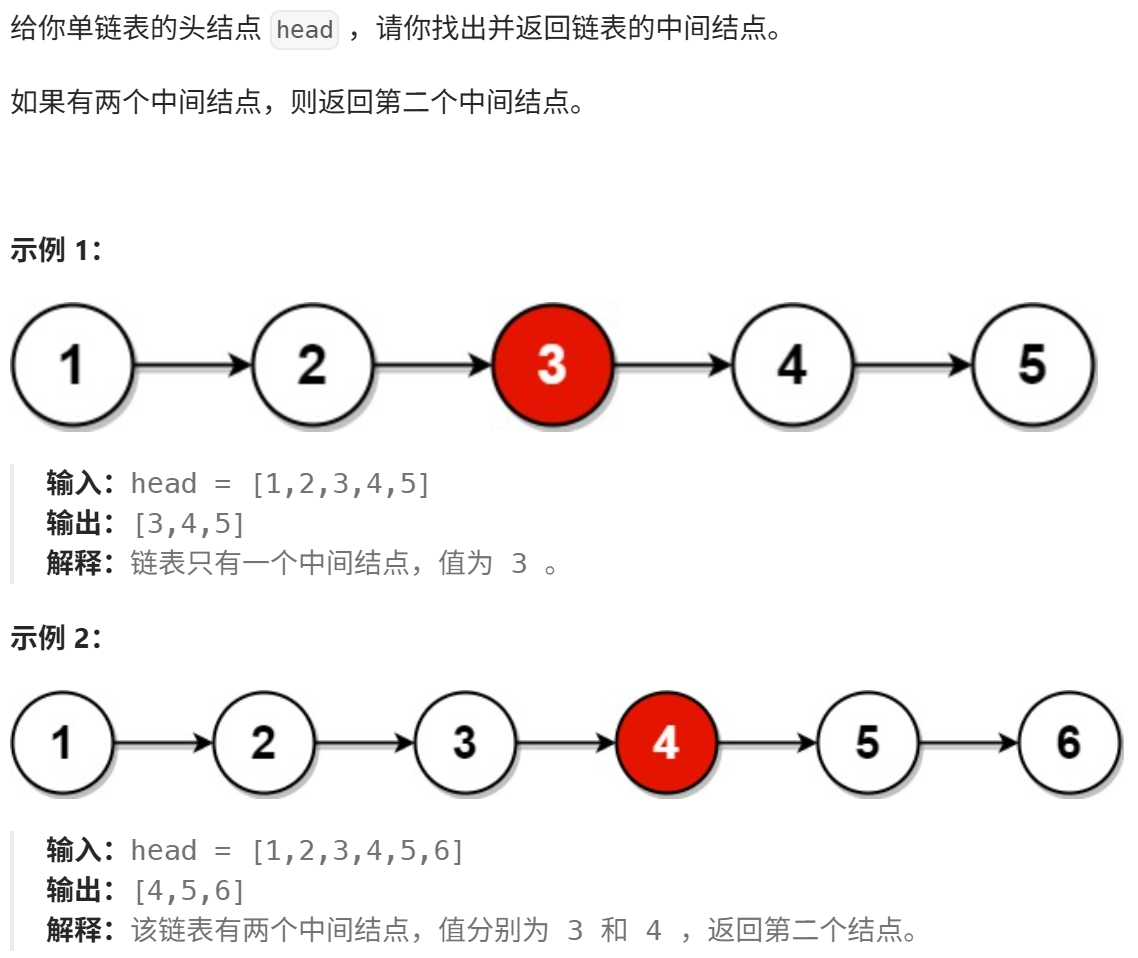
思路:
快慢指针实现代码
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {ListNode*l1,*l2;l1=l2=head;while(l1&&l1->next){l1=l1->next->next;l2=l2->next;}return l2;
}循环逻辑:
- 当
l1能继续移动(即l1不为空且l1->next不为空)时,继续循环。 - 每次循环中,
l1前进 2 步,l2前进 1 步,保持l1的速度是l2的 2 倍。 - 当循环结束时,
l1已到达或超过链表末尾,此时l2刚好在中间位置。
注意事项
-
边界情况处理:
- 若链表为空(
head=NULL),快慢指针均为NULL,直接返回NULL,符合预期。 - 若链表只有一个节点,循环不执行,直接返回该节点,正确。
- 若链表为空(
-
偶数长度的中间节点定义:
- 代码返回的是偶数长度链表的第二个中间节点(如
1->2->3->4返回3)。 - 若需要返回第一个中间节点(如
1->2->3->4返回2),只需调整循环条件为while(l1->next && l1->next->next)即可。
- 代码返回的是偶数长度链表的第二个中间节点(如
合并两个有序链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/description/
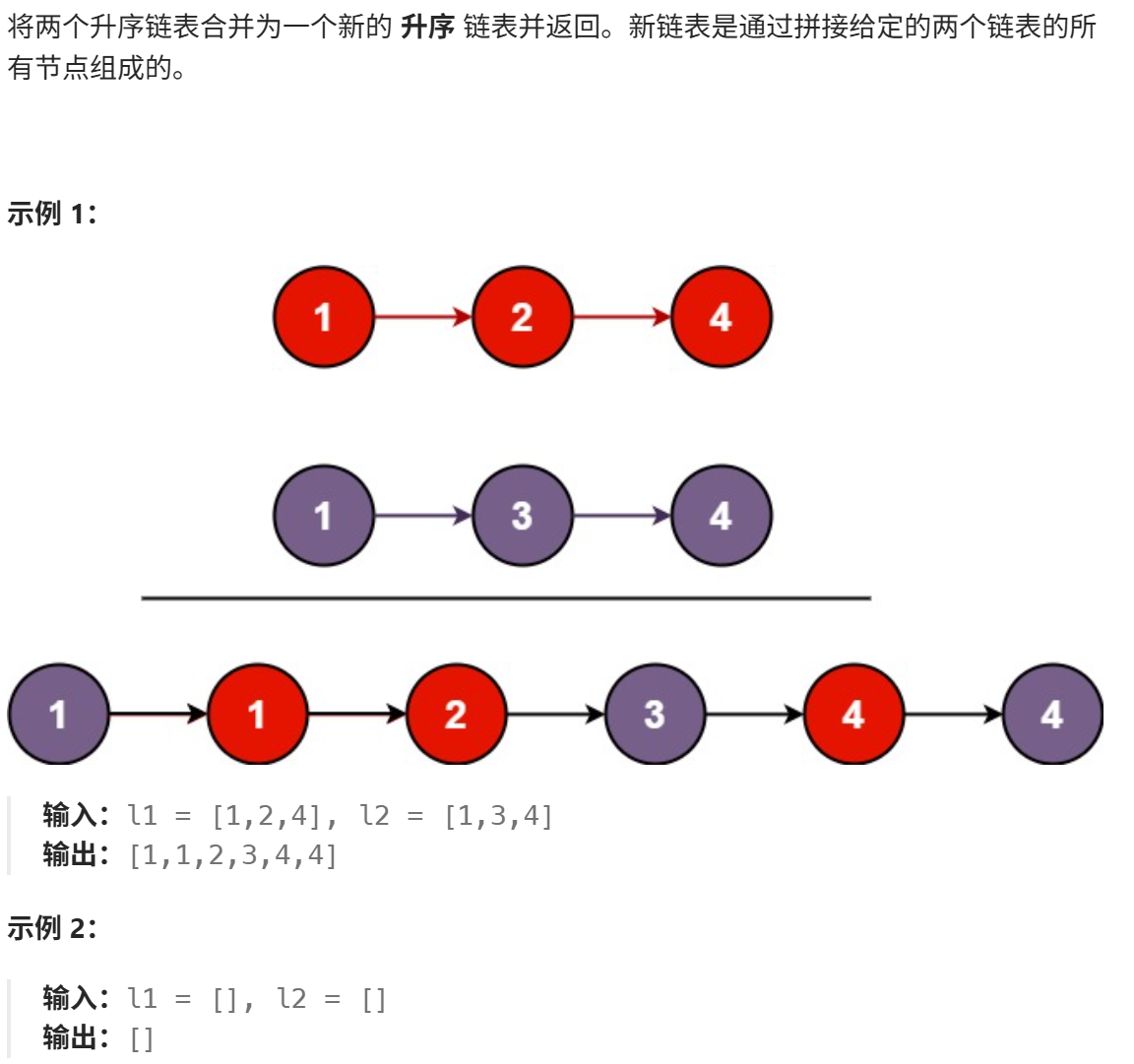
思路:

