<RT1176系列13>LWIP Ping功能入门级应用和基础API解析
1、概述
本文通过NXP官方SDK讲解如何移植LWIP Ping相关功能的驱动,面向刚入门的小白。
官方IDE:MCUXpresso,SDK:MIMXRT1170-EVK。
2、SDK工程导入
详细步骤参照文章:<RT1176系列3>LPSPI入门级应用和基础API解析-CSDN博客
这次导入lwip_ping_bm_cm7的例程做代码分析: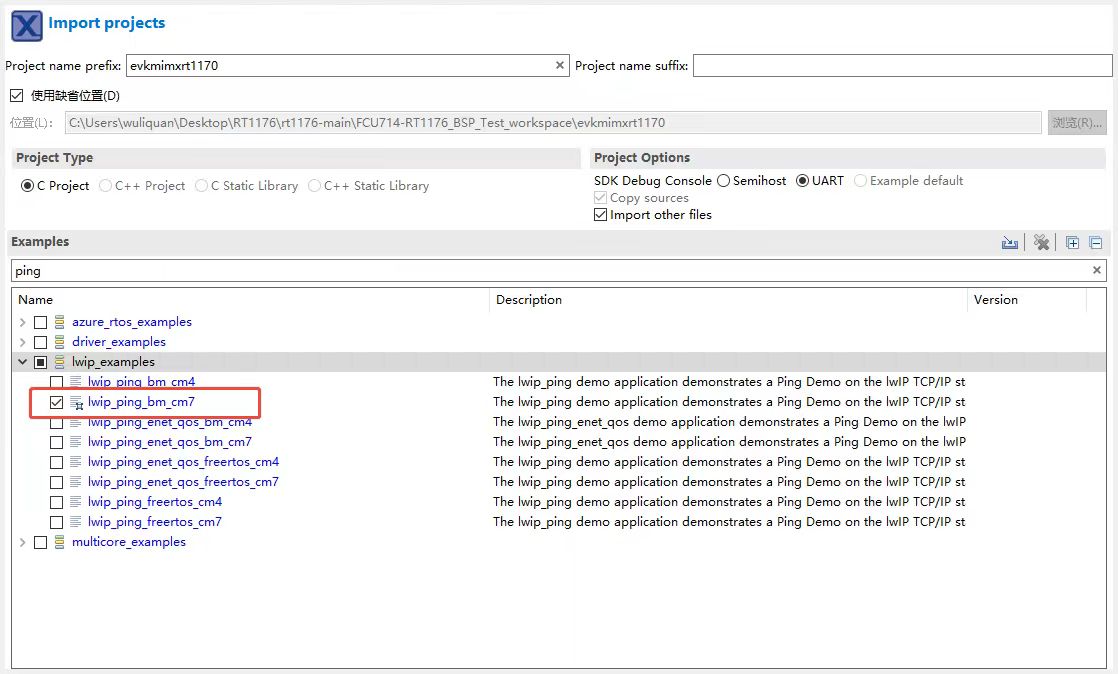
3、lwip ping的移植概要
LwIP 协议栈配置(启用ICMP)——>MAC/PHY初始化——>网络接口初始化——>Ping 功能初始化与实现——>处理 Ping 应答(ICMP 接收回调)
4、核心结构体解析
/** Generic data structure used for all lwIP network interfaces.
* The following fields should be filled in by the initialization
* function for the device driver: hwaddr_len, hwaddr[], mtu, flags */
struct netif {
#if !LWIP_SINGLE_NETIF
/** pointer to next in linked list */
struct netif *next;
#endif#if LWIP_IPV4
/** IP address configuration in network byte order */
ip_addr_t ip_addr;
ip_addr_t netmask;
ip_addr_t gw;
#endif /* LWIP_IPV4 */
#if LWIP_IPV6
/** Array of IPv6 addresses for this netif. */
ip_addr_t ip6_addr[LWIP_IPV6_NUM_ADDRESSES];
/** The state of each IPv6 address (Tentative, Preferred, etc).
* @see ip6_addr.h */
u8_t ip6_addr_state[LWIP_IPV6_NUM_ADDRESSES];
#if LWIP_IPV6_ADDRESS_LIFETIMES
/** Remaining valid and preferred lifetime of each IPv6 address, in seconds.
