ECMAScript2023(ES14)新特性
概述
ECMAScript2023 于2023年6月27日正式发布, 本文会介绍ECMAScript2023(ES14),即ECMAScript的第14个版本的新特性。
以下摘自官网:ecma-262
ECMAScript 2023, the 14th edition, introduced the toSorted, toReversed, with, findLast, and findLastIndex methods on Array.prototype and TypedArray.prototype, as well as the toSpliced method on Array.prototype; added support for #! comments at the beginning of files to better facilitate executable ECMAScript files; and allowed the use of most Symbols as keys in weak collections.
ES2023新增的特性如下:
Array.prototype.findLast/Array.prototype.findLastIndex- 数组的拷贝修改:
toReversed/toSorted/toSpliced/with - shebang(
#!)支持 - 允许使用
Symbol作为WeakMap的键
findLast/findLastIndex
findLast方法用于查找数组中最后一个满足条件的元素,findLastIndex方法用于查找数组中最后一个满足条件的元素的索引。
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const lastEven = arr.findLast(num => num % 2 === 0); // 4(从末尾找第一个偶数)const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const lastEvenIndex = arr.findLastIndex(num => num % 2 === 0); // 3(元素4的索引)
兼容性
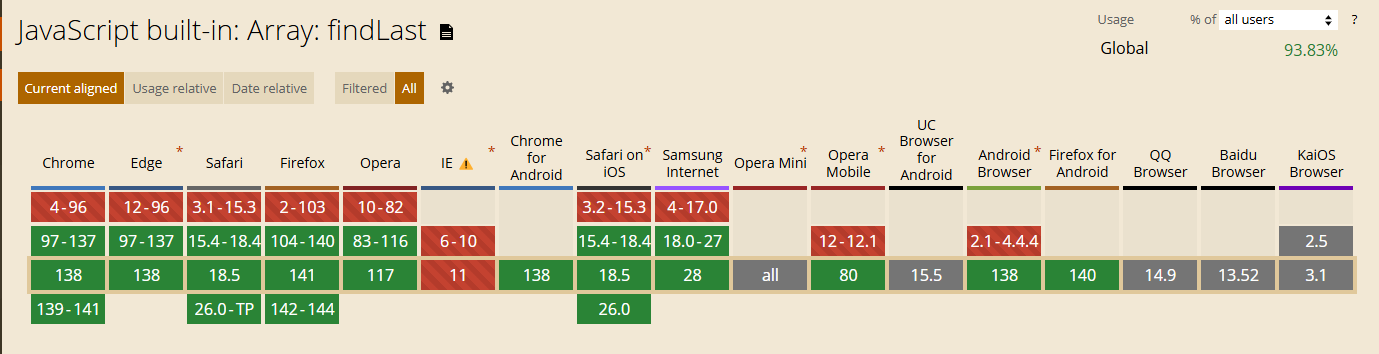

数组的拷贝修改
ES2023引入了数组的拷贝修改方法,包括toReversed、toSorted、toSpliced和with方法,这些方法都不会修改原始数组,而是返回经过变更的新数组
toReversed:返回倒序新数组
const arr = [1, 2, 3];
const reversedArr = arr.toReversed(); // [3, 2, 1]
console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 3](原数组未变)
toSorted:返回排序新数组
const arr = [3, 1, 2];
const sortedArr = arr.toSorted(); // [1, 2, 3]
console.log(arr); // [3, 1, 2](原数组未变)
toSpliced:返回一个移除或替换元素后的新数组
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4];
const newArr = arr.toSpliced(1, 2, 5); // 从索引1删除2个元素,插入5 → [1, 5, 4]
console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 3, 4](原数组未变)
with:返回一个特定索引处被替换的新数组
const arr = [1, 2, 3];
const newArr = arr.with(1, 4); // [1, 4, 3]
console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 3](原数组未变)
兼容性
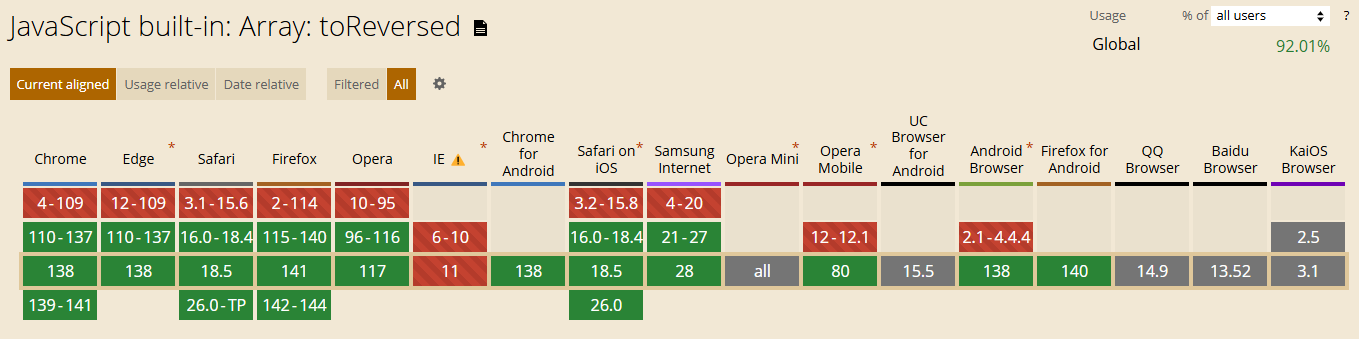


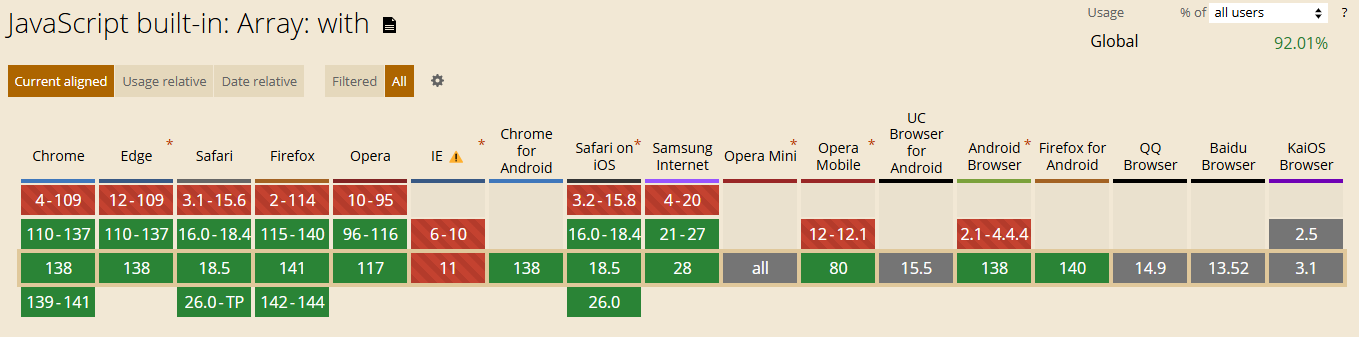
支持文件开头的shebang(#!)
ES2023支持在文件开头使用Hashbang(#!)注释,用于指定执行该文件的解释器路径,方便将文件作为可执行文件运行。
#!/usr/bin/env node
console.log('Hello, world!');
兼容性

支持使用Symbol作为WeakMap/WeakSet的键
ES2023允许使用Symbol作为WeakMap/WeakSet的键,这在之前是不支持的。
const sym = Symbol('mySymbol');
const weakMap = new WeakMap();
weakMap.set(sym, 'value');
console.log(weakMap.get(sym)); // 'value'
兼容性

