嵌入式开发学习———Linux环境下IO进程线程学习(二)
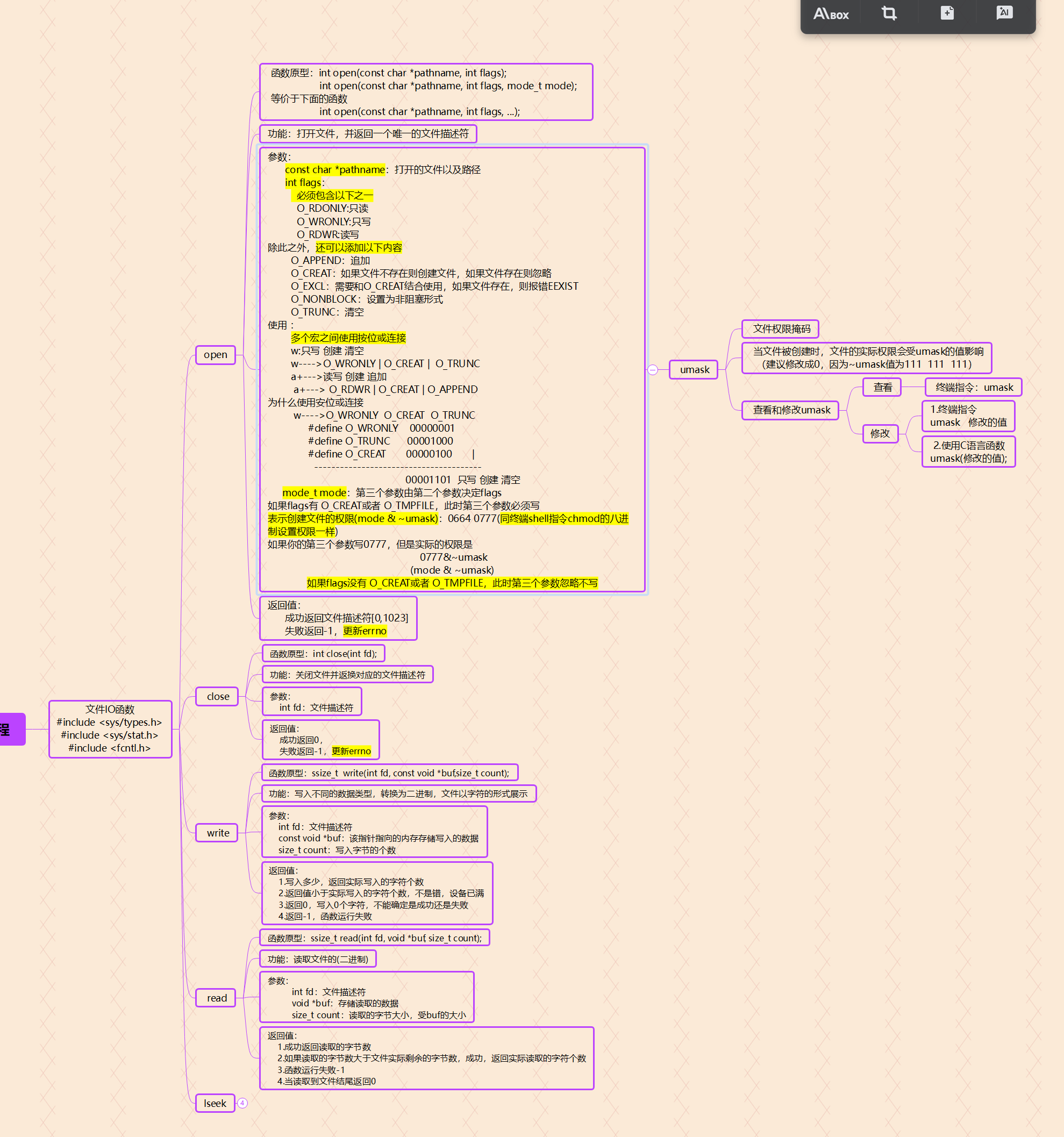
Linux文件I/O基础
Linux文件I/O主要通过系统调用实现,分为低级I/O(无缓冲)和标准I/O(带缓冲)两类。核心系统调用包括:
int open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode);
ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count);
ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count);
int close(int fd);
关键特点
- 文件描述符(fd)是非负整数,代表打开的文件
- 所有设备均抽象为文件操作
- 默认使用缓冲I/O提升性能
示例代码