* For valid lifetimes, the special value of IP6_ADDR_LIFE_STATIC (0)
* indicates the address is static and has no lifetimes. */
u32_t ip6_addr_valid_life[LWIP_IPV6_NUM_ADDRESSES];
u32_t ip6_addr_pref_life[LWIP_IPV6_NUM_ADDRESSES];
#endif /* LWIP_IPV6_ADDRESS_LIFETIMES */
#endif /* LWIP_IPV6 */
/** This function is called by the network device driver
* to pass a packet up the TCP/IP stack. */
netif_input_fn input;
#if LWIP_IPV4
/** This function is called by the IP module when it wants
* to send a packet on the interface. This function typically
* first resolves the hardware address, then sends the packet.
* For ethernet physical layer, this is usually etharp_output() */
netif_output_fn output;
#endif /* LWIP_IPV4 */
/** This function is called by ethernet_output() when it wants
* to send a packet on the interface. This function outputs
* the pbuf as-is on the link medium. */
netif_linkoutput_fn linkoutput;
#if LWIP_IPV6
/** This function is called by the IPv6 module when it wants
* to send a packet on the interface. This function typically
* first resolves the hardware address, then sends the packet.
* For ethernet physical layer, this is usually ethip6_output() */
netif_output_ip6_fn output_ip6;
#endif /* LWIP_IPV6 */
#if LWIP_NETIF_STATUS_CALLBACK
/** This function is called when the netif state is set to up or down
*/
netif_status_callback_fn status_callback;
#endif /* LWIP_NETIF_STATUS_CALLBACK */
#if LWIP_NETIF_LINK_CALLBACK
/** This function is called when the netif link is set to up or down
*/
netif_status_callback_fn link_callback;
#endif /* LWIP_NETIF_LINK_CALLBACK */
#if LWIP_NETIF_REMOVE_CALLBACK
/** This function is called when the netif has been removed */
netif_status_callback_fn remove_callback;
#endif /* LWIP_NETIF_REMOVE_CALLBACK */
/** This field can be set by the device driver and could point
* to state information for the device. */
void *state;
#ifdef netif_get_client_data
void* client_data[LWIP_NETIF_CLIENT_DATA_INDEX_MAX + LWIP_NUM_NETIF_CLIENT_DATA];
#endif
#if LWIP_NETIF_HOSTNAME
/* the hostname for this netif, NULL is a valid value */
const char* hostname;
#endif /* LWIP_NETIF_HOSTNAME */
#if LWIP_CHECKSUM_CTRL_PER_NETIF
u16_t chksum_flags;
#endif /* LWIP_CHECKSUM_CTRL_PER_NETIF*/
/** maximum transfer unit (in bytes) */
u16_t mtu;
#if LWIP_IPV6 && LWIP_ND6_ALLOW_RA_UPDATES
/** maximum transfer unit (in bytes), updated by RA */
u16_t mtu6;
#endif /* LWIP_IPV6 && LWIP_ND6_ALLOW_RA_UPDATES */
/** link level hardware address of this interface */
u8_t hwaddr[NETIF_MAX_HWADDR_LEN];
/** number of bytes used in hwaddr */
u8_t hwaddr_len;
/** flags (@see @ref netif_flags) */
u8_t flags;
/** descriptive abbreviation */
char name[2];
/** number of this interface. Used for @ref if_api and @ref netifapi_netif,
* as well as for IPv6 zones */
u8_t num;
#if LWIP_IPV6_AUTOCONFIG
/** is this netif enabled for IPv6 autoconfiguration */