代码实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {if (list1 == NULL)return list2;if (list2 == NULL)return list1;ListNode *newhead, *newtail;newhead=newtail = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));//申请一个节点空间,非空结点while (list1 && list2) {if (list1->val < list2->val) {// 将1插入newhead后面newtail->next = list1;newtail = newtail->next;list1 = list1->next;}else{newtail->next = list2;newtail = newtail->next;list2 = list2->next;}}//总有一个先结束if(list1){newtail->next=list1;}if(list2){newtail->next=list2;}ListNode*rethead=newhead->next;free(newhead);newhead=NULL;return rethead;}- 哨兵节点(也称哑节点)是一个临时创建的空节点,用于简化链表操作(避免处理头节点为空的特殊情况)。
newhead指向哨兵节点,newtail始终指向新链表的尾节点(初始时与newhead相同)。
核心循环
while (list1 && list2) { // 当两个链表都不为空时if (list1->val < list2->val) {newtail->next = list1; // 将list1的当前节点接入新链表newtail = newtail->next; // 尾指针后移list1 = list1->next; // list1指针后移} else {newtail->next = list2; // 将list2的当前节点接入新链表newtail = newtail->next;list2 = list2->next;}
}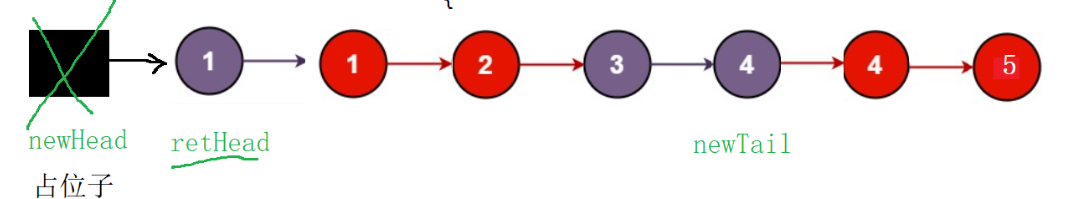
- 循环结束条件:其中一个链表的节点被全部接入(
list1或list2为空)。 - 循环结束后,剩余未接入的节点一定是有序的(原链表本身有序),直接将其整体接入新链表尾部即可。
申请空间,要释放
ListNode* rethead = newhead->next; // 新链表的真实头节点是哨兵节点的下一个
free(newhead); // 释放哨兵节点(避免内存泄漏)
newhead = NULL;
return rethead;优势:
- 时间复杂度:O (n + m),其中 n 和 m 分别是两个链表的长度(每个节点仅遍历一次)。
- 空间复杂度:O (1),仅使用常数级额外空间(哨兵节点在最后释放,不算有效空间)。
- 稳定性:保持原链表中相同值节点的相对顺序(例如:若两节点值相等,优先接入
list2的节点,符合代码逻辑)。
改进:
newtail->next = list1 ? list1 : list2;
有一组遍历完后,使用这组更简便
链表的回文结构
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/d281619e4b3e4a60a2cc66ea32855bfa
思路1:

代码实现:
/*
struct ListNode {int val;struct ListNode *next;ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class PalindromeList {public:bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A) {