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>int fd = open("test.txt", O_RDWR | O_CREAT, 0644);
char buf[100];
read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
write(fd, "data", 4);
close(fd);
作业:
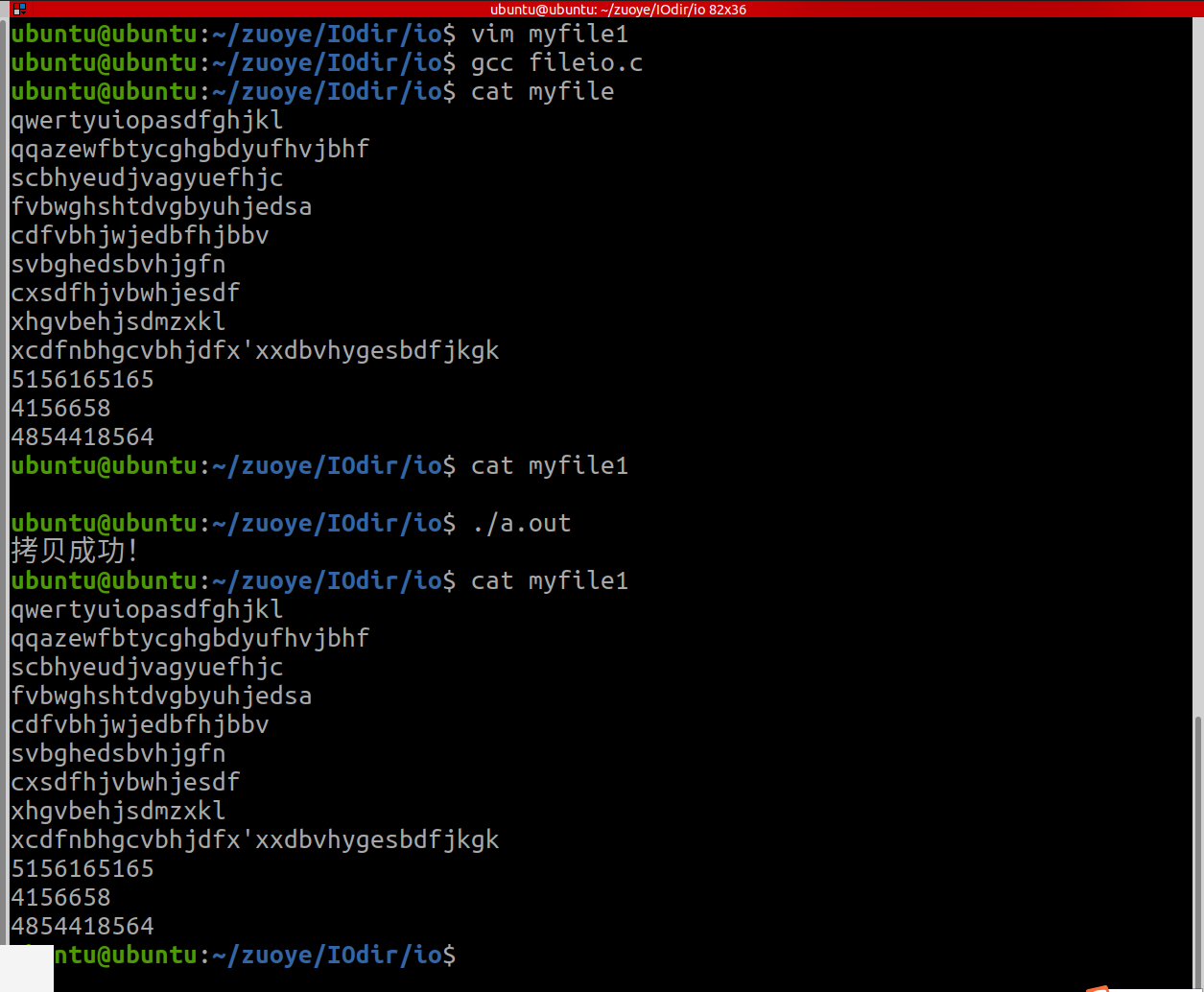
1·使用文件10函数,实现文件的拷贝
#include <myhead.h>int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{int fd1=open("./myfile",O_RDONLY);int fd2=open("./myfile1",O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC,0770);char buf[1024]="";while(read(fd1,buf,sizeof(buf))!