u8_t ip6_autoconfig_enabled;
#endif /* LWIP_IPV6_AUTOCONFIG */
#if LWIP_IPV6_SEND_ROUTER_SOLICIT
/** Number of Router Solicitation messages that remain to be sent. */
u8_t rs_count;
#endif /* LWIP_IPV6_SEND_ROUTER_SOLICIT */
#if LWIP_IPV6_SEND_ROUTER_ADVERTISE
/** Index of IPv6 address used as prefix or -1 to disable ra */
s8_t ra_prefix_idx;
/** For how long will be valid default route via us. IP6_RA_RT_LIFETIME_NO_DEFAULT_ROUTE (0)
* means we will never be default router.*/
u16_t ra_router_lifetime;
/* Flag to indicates whether we are in the initial phase of Router Advertisement sending */
u8_t ra_is_initial;
/** Number of Router Advertisement messages that remain to be sent in the initial phase. */
u8_t ra_initial_count;
/* Timer to decide when to send a Router Advertisement */
u32_t ra_timer;#if LWIP_IPV6_RA_NUM_ROUTE_INFOS > 0
/** Sending of route information option in RA enabled. */
u8_t ra_rio_enabled[LWIP_IPV6_RA_NUM_ROUTE_INFOS];/** The number of leading bits in the Prefix that are valid. The value ranges from 0 to 128. */
u8_t ra_rio_prefix_length[LWIP_IPV6_RA_NUM_ROUTE_INFOS];/** The length of time in seconds (relative to the time the packet is sent) that the prefix
* is valid for route determination. A value of all one bits (0xffffffff) represents
* infinity. */
u32_t ra_rio_route_lifetime[LWIP_IPV6_RA_NUM_ROUTE_INFOS];/** IP address or a prefix of an IP address. */
ip6_addr_t ra_rio_prefix[LWIP_IPV6_RA_NUM_ROUTE_INFOS];
#endif /* LWIP_IPV6_RA_NUM_ROUTE_INFOS > 0 */#endif /* LWIP_IPV6_SEND_ROUTER_ADVERTISE */
#if MIB2_STATS
/** link type (from "snmp_ifType" enum from snmp_mib2.h) */
u8_t link_type;
/** (estimate) link speed */
u32_t link_speed;
/** timestamp at last change made (up/down) */
u32_t ts;
/** counters */
struct stats_mib2_netif_ctrs mib2_counters;
#endif /* MIB2_STATS */
#if LWIP_IPV4 && LWIP_IGMP
/** This function could be called to add or delete an entry in the multicast
filter table of the ethernet MAC.*/
netif_igmp_mac_filter_fn igmp_mac_filter;
#endif /* LWIP_IPV4 && LWIP_IGMP */
#if LWIP_IPV6 && LWIP_IPV6_MLD
/** This function could be called to add or delete an entry in the IPv6 multicast
filter table of the ethernet MAC. */
netif_mld_mac_filter_fn mld_mac_filter;
#endif /* LWIP_IPV6 && LWIP_IPV6_MLD */
#if LWIP_ACD
struct acd *acd_list;
#endif /* LWIP_ACD */
#if LWIP_NETIF_USE_HINTS
struct netif_hint *hints;
#endif /* LWIP_NETIF_USE_HINTS */
#if ENABLE_LOOPBACK
/* List of packets to be queued for ourselves. */
struct pbuf *loop_first;
struct pbuf *loop_last;
#if LWIP_LOOPBACK_MAX_PBUFS
u16_t loop_cnt_current;
#endif /* LWIP_LOOPBACK_MAX_PBUFS */
#if LWIP_NETIF_LOOPBACK_MULTITHREADING
/* Used if the original scheduling failed. */
u8_t reschedule_poll;
#endif /* LWIP_NETIF_LOOPBACK_MULTITHREADING */
#endif /* ENABLE_LOOPBACK */
};4.1链表管理
- 当系统支持多个网络接口(如以太网 + Wi-Fi)时,通过
next指针将所有netif结构体连成链表,便于统一管理。 LWIP_SINGLE_NETIF宏定义为 1 时,仅支持单接口,此成员会被编译移除。