//创建数组-900int arr[900];
//遍历链表将值保存在数组中ListNode* pcur=A;int i = 0;while (pcur) {arr[i++] = pcur->val;pcur = pcur->next;}
//判断数组是否为回文结构int left = 0;int right = i - 1;while (left < right) {if (arr[left] != arr[right]) {return false;}left++;right--;}return true;}
};潜在改进点
-
数组大小固定的问题
- 目前数组大小固定为 900,如果链表长度超过 900,会导致数组越界
- 可以考虑使用动态分配内存(如new 操作符),根据实际链表长度创建数组
-
空间复杂度优化
- 目前空间复杂度为 O (n),可以优化到 O (1):
- 找到链表中点
- 反转后半部分链表
- 比较前半部分和反转后的后半部分
- 目前空间复杂度为 O (n),可以优化到 O (1):
思路2:
![]()
代码
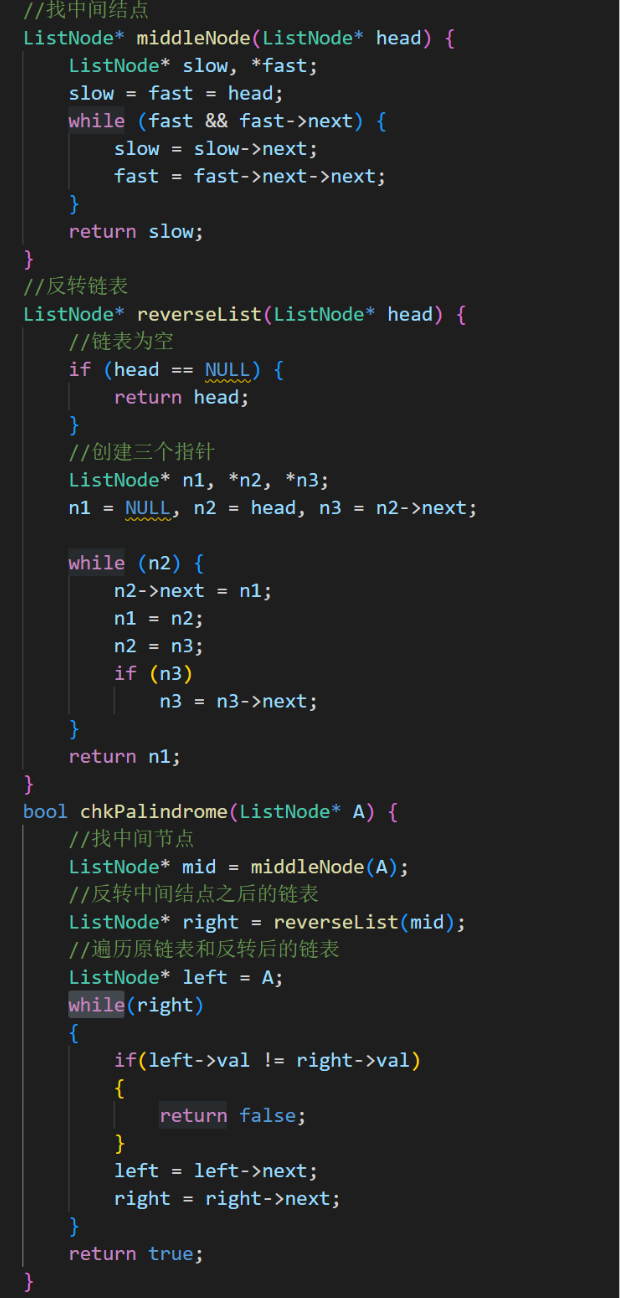
该方法相对复杂,但空间复杂度为o(1)
相交链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/description/
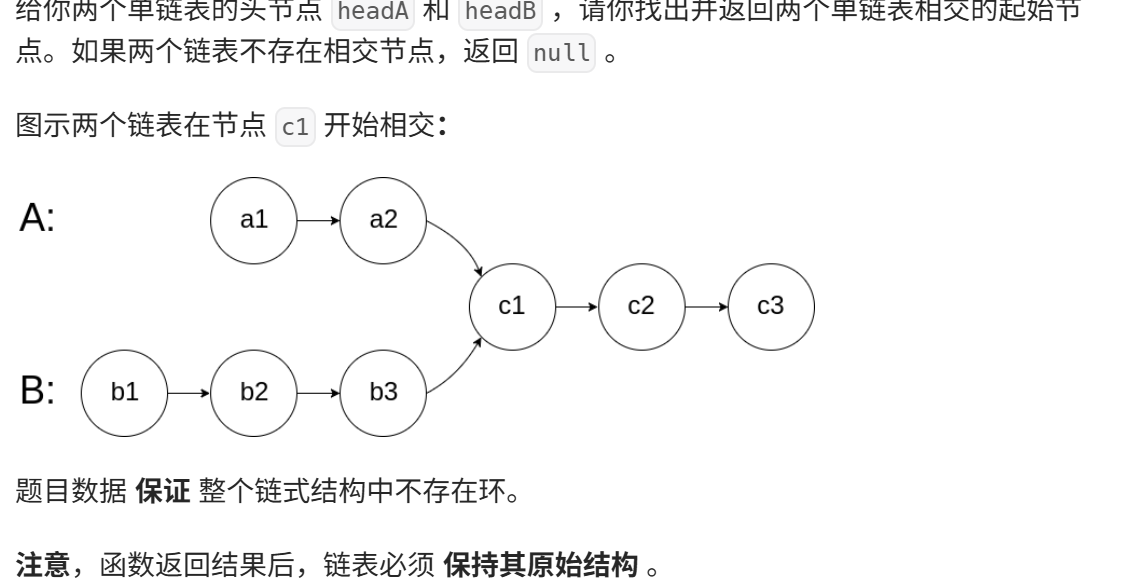
思路:
![]()
代码:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/typedef struct ListNode ListNode;// 计算链表长度的函数