=0){write(fd2,buf,strlen(buf));}close(fd1);close(fd2);puts("拷贝成功!");return 0;
}运行结果:
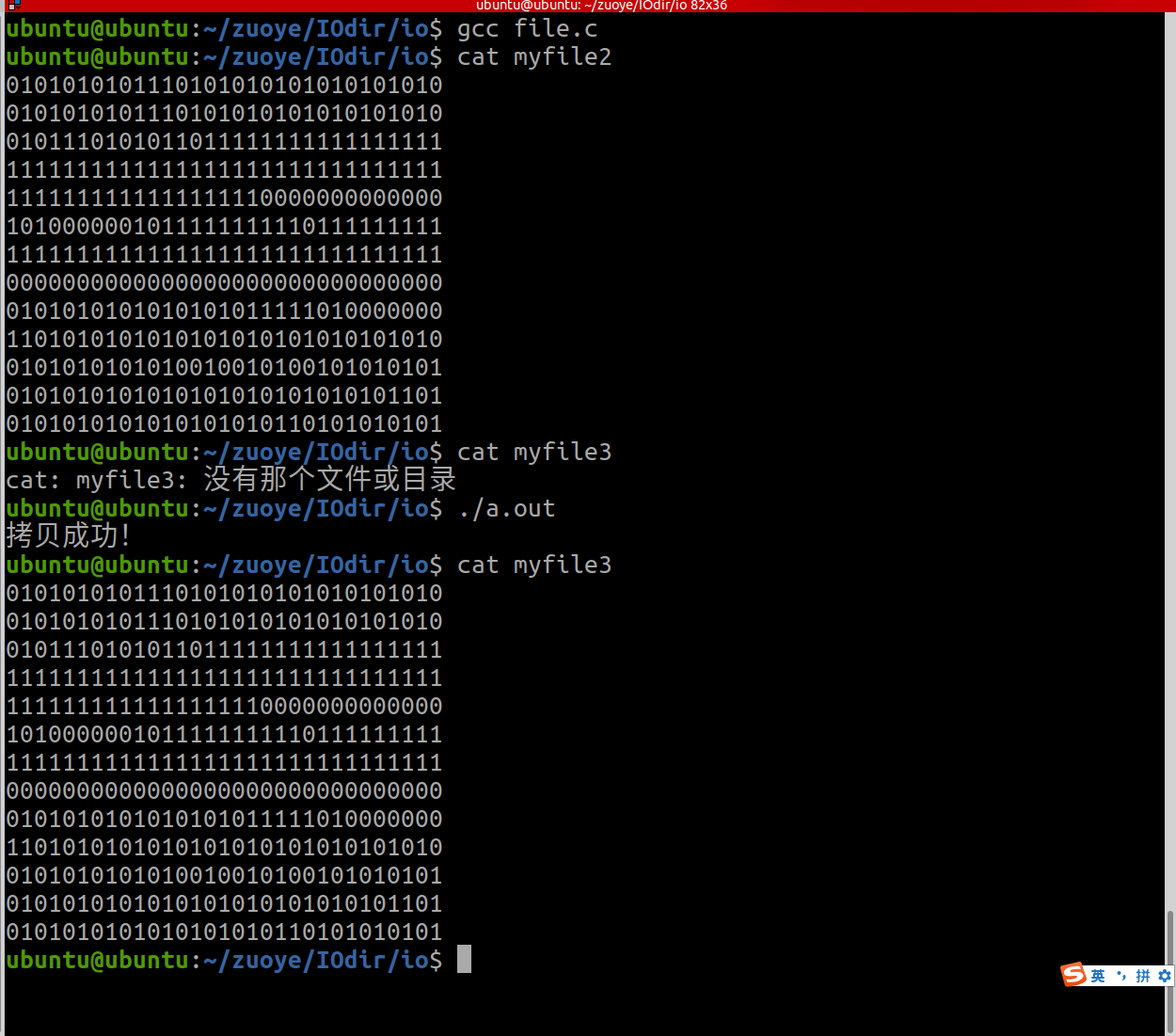
2.使用标准1O函数,实现图片的拷贝
#include <myhead.h>int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{FILE *fp1=NULL,*fp2=NULL;fp1=fopen("./myfile2","r");if(fp1==NULL){ERROR_MSG("fopen error");}fp2=fopen("./myfile3","w");if(fp2==NULL){ERROR_MSG("fopen error");}char