#if !LWIP_SINGLE_NETIF
struct netif *next; // 指向链表中的下一个网络接口
#endif4.2 IP 地址配置
4.2.1 ipv4
ip_addr_t是 LwIP 定义的 IP 地址通用类型,IPv4 场景下本质是 32 位无符号整数。
#if LWIP_IPV4
ip_addr_t ip_addr; // 接口的IPv4地址(网络字节序)
ip_addr_t netmask; // 子网掩码(网络字节序)
ip_addr_t gw; // 网关地址(网络字节序)
#endif4.2.2 ipv6
- 支持 IPv6 多地址特性,
LWIP_IPV6_NUM_ADDRESSES定义最大可配置的 IPv6 地址数量(默认 3)。 - 地址状态遵循 IPv6 协议规范(如 RFC 4862),包括临时(Tentative)、首选(Preferred)等。
#if LWIP_IPV6
ip_addr_t ip6_addr[LWIP_IPV6_NUM_ADDRESSES]; // IPv6地址数组(一个接口可配置多个IPv6地址)
u8_t ip6_addr_state[LWIP_IPV6_NUM_ADDRESSES]; // 每个IPv6地址的状态(如临时地址、首选地址等)
#if LWIP_IPV6_ADDRESS_LIFETIMES
u32_t ip6_addr_valid_life[...]; // 地址有效期(秒)
u32_t ip6_addr_pref_life[...]; // 地址首选期(秒)
#endif
#endif4.3 核心回调
- 调用流程:协议栈(如 TCP/UDP)→
output(地址解析)→linkoutput(硬件发送);硬件接收→input→ 协议栈处理。
// 接收数据包回调:硬件驱动收到数据包后,调用此函数将数据上传到TCP/IP协议栈
netif_input_fn input;#if LWIP_IPV4
// IPv4发送回调:IP层需要发送数据包时调用,通常用于ARP地址解析后发送(如etharp_output)
netif_output_fn output;
#endif// 链路层发送回调:直接将数据包通过硬件发送(如以太网的MAC层发送函数)
netif_linkoutput_fn linkoutput;#if LWIP_IPV6
// IPv6发送回调:类似IPv4的output,用于IPv6的邻居发现(如ethip6_output)
netif_output_ip6_fn output_ip6;
#endif4.4 状态回调
用于监控接口状态变化,由用户或应用层注册
#if LWIP_NETIF_STATUS_CALLBACK
netif_status_callback_fn status_callback; // 接口启用/禁用状态变化时触发
#endif#if LWIP_NETIF_LINK_CALLBACK
netif_status_callback_fn link_callback; // 链路连接/断开(如网线插拔)时触发
#endif#if LWIP_NETIF_REMOVE_CALLBACK
netif_status_callback_fn remove_callback; // 接口被移除时触发
#endif4.5 硬件接口
u16_t mtu; // 最大传输单元(字节),以太网通常为1500
u8_t hwaddr[NETIF_MAX_HWADDR_LEN]; // 硬件地址(如MAC地址),默认最长6字节
u8_t hwaddr_len; // 硬件地址长度(以太网为6)
u8_t flags; // 接口标志
char name[2]; // 接口名称缩写(如"en"、"wl")
u8_t num; // 接口编号(如"en0"中的0)4.6 ipv6功能
#if LWIP_IPV6_AUTOCONFIG
u8_t ip6_autoconfig_enabled; // 是否启用IPv6自动配置(SLAAC)
#endif#if LWIP_IPV6_SEND_ROUTER_SOLICIT
u8_t rs_count; // 待发送的路由器请求(RS)报文数量
#endif#if LWIP_IPV6_SEND_ROUTER_ADVERTISE
// 路由器通告(RA)相关配置,用于接口作为IPv6路由器时发送通告
u8_t ra_prefix_idx; // 前缀索引
u16_t ra_router_lifetime; // 路由生存期
u32_t ra_timer; // RA发送定时器
#endif4.7 组播过滤
#if LWIP_IPV4 && LWIP_IGMP
netif_igmp_mac_filter_fn igmp_mac_filter; // IGMP组播过滤回调
#endif#if LWIP_IPV6 && LWIP_IPV6_MLD
netif_mld_mac_filter_fn mld_mac_filter; // MLDv2组播过滤回调
#endif4.8 环回功能
#if ENABLE_LOOPBACK
struct pbuf *loop_first, *loop_last; // 环回数据包队列
#endif4.9 统计信息
#if MIB2_STATS
struct stats_mib2_netif_ctrs mib2_counters; // SNMP MIB-II统计计数器
#endif5、代码解析
5.1 配置网络接口的 IP 地址、子网掩码和网关地址
/* IP address configuration. */
#ifndef configIP_ADDR0
#define configIP_ADDR0 192
#endif
#ifndef configIP_ADDR1
#define configIP_ADDR1 168
#endif
#ifndef configIP_ADDR2
#define configIP_ADDR2 0
#endif
#ifndef configIP_ADDR3
#define configIP_ADDR3 102
#endif/* Netmask configuration. */
#ifndef configNET_MASK0
#define configNET_MASK0 255
#endif
#ifndef configNET_MASK1
#define configNET_MASK1 255
#endif
#ifndef configNET_MASK2
#define configNET_MASK2 255
#endif
#ifndef configNET_MASK3
#define configNET_MASK3 0