int getLength(ListNode* head) {int count = 0;ListNode* current = head;while (current) {count++;current = current->next;}return count;
}
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {// 计算两个链表的长度int lenA = getLength(headA);int lenB = getLength(headB);// 确定较长的链表和较短的链表ListNode* longList = lenA > lenB ? headA : headB;ListNode* shortList = lenA > lenB ? headB : headA;// 让较长的链表先走长度差的步数int diff = abs(lenA - lenB);for (int i = 0; i < diff; i++) {longList = longList->next;}// 同时移动两个链表的指针,寻找交点while (longList && shortList) {// 找到交点if (longList == shortList) {return longList;}longList = longList->next;shortList = shortList->next;}// 没有交点return NULL;
}- 时间复杂度:O (n + m),其中 n 和 m 分别是两个链表的长度
- 空间复杂度:O (1),只使用了常数个额外空间
环形链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/description/
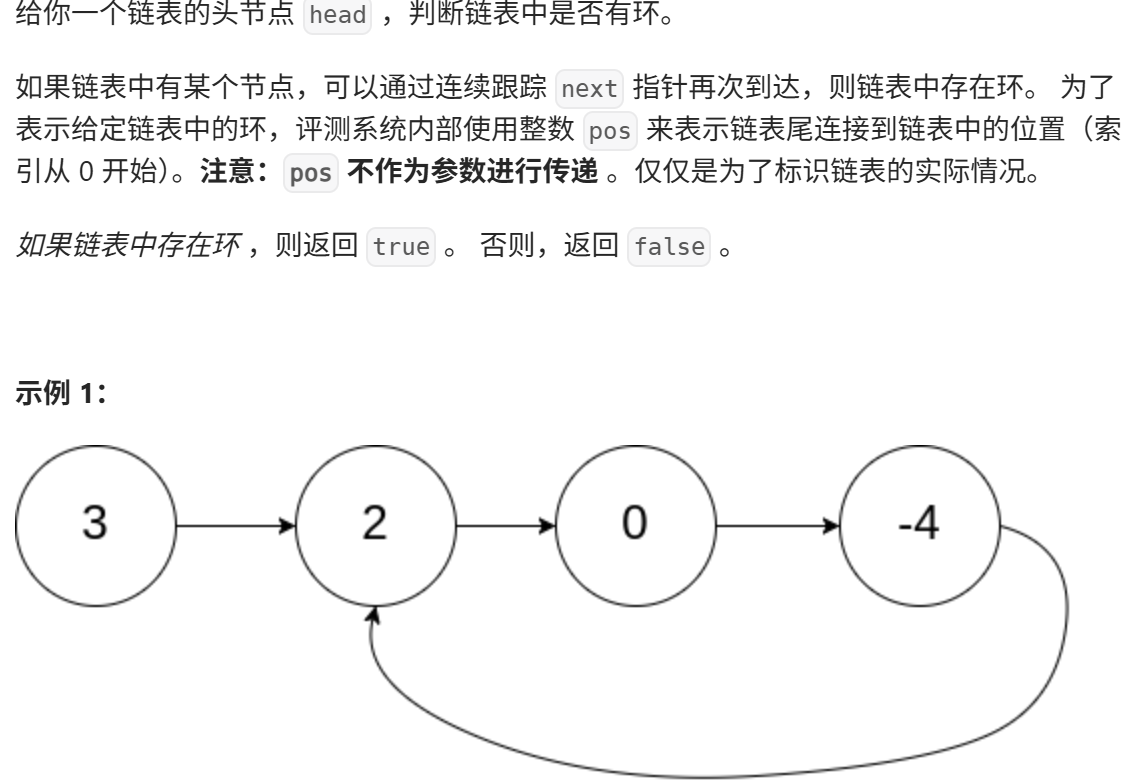
思路:
代码:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*///快慢指针typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head) {ListNode*fast=head;ListNode*slow=head;while(fast&&fast->next){fast=fast->next->next;slow=slow->next;if(slow==fast){return true;}}return false;
}- 时间复杂度:O (n),其中 n 是链表的长度。在有环的情况下,快指针最多绕环一周就能追上慢指针
- 空间复杂度:O (1),只使用了常数个额外空间,这是该算法相比哈希表方法的优势
环形链表2
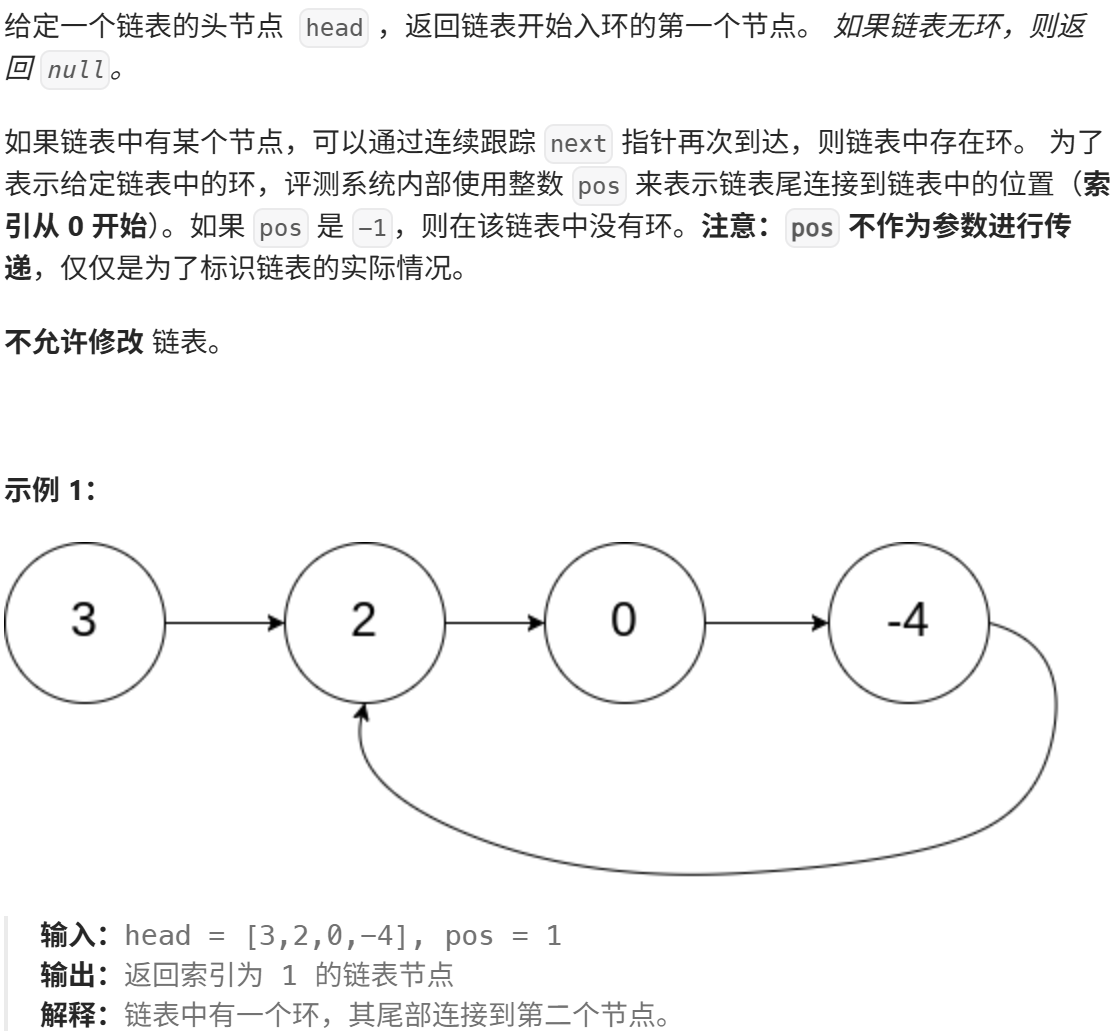
思路:
代码:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) {//快慢指针ListNode*slow=head;ListNode*fast=head;while(fast&&fast->next){slow=slow->next;fast=fast->next->next;if(fast==slow){ListNode*pcur=head;while(pcur!=slow){//找进入环点pcur=pcur->next;slow=slow->next;} return pcur;}}return NULL;}- 若链表存在环,快慢指针必定会在环内相遇(这是判断环存在的基础)
- 当快慢指针相遇后,将一个指针移到链表头部,两个指针以相同速度前进,它们再次相遇的位置就是环的入口节点
- 时间复杂度:O (n),其中 n 是链表的长度
- 空间复杂度:O (1),只使用了常数个额外空间