buf[2048]="";while(fread(buf,1,sizeof(buf),fp1)){fwrite(buf,1,strlen(buf),fp2);}puts("拷贝成功!");fclose(fp1);fclose(fp2);return 0;
}运行结果:
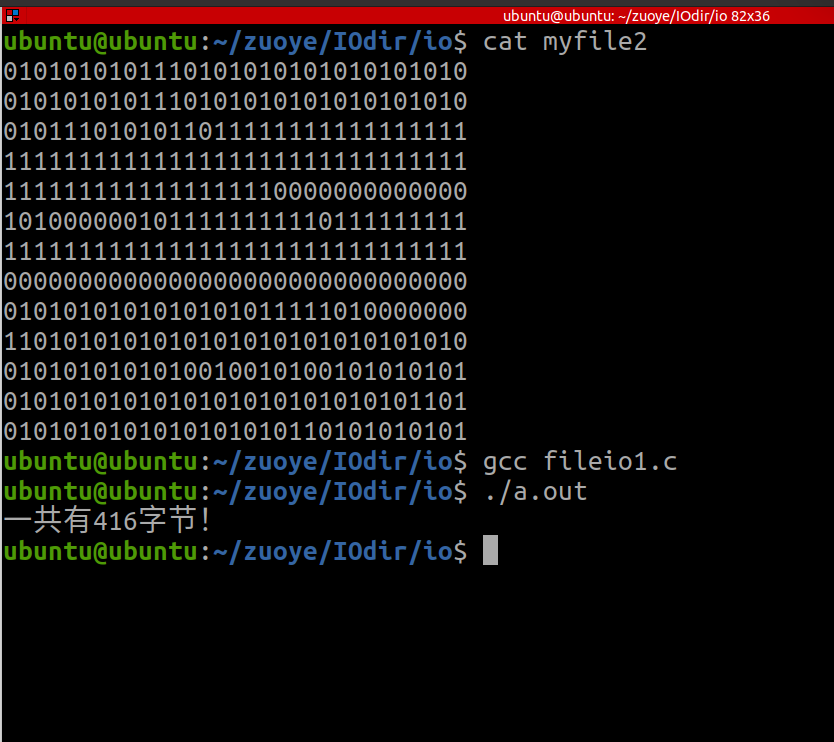
3.使用文件10函数,计算文件的大小
#include <myhead.h>int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{int fd=open("./myfile2",O_RDONLY);char buf[1024]="";int sum=0;while(read(fd,buf,sizeof(buf))!=0){sum=sum+strlen(buf); }close(fd);printf("一共有%d字节!\n",sum);return 0;
}
运行结果:
5.牛客网