#endif/* Gateway address configuration. */
#ifndef configGW_ADDR0
#define configGW_ADDR0 192
#endif
#ifndef configGW_ADDR1
#define configGW_ADDR1 168
#endif
#ifndef configGW_ADDR2
#define configGW_ADDR2 0
#endif
#ifndef configGW_ADDR3
#define configGW_ADDR3 100
#endifIP4_ADDR(&netif_ipaddr, configIP_ADDR0, configIP_ADDR1, configIP_ADDR2, configIP_ADDR3);
IP4_ADDR(&netif_netmask, configNET_MASK0, configNET_MASK1, configNET_MASK2, configNET_MASK3);
IP4_ADDR(&netif_gw, configGW_ADDR0, configGW_ADDR1, configGW_ADDR2, configGW_ADDR3);5.2 LwIP 协议栈初始化网络接口并完成基础网络功能配置
注册接口→设为默认→启用接口→等待物理连接→初始化诊断功能。
执行完成后,设备将具备基本的网络通信能力,可进一步启动 TCP、UDP 等协议进行数据传输。其中,链路检测(ethernetif_wait_linkup)是关键的硬件验证步骤,直接影响后续网络功能的可用性。
netif_add(&netif, &netif_ipaddr, &netif_netmask, &netif_gw, &enet_config, EXAMPLE_NETIF_INIT_FN, ethernet_input);
netif_set_default(&netif);
netif_set_up(&netif);while (ethernetif_wait_linkup(&netif, 5000) != ERR_OK)
{
PRINTF("PHY Auto-negotiation failed. Please check the cable connection and link partner setting.\r\n");
}ping_init(&netif_gw);5.3 LWIP 协议栈运行
LwIP 协议栈在裸机环境下的核心主循环,负责处理网络数据包收发和协议栈超时事件,确保网络功能的持续运行。
while (1)
{
/* Poll the driver, get any outstanding frames */
ethernetif_input(&netif);sys_check_timeouts(); /* Handle all system timeouts for all core protocols */
}6、API解析
6.1 lwip_init
LWIP初始化,LwIP 协议栈在裸机下的核心初始化函数
/**
* @ingroup lwip_nosys
* Initialize all modules.
* Use this in NO_SYS mode. Use tcpip_init() otherwise.
*/
void
lwip_init(void)
{
#ifndef LWIP_SKIP_CONST_CHECK
int a = 0;
#ifdef LWIP_NOASSERT /* Caused compiler warning. */
LWIP_UNUSED_ARG(a);
#endif
LWIP_ASSERT("LWIP_CONST_CAST not implemented correctly. Check your lwIP port.", LWIP_CONST_CAST(void *, &a) == &a);
#endif
#ifndef LWIP_SKIP_PACKING_CHECK
LWIP_ASSERT("Struct packing not implemented correctly. Check your lwIP port.", sizeof(struct packed_struct_test) == PACKED_STRUCT_TEST_EXPECTED_SIZE);
#endif/* Modules initialization */
stats_init();
#if !NO_SYS
sys_init();
#endif /* !NO_SYS */
mem_init();
memp_init();
pbuf_init();
netif_init();
#if LWIP_IPV4
ip_init();
#if LWIP_ARP
etharp_init();
#endif /* LWIP_ARP */
#endif /* LWIP_IPV4 */
#if LWIP_RAW
raw_init();
#endif /* LWIP_RAW */
#if LWIP_UDP
udp_init();
#endif /* LWIP_UDP */
#if LWIP_TCP
tcp_init();
#endif /* LWIP_TCP */
#if LWIP_IGMP
igmp_init();
#endif /* LWIP_IGMP */
#if LWIP_DNS
dns_init();
#endif /* LWIP_DNS */
#if PPP_SUPPORT
ppp_init();
#endif#if LWIP_TIMERS
sys_timeouts_init();
#endif /* LWIP_TIMERS */
}6.2 netif_add
向 LwIP 协议栈注册一个新的网络接口,初始化其基本参数(IP 地址、回调函数等),并将其加入系统的网络接口链表中,使其成为协议栈可管理的网络设备。
struct netif *
netif_add(struct netif *netif,
#if LWIP_IPV4
const ip4_addr_t *ipaddr, const ip4_addr_t *netmask, const ip4_addr_t *gw,
#endif /* LWIP_IPV4 */
void *state, netif_init_fn init, netif_input_fn input)
{
#if LWIP_IPV6
s8_t i;
#endifLWIP_ASSERT_CORE_LOCKED();#if LWIP_SINGLE_NETIF
if (netif_default != NULL) {
LWIP_ASSERT("single netif already set", 0);
return NULL;
}
#endifLWIP_ERROR("netif_add: invalid netif", netif != NULL, return NULL);
LWIP_ERROR("netif_add: No init function given", init != NULL, return NULL);#if LWIP_IPV4
if (ipaddr == NULL) {
ipaddr = ip_2_ip4(IP4_ADDR_ANY);
}
if (netmask == NULL) {
netmask = ip_2_ip4(IP4_ADDR_ANY);
}
if (gw == NULL) {
gw = ip_2_ip4(IP4_ADDR_ANY);
}/* reset new interface configuration state */
ip_addr_set_zero_ip4(&netif->ip_addr);
ip_addr_set_zero_ip4(&netif->netmask);
ip_addr_set_zero_ip4(&netif->gw);
netif->output = netif_null_output_ip4;
#endif /* LWIP_IPV4 */
#if LWIP_IPV6
for (i = 0; i < LWIP_IPV6_NUM_ADDRESSES; i++) {
ip_addr_set_zero_ip6(&netif->ip6_addr[i]);
netif->ip6_addr_state[i] = IP6_ADDR_INVALID;
#if LWIP_IPV6_ADDRESS_LIFETIMES
netif->ip6_addr_valid_life[i] = IP6_ADDR_LIFE_STATIC;
netif->ip6_addr_pref_life[i] = IP6_ADDR_LIFE_STATIC;
#endif /* LWIP_IPV6_ADDRESS_LIFETIMES */
}
netif->output_ip6 = netif_null_output_ip6;
#endif /* LWIP_IPV6 */
NETIF_SET_CHECKSUM_CTRL(netif, NETIF_CHECKSUM_ENABLE_ALL);
netif->mtu = 0;
netif->flags = 0;
#ifdef netif_get_client_data
memset(netif->client_data, 0, sizeof(netif->client_data));
#endif /* LWIP_NUM_NETIF_CLIENT_DATA */
#if LWIP_IPV6
#if LWIP_IPV6_AUTOCONFIG
/* IPv6 address autoconfiguration should be enabled by default */
netif->ip6_autoconfig_enabled = 1;
#endif /* LWIP_IPV6_AUTOCONFIG */
#if LWIP_IPV6_SEND_ROUTER_ADVERTISE
/* Don't send router advertisements on this interface by default */
netif->ra_prefix_idx = -1;
#if LWIP_IPV6_RA_NUM_ROUTE_INFOS > 0
for(i=0; i < LWIP_IPV6_RA_NUM_ROUTE_INFOS; i++) {
netif->ra_rio_enabled[i] = 0;
}
#endif /* LWIP_IPV6_RA_NUM_ROUTE_INFOS > 0 */
#endif
nd6_restart_netif(netif);
#endif /* LWIP_IPV6 */
#if LWIP_NETIF_STATUS_CALLBACK
netif->status_callback = NULL;
#endif /* LWIP_NETIF_STATUS_CALLBACK */
#if LWIP_NETIF_LINK_CALLBACK
netif->link_callback = NULL;
#endif /* LWIP_NETIF_LINK_CALLBACK */
#if LWIP_IGMP
netif->igmp_mac_filter = NULL;
#endif /* LWIP_IGMP */
#if LWIP_IPV6 && LWIP_IPV6_MLD
netif->mld_mac_filter = NULL;
#endif /* LWIP_IPV6 && LWIP_IPV6_MLD *//* remember netif specific state information data */
netif->state = state;
netif->num = netif_num;
netif->input = input;#if LWIP_ACD
netif->acd_list = NULL;
#endif /* LWIP_ACD */
NETIF_RESET_HINTS(netif);
#if ENABLE_LOOPBACK
netif->loop_first = NULL;
netif->loop_last = NULL;
#if LWIP_LOOPBACK_MAX_PBUFS
netif->loop_cnt_current = 0;
#endif /* LWIP_LOOPBACK_MAX_PBUFS */
#if LWIP_NETIF_LOOPBACK_MULTITHREADING
netif->reschedule_poll = 0;
#endif /* LWIP_NETIF_LOOPBACK_MULTITHREADING */
#endif /* ENABLE_LOOPBACK */#if LWIP_IPV4
netif_set_addr(netif, ipaddr, netmask, gw);
#endif /* LWIP_IPV4 *//* call user specified initialization function for netif */
if (init(netif) != ERR_OK) {
return NULL;
}
#if LWIP_IPV6 && LWIP_ND6_ALLOW_RA_UPDATES
/* Initialize the MTU for IPv6 to the one set by the netif driver.
This can be updated later by RA. */
netif->mtu6 = netif->mtu;
#endif /* LWIP_IPV6 && LWIP_ND6_ALLOW_RA_UPDATES */#if !LWIP_SINGLE_NETIF
/* Assign a unique netif number in the range [0..254], so that (num+1) can
serve as an interface index that fits in a u8_t.
We assume that the new netif has not yet been added to the list here.
This algorithm is O(n^2), but that should be OK for lwIP.
*/
{
struct netif *netif2;
int num_netifs;
do {
if (netif->num == 255) {
netif->num = 0;
}
num_netifs = 0;
for (netif2 = netif_list; netif2 != NULL; netif2 = netif2->next) {
LWIP_ASSERT("netif already added", netif2 != netif);
num_netifs++;
LWIP_ASSERT("too many netifs, max. supported number is 255", num_netifs <= 255);
if (netif2->num == netif->num) {
netif->num++;
break;
}
}
} while (netif2 != NULL);
}
if (netif->num == 254) {
netif_num = 0;
} else {
netif_num = (u8_t)(netif->num + 1);
}/* add this netif to the list */
netif->next = netif_list;
netif_list = netif;
#endif /* "LWIP_SINGLE_NETIF */
mib2_netif_added(netif);#if LWIP_IGMP
/* start IGMP processing */
if (netif->flags & NETIF_FLAG_IGMP) {
igmp_start(netif);
}
#endif /* LWIP_IGMP */LWIP_DEBUGF(NETIF_DEBUG, ("netif: added interface %c%c IP",
netif->name[0], netif->name[1]));
#if LWIP_IPV4
LWIP_DEBUGF(NETIF_DEBUG, (" addr "));
ip4_addr_debug_print(NETIF_DEBUG, ipaddr);
LWIP_DEBUGF(NETIF_DEBUG, (" netmask "));
ip4_addr_debug_print(NETIF_DEBUG, netmask);
LWIP_DEBUGF(NETIF_DEBUG, (" gw "));
ip4_addr_debug_print(NETIF_DEBUG, gw);
#endif /* LWIP_IPV4 */
LWIP_DEBUGF(NETIF_DEBUG, ("\n"));netif_invoke_ext_callback(netif, LWIP_NSC_NETIF_ADDED, NULL);return netif;
}6.3 netif_set_up
启用网络接口的核心函数,其作用是将指定的网络接口(struct netif)标记为 “可用状态”,使其能够处理网络流量(收发数据包)。
/**
* @ingroup netif
* Bring an interface up, available for processing
* traffic.
*/
void
netif_set_up(struct netif *netif)
{
LWIP_ASSERT_CORE_LOCKED();LWIP_ERROR("netif_set_up: invalid netif", netif != NULL, return);if (!(netif->flags & NETIF_FLAG_UP)) {
netif_set_flags(netif, NETIF_FLAG_UP);MIB2_COPY_SYSUPTIME_TO(&netif->ts);NETIF_STATUS_CALLBACK(netif);#if LWIP_NETIF_EXT_STATUS_CALLBACK
{
netif_ext_callback_args_t args;
args.status_changed.state = 1;
netif_invoke_ext_callback(netif, LWIP_NSC_STATUS_CHANGED, &args);
}
#endifnetif_issue_reports(netif, NETIF_REPORT_TYPE_IPV4 | NETIF_REPORT_TYPE_IPV6);
#if LWIP_IPV6
nd6_restart_netif(netif);
#endif /* LWIP_IPV6 */
